Abstract
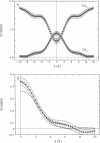
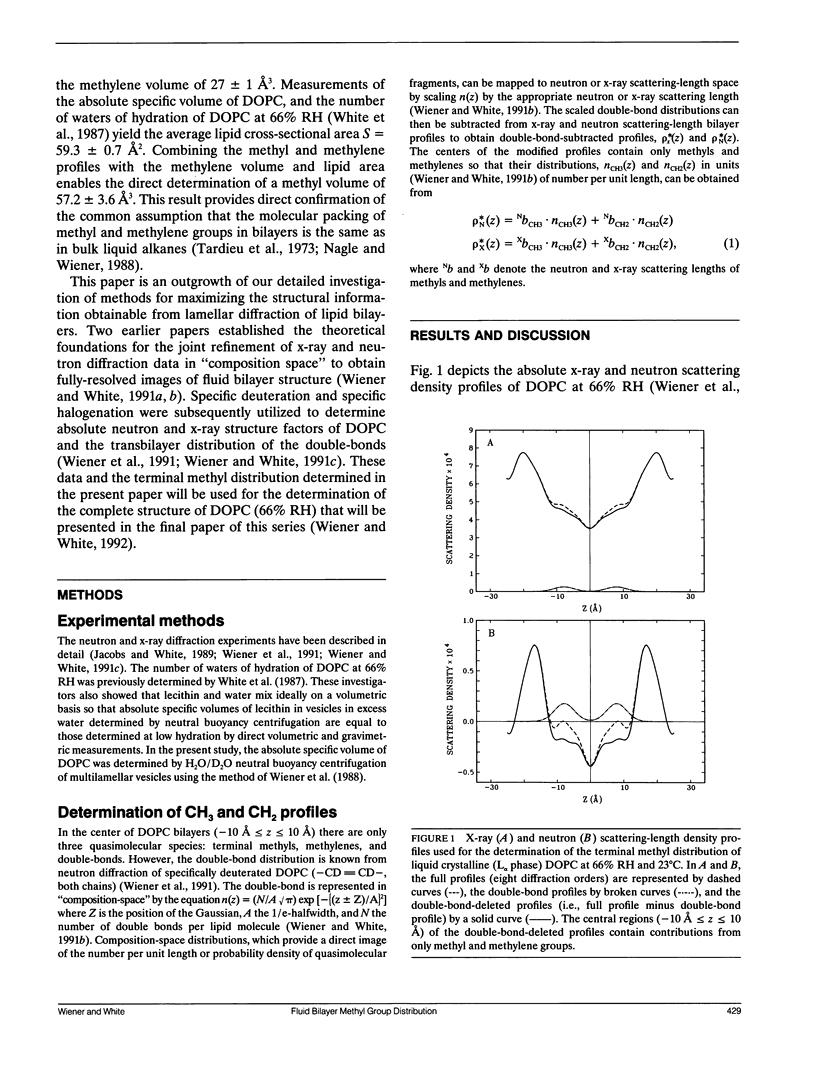
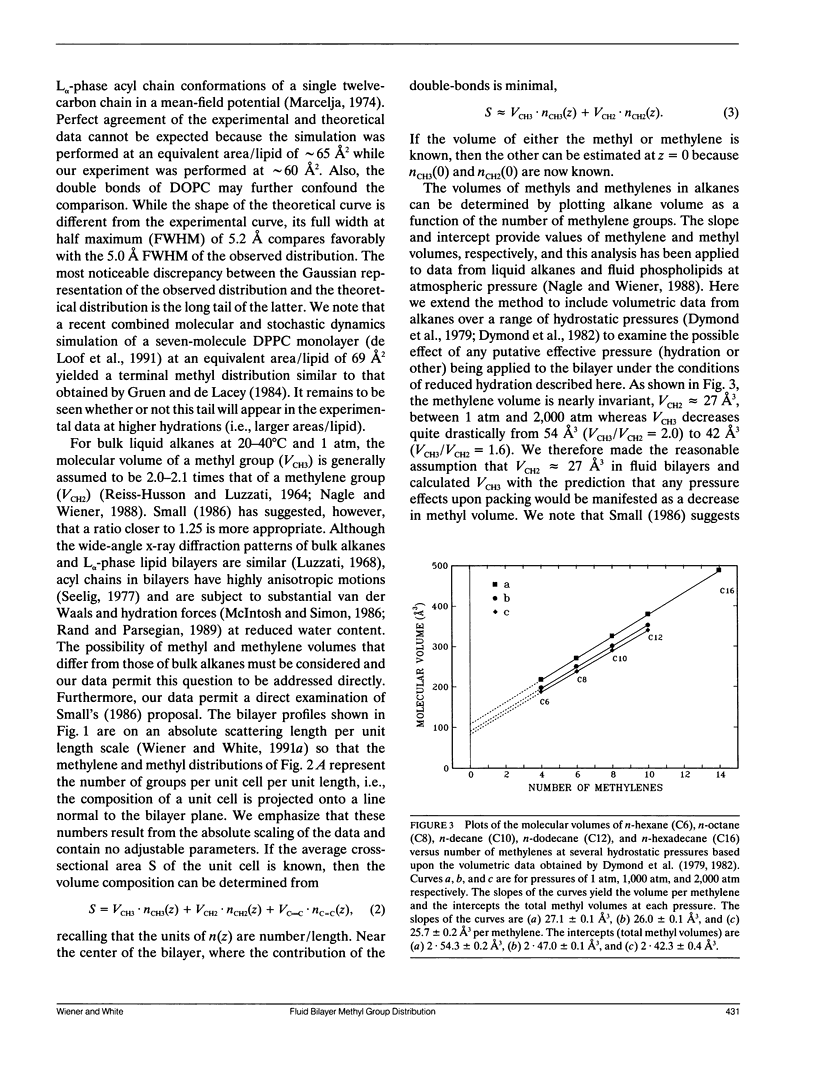
We continue in this paper the presentation of theoretical and experimental methods for the joint refinement of neutron and x-ray lamellar diffraction data for the analysis of fluid (L alpha phase) bilayer structure (Wiener, M. C., and S. H. White. 1991 a, b, c. Biophys. J. 59:162-173 and 174-185; Biochemistry. 30:6997-7008; Wiener, M. C., G. I. King, and S. H. White. Biophys. J. 60: 568-576). We show how to obtain the distribution and packing of the terminal methyls in the interior of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer (66% RH) by combining x-ray and neutron scattering-length transbilayer profiles with no a priori assumptions about the functional form of the distribution. We find that the methyls can be represented by a Gaussian function with 1/e-halfwidth of 2.95 +/- 0.28 A situated at the bilayer center. There is substantial mixing of the methyls and methylenes in the bilayer center. The Gaussian representation of the methyl distribution is narrower and has a different shape than predicted by several simulations of fluid bilayers (Gruen, D. W. R., and E. H. B. de Lacey. 1984. Surfactants in Solution, Vol. 1. Plenum Publishing Corp., New York. 279-306; de Loof, H., et al. 1991. Biochemistry. 30:2099-2133) but this may be due to the smaller area/lipid of our experiments and the presence of the double-bonds. Determination of the absolute specific volume of DOPC and an analysis of bulk alkane volumetric data over a range of hydrostatic pressures lead to estimates of methylene and methyl volumes at the bilayer center of 27 +/- 1 A3 and 57.2 +/- 3.6 A3, respectively. This result provides direct confirmation of the common assumption that the molecular packing of methyl and methylene groups in bilayers is the same as in bulk liquid alkanes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Loof H., Harvey S. C., Segrest J. P., Pastor R. W. Mean field stochastic boundary molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid in a membrane. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2099–2113. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Naghizadeh J., Marqusee J. A. Chain molecules at high densities at interfaces. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1988;39:425–461. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.39.100188.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruen D. W. A statistical mechanical model of the lipid bilayer above its phase transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):161–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. E., White S. H. The nature of the hydrophobic binding of small peptides at the bilayer interface: implications for the insertion of transbilayer helices. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Chain ordering in liquid crystals. II. Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 29;367(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Hydration force and bilayer deformation: a reevaluation. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4058–4066. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraldi J. P., Schlitter J. A statistical mechanical treatment of fatty acyl chain order in phospholipid bilayers and correlation with experimental data. A. Theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraldi J. P., Schlitter J. A statistical mechanical treatment of fatty acyl chain order in phospholipid bilayers and correlation with experimental data. B. Dipalmitoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):193–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Structure of fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastor R. W., Venable R. M., Karplus M. Model for the structure of the lipid bilayer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):892–896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Engelman D. M. Membrane protein folding and oligomerization: the two-stage model. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4031–4037. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Seelig J. Deuterium order parameters in relation to thermodynamic properties of a phospholiped bilayer. A statistical mechanical interpretation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2283–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Jr Monte Carlo studies of the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 19;469(3):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. Deuterium magnetic resonance: theory and application to lipid membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Aug;10(3):353–418. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Jacobs R. E., King G. I. Partial specific volumes of lipid and water in mixtures of egg lecithin and water. Biophys J. 1987 Oct;52(4):663–665. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83259-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., King G. I., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. I. Scaling of neutron data and the distributions of double bonds and water. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82086-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., Tristram-Nagle S., Wilkinson D. A., Campbell L. E., Nagle J. F. Specific volumes of lipids in fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 18;938(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of x-ray and neutron diffraction. I. Fluid bilayer models and the limits of resolution. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):162–173. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82208-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of x-ray and neutron diffraction. II. "Composition-space" refinement method. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82209-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure. Biophys J. 1992 Feb;61(2):434–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Transbilayer distribution of bromine in fluid bilayers containing a specifically brominated analogue of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6997–7008. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai G., Büldt G., Seelig A., Seelig J. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. II. Chain conformation and segmental disorder. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):693–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]