Abstract
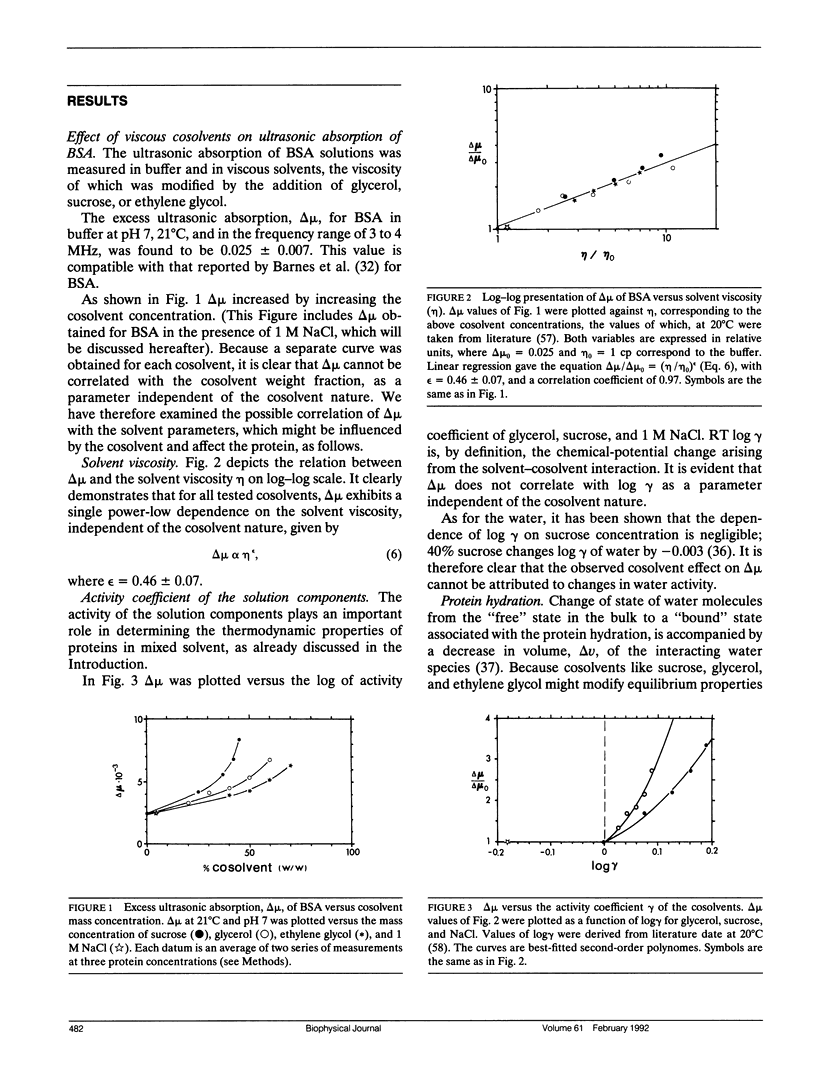
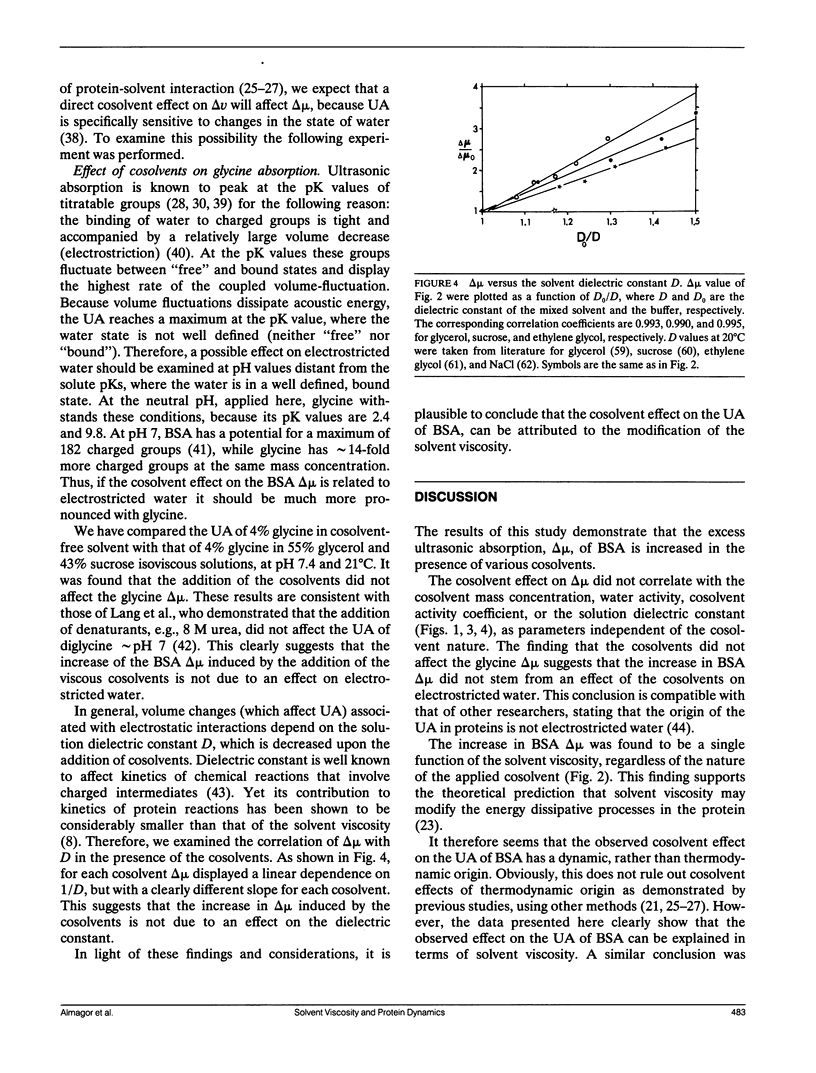
Protein-ligand binding and enzyme activity have been shown to be regulated by solvent viscosity, induced by the addition of viscous cosolvents. This was indirectly interpreted as an effect on protein dynamics. However, viscous cosolvents might affect dynamic, e.g., viscosity, as well as thermodynamic properties of the solution, e.g., activity of solution components. This work was undertaken to examine the effect of viscous cosolvent on the structural dynamics of proteins and its correlation with dynamic and thermodynamic solution properties. For this purpose we studied the effect of viscous cosolvent on the specific ultrasonic absorption, delta mu, of bovine serum albumin, at pH = 7.0 and at 21 degrees C, and frequency range of 3-4 MHz. Ultrasonic absorption (UA) directly probes protein dynamics related to energy dissipation processes. It was found that the addition of sucrose, glycerol, or ethylene glycol increased the BSA delta mu. This increase correlates well with the solvent viscosity, but not with the cosolvent mass concentration, activity of the solvent components, dielectric constant, or the hydration of charged groups. On the grounds of these results and previously reported findings, as well as theoretical considerations, we propose the following mechanism for the solvent viscosity effect on the protein structural fluctuations, reflected in the UA: increased solvent viscosity alters the frequency spectrum of the polypeptide chain movements; attenuating the fast (small amplitude) movements, and enhancing the slow (large amplitude) ones. This modulates the interaction strength between the polypeptide and water species that "lubricates" the chain's movements, leading to larger protein-volume fluctuation and higher ultrasonic absorption. This study demonstrates that solvent viscosity is a regulator of protein structural fluctuations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa T., Timasheff S. N. Preferential interactions of proteins with salts in concentrated solutions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6545–6552. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale A. D., Stuehr J. E. Kinetics of the helix-coil transition in aqueous poly(L-glutamic acid). J Am Chem Soc. 1972 May 17;94(10):3334–3338. doi: 10.1021/ja00765a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes C., Evans J. A., Lewis T. J. Ultrasonic absorption of bovine serum albumin solutions in the frequency range 200 kHz-1 MHz. J Acoust Soc Am. 1985 Jul;78(1 Pt 1):6–11. doi: 10.1121/1.392455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes C., Evans J. A., Lewis T. J. Ultrasonic absorption of bovine serum albumin solutions in the frequency range 60 to 160 kHz. J Acoust Soc Am. 1986 Nov;80(5):1291–1296. doi: 10.1121/1.394432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beece D., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Good D., Marden M. C., Reinisch L., Reynolds A. H., Sorensen L. B., Yue K. T. Solvent viscosity and protein dynamics. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5147–5157. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Careri G., Geraci M., Giansanti A., Rupley J. A. Protonic conductivity of hydrated lysozyme powders at megahertz frequencies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5342–5346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgadze Y. N., Ovsepyan A. M. Hydration mobility in peptide structures. Biopolymers. 1972;11(10):2179–2186. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360111017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. C., Leung W. P., Mok H. Y., Choy C. L. Ultrasonic absorption in myoglobin and other globular proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 18;830(1):36–44. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demchenko A. P., Ruskyn O. I., Saburova E. A. Kinetics of the lactate dehydrogenase reaction in high-viscosity media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 5;998(2):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers F., Funck T. Ultrasonic measurements with milliliter liquid samples in the 0.5-100 MHz range. Rev Sci Instrum. 1973 Aug;44(8):969–977. doi: 10.1063/1.1686339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish B., Gratton E., Hardy C. J. Adiabatic compressibility of globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish B. The role of geometry and elastic strains in dynamic states of proteins. Biophys Struct Mech. 1977 Dec 27;4(1):37–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00538839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish B., Werber M. M. Viscosity-dependent structural fluctuations in enzyme catalysis. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1269–1275. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Mechanism of protein stabilization by glycerol: preferential hydration in glycerol-water mixtures. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4667–4676. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovav E., Halle D., Yedgar S. Viscous macromolecules inhibit erythrocyte hemolysis induced by snake venom phospholipase A2. Biorheology. 1987;24(4):377–384. doi: 10.3233/bir-1987-24403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler L. W., Dunn F. Ultrasonic investigation of the conformal changes of bovine serum albumin in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem. 1969 Dec;73(12):4256–4263. doi: 10.1021/j100846a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J., Tondre C., Zana R. Effect of urea and other organic substances on the ultrasonic absorption of protein solutions. J Phys Chem. 1971 Feb 4;75(3):374–379. doi: 10.1021/j100673a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavalette D., Tetreau C. Viscosity-dependent energy barriers and equilibrium conformational fluctuations in oxygen recombination with hemerythrin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):97–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Timasheff S. N. The stabilization of proteins by sucrose. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7193–7201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnie R. E., Olson J. S. Effects of solvent composition and viscosity on the rates of CO binding to heme proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8928–8932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K., Rosenberg A. Possible coupling of chemical to structural dynamics in subtilisin BPN' catalyzed hydrolysis. Biophys Chem. 1991 Jan;39(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(91)85006-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. D., Jr, Dunn F. Ultrasonic absorption mechanisms in aqueous solutions of bovine hemoglobin. J Phys Chem. 1972 Feb 17;76(4):528–533. doi: 10.1021/j100648a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Khaleque M. A. Laser photolysis study of conformational change rates for hemoglobin in viscous solutions. Biophys J. 1983 Nov;44(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84291-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi B., Norman J. A., Zempel L., Rosenberg A. Viscosity and transient solvent accessibility of Trp-63 in the native conformation of lysozyme. Biophys Chem. 1988 Oct;32(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)85028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers F., Douzou P. Dielectric constant of mixed solvents used for a low temperature biochemistry. Biochimie. 1974;56(4):509–514. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. D., Slutsky L. J. Ultrasonic absorption and relaxation spectra in aqueous bovine hemoglobin. Biopolymers. 1972;11(9):1973–1984. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedgar S., Reisfeld-Granot N., Sela B. A. Regulation of liver cell ganglioside composition by extracellular fluid viscosity. Lipids. 1986 Oct;21(10):629–633. doi: 10.1007/BF02537211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedgar S., Reisfeld N., Halle D., Yuli I. Medium viscosity regulates the activity of membrane-bound and soluble phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3395–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedgar S., Weinstein D. B., Patsch W., Schonfeld G., Casanada F. E., Steinberg D. Viscosity of culture medium as a regulator of synthesis and secretion of very low density lipoproteins by cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2188–2192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaks A., Klibanov A. M. Enzymatic catalysis in nonaqueous solvents. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3194–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaks A., Klibanov A. M. The effect of water on enzyme action in organic media. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8017–8021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zana R., Lang J. Effect of pH on the ultrasonic absorption of aqueous solutions of proteins. J Phys Chem. 1970 Jun 25;74(13):2734–2736. doi: 10.1021/j100707a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


