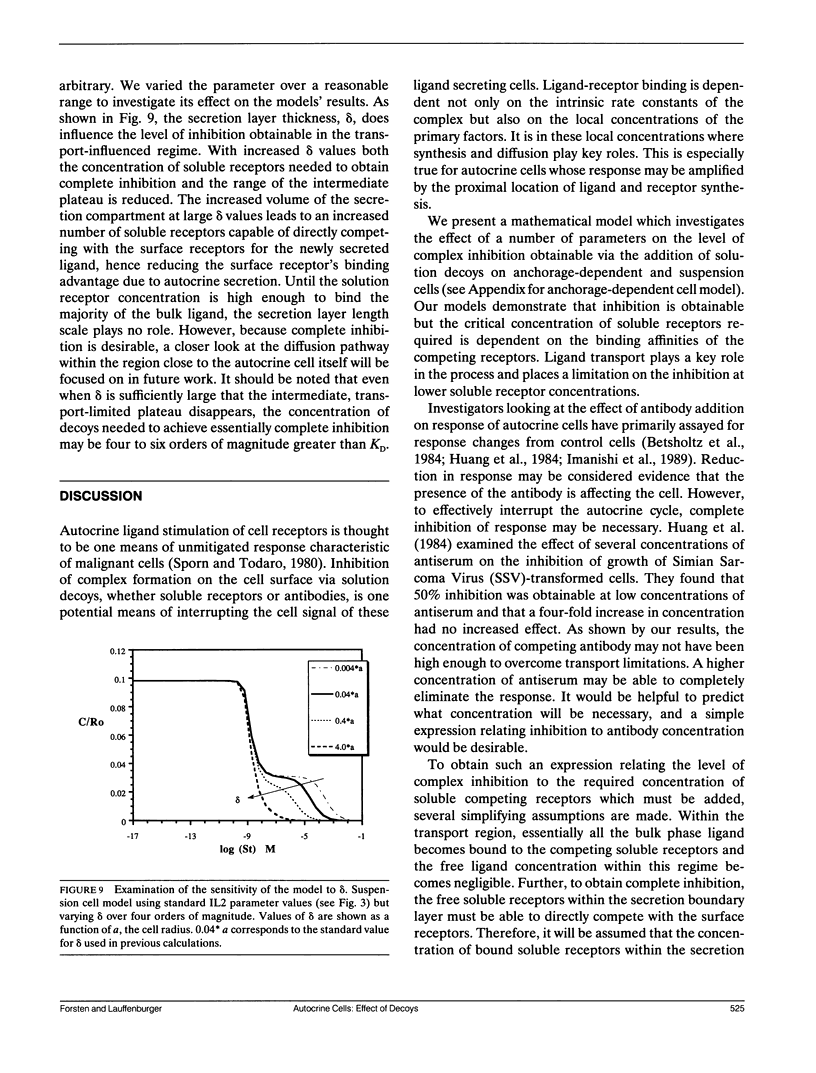
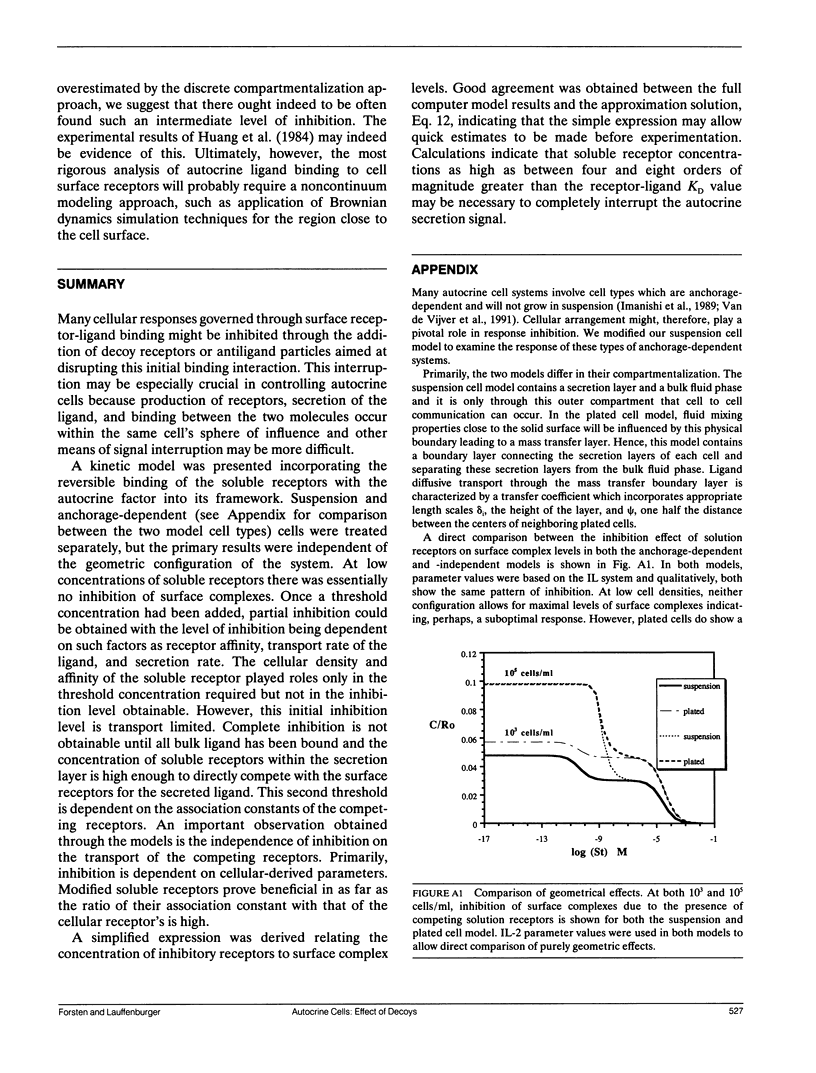
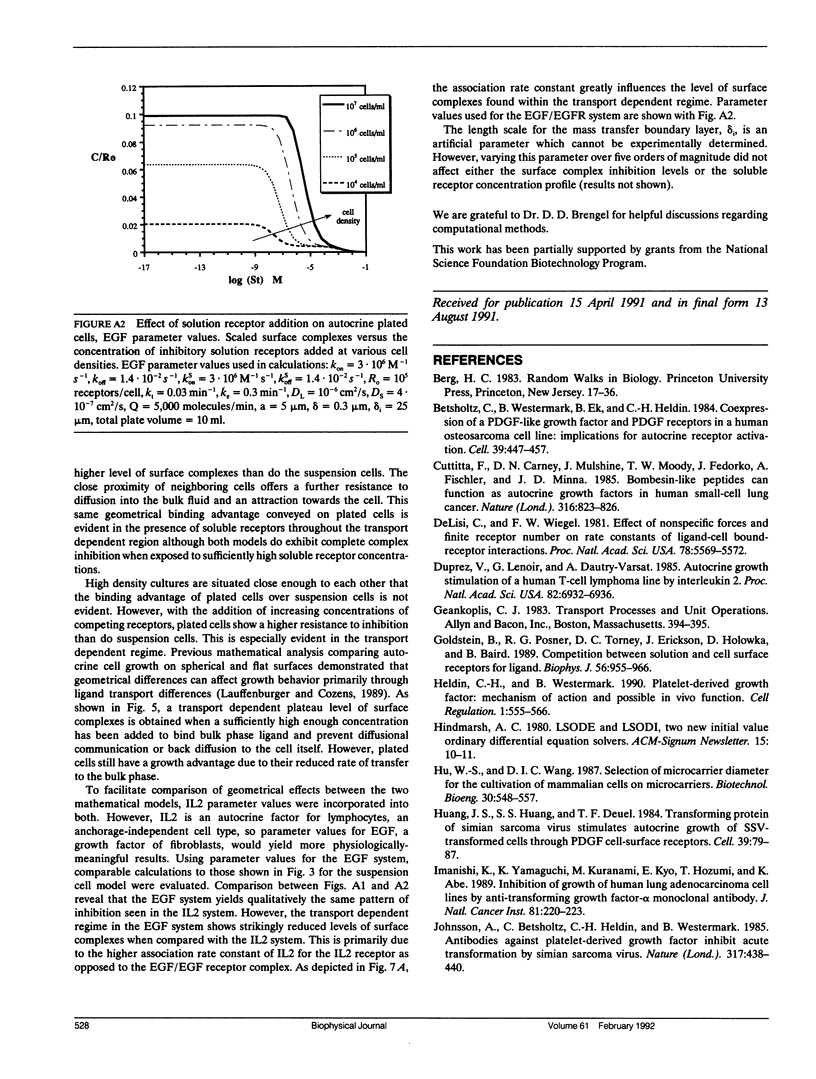
Abstract
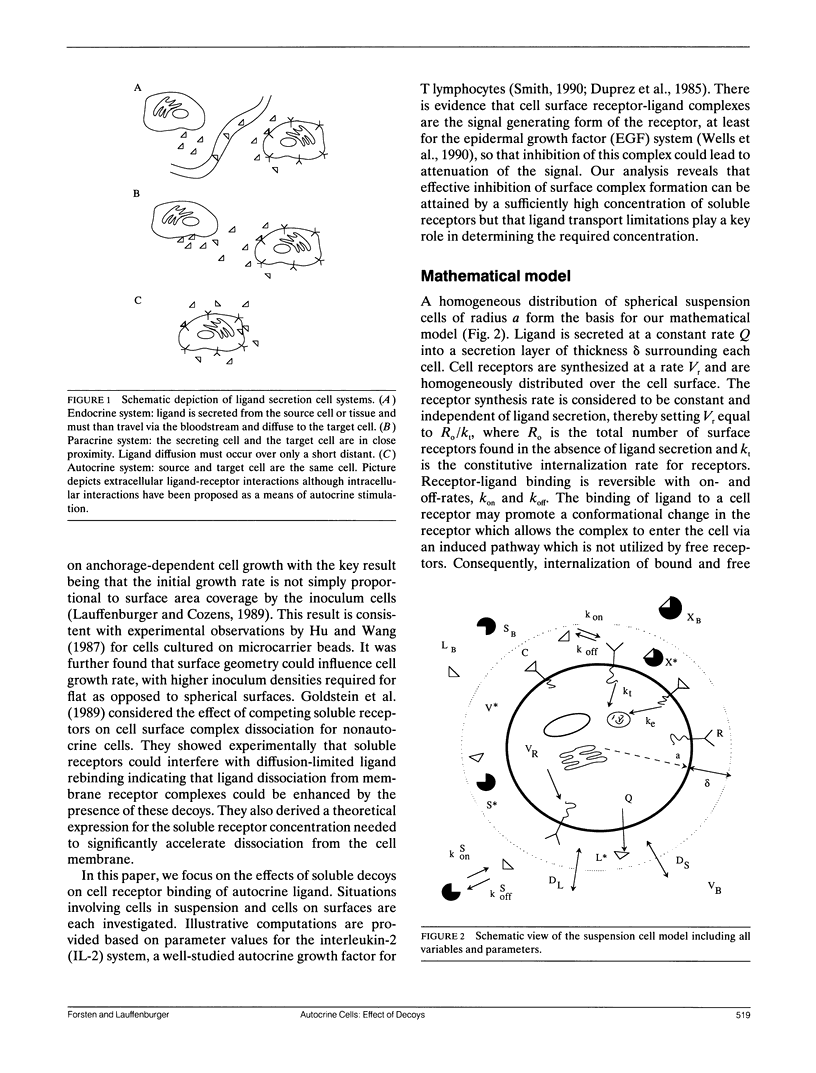
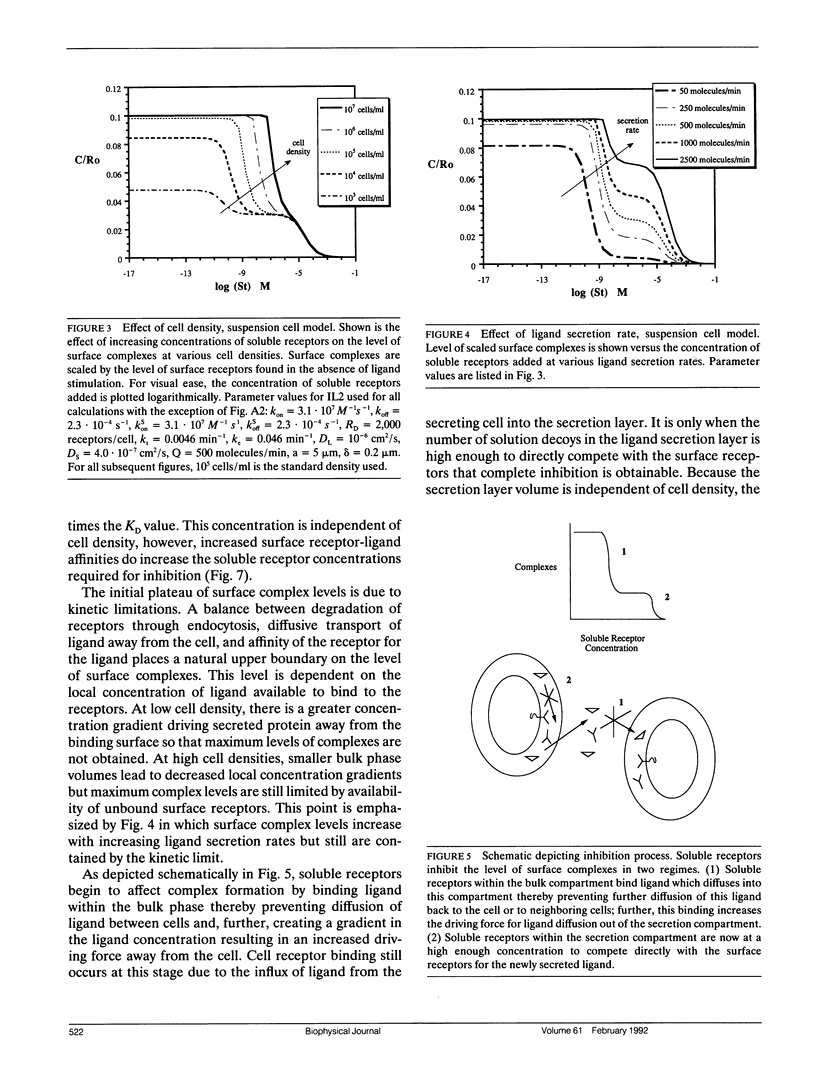
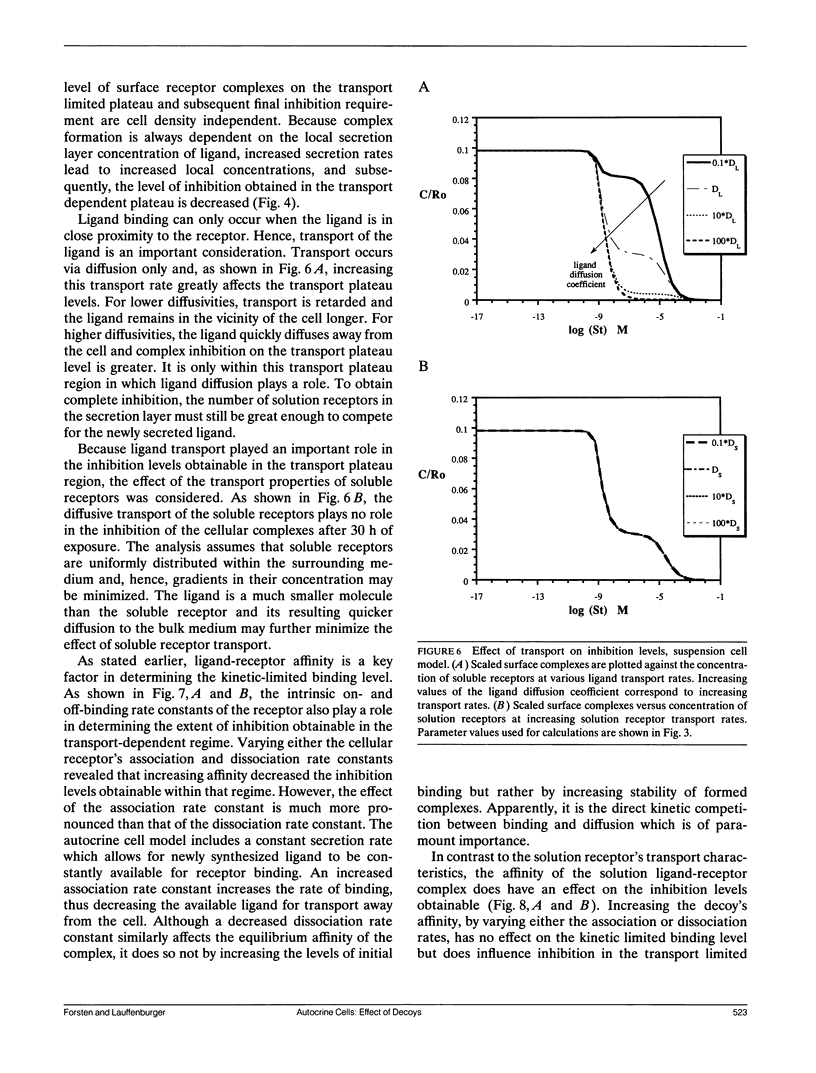
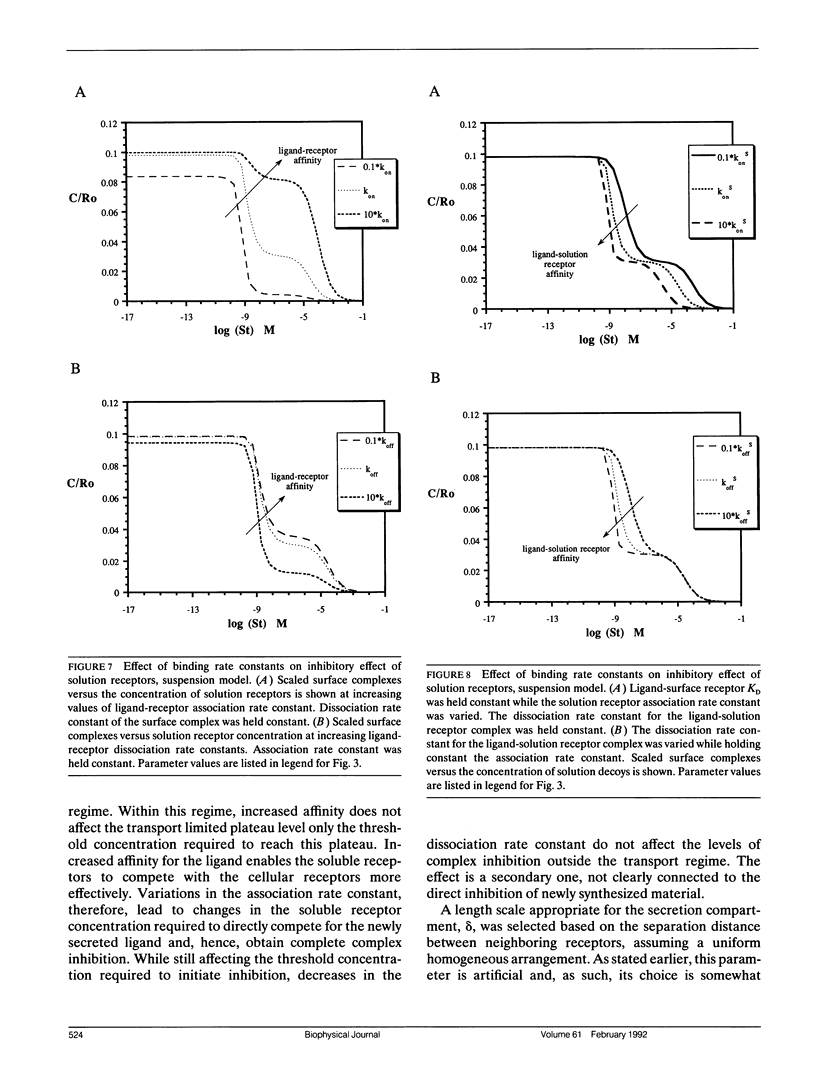
Autocrine ligands have been demonstrated to regulate cell proliferation, cell adhesion, and cell migration in a number of different systems and are believed to be one of the underlying causes of malignant cell transformation. Binding of these ligands to their cellular receptors can be compromised by diffusive transport of ligand away from the secreting cell. Exogenous addition of antibodies or solution receptors capable of competing with cellular receptors for these autocrine ligands has been proposed as a means of inhibiting autocrine-stimulated cell behavioral responses. Such "decoys" complicate cellular binding by offering alternative binding targets, which may also be capable of aiding or abating transport of the ligand away from the cell surface. We present a mathematical model incorporating autocrine ligand production and the presence of competing cellular and solution receptors. We elucidate effects of key system parameters including ligand diffusion rate, binding rate constants, cell density, and secretion rate on the ability of solution receptors to inhibit cellular receptor binding. Both plated and suspension cell systems are considered. An approximate analytical expression relating the key parameters to the critical concentration of solution "decoys" required for inhibition is derived and compared to the numerical calculations. We find that in order to achieve essentially complete inhibition of surface receptor binding, the concentration of decoys may need to be as much as four to eight orders of magnitude greater than the equilibrium disociation constant for ligand binding to surface receptors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betsholtz C., Westermark B., Ek B., Heldin C. H. Coexpression of a PDGF-like growth factor and PDGF receptors in a human osteosarcoma cell line: implications for autocrine receptor activation. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttitta F., Carney D. N., Mulshine J., Moody T. W., Fedorko J., Fischler A., Minna J. D. Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):823–826. doi: 10.1038/316823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Wiegel F. W. Effect of nonspecific forces and finite receptor number on rate constants of ligand--cell bound-receptor interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5569–5572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duprez V., Lenoir G., Dautry-Varsat A. Autocrine growth stimulation of a human T-cell lymphoma line by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B., Posner R. G., Torney D. C., Erickson J., Holowka D., Baird B. Competition between solution and cell surface receptors for ligand. Dissociation of hapten bound to surface antibody in the presence of solution antibody. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):955–966. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82741-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: mechanism of action and possible in vivo function. Cell Regul. 1990 Jul;1(8):555–566. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Transforming protein of simian sarcoma virus stimulates autocrine growth of SSV-transformed cells through PDGF cell-surface receptors. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi K., Yamaguchi K., Kuranami M., Kyo E., Hozumi T., Abe K. Inhibition of growth of human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines by anti-transforming growth factor-alpha monoclonal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Feb 1;81(3):220–223. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.3.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Betsholtz C., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Antibodies against platelet-derived growth factor inhibit acute transformation by simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):438–440. doi: 10.1038/317438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer D. J., Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. Relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy and mitogenic response. Quantitative analysis using a steady state model system. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5623–5631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K. A., Opresko L. K., Starbuck C., Walsh B. J., Wiley H. S. Quantitative analysis of the endocytic system involved in hormone-induced receptor internalization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15713–15723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge M., Green M. R., Langdon J. D., Feldmann M. Production of TGF-alpha and TGF-beta by cultured keratinocytes, skin and oral squamous cell carcinomas--potential autocrine regulation of normal and malignant epithelial cell proliferation. Br J Cancer. 1989 Oct;60(4):542–548. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Lindquist P. B., Bringman T. S., Goeddel D. V., Derynck R. Expression in rat fibroblasts of a human transforming growth factor-alpha cDNA results in transformation. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup D., Szabo A. Role of diffusion in ligand binding to macromolecules and cell-bound receptors. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84455-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. J., Derynck R., Korc M. Production of transforming growth factor alpha in human pancreatic cancer cells: evidence for a superagonist autocrine cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7567–7570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2. Sci Am. 1990 Mar;262(3):50–57. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0390-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vijver M. J., Kumar R., Mendelsohn J. Ligand-induced activation of A431 cell epidermal growth factor receptors occurs primarily by an autocrine pathway that acts upon receptors on the surface rather than intracellularly. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7503–7508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. M., Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Functional consequences of its bimolecular structure. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1055–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Welsh J. B., Lazar C. S., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):962–964. doi: 10.1126/science.2305263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Serrero G. Autocrine growth induced by the insulin-related factor in the insulin-independent teratoma cell line 1246-3A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5936–5940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Kyo E., Tsuda T., Tsujino T., Ito M., Niimoto M., Tahara E. EGF and TGF-alpha, the ligands of hyperproduced EGFR in human esophageal carcinoma cells, act as autocrine growth factors. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jan 15;45(1):131–135. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


