Abstract
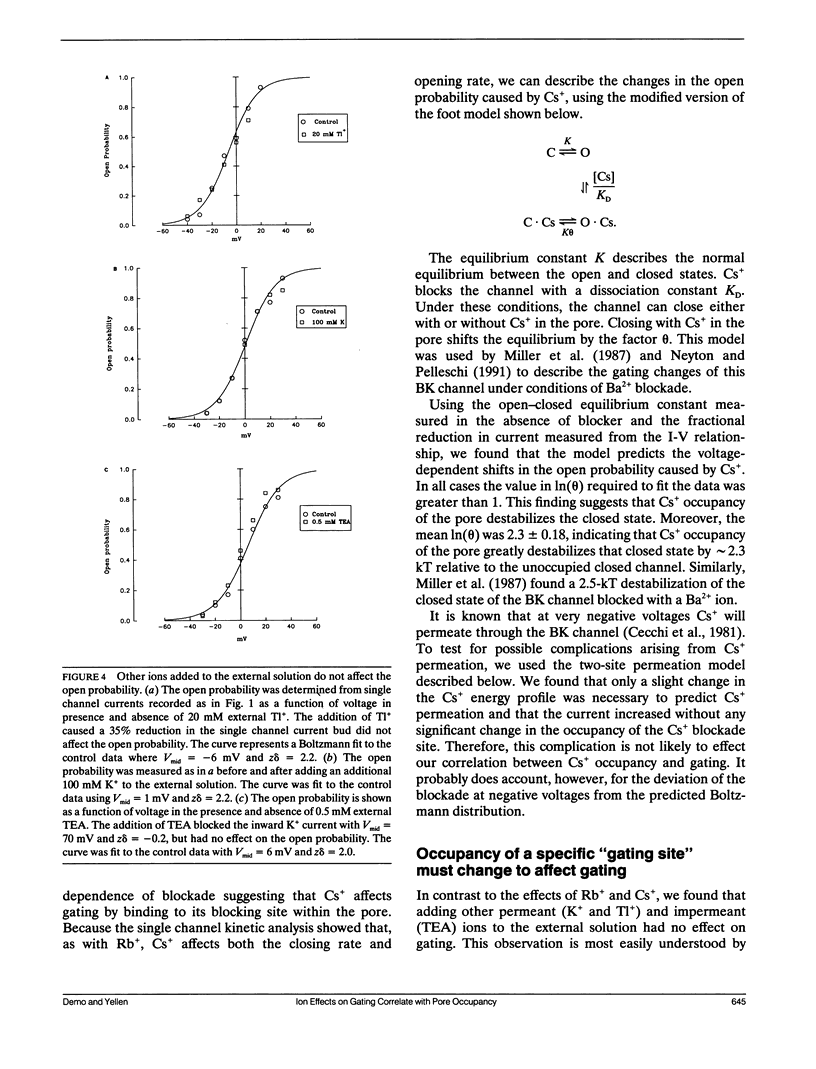
We studied the effects of permeant ions on the gating of the large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel from rat skeletal muscle. Rb+ blockade of inward K+ current caused an increase in the open probability as though Rb+ occupancy of the pore interferes with channel closing. In support of this hypothesis, we directly measured the occupancy of the pore by the impermeant ion Cs+ and found that it strongly correlates with its effect on gating. This is consistent with the "foot-in-the-door" model of gating, which states that channels cannot close with an ion in the pore. However, because Rb+ and Cs+ not only slow the closing rate (as predicted by the model), but also speed the opening rate, our results are more consistent with a modified version of the model in which the channel can indeed close while occupied, but the occupancy destabilizes the closed state. Increasing the occupancy of the pore by the addition of other permeant (K+ and Tl+) and impermeant (tetraethylammonium) ions did not affect the open probability. To account for this disparity, we used a two-site permeation model in which only one of the sites influenced gating. Occupancy of this "gating site" interferes with channel closing and hastens opening. Ions that directly or indirectly increase the occupancy of this site will increase the open probability.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W., Hamill O. P. Inhibitory postsynaptic currents at Aplysia cholinergic synapses: effects of permeant anions and depressant drugs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Feb 22;214(1196):335–350. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of rubidium, caesium, strontium, barium and lanthanum on ionic currents in myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Jan;108(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Marty A., Neild T. O. Life time and elementary conductance of the channels mediating the excitatory effects of acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:177–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Donaldson P. L. Slow components of potassium tail currents in rat skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Apr;81(4):513–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Correcting single channel data for missed events. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):967–980. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83725-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Block of sodium conductance and gating current in squid giant axons poisoned with quaternary strychnine. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85202-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Pappone P. A. Chemical modification of potassium channel gating in frog myelinated nerve by trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:119–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Latorre R., Miller C. Multi-ion conduction and selectivity in the high-conductance Ca++-activated K+ channel from skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83546-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Kinetics of unliganded acetylcholine receptor channel gating. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):663–672. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83693-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchais D., Marty A. Interaction of permeant ions with channels activated by acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):9–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Swenson R. P., Jr External monovalent cations that impede the closing of K channels. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):795–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Latorre R., Reisin I. Coupling of voltage-dependent gating and Ba++ block in the high-conductance, Ca++-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Sep;90(3):427–449. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E. G., Latorre R. Saxitoxin and ouabain binding activity of isolated skeletal muscle membrane as indicators of surface origin and purity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Miller C. Potassium blocks barium permeation through a calcium-activated potassium channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Nov;92(5):549–567. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
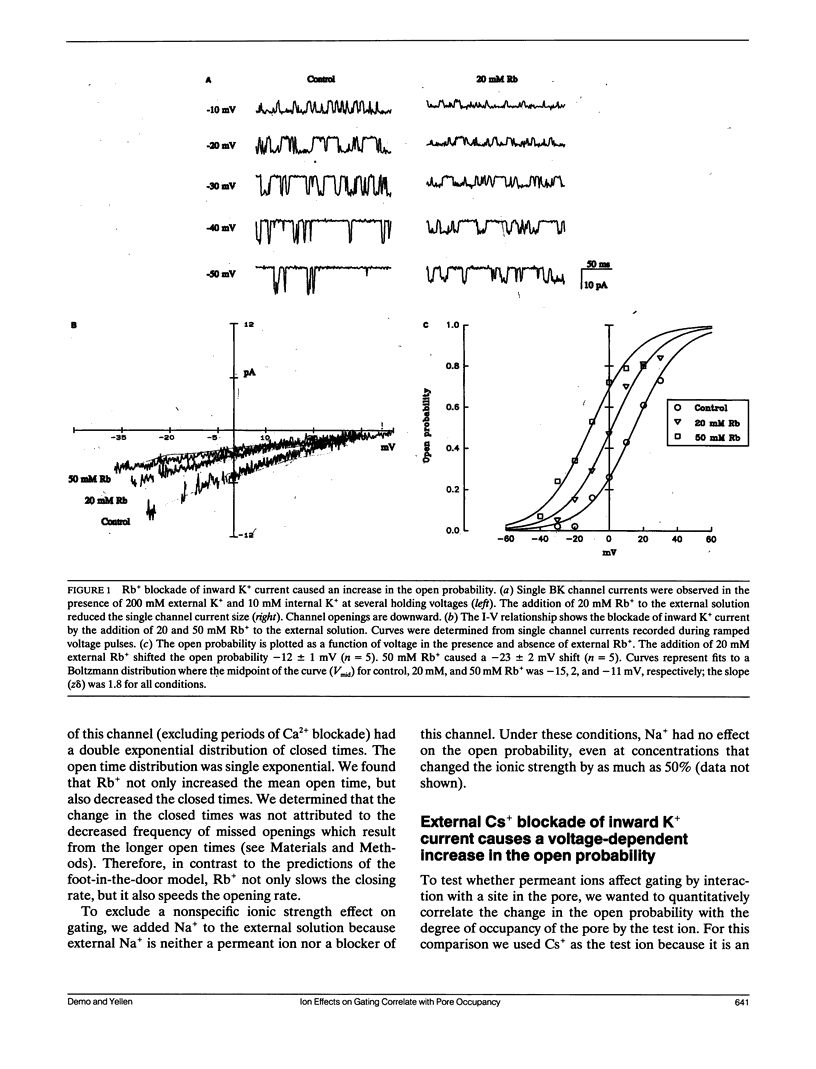
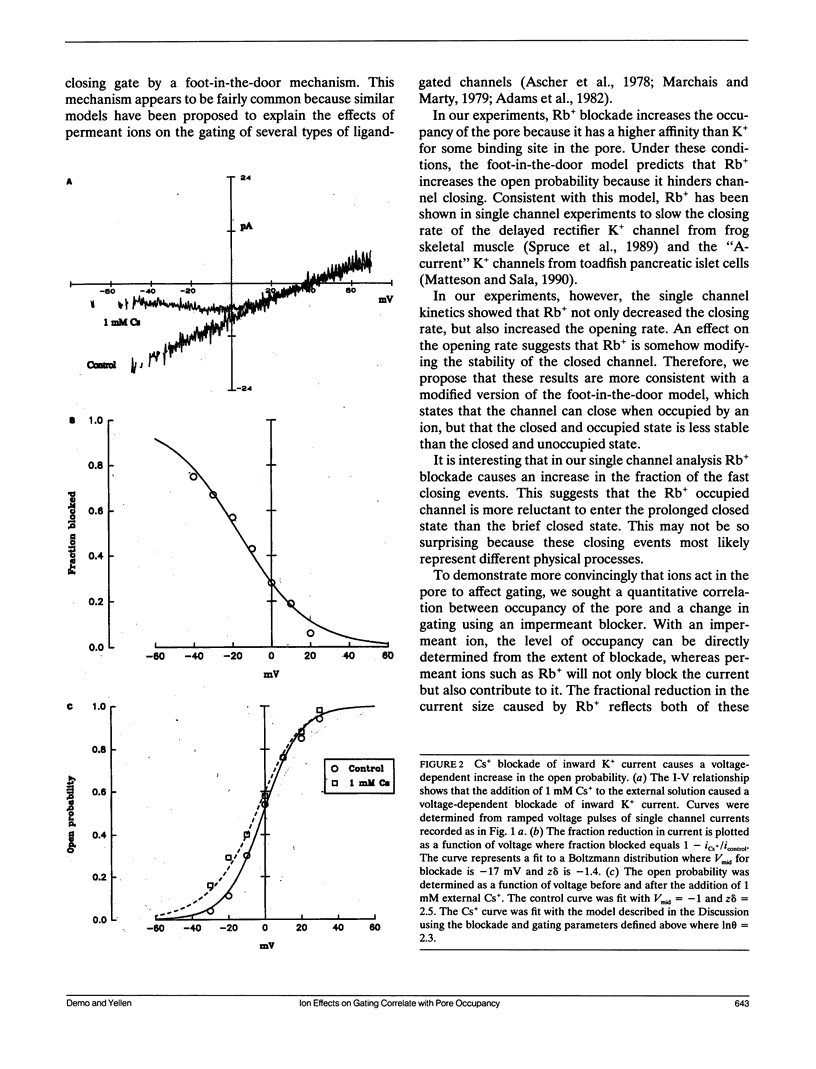
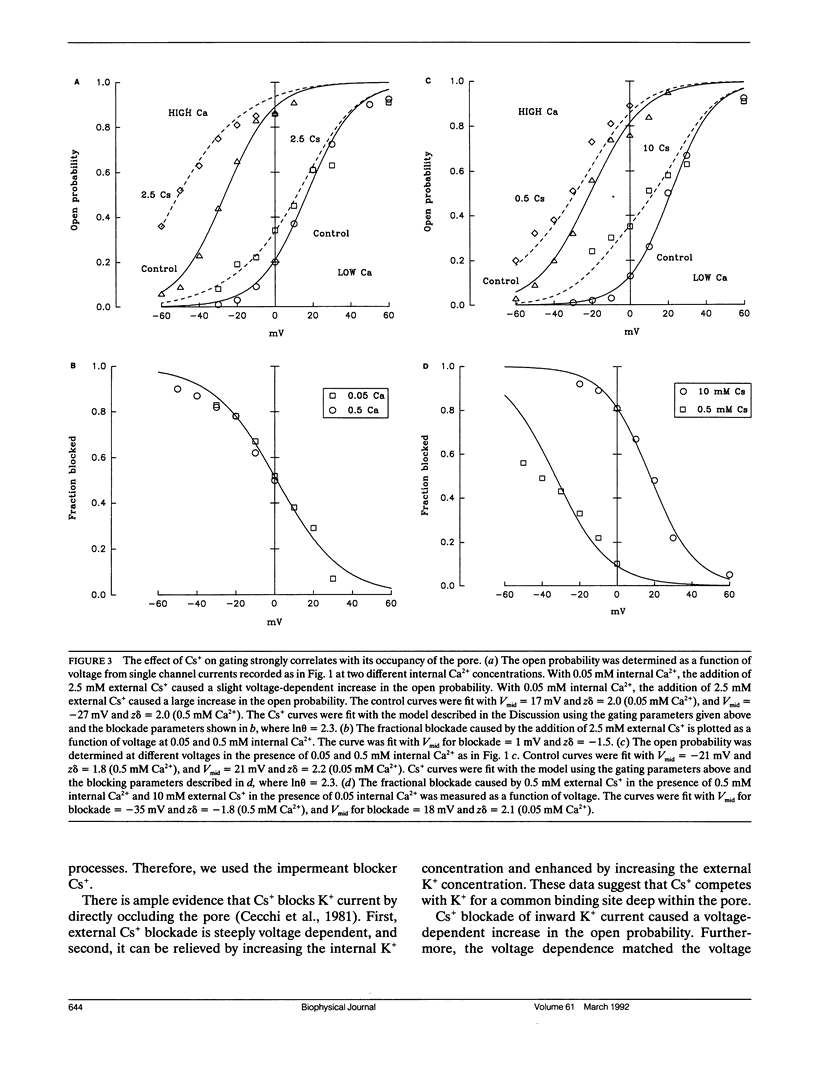
- Neyton J., Pelleschi M. Multi-ion occupancy alters gating in high-conductance, Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Apr;97(4):641–665. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Sine S. M. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83298-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Rubidium ions and the gating of delayed rectifier potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:597–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Jr, Armstrong C. M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):427–429. doi: 10.1038/291427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Latorre R. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):543–568. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Conduction, Blockade and Gating in a Ca -activated K Channel Incorporated into Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84114-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Armstrong C. M. Immobilisation of gating charge by a substance that simulates inactivation. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):387–389. doi: 10.1038/273387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]