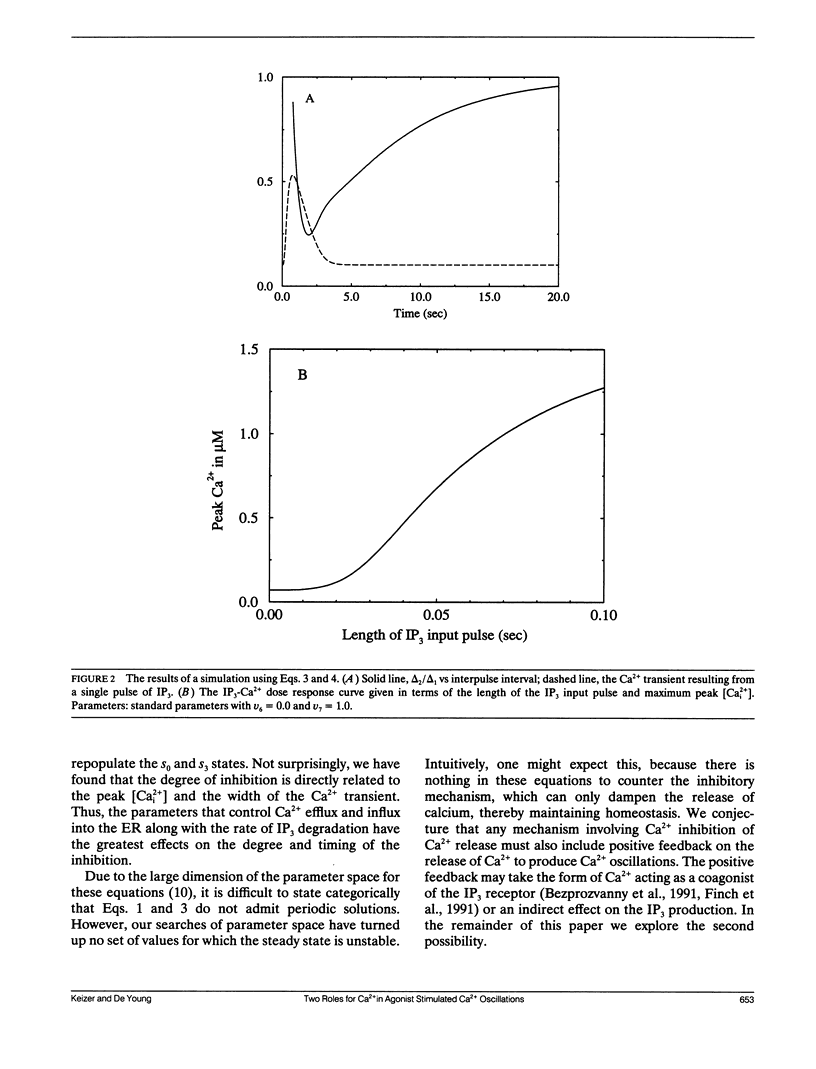
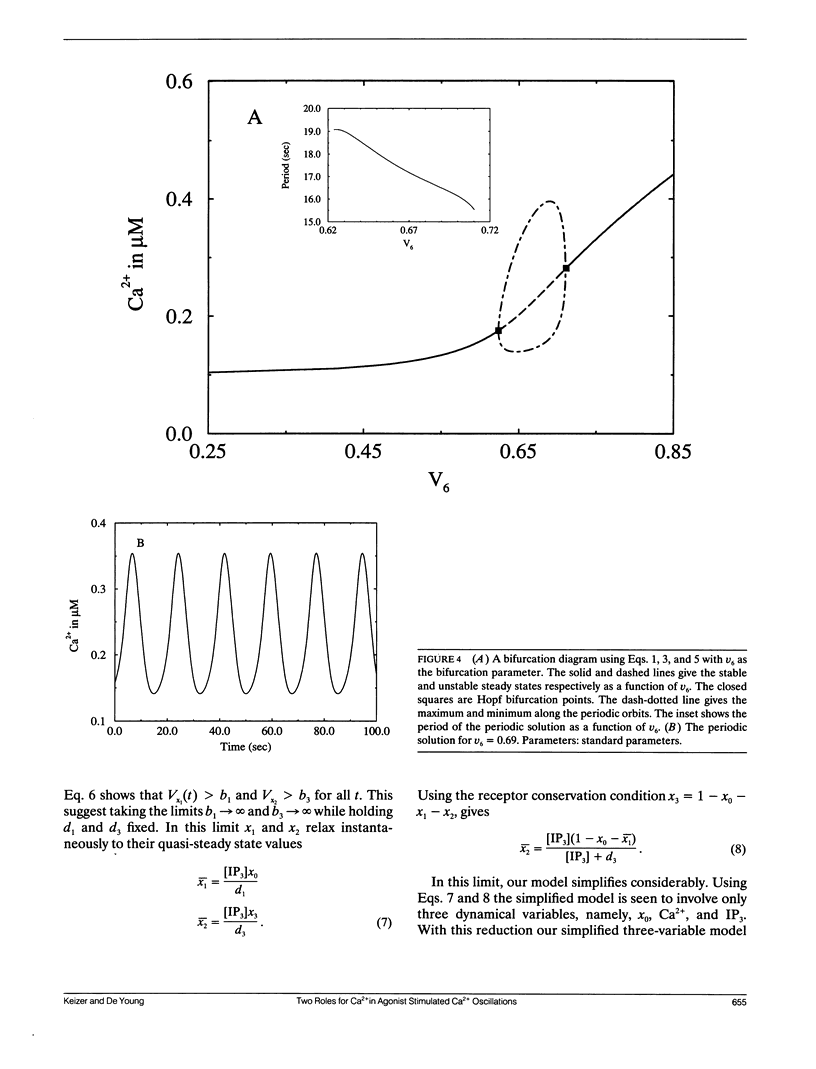
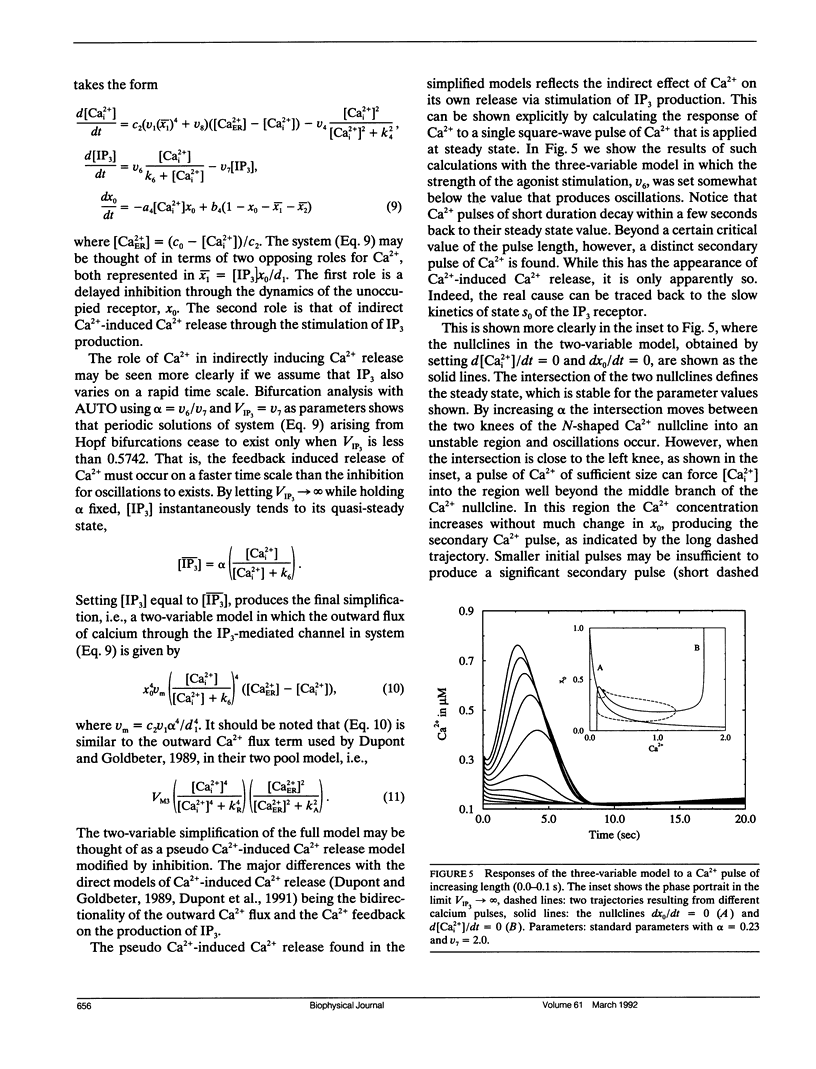
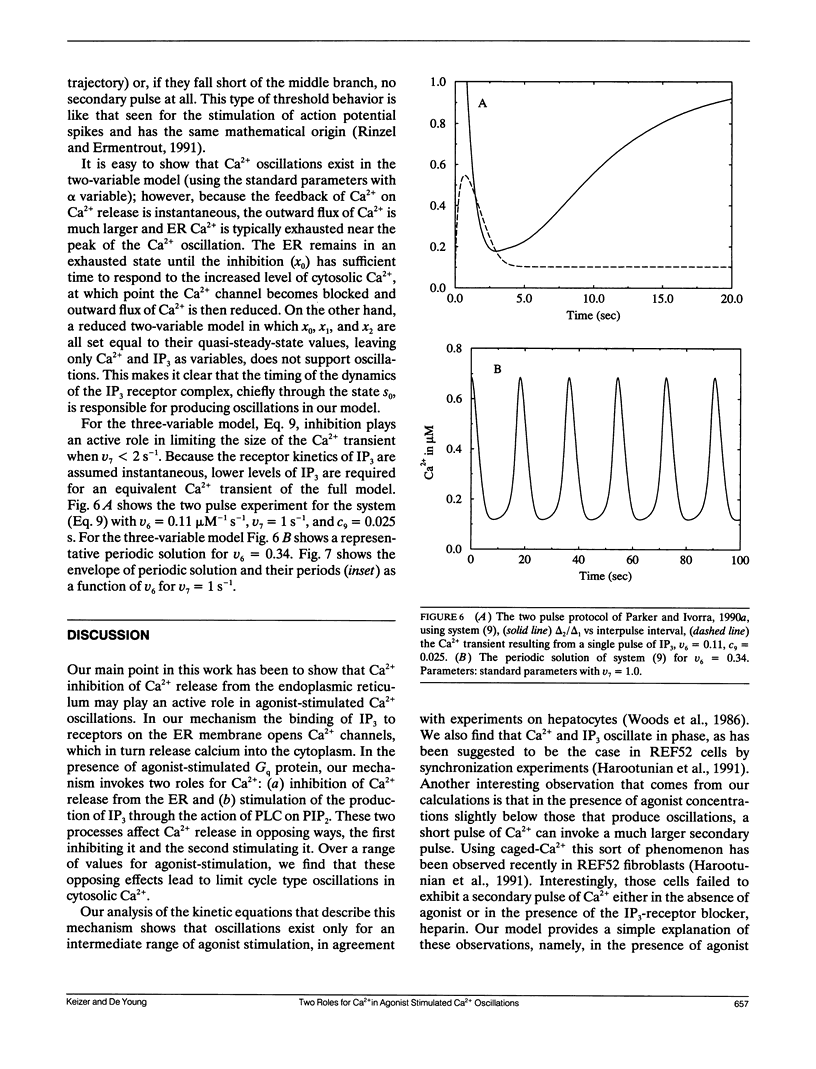
Abstract
We propose a mechanism for agonist-stimulated Ca2+ oscillations that involves two roles for cytosolic Ca2+: (a) inhibition of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) stimulated Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and (b) stimulation of the production of IP3 through its action on phospholipase C (PLC), via a Gq protein related mechanism. Relying on quantitative experiments by Parker, I., and I. Ivorra (1990. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 87:260-264) on the inhibition of Ca2+ release from the ER using caged-IP3, we develop a kinetic model of inhibition that allows us to simulate closely their experiments. The model assumes that the ER IP3 receptor is a tetramer of independent subunits that can bind both Ca2+ and IP3. Upon incorporation of the action of Ca2+ on PLC that leads to production of IP3, we observe in-phase-oscillations of Ca2+ and IP3 at intermediate values of agonist stimulation. The oscillations occur on a time scale of 10-20 s, which is comparable to the time scale for inhibition in Xenopus oocytes. Analysis of the mechanism shows that Ca(2+)-inhibition of IP3-stimulated Ca2+ release from the ER is an essential step in the mechanism. We also find that the effect of Ca2+ on PLC can lead to an indirect increase of cytosolic Ca2+, superficially resembling "Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+)-release." The mechanism that we propose appears to be consistent with recent experiments on REF52 cells by Harootunian, A. T., J. P. Y. Kao, S. Paranjape, and R. Y. Tsien. (1991. Science [Wash. DC]. 251:75-78.) and we propose additional experiments to help test its underlying assumptions.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Cytoplasmic calcium oscillations: a two pool model. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chueh S. H., Gill D. L. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and guanine nucleotides activate calcium release from endoplasmic reticulum via distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13883–13886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson K. S., Chay T. R. Modelling receptor-controlled intracellular calcium oscillators. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont G., Berridge M. J., Goldbeter A. Signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations: properties of a model based on Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90010-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Föhr K. J., Ahnert-Hilger G., Stecher B., Scott J., Gratzl M. GTP and Ca2+ modulate the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Ca2+ release in streptolysin O-permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):665–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grapengiesser E., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Three types of cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations in stimulated pancreatic beta-cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):404–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90602-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Paranjape S., Tsien R. Y. Generation of calcium oscillations in fibroblasts by positive feedback between calcium and IP3. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1986413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Rice H. L., Williamson J. R. The effect of external calcium and pH on inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium release from cerebellum microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):261–265. doi: 10.1042/bj2580261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Takeshita S. Simulation of intracellular Ca2+ oscillation in a sympathetic neurone. J Theor Biol. 1981 Dec 21;93(4):1009–1031. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Calcium spiking. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:153–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Molecular model for receptor-stimulated calcium spiking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Wensel T., Stryer L. Kinetics of calcium channel opening by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):32–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillac B., Balestre M. N., Guillon G. Positive feedback regulation of phospholipase C by vasopressin-induced calcium mobilization in WRK1 cells. Cell Signal. 1990;2(5):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90046-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. Inhibition by Ca2+ of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ liberation: a possible mechanism for oscillatory release of Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. Localized all-or-none calcium liberation by inositol trisphosphate. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):977–979. doi: 10.1126/science.2237441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R., Flores T. M., Fein A. Feedback inhibition by calcium limits the release of calcium by inositol trisphosphate in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90112-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. M., Burgoyne R. D. Characterisation of distinct inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive and caffeine-sensitive calcium stores in digitonin-permeabilised adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1587–1593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Mercan D. Computer simulation of a cytosolic calcium oscillator. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):835–838. doi: 10.1042/bj2710835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Exton J. H. Guanine-nucleotide and hormone regulation of polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C activity of rat liver plasma membranes. Bivalent-cation and phospholipid requirements. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):791–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2480791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. The role of phospholipid-derived mediators including arachidonic acid, its metabolites, and inositoltrisphosphate and of intracellular Ca2+ in glucose-induced insulin secretion by pancreatic islets. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(2):125–181. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by acetylcholine or intracellular infusion of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+ can be inhibited by internal Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):206–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81374-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Potter B. V., Petersen O. H. Pulsatile intracellular calcium release does not depend on fluctuations in inositol trisphosphate concentration. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):317–320. doi: 10.1038/339317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. H., De Jong M. D., De Pont J. J., Van Os C. H. Ca2(+)-sensitivity of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release in permeabilized pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):681–687. doi: 10.1042/bj2650681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H., Muallem S. Inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release by Ca2+ in cells from peripheral tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21419–21422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


