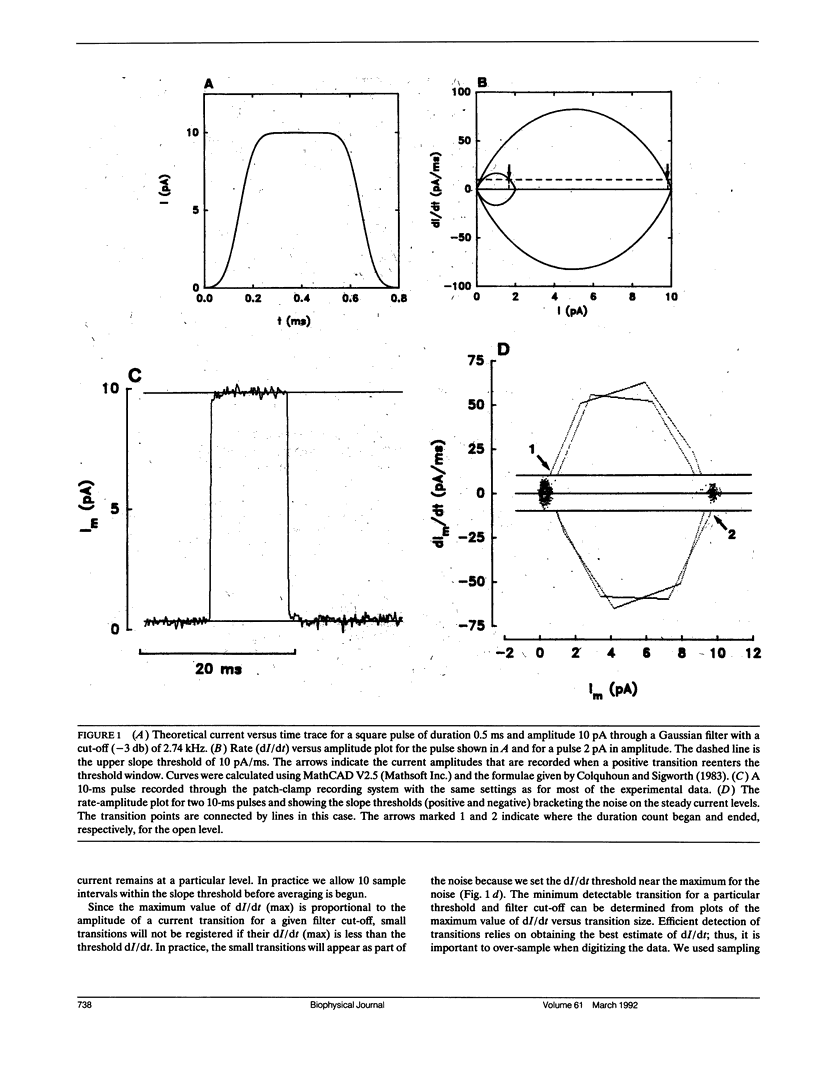
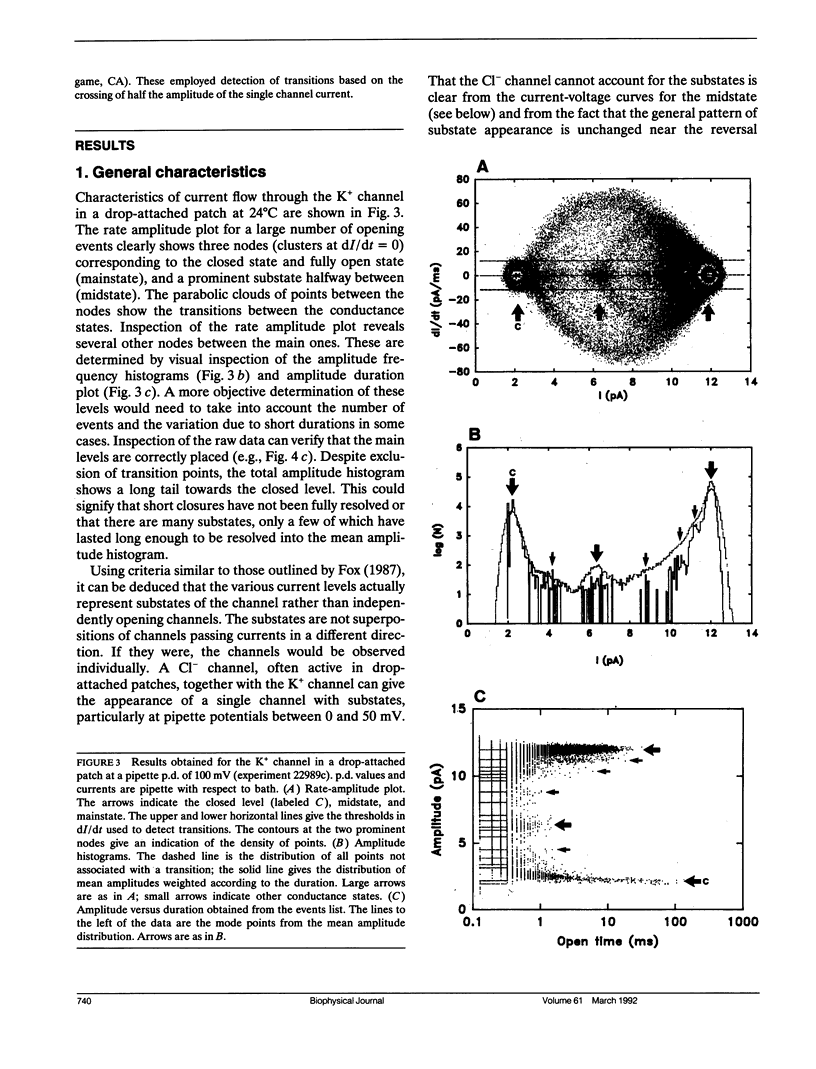
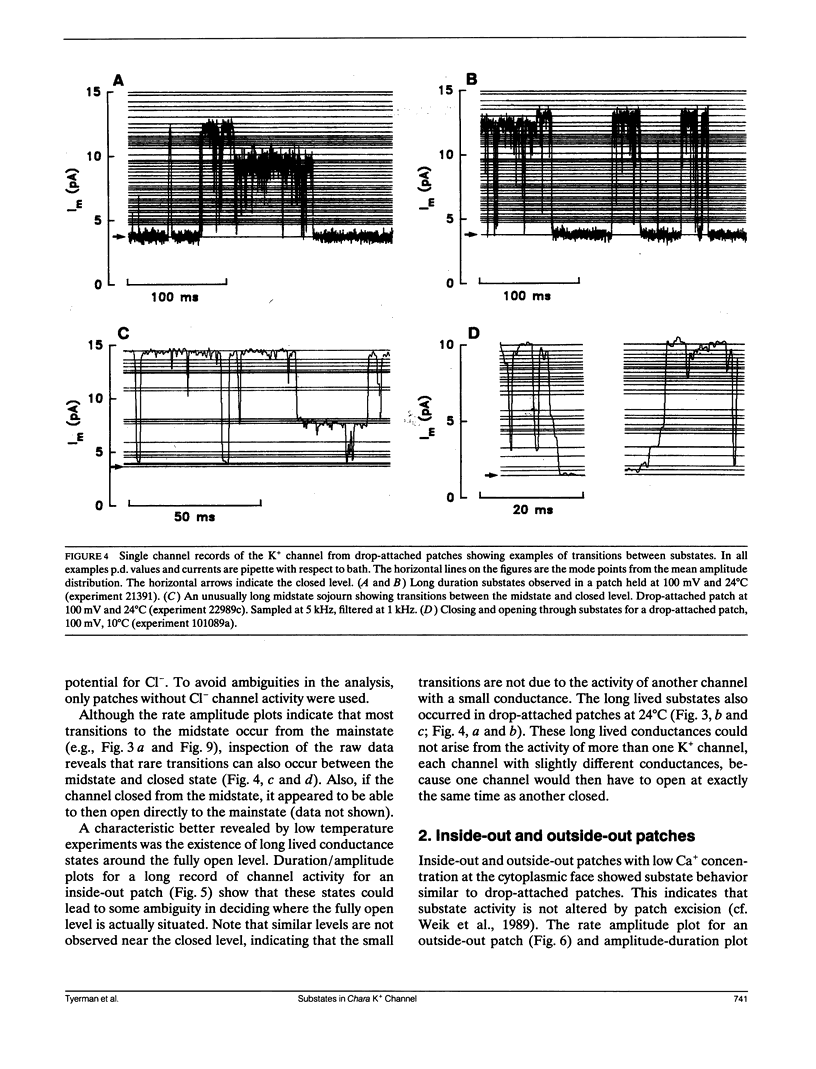
Abstract
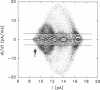
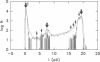
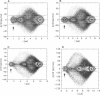
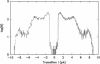
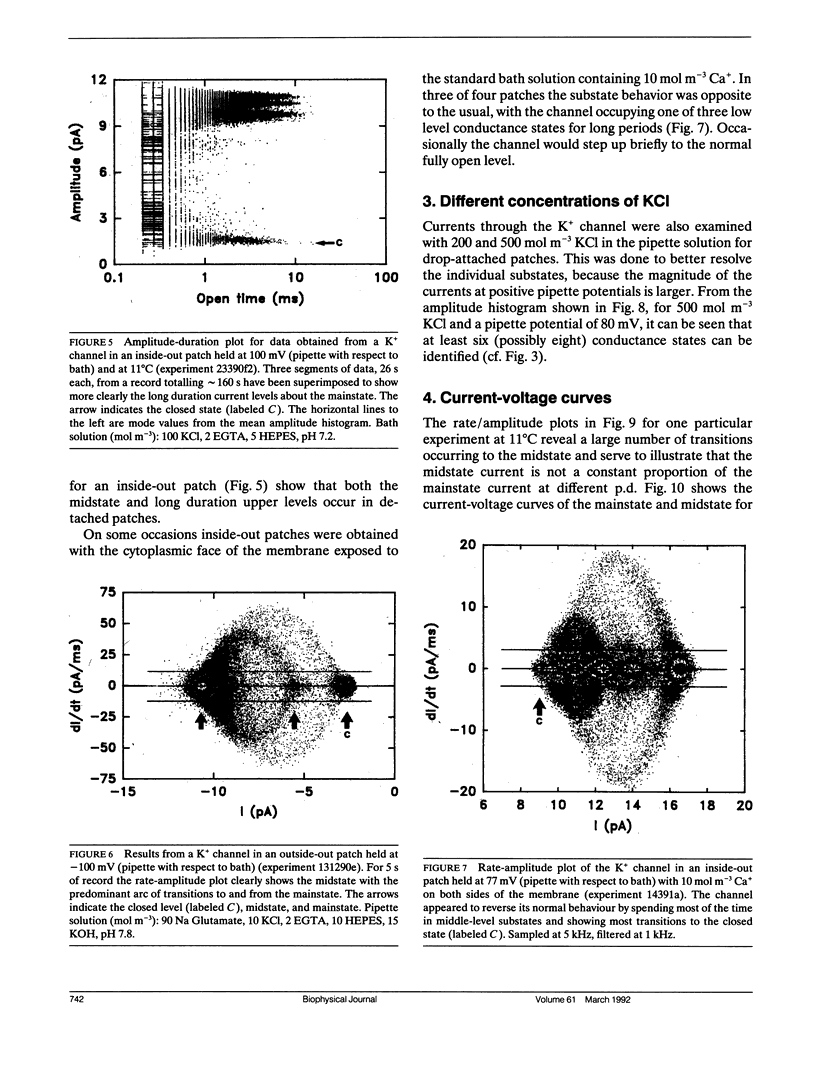
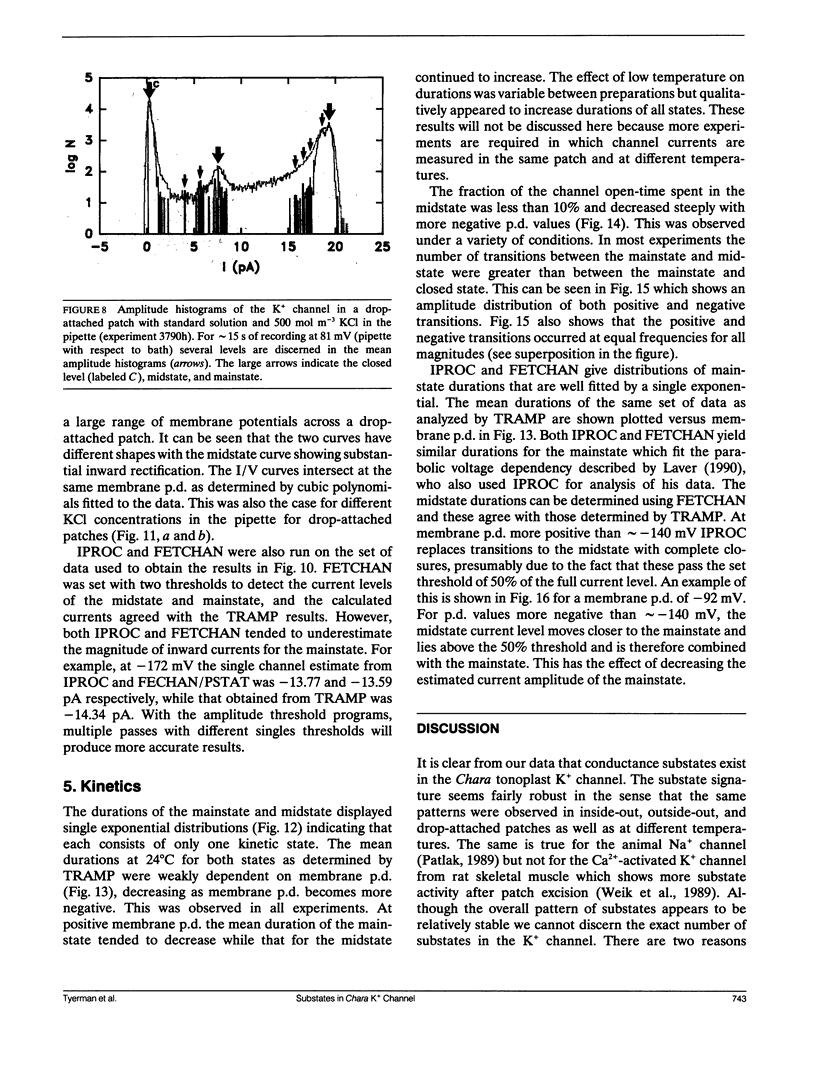
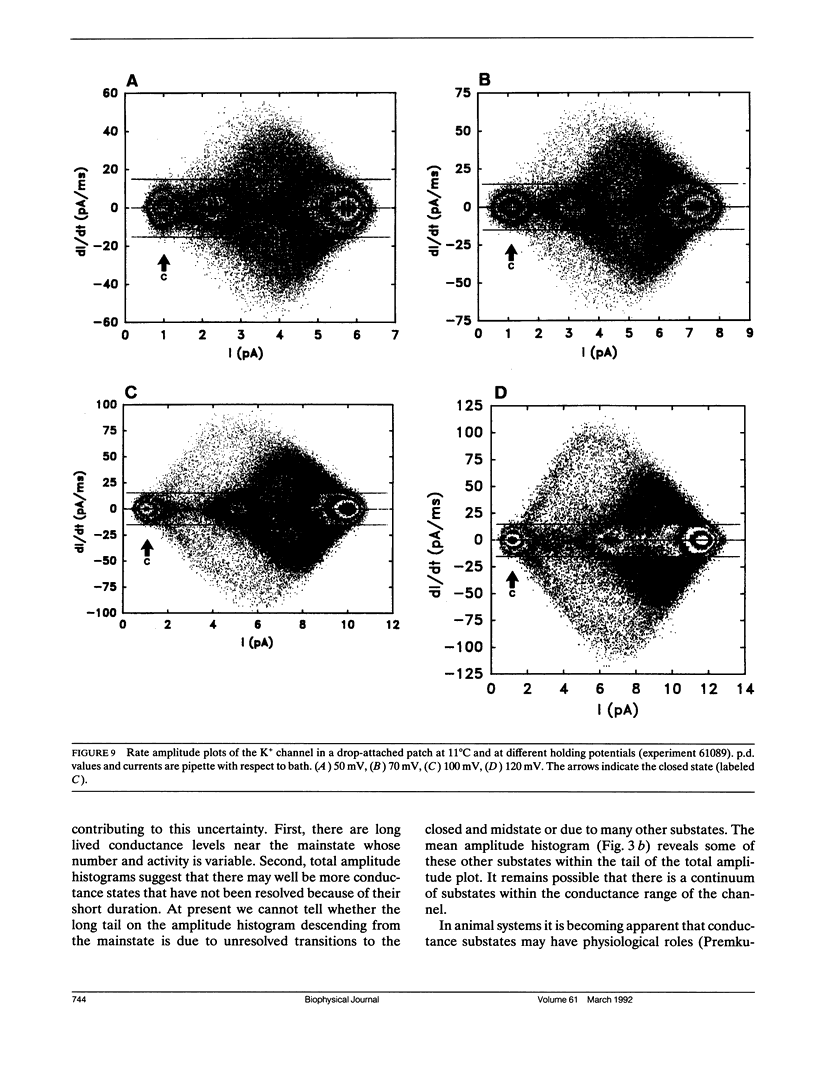
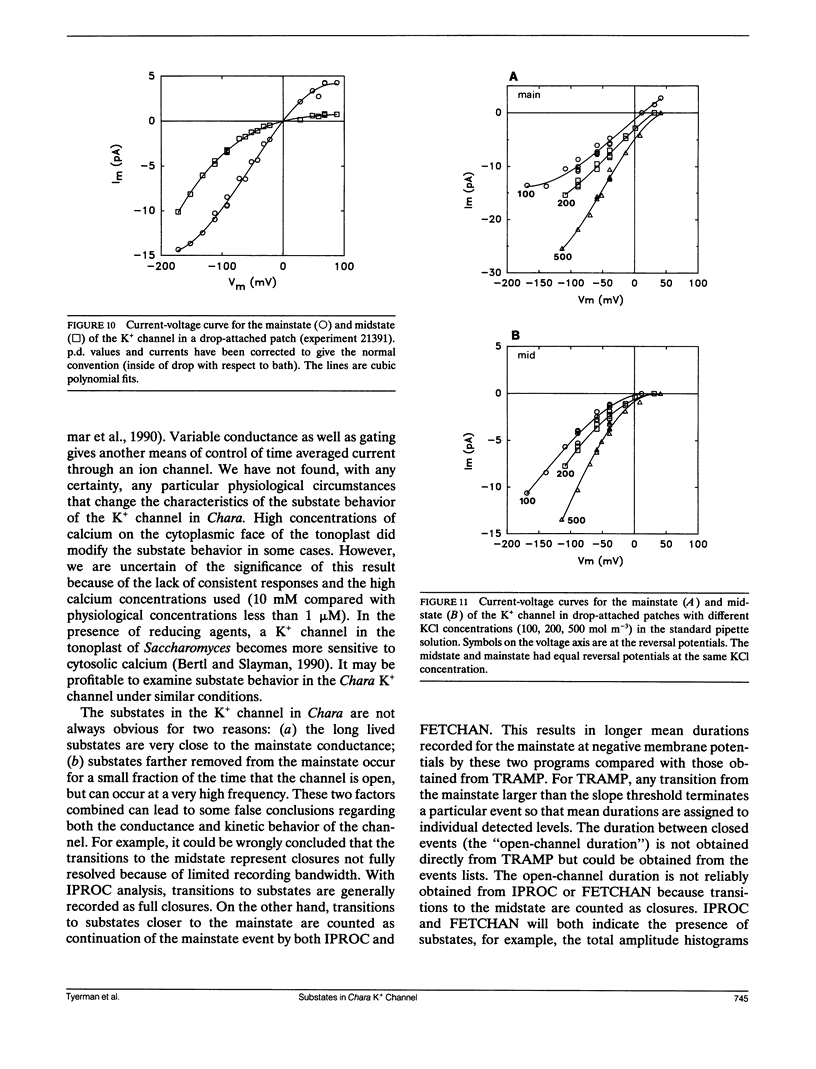
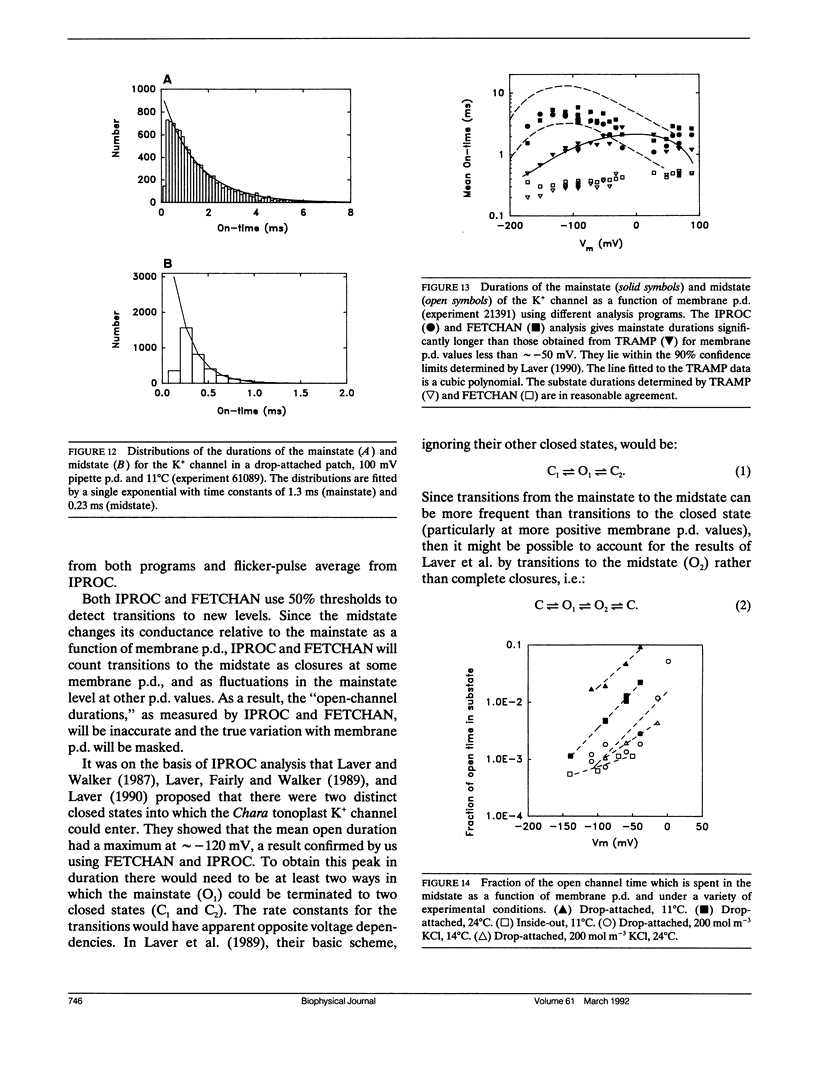
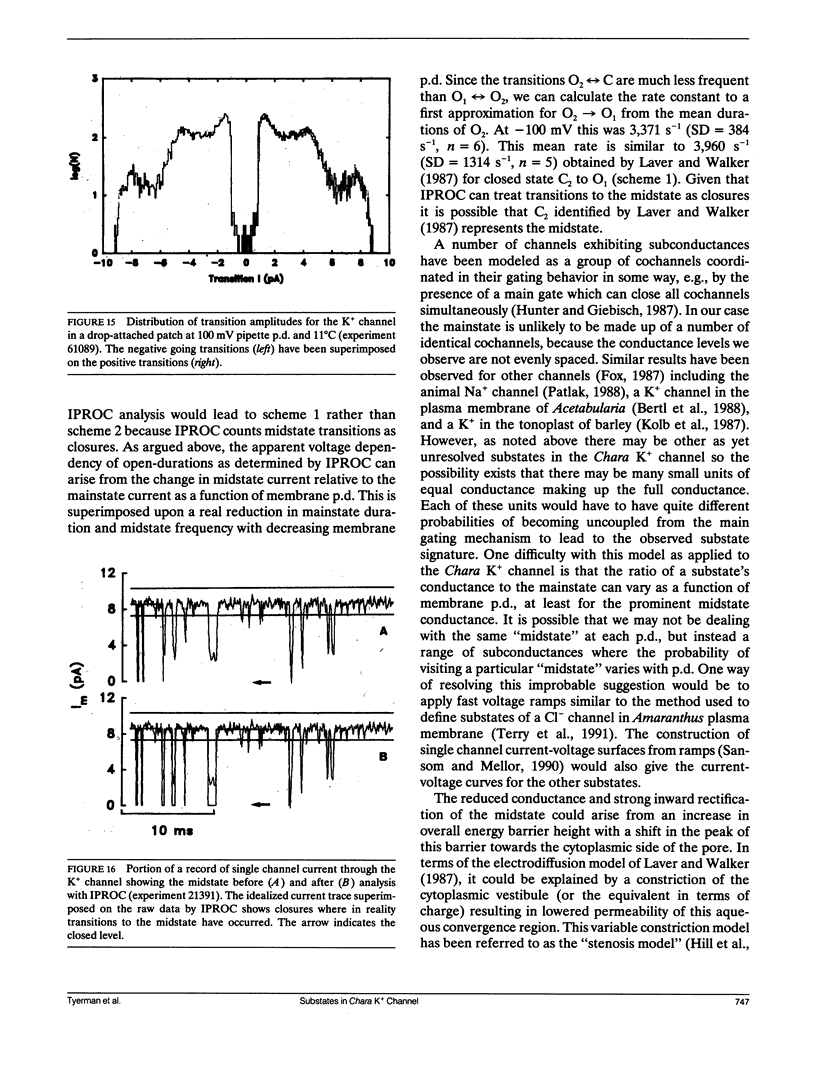
The large conductance K+ channel in the tonoplast of Chara corallina has subconductance states (substates). We describe a method that detects substates by monitoring the time derivative of channel current. Substates near to the full conductance tend to have long durations and high probabilities, while those of smaller amplitude occur with less probability and short duration. The substate pattern is similar in cell-attached, inside-out and outside-out patches over a range of temperatures. The pattern changes at high Ca2+ concentration (10 mol m-3) on the cytoplasmic face of inside-out patches. One substate at approximately 50% of the full conductance is characterized by a high frequency of transitions from the full conductance level. This midstate conductance is not a constant proportion of the full conductance but changes as a function of membrane potential difference (p.d.) showing strong inward rectification. We suggest that the channel is a single pore that can change conformation and/or charge profile to give different conductances. The mean durations of the full conductance level and the midstate decrease as the membrane p.d. becomes more negative. Programs for analysis of channel kinetics based on an half-amplitude detection criterion are shown to be unsuitable for analysis of the K+ channel.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Flickering of a nicotinic ion channel to a subconductance state. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84362-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Single-channel currents from acetylcholine receptors in embryonic chick muscle. Kinetic and conductance properties of gaps within bursts. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):187–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84147-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertl A., Slayman C. L. Cation-selective channels in the vacuolar membrane of Saccharomyces: dependence on calcium, redox state, and voltage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7824–7828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Moore J. B., Xia L. G., Premkumar L. S., Gage P. W. Characterization of single channel currents using digital signal processing techniques based on Hidden Markov Models. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Sep 29;329(1254):265–285. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. Ion channel subconductance states. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01869609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geletyuk V. I., Kazachenko V. N. Single Cl- channels in molluscan neurones: multiplicity of the conductance states. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01871605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M., Giebisch G. Multi-barrelled K channels in renal tubules. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):522–524. doi: 10.1038/327522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Dependence of acetylcholine receptor channel kinetics on agonist concentration in cultured mouse muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:555–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazachenko V. N., Geletyuk V. I. The potential-dependent K+ channel in molluscan neurones is organized in a cluster of elementary channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):132–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90558-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver D. R. Coupling of K(+)-gating and permeation with Ca2+ block in the Ca2(+)-activated K+ channel in Chara australis. J Membr Biol. 1990 Oct;118(1):55–67. doi: 10.1007/BF01872204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi K., Moczydlowski E. Subconductance behavior in a maxi Ca2(+)-activated K+ channel induced by dendrotoxin-I. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90450-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistry D. K., Hablitz J. J. Activation of subconductance states by gamma-aminobutyric acid and its analogs in chick cerebral neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):454–461. doi: 10.1007/BF00370754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Prod'hom B., Hess P. Conformational changes associated with ion permeation in L-type calcium channels. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):373–376. doi: 10.1038/333373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar L. S., Gage P. W., Chung S. H. Coupled potassium channels induced by arachidonic acid in cultured neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Oct 22;242(1303):17–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prod'hom B., Pietrobon D., Hess P. Direct measurement of proton transfer rates to a group controlling the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):243–246. doi: 10.1038/329243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard E. A., Miller C. Steady-state coupling of ion-channel conformations to a transmembrane ion gradient. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1208–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.2156338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer D. B., Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Andersen O. S. Induction of conductance heterogeneity in gramicidin channels. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6571–6583. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Urry D. W., Prasad K. U. Open channel noise. III. High-resolution recordings show rapid current fluctuations in gramicidin A and four chemical analogues. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83299-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strecker G. J., Jackson M. B. Curare binding and the curare-induced subconductance state of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):795–806. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82726-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. R., Tyerman S. D., Findlay G. P. Ion channels in the plasma membrane of Amaranthus protoplasts: one cation and one anion channel dominate the conductance. J Membr Biol. 1991 May;121(3):223–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01951556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivaudou M. B., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr An automated technique for analysis of current transitions in multilevel single-channel recordings. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Oct;407(4):355–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00652618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R., Lönnendonker U., Neumcke B. Low-conductance states of K+ channels in adult mouse skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 7;983(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]