Abstract
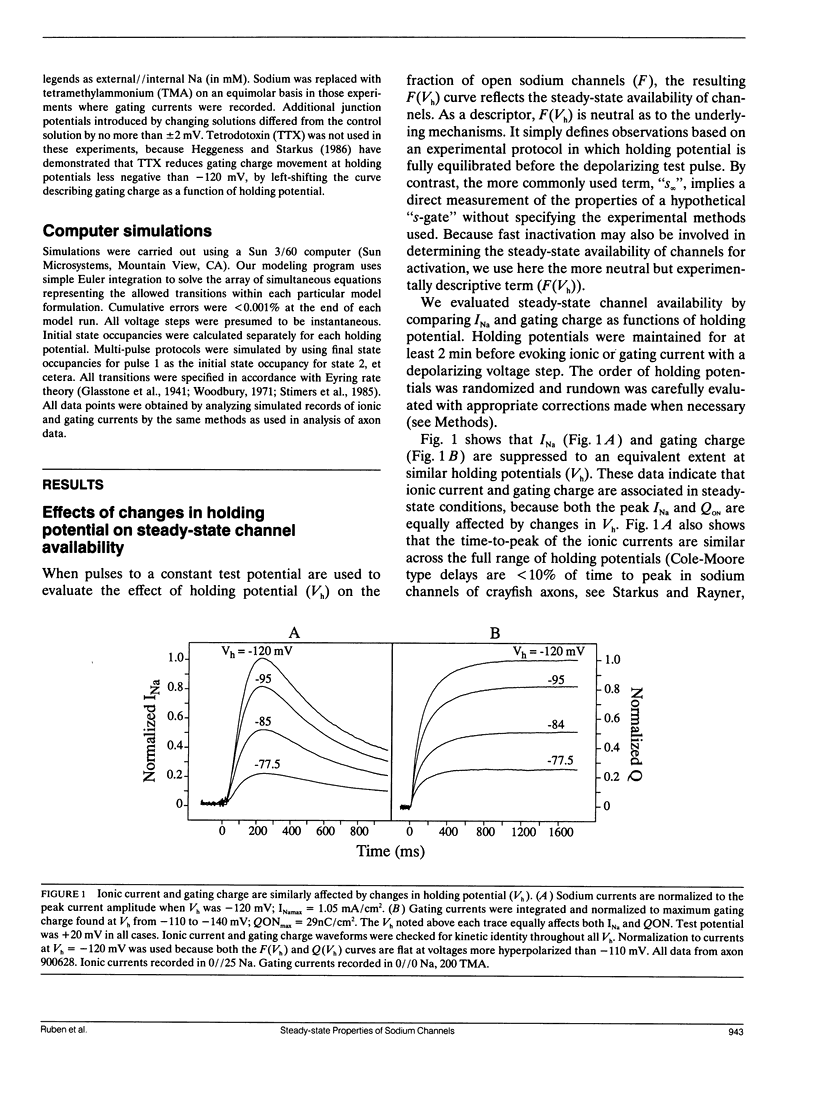
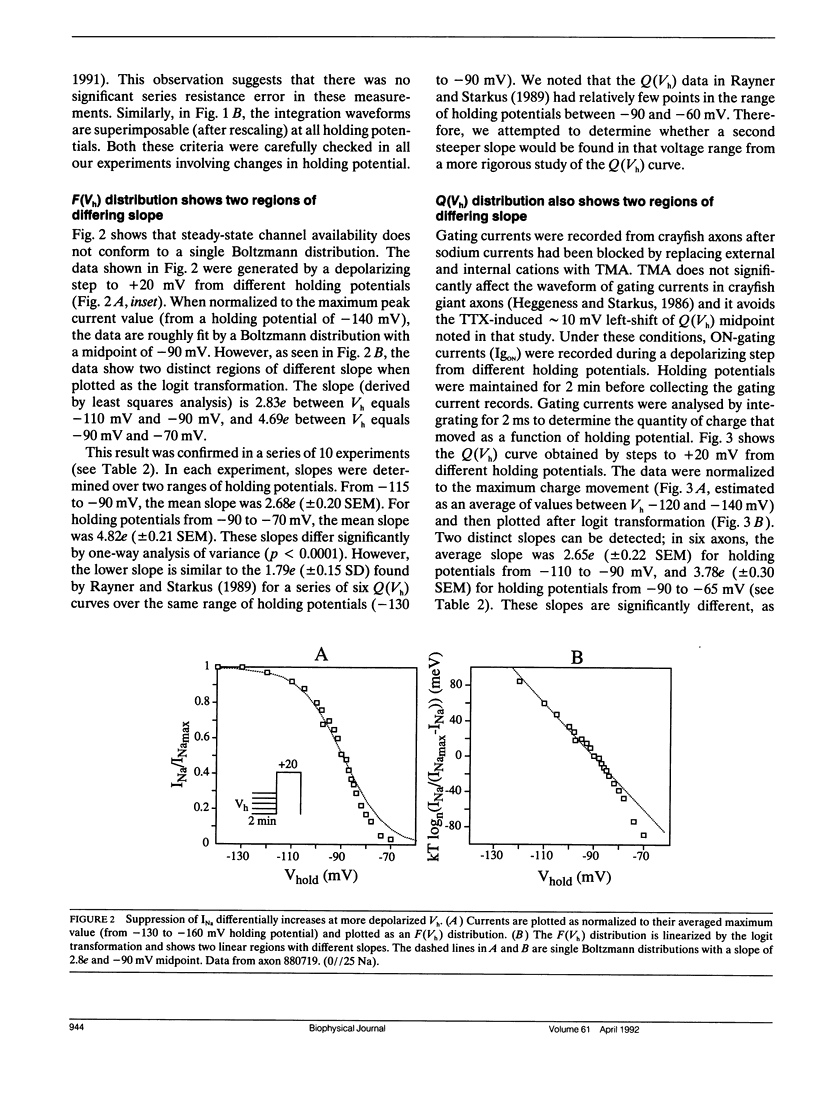
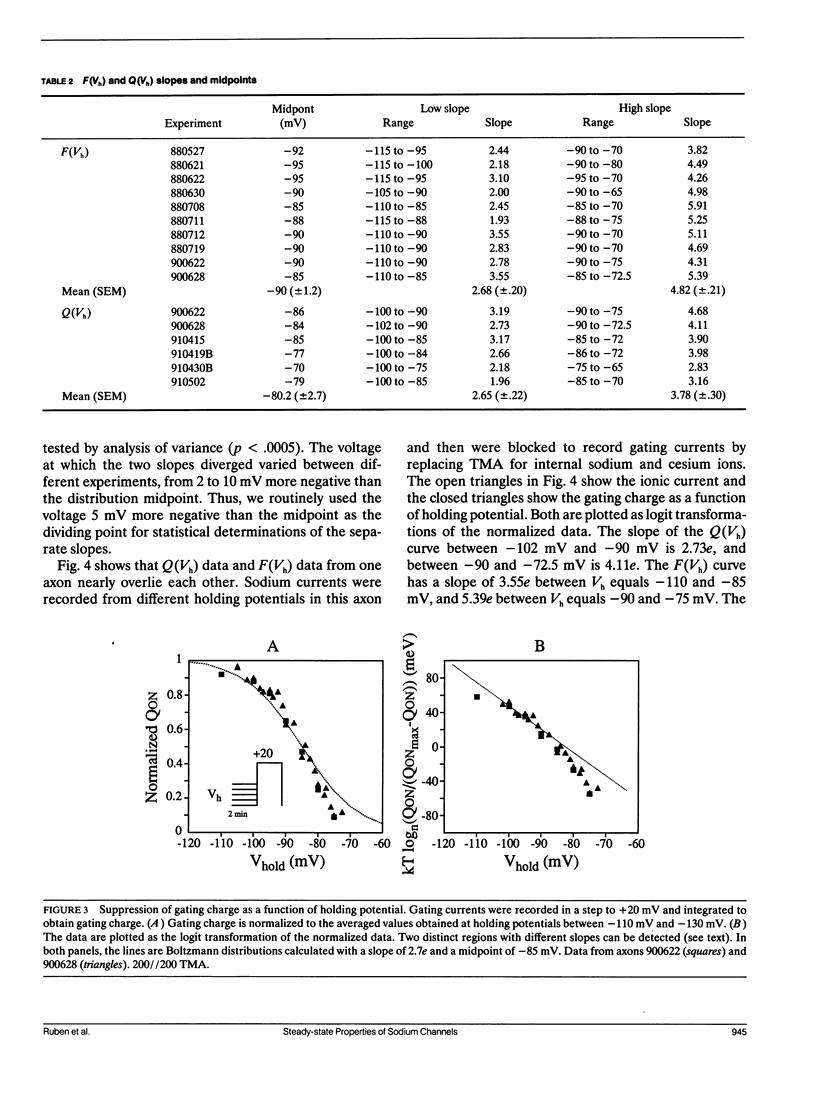
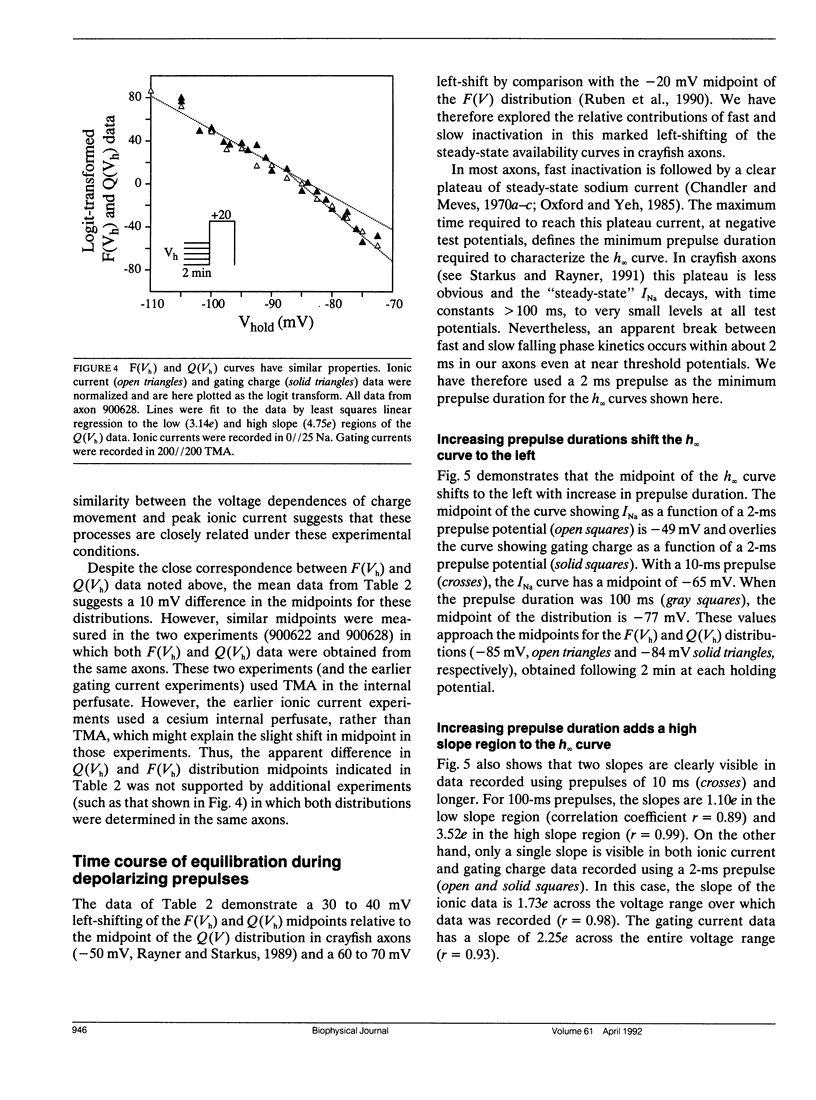
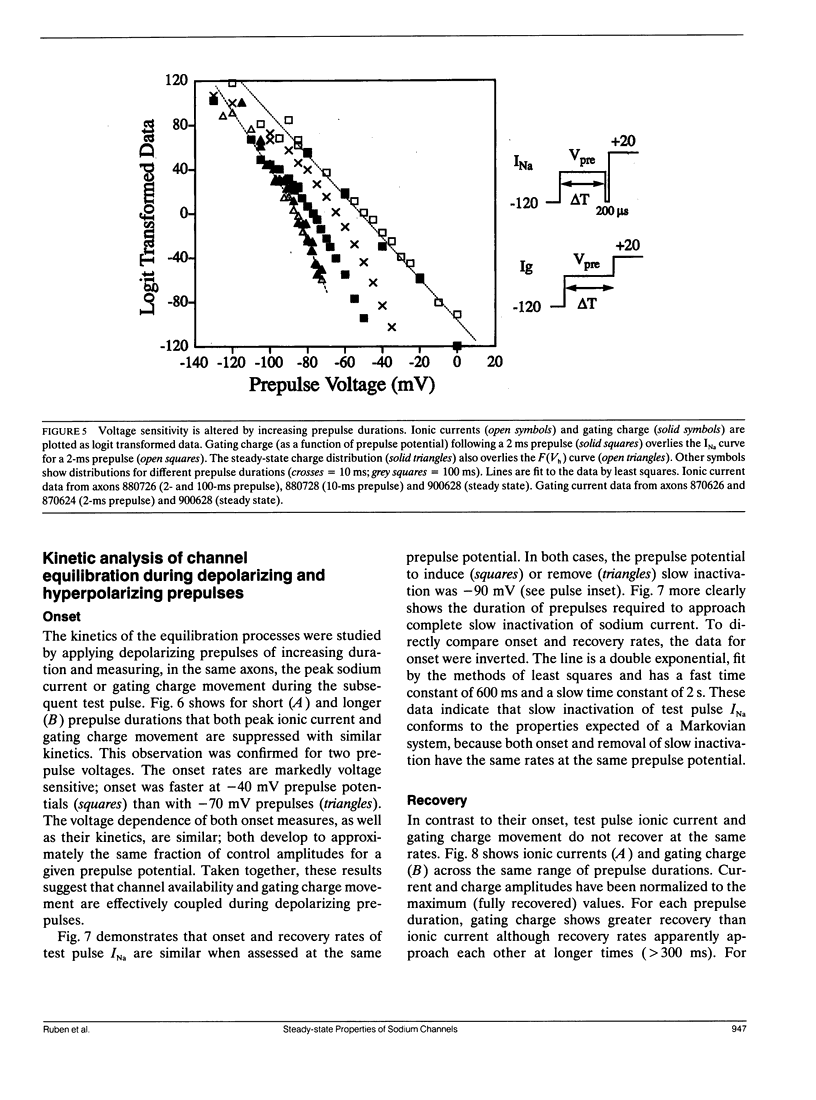
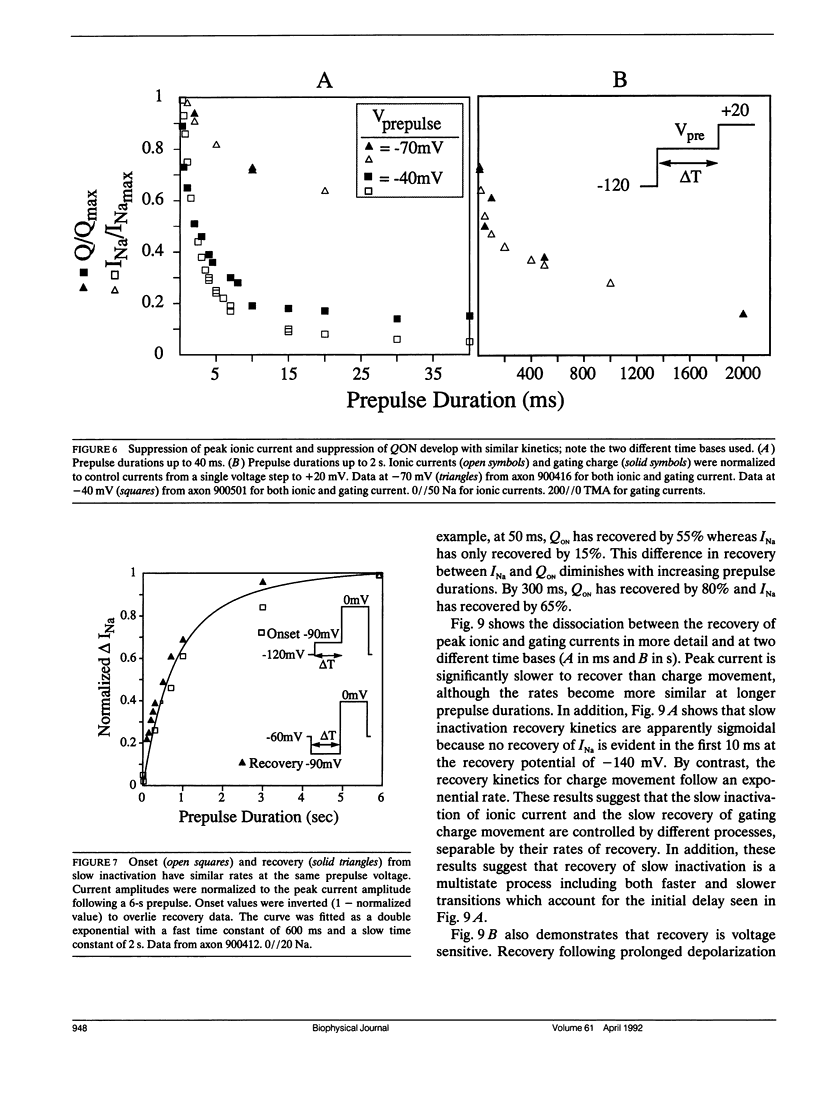
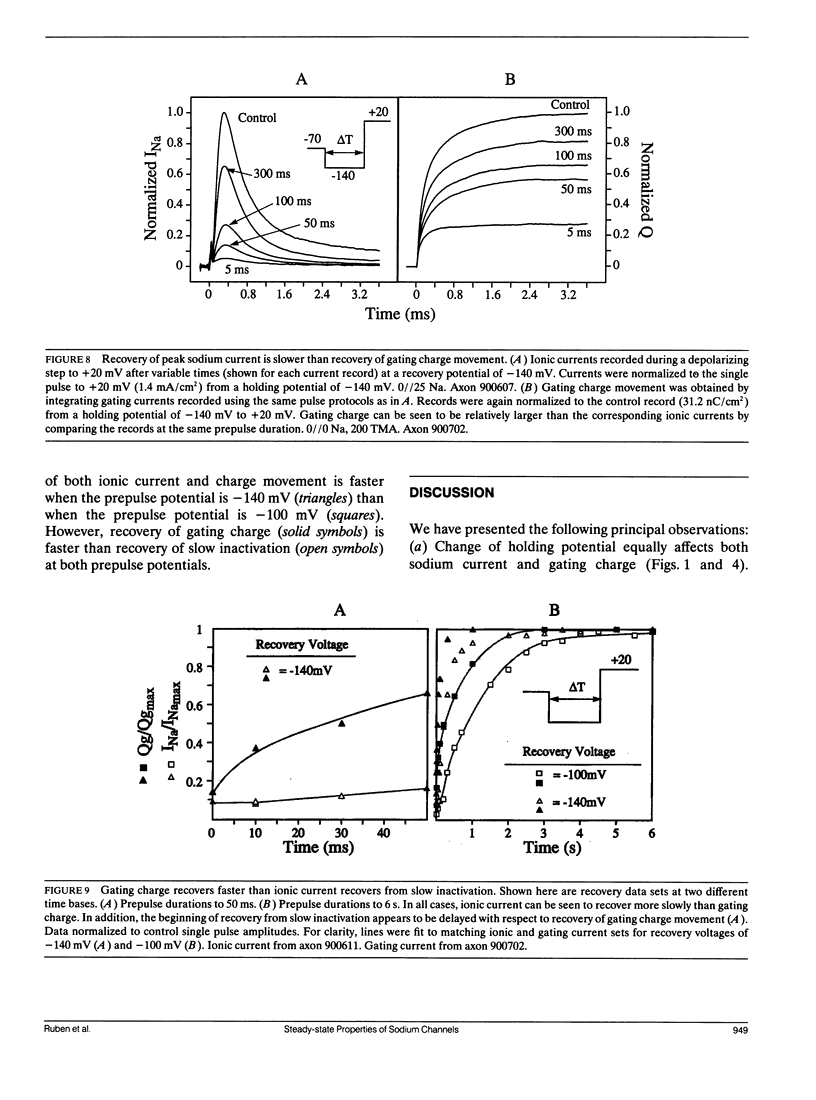
Changes in holding potential (Vh), affect both gating charge (the Q(Vh) curve) and peak ionic current (the F(Vh) curve) seen at positive test potentials. Careful comparison of the Q(Vh) and F(Vh) distributions indicates that these curves are similar, having two slopes (approximately 2.5e for Vh from -115 to -90 mV and approximately 4e for Vh from -90 to -65 mV) and very negative midpoints (approximately -86 mV). Thus, gating charge movement and channel availability appear closely coupled under fully-equilibrated conditions. The time course by which channels approach equilibration was explored using depolarizing prepulses of increasing duration. The high slope component seen in the F(Vh) and Q(Vh) curves is not evident following short depolarizing prepulses in which the prepulse duration approximately corresponds to the settling time for fast inactivation. Increasing the prepulse duration to 10 ms or longer reveals the high slope, and left-shifts the midpoint to more negative voltages, towards the F(Vh) and Q(Vh) distributions. These results indicate that a separate slow-moving voltage sensor affects the channels at prepulse durations greater than 10 ms. Charge movement and channel availability remain closely coupled as equilibrium is approached using depolarizing pulses of increasing durations. Both measures are 50% complete by 50 ms at a prepulse potential of -70 mV, with proportionately faster onset rates when the prepulse potential is more depolarized. By contrast, charge movement and channel availability dissociate during recovery from prolonged depolarizations. Recovery of gating charge is considerably faster than recovery of sodium ionic current after equilibration at depolarized potentials. Recovery of gating charge at -140 mV, is 65% complete within approximately 100 ms, whereas less than 30% of ionic current has recovered by this time. Thus, charge movement and channel availability appear to be uncoupled during recovery, although both rates remain voltage sensitive. These data suggest that channels remain inactivated due to a separate process operating in parallel with the fast gating charge. We demonstrate that this behavior can be simulated by a model in which the fast charge movement associated with channel activation is electrostatically-coupled to a separate slow voltage sensor responsible for the slow inactivation of channel conductance.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The effects of external potassium and long duration voltage conditioning on the amplitude of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):589–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alicata D. A., Rayner M. D., Starkus J. G. Osmotic and pharmacological effects of formamide on capacity current, gating current, and sodium current in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82811-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A neutral amino acid change in segment IIS4 dramatically alters the gating properties of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E., Fernández J. M. Distribution and kinetics of membrane dielectric polarization. 1. Long-term inactivation of gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):21–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Slow mechanism for sodium permeability inactivation in myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):283–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Rios E. Intramembrane charge movement in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Properties of charge 2. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:489–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Evidence for two types of sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride solution. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):653–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Rate constants associated with changes in sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):679–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Sodium and potassium currents in squid axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):623–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández J. M., Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E. Distribution and kinetics of membrane dielectric polarization. II. Frequency domain studies of gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):41–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L. Gating current kinetics in Myxicola giant axons. Order of the back transition rate constants. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):574–589. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82273-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Hille B. Gating of Na channels. Inactivation modifiers discriminate among models. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Feb;89(2):253–274. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness S. T., Starkus J. G. Saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin. Electrostatic effects on sodium channel gating current in crayfish axons. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):629–643. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83690-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D. On the voltage dependence of inactivation in the sodium channel of the squid giant axon. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jan 22;243(1306):47–53. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Vogel W. Slow recovery of sodium current and 'gating current' from inactivation. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):395–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., VanDongen A. M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Fast and slow gating of sodium channels encoded by a single mRNA. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Yeh J. Z. Interactions of monovalent cations with sodium channels in squid axon. I. Modification of physiological inactivation gating. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):583–602. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N. Burst kinetics of sodium channels which lack fast inactivation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:563–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner M. D., Starkus J. G. The steady-state distribution of gating charge in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82775-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben P. C., Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Holding potential affects the apparent voltage-sensitivity of sodium channel activation in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82458-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Comparison between slow sodium channel inactivation in rat slow- and fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:339–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Pencek T. L., Davis F. A. Slow sodium inactivation in Myxicola axons. Evidence for a second inactive state. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):771–778. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85727-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Ionic conductance changes in voltage clamped crayfish axons at low pH. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):666–690. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Slow sodium channel inactivation in rat fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:327–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Gating current "fractionation" in crayfish giant axons. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1101–1119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82146-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Shrager P. Modification of slow sodium inactivation in nerve after internal perfusion with trypsin. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C238–C244. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimers J. R., Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E. Sodium channel activation in the squid giant axon. Steady state properties. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):65–82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2122520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Bezanilla F., Parsegian V. A. Solute inaccessible aqueous volume changes during opening of the potassium channel of the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1990 May;57(5):1049–1064. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82623-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



