Abstract
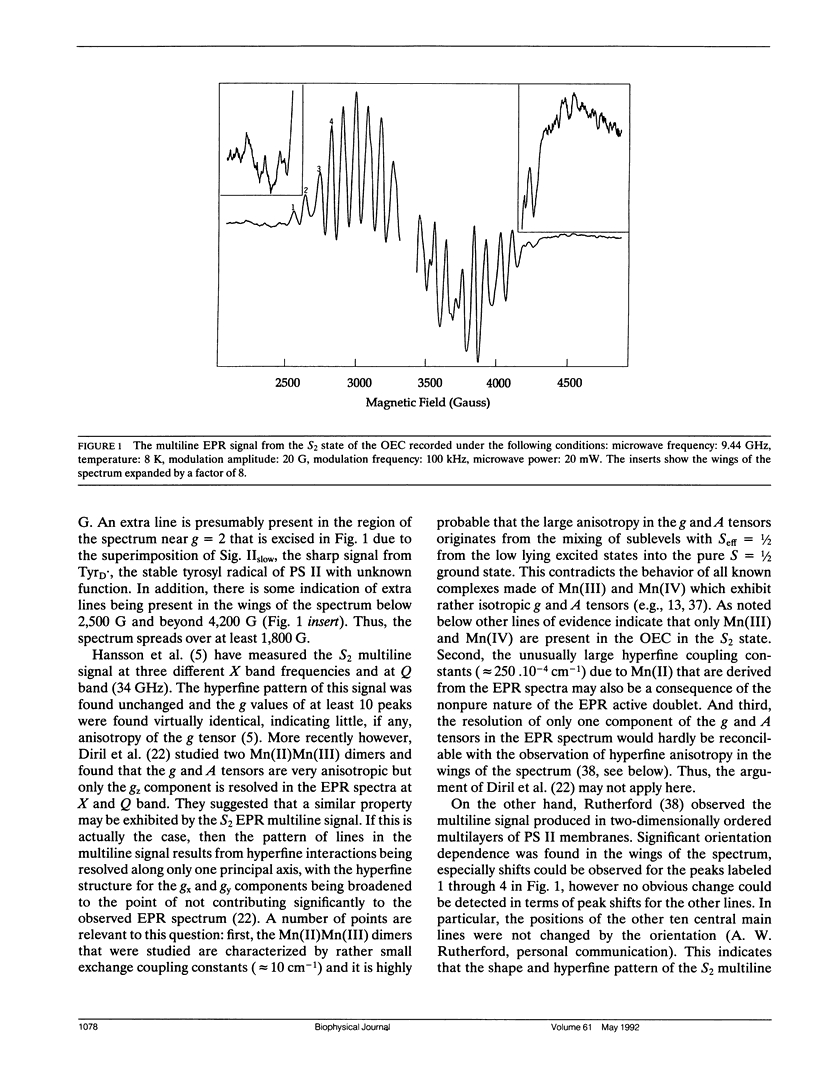
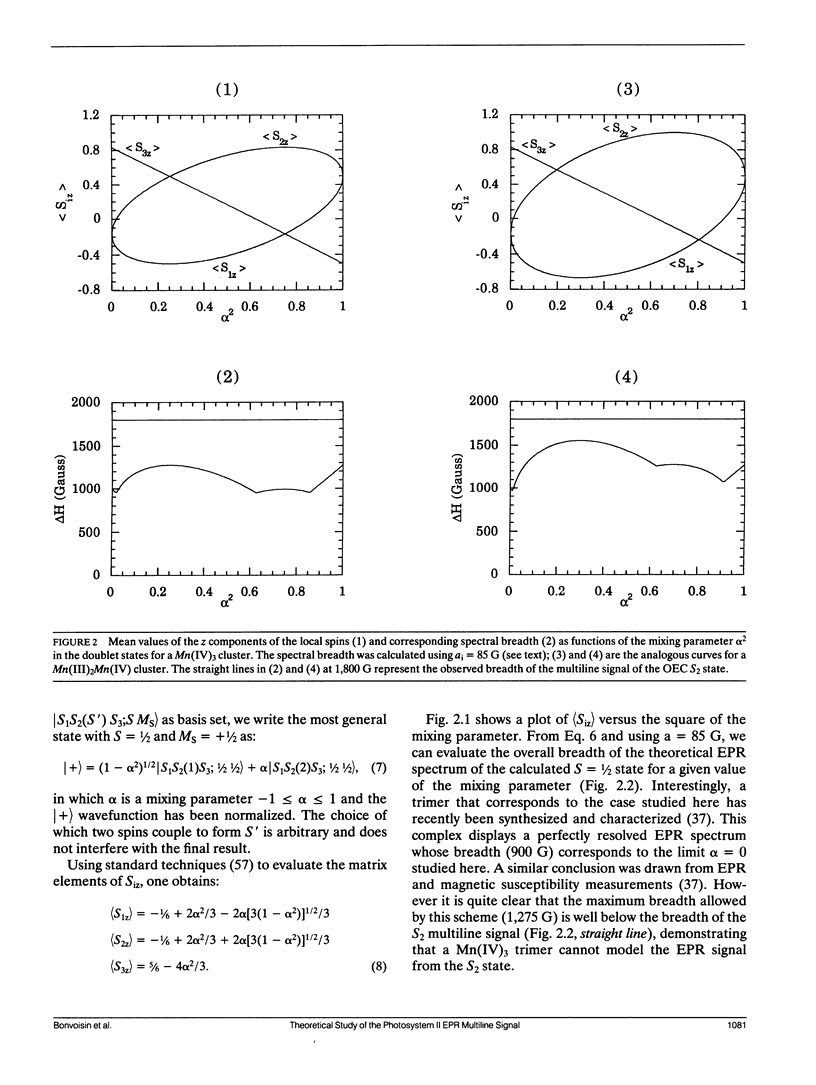
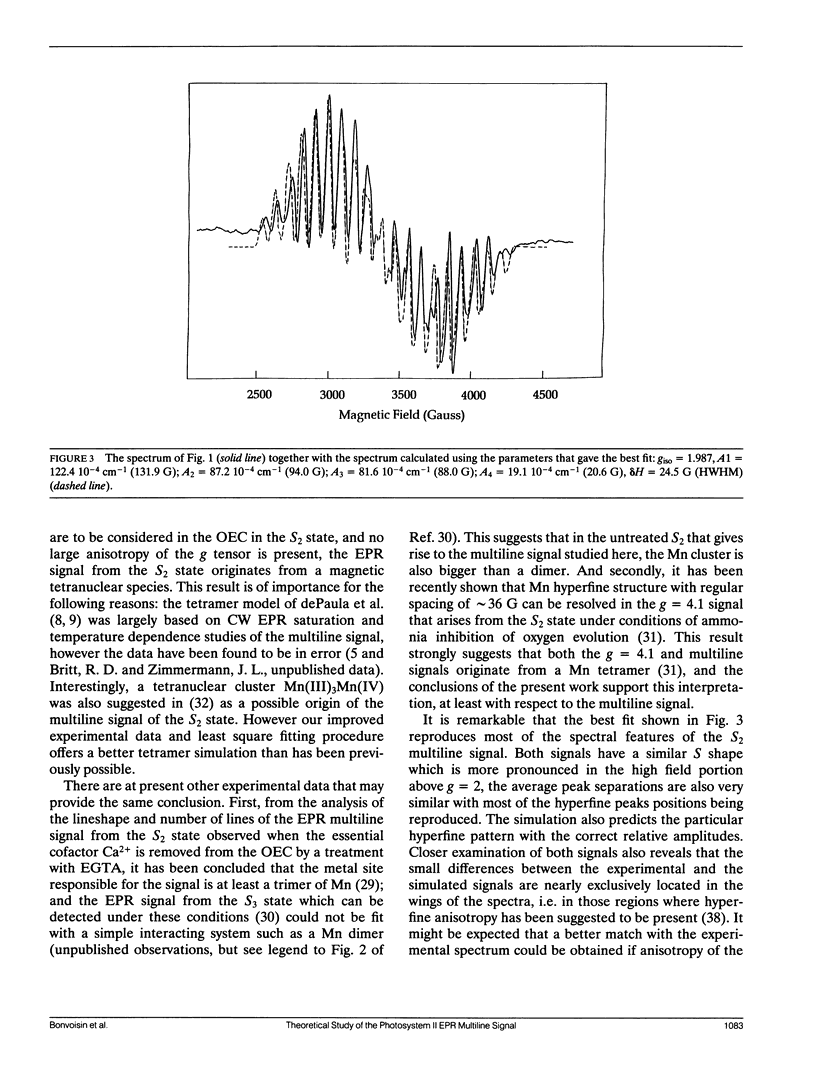
The Oxygen evolving complex of plant photosystem II is made of a manganese cluster that gives rise to a low temperature EPR multiline signal in the S2 oxidation state. The origin of this EPR signal has been addressed with respect to the question of the magnetic couplings between the electron and nuclear spins of the four possible Mn ions that make up this complex. Considering Mn(III) and Mn(IV) as the only possible oxidation states present in the S2 state, and no large anisotropy of the magnetic tensors, the breadths of the EPR spectra calculated for dimers and trimers with S = ½ have been compared with that of the biological site. It is concluded that neither a dinuclear nor a trinuclear complex made of Mn(III) and Mn(IV) can be responsible for the multiline signal; but that, by contrast, a tetranuclear Mn complex can be the origin of this signal. The general shape of the experimental spectrum, its particular hyperfine pattern, the positions of most of the hyperfine lines and their relative intensities can be fit by a tetramer model described by the following six fitting parameters: g ≈ 1.987, A1 ≈ 122.4 10-4 cm-1, A2 ≈ 87.2 10-4 cm-1, A3 ≈ 81.6 10-4 cm-1, A4 ≈ 19.1 10-4 cm-1 and δH = 24.5 G. A second model described by parameters very close to those given above except for A4 ≈ 77.5 10-4 cm-1 gives an equally good fit. However, no other set of parameters gives an EPR spectrum that reproduces the hyperfine pattern of the S2 multiline signal. This demonstrates that in the S2 state of the oxygen evolving complex, the four manganese ions are organized in a magnetic tetramer.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boussac A., Zimmermann J. L., Rutherford A. W. EPR signals from modified charge accumulation states of the oxygen evolving enzyme in Ca2+-deficient photosystem II. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):8984–8989. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRose V. J., Yachandra V. K., McDermott A. E., Britt R. D., Sauer K., Klein M. P. Nitrogen ligation to manganese in the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving complex: continuous-wave and pulsed EPR studies of photosystem II particles containing 14N or 15N. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1335–1341. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes G. C., Siderer Y. Intermediates of a polynuclear manganese center involved in photosynthetic oxidation of water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):274–278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G. N., Prince R. C., Cramer S. P. The manganese site of the photosynthetic water-splitting enzyme. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):789–791. doi: 10.1126/science.2916124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiles R. D., Zimmermann J. L., McDermott A. E., Yachandra V. K., Cole J. L., Dexheimer S. L., Britt R. D., Wieghardt K., Bossek U., Sauer K. The S3 state of photosystem II: differences between the structure of the manganese complex in the S2 and S3 states determined by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):471–485. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson O., Aasa R., Vänngard T. The Origin of the Multiline and g = 4.1 Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Signals from the Oxygen-Evolving System of Photosystem II. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):825–832. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(87)83409-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. A., Huynh B. H., Münck E. Iron-sulfur proteins: spin-coupling model for three-iron clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6574–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachandra V. K., Guiles R. D., McDermott A. E., Cole J. L., Britt R. D., Dexheimer S. L., Sauer K., Klein M. P. Comparison of the structure of the manganese complex in the S1 and S2 states of the photosynthetic O2-evolving complex: an x-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):5974–5981. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


