Abstract
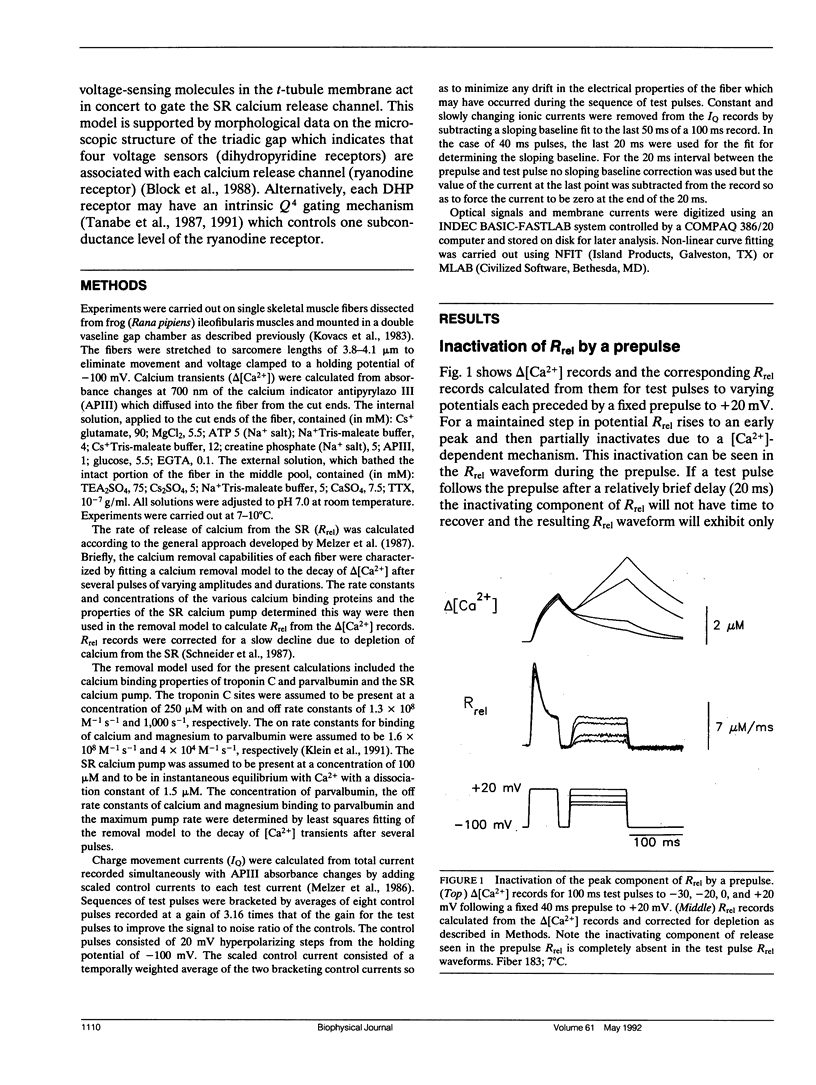
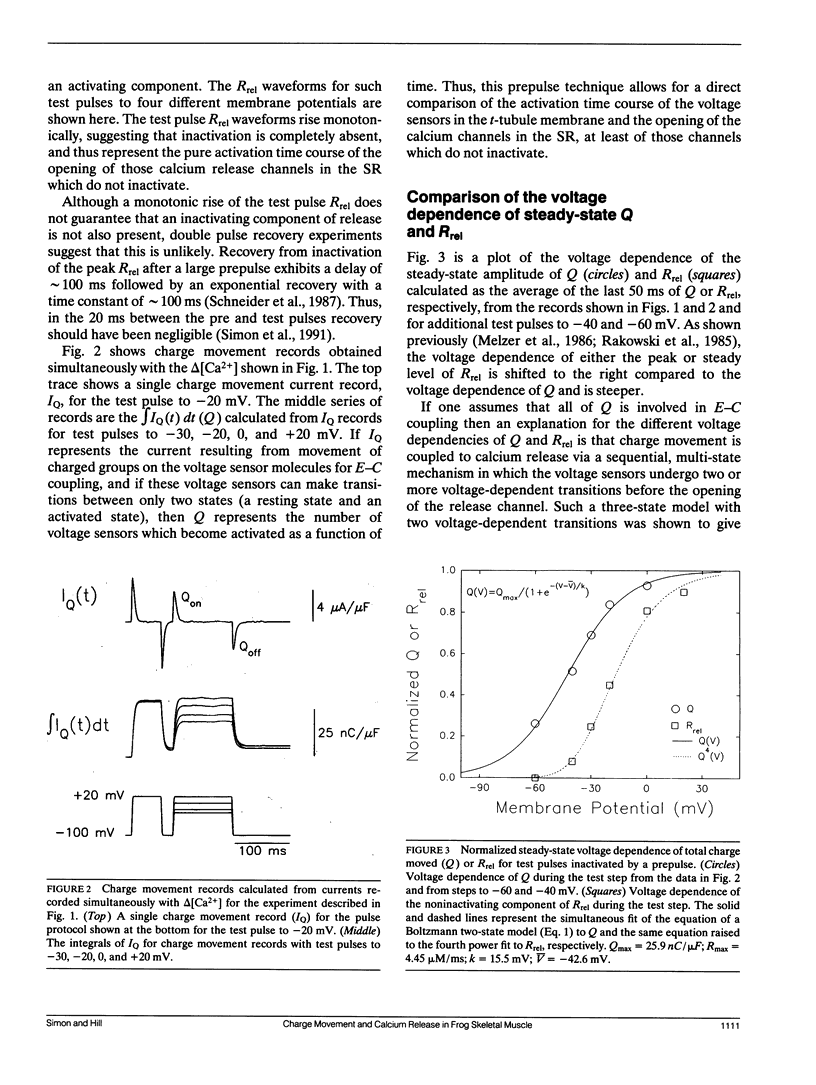
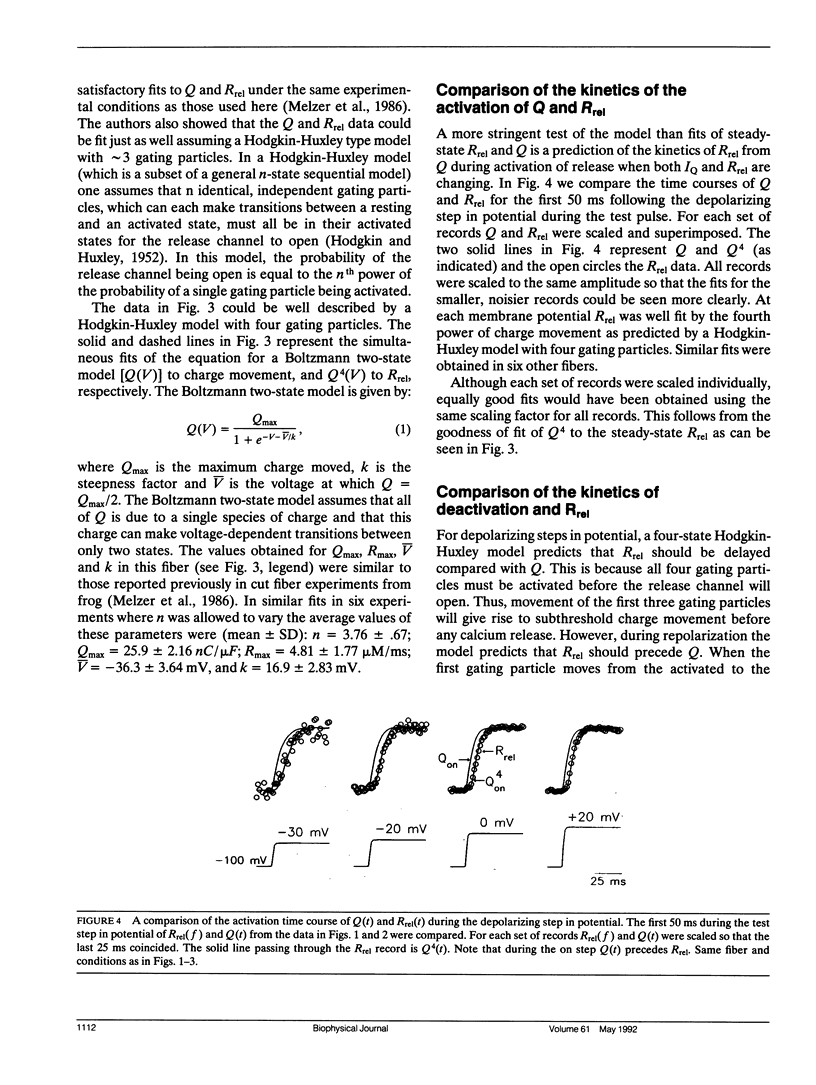
Charge movement currents (IQ) and calcium transients (delta[Ca2+]) were measured simultaneously in frog skeletal muscle fibers, voltage clamped in a double vaseline gap chamber, using Antipyrylazo III as the calcium indicator. The rate of release of calcium from the SR (Rrel) was calculated from the calcium transients using the removal model of Melzer, W., E. Rios, and M. F. Schneider (1987. Biophys. J. 51:849-863.). IQ and delta [Ca2+] were calculated for 100 ms depolarizing test pulses to membrane potentials from -30 to +20 mV. To eliminate an inactivating component of Rrel, each test pulse was preceded by a large, fixed prepulse to +20 mV. The resulting Rrel records, which represent the noninactivating component of Rrel, were compared with integral of IQdt.(Q), the total charge that moves. The voltage dependence of the steady state Rrel was steeper then that of Q and shifted to the right. During depolarization, the Rrel waveform was similar to that of Q but was delayed by several ms, while, during repolarization, Rrel preceded Q. All of these results could be explained with a Hodgkin-Huxley type model for E-C coupling in which four voltage sensors in the t-tubule membrane which give rise to IQ must all be in their activating positions for the calcium release channel in the SR membrane to open. his model is consistent with the structural architecture of the triadic junction in which four dihydropyridine receptors (the voltage sensors for E-C coupling) in the t-tubule membrane are closely associated with each ryanodine receptor(the calcium release channel) in the SR membrane [Block, B. A., T. Imagawa, K. P. Campbell, and C. Franzini-Armstrong. 1988. J.Cell. Biol. 107:2587-2600.]). Some aspects of this work have appeared in abstract form (Simon, B. J., and D. Hill. 1991. Biophys. J.59:64a. ([Abstr.]).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csernoch L., Pizarro G., Uribe I., Rodríguez M., Ríos E. Interfering with calcium release suppresses I gamma, the "hump" component of intramembranous charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):845–884. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Ogunbunmi E. M., Dixon M. C., Fleer E. A. Localization of Ca2+ release channels with ryanodine in junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7256–7259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J., Pizarro G., Ríos E., Stefani E. Effect of the calcium buffer EGTA on the "hump" component of charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):885–896. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiny J. A., Jong D. S. A nonlinear electrostatic potential change in the T-system of skeletal muscle detected under passive recording conditions using potentiometric dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):147–175. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge moved at contraction thresholds in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:595–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Intramembrane charge movements in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1988 Oct;68(4):1197–1147. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.4.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S., Chandler W. K. Intramembranous charge movement in frog cut twitch fibers mounted in a double vaseline-gap chamber. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):257–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Differential properties of two charge components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:531–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. A general procedure for determining the rate of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):849–863. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83413-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Time course of calcium release and removal in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):637–641. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84203-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:481–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro G., Csernoch L., Uribe I., Rodríguez M., Ríos E. The relationship between Q gamma and Ca release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):913–947. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F., Best P. M., James-Kracke M. R. Voltage dependence of membrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):403–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00712580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J. Inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:727–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Depletion of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum during calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:167–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Beam K. G. The influence of transverse tubular delays on the kinetics of charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):21–42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Klein M. G., Schneider M. F. Calcium dependence of inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Mar;97(3):437–471. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.3.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Time course of activation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1159–1163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83050-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szücs G., Csernoch L., Magyar J., Kovács L. Contraction threshold and the "hump" component of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):897–911. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Adams B. A., Numa S., Beam K. G. Repeat I of the dihydropyridine receptor is critical in determining calcium channel activation kinetics. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):800–803. doi: 10.1038/352800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Delay M. A transmission delay and the effect of temperature at the triadic junction of skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Oct 22;229(1254):97–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


