Abstract
The kinetics of Ca2+ release induced by the second messenger D-myoinositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate (IP3), by the hydrolysis-resistant analogue D-myoinositol 1,4,5 trisphosphorothioate (IPS3), and by micromolar Ca2+ were resolved on a millisecond time scale in the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of rabbit skeletal muscle. The total Ca2+ mobilized by IP3 and IPS3 varied with concentration and with time of exposure. Approximately 5% of the 45Ca2+ passively loaded into the SR was released by 2 microM IPS3 in 150 ms, 10% was released by 10 microM IPS3 in 100 ms, and 20% was released by 50 microM IPS3 in 20 ms. Released 45Ca2+ reached a limiting value of approximately 30% of the original load at a concentration of 10 microM IP3 or 25-50 microM IPS3. Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) was studied by elevating the extravesicular Ca2+ while maintaining a constant 5-mM intravesicular 45Ca2+. An increase in extravesicular Ca2+ from 7 nM to 10 microM resulted in a release of 55 +/- 7% of the passively loaded 45Ca2+ in 150 ms. CICR was blocked by 5 mM Mg2+ or by 10 microM ruthenium red, but was not blocked by heparin at concentrations as high as 2.5 mg/ml. In contrast, the release produced by IPS3 was not affected by Mg2+ or ruthenium red but was totally inhibited by heparin at concentrations of 2.5 mg/ml or lower. The release produced by 10 microM Ca2+ plus 25 microM IPS3 was similar to that produced by 10 microM Ca2+ alone and suggested that IP3-sensitive channels were present in SR vesicles also containing ruthenium red-sensitive Ca2+ release channels. The junctional SR of rabbit skeletal muscle may thus have two types of intracellular Ca2+ releasing channels displaying fast activation kinetics, namely, IP3-sensitive and Ca(2+)-sensitive channels.
Full text
PDF

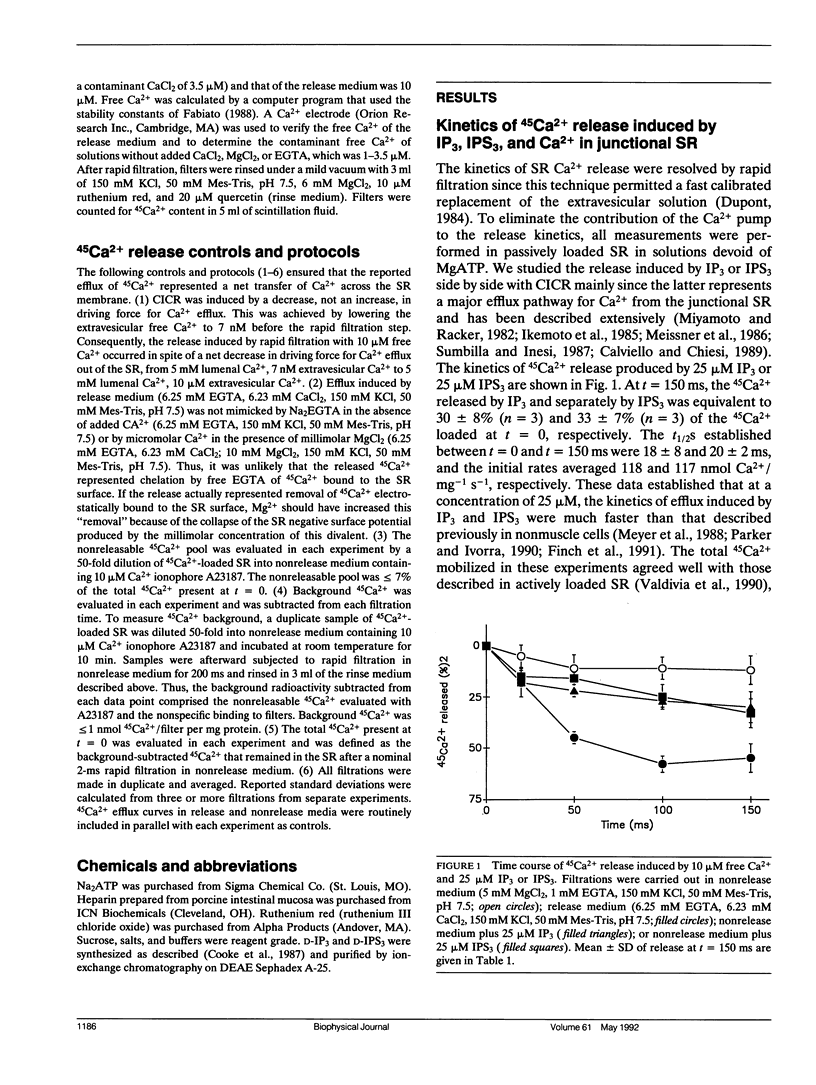
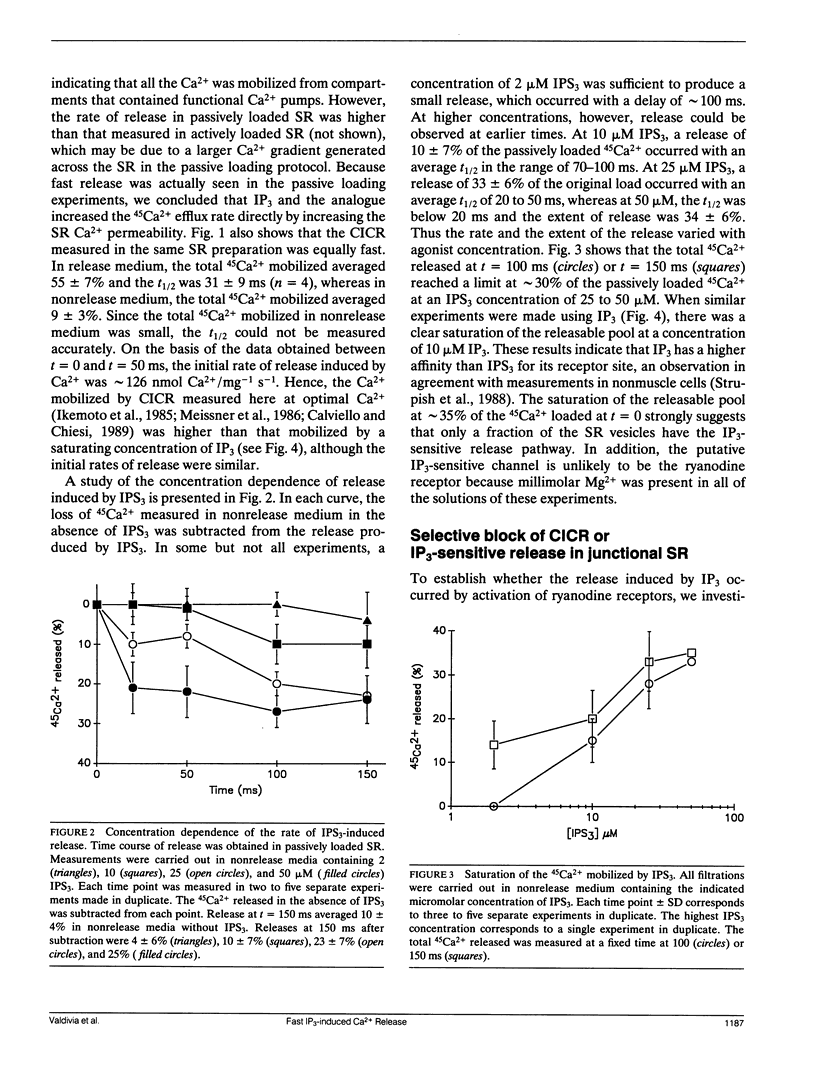
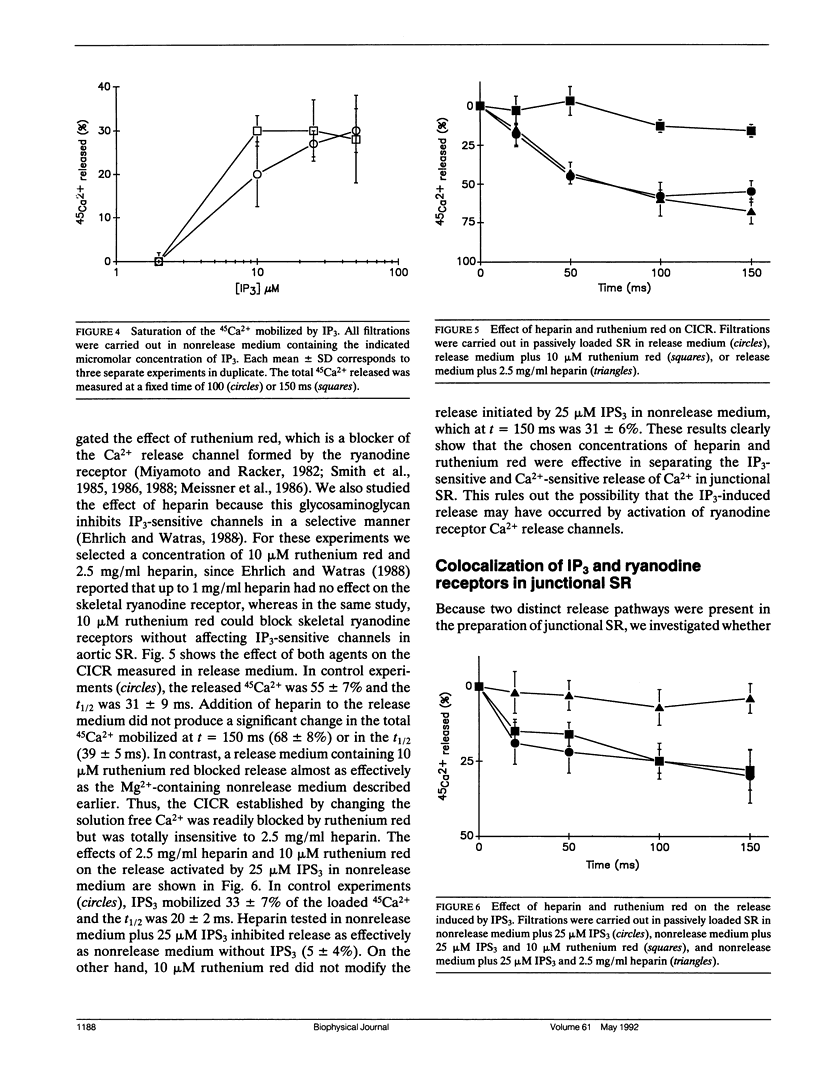
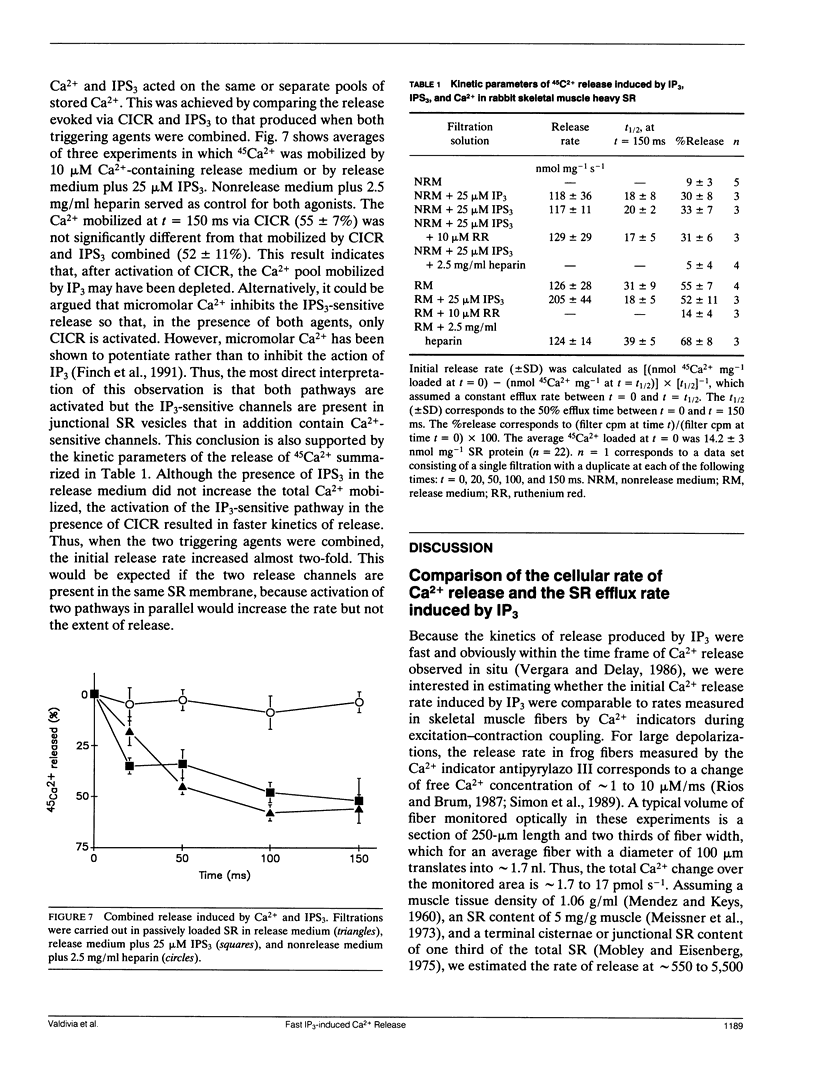




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird J. G., Nahorski S. R. Increased intracellular calcium stimulates 3H-inositol polyphosphate accumulation in rat cerebral cortical slices. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Mechanism of release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Ríos E., Stéfani E. Effects of extracellular calcium on calcium movements of excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:441–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calviello G., Chiesi M. Rapid kinetic analysis of the calcium-release channels of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: the effect of inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1301–1306. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson S. K., Goldberg N. D., Walseth T. F., Huetteman D. A. Inositol trisphosphate stimulates calcium release from peeled skeletal muscle fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 19;927(1):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. A rapid-filtration technique for membrane fragments or immobilized enzymes: measurements of substrate binding or ion fluxes with a few-millisecond time resolution. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90496-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Watras J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):583–586. doi: 10.1038/336583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Deerinck T. J., Ouyang Y., Beck C. F., Tanksley S. J., Walton P. D., Airey J. A., Sutko J. L. Identification and localization of ryanodine binding proteins in the avian central nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Aug;5(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Rapid ionic modifications during the aequorin-detected calcium transient in a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):189–246. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Carrasco M. A., Magendzo K., Jaimovich E. Phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol by transverse tubule vesicles and its possible role in excitation-contraction coupling. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 23;202(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80651-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto N., Antoniu B., Mészáros L. G. Rapid flow chemical quench studies of calcium release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14096–14100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentish J. C., Barsotti R. J., Lea T. J., Mulligan I. P., Patel J. R., Ferenczi M. A. Calcium release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum induced by photorelease of calcium or Ins(1,4,5)P3. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):H610–H615. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.2.H610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagos N., Vergara J. Phosphoinositides in frog skeletal muscle: a quantitative analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 17;1043(3):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90022-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T. J., Griffiths P. J., Tregear R. T., Ashley C. C. An examination of the ability of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to induce calcium release and tension development in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of frog and crustacea. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Fill M., Knudson C. M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle is a gap junction-type channel. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.2459777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Fesce R., Meldolesi J. Spontaneous [Ca2+]i fluctuations in rat chromaffin cells do not require inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate elevations but are generated by a caffeine- and ryanodine-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ store. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3005–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D. W., Godt R. E. Equilibrium distribution of ions in a muscle fiber. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):717–722. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82719-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):83–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Adenine nucleotide stimulation of Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2365–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikos G. J., Snow T. R. Failure of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to elicit or potentiate Ca2+ release from isolated skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 18;927(2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto H., Racker E. Mechanism of calcium release from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Eisenberg B. R. Sizes of components in frog skeletal muscle measured by methods of stereology. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):31–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movsesian M. A., Thomas A. P., Selak M., Williamson J. R. Inositol trisphosphate does not release Ca2+ from permeabilized cardiac myocytes and sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):328–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80932-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lederer W. J. Voltage-independent calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):565–568. doi: 10.1126/science.2173135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osipchuk Y. V., Wakui M., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by receptor stimulation, G-protein activation, internal application of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+: simultaneous microfluorimetry and Ca2+ dependent Cl- current recording in single pancreatic acinar cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape P. C., Konishi M., Baylor S. M., Somlyo A. P. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibers injected with the InsP3 blocker, heparin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. Localized all-or-none calcium liberation by inositol trisphosphate. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):977–979. doi: 10.1126/science.2237441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Nassar-Gentina V., Luxoro M., Pollard M. E., Carrasco M. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and contraction in crustacean muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;65(4):672–680. doi: 10.1139/y87-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer N. M., Ferguson J. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is not effective in releasing calcium from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1064–1070. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J. Inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:727–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Klein M. G., Schneider M. F. Caffeine slows turn-off of calcium release in voltage clamped skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):793–797. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82878-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Walker J. W., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R., Kobayashi S., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. V. Inositol trisphosphate, calcium and muscle contraction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):399–414. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strupish J., Cooke A. M., Potter B. V., Gigg R., Nahorski S. R. Stereospecific mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. Comparison with inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphorothioate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):901–905. doi: 10.1042/bj2530901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumbilla C., Inesi G. Rapid filtration measurements of Ca2+ release from cisternal sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 1;210(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Isla B. A., Irribarra V., Oberhauser A., Larralde L., Bull R., Hidalgo C., Jaimovich E. Inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate activates a calcium channel in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):737–741. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83009-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez X., Carrasco M. A., Vergara J., Hidalgo C. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate phosphatase activity in membranes isolated from amphibian skeletal muscle [corrected]. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):58–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S. Regions of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor critical for excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):567–569. doi: 10.1038/346567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Berridge M. J., Cooke A. M., Potter B. V. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphorothioate, a stable analogue of inositol trisphosphate which mobilizes intracellular calcium. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):645–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2590645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiger G., Björklund P. E., Cowburn R. F., Fowler C. J. Enhancement by potassium of carbachol-stimulated inositol phospholipid breakdown in rat cerebral cortical miniprisms: comparison with other depolarising agents. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1843–1853. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia C., Valdivia H. H., Potter B. V., Coronado R. Ca2+ release by inositol-trisphosphorothioate in isolated triads of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1990 Jun;57(6):1233–1243. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82642-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Delay M. A transmission delay and the effect of temperature at the triadic junction of skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Oct 22;229(1254):97–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Tsien R. Y., Delay M. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate: a possible chemical link in excitation-contraction coupling in muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6352–6356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Salviati G., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate induces calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):347–349. doi: 10.1038/316347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Somlyo A. V., Goldman Y. E., Somlyo A. P., Trentham D. R. Kinetics of smooth and skeletal muscle activation by laser pulse photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):249–252. doi: 10.1038/327249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcocks A. L., Potter B. V., Cooke A. M., Nahorski S. R. Myo-inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphorothioate binds to specific [3H]inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate sites in rat cerebellum and is resistant to 5-phosphatase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 11;155(1-2):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


