Abstract
The average lifetime of gramicidin A channels in monoolein/decane bilayer membranes was measured. The results support the hypothesis of channel stabilization by ion occupancy. The effects of electric field and salt concentration are consistent with the expected effects on both occupancy and membrane compression. The lifetime in asymmetric solutions with divalent cation blockers on one side of the membrane shows a voltage dependence such that the lifetime decreases for positive voltages applied from the blocking side and increases for negative voltages. This result strongly supports the occupancy hypothesis. The lifetime increases with permeant ion concentration, and at the one molar level it also increases with voltage. The voltage dependence of lifetime for a low concentration of permeant ion depends on the total salt level. The results for these conditions are consistent with the assumption that membrane compression also influences the lifetime, even for the "soft" solvent-containing membrane considered here. It is proposed that the channel nearest neighbor lipids need not be fixed in a plane at the channel end. Using a liquid crystal model it may then be shown that surface tension is the major component of the membrane deformation free energy, which may explain the significant effects of the membrane compression on the lifetime.
Full text
PDF

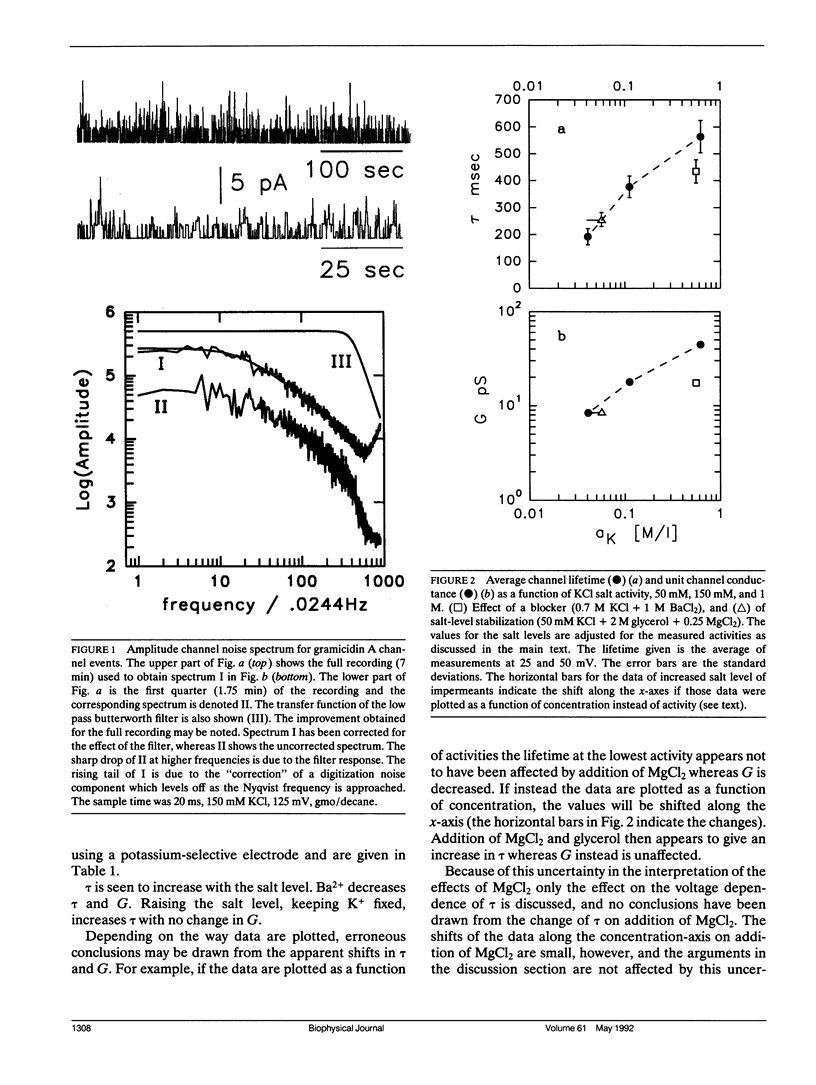
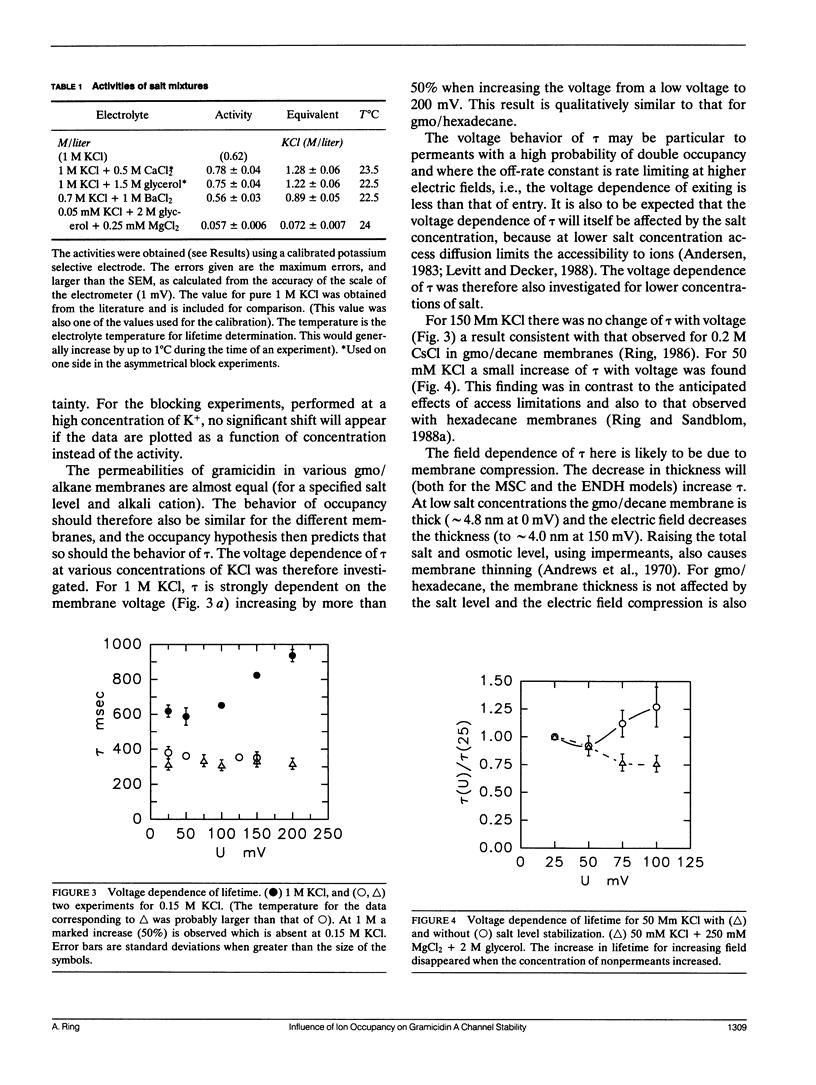
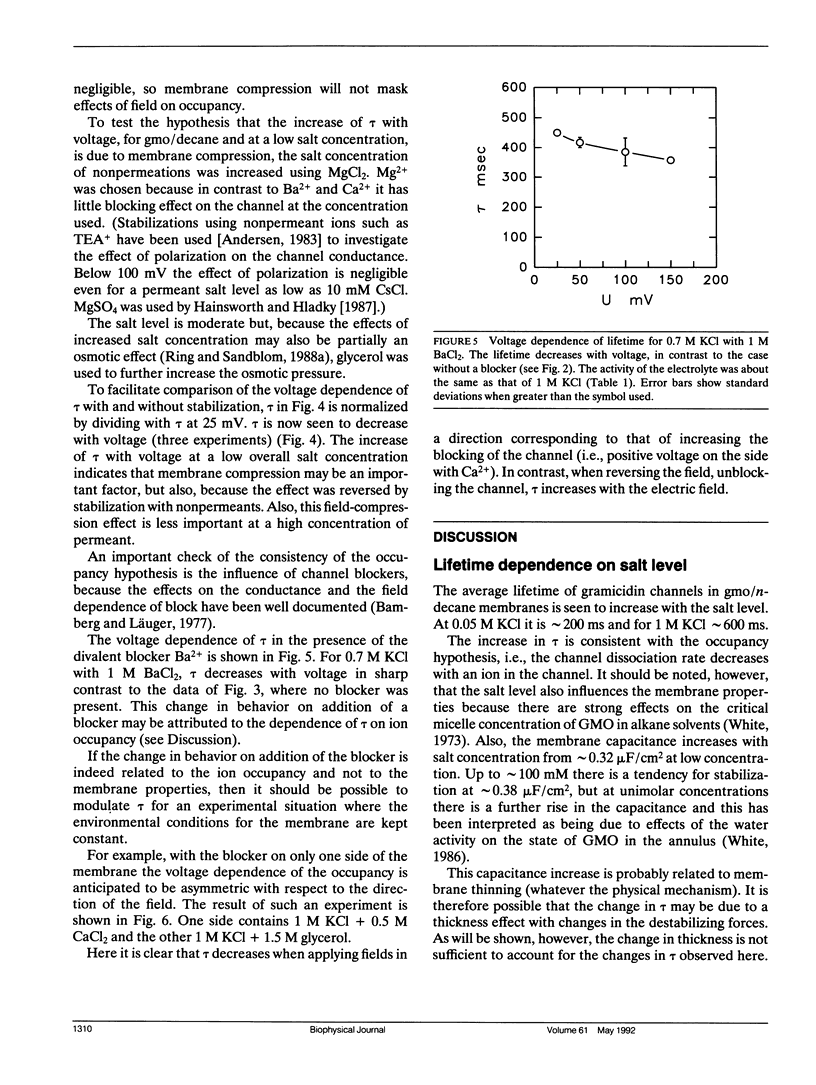
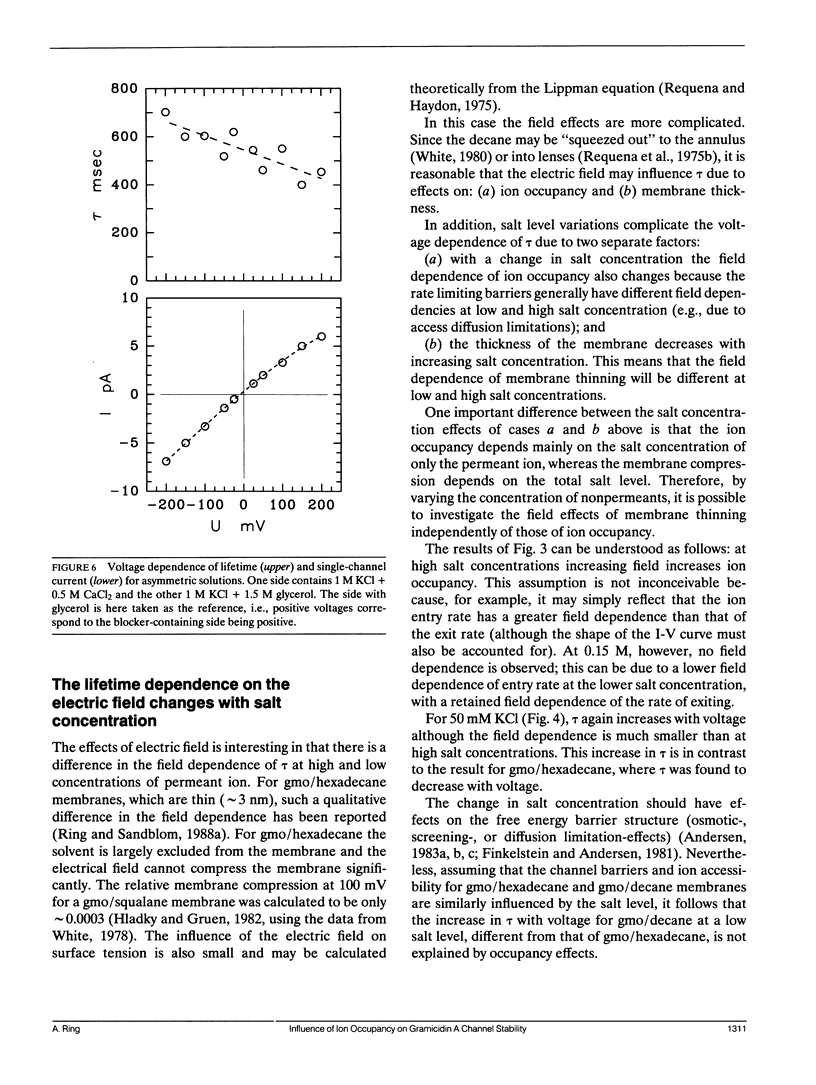




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Single-channel measurements at very high potentials. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):119–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84414-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aqvist J., Warshel A. Energetics of ion permeation through membrane channels. Solvation of Na+ by gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1989 Jul;56(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82662-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Apell H. J., Alpes H., Gross E., Morell J. L., Harbaugh J. F., Janko K., Läuger P. Ion channels formed by chemical analogs of gramicidin A. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2633–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Subramaniam S., Jakobsson E., McCammon J. A. Water and polypeptide conformations in the gramicidin channel. A molecular dynamics study. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82671-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton P. L., Hinton J. F., Newkirk D. K. Kinetics of channel formation of gramicidins A and B in phospholipid vesicle membranes. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82507-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. R., Needham D., Dilger J. P., Brandt O., Haydon D. A. A quantitative explanation of the effects of some alcohols on gramicidin single-channel lifetime. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 11;814(2):401–404. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. R., Needham D., Dilger J. P., Haydon D. A. The effects of bilayer thickness and tension on gramicidin single-channel lifetime. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 26;735(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchebest C., Pullman A. Energy profile of Cs+ in gramicidin A in the presence of water. Problem of the ion selectivity of the channel. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Apr;5(5):1111–1125. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Brickmann J., Läuger P. Molecular dynamics study of ion transport in transmembrane protein channels. Biophys Chem. 1981 Apr;13(2):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainsworth A. H., Hladky S. B. Gramicidin-mediated currents at very low permeant ion concentrations. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83194-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Sigworth F. J. Open channel noise. V. Fluctuating barriers to ion entry in gramicidin A channels. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):499–514. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82566-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz F., Spach G., Trudelle Y. Single channels of 9, 11, 13, 15-destryptophyl-phenylalanyl-gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84462-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich P., Jakobsson E. Calculation of deformation energies and conformations in lipid membranes containing gramicidin channels. Biophys J. 1990 May;57(5):1075–1084. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82625-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich W. Elastic properties of lipid bilayers: theory and possible experiments. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Nov-Dec;28(11):693–703. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Gruen D. W. Thickness fluctuations in black lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Jun;38(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84556-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Discreteness of conductance change in bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):451–453. doi: 10.1038/225451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. W. Deformation free energy of bilayer membrane and its effect on gramicidin channel lifetime. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83550-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Mazet J. L., Andersen O. S. Distinction between dipolar and inductive effects in modulating the conductance of gramicidin channels. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):512–520. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Bamberg E. Influence of membrane thickness and ion concentration on the properties of the gramicidin a channel. Autocorrelation, spectral power density, relaxation and single-channel studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: Lenses and the compression of black lipid membranes by an electric field. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85793-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Decker E. R. Electrostatic radius of the gramicidin channel determined from voltage dependence of H+ ion conductance. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83063-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay D. H., Berens P. H., Wilson K. R., Hagler A. T. Structure and dynamics of ion transport through gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):229–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84016-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazet J. L., Andersen O. S., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid sequences. A comparison of phenylalanine, tryptophane, and tyrosine substitutions at positions 1 and 11. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84153-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molecular interactions in ordered lipid systems. Chem Phys Lipids. 1982 May;30(2-3):105–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Eibl H. The influence of phospholipid polar groups on gramicidin channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sandblom J., Eisenman G. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in gramicidin A channels. II. Saturation behavior of single channel conductances and evidence for the existence of multiple binding sites in the channel. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 26;40(2):97–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01871143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring A. Brief closures of gramicidin A channels in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 25;856(3):646–653. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring A., Sandblom J. Evaluation of surface tension and ion occupancy effects on gramicidin A channel lifetime. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):541–548. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83134-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring A., Sandblom J. Modulation of gramicidin A open channel lifetime by ion occupancy. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):549–559. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83135-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Karplus M. The normal modes of the gramicidin-A dimer channel. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):297–309. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83107-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnev V. S., Ermishkin L. N., Fonina L. A., Rovin YuG The dependence of the conductance and lifetime of gramicidin channels on the thickness and tension of lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 20;642(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi H., Nemoto Y., Harada I. Environments and conformations of tryptophan side chains of gramicidin A in phospholipid bilayers studied by Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1572–1579. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban B. W., Hladky S. B. Ion transport in the simplest single file pore. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):410–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Jing N., Prasad K. U. On the mechanism of channel-length dependence of gramicidin single-channel conductance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 7;902(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Venkatachalam C. M., Spisni A., Läuger P., Khaled M. A. Rate theory calculation of gramicidin single-channel currents using NMR-derived rate constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2028–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Walker J. T., Trapane T. L. Ion interactions in (1-13C)D-Val8 and D-Leu14 analogs of gramicidin A, the helix sense of the channel and location of ion binding sites. J Membr Biol. 1982;69(3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01870401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Stryer L. The dimeric nature of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: conductance and fluorescence energy transfer studies of hybrid channels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. Conformation of gramicidin A in phospholipid vesicles: circular dichroism studies of effects of ion binding, chemical modification, and lipid structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5754–5760. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. Formation of "solvent-free" black lipid bilayer membranes from glyceryl monooleate dispersed in squalene. Biophys J. 1978 Sep;23(3):337–347. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85453-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. How electric fields modify alkane solubility in lipid bilayers. Science. 1980 Mar 7;207(4435):1075–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.207.4435.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. The surface charge and double layers of thin lipid films formed from neutral lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing J., Scott H. L. Monte Carlo studies of lipid chains and gramicidin A in a model membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingsheim H. P., Neher E. The equivalence of fluctuation analysis and chemical relaxation measurements: a kinetic study of ion pore formation in thin lipid membranes. Biophys Chem. 1974 Oct;2(3):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


