Abstract
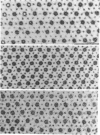
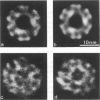
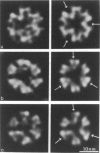
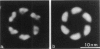
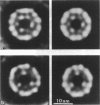
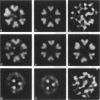
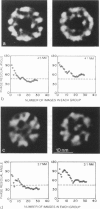
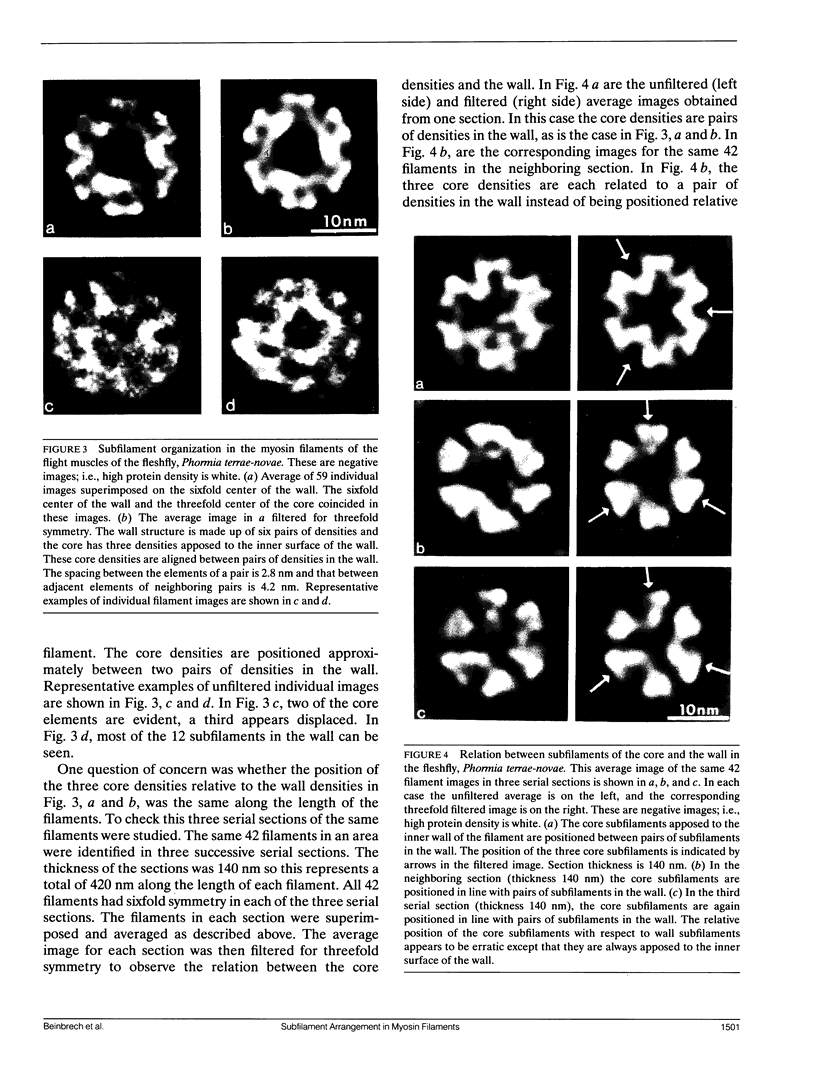
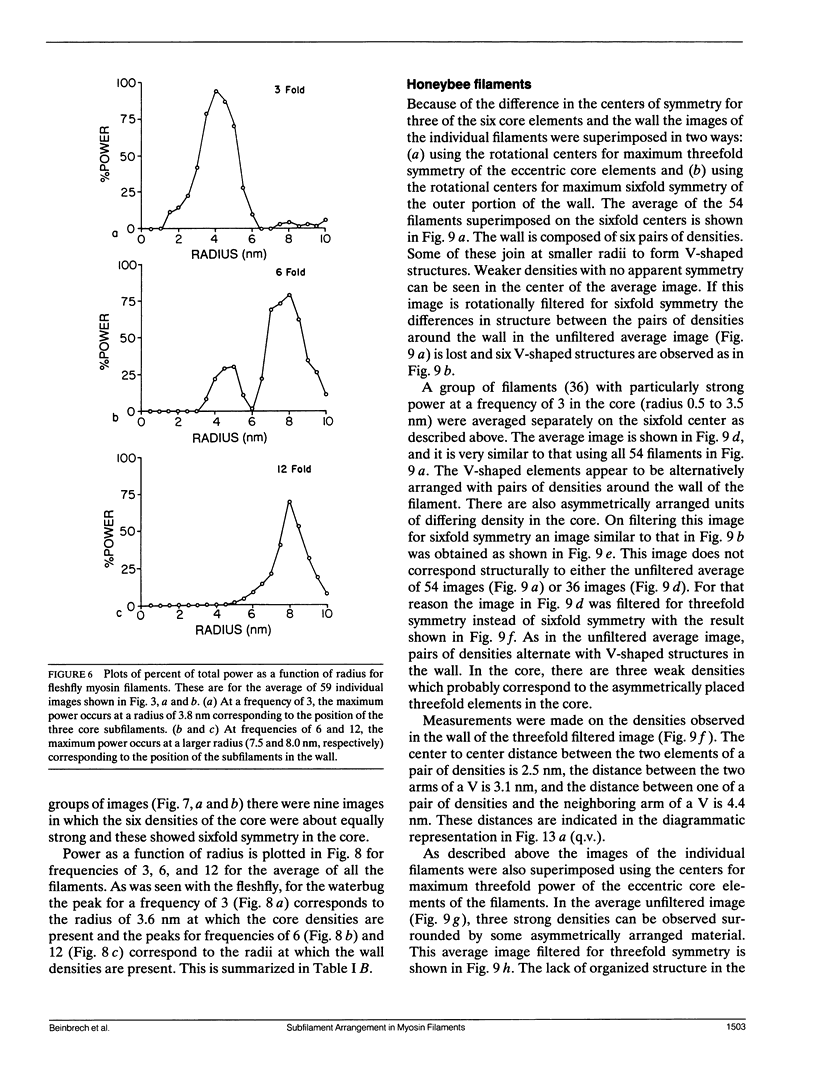
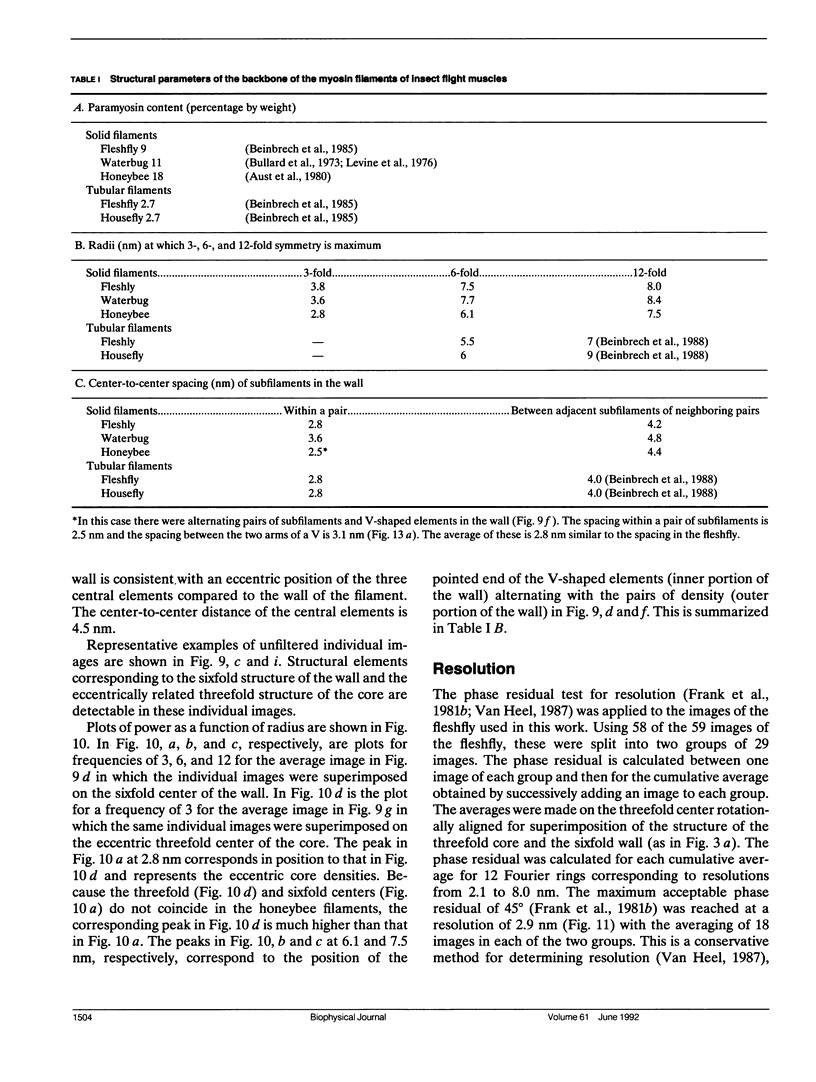
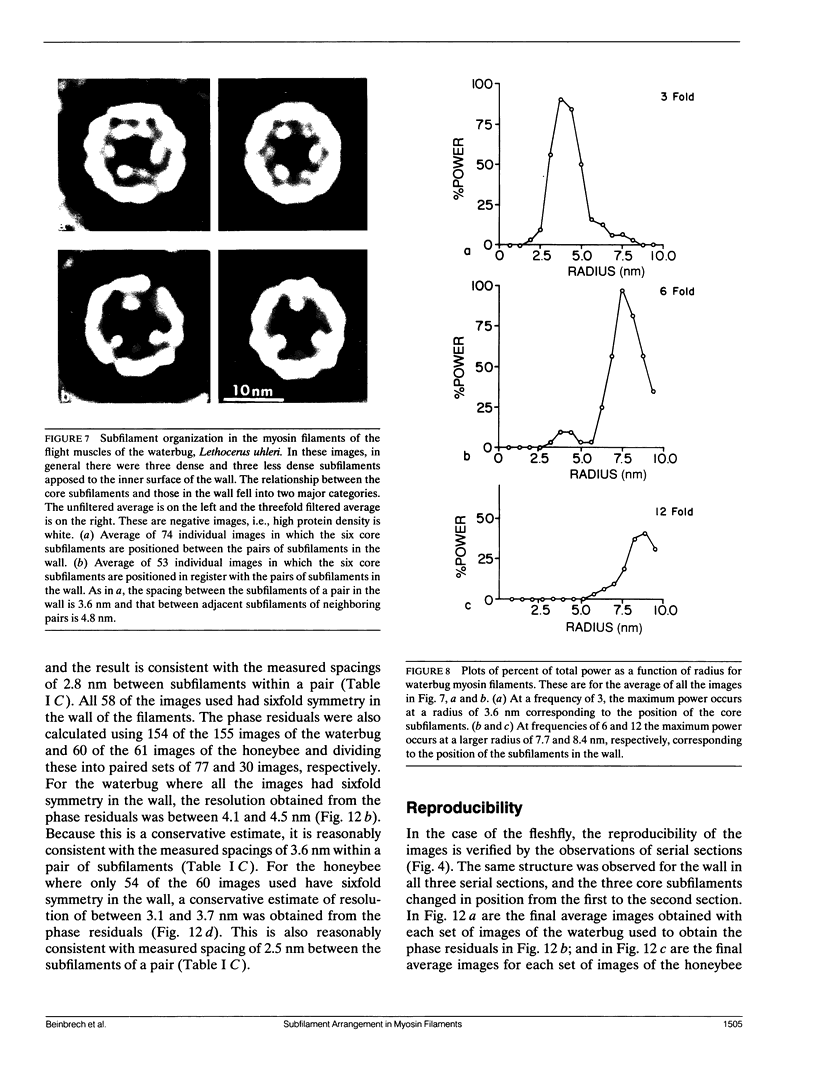
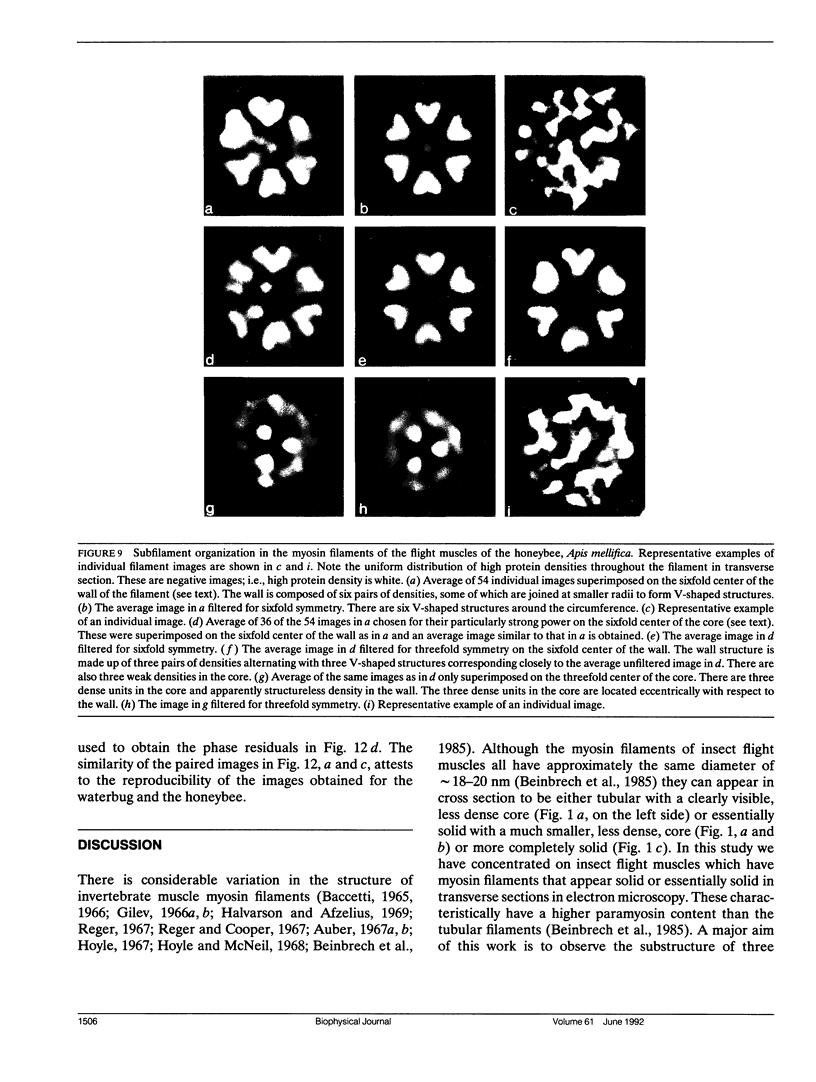
Transverse sections (approximately 140 nm thick) of solid myosin filaments of the flight muscles of the fleshfly, Phormia terrae-novae, the honey bee, Apis mellifica, and the waterbug, Lethocerus uhleri, were photographed in a JEM model 200A electron microscope at 200 kV. The images were digitized and computer processed by rotational filtering. In each of these filaments it was found that the symmetry of the core and the wall was not the same. The power spectra of the images showed sixfold symmetry for the wall and threefold symmetry for the core of the filaments. The images of the filaments in each muscle were superimposed according to the sixfold center of the wall. These averaged images for all three muscles showed six pairs of subunits in the wall similar to those found in the wall of tubular filaments. From serial sections of the fleshfly filaments, we conclude that the subunits in the wall of the filaments represent subfilaments essentially parallel to the long axis of the filament. In each muscle there are additional subunits in the core, closely related to the subunits in the wall. Evaluation of serial sections through fleshfly filaments suggests that the relationship of the three subunits observed in the core to those in the wall varies along the length of the filaments. In waterbug filaments there are three dense and three less dense subunits for a total of six all closely related to the wall. Bee filaments have three subunits related to the wall and three subunits located eccentrically in the core of the filaments. The presence of core subunits can be related to the paramyosin content of the filaments.
Full text
PDF






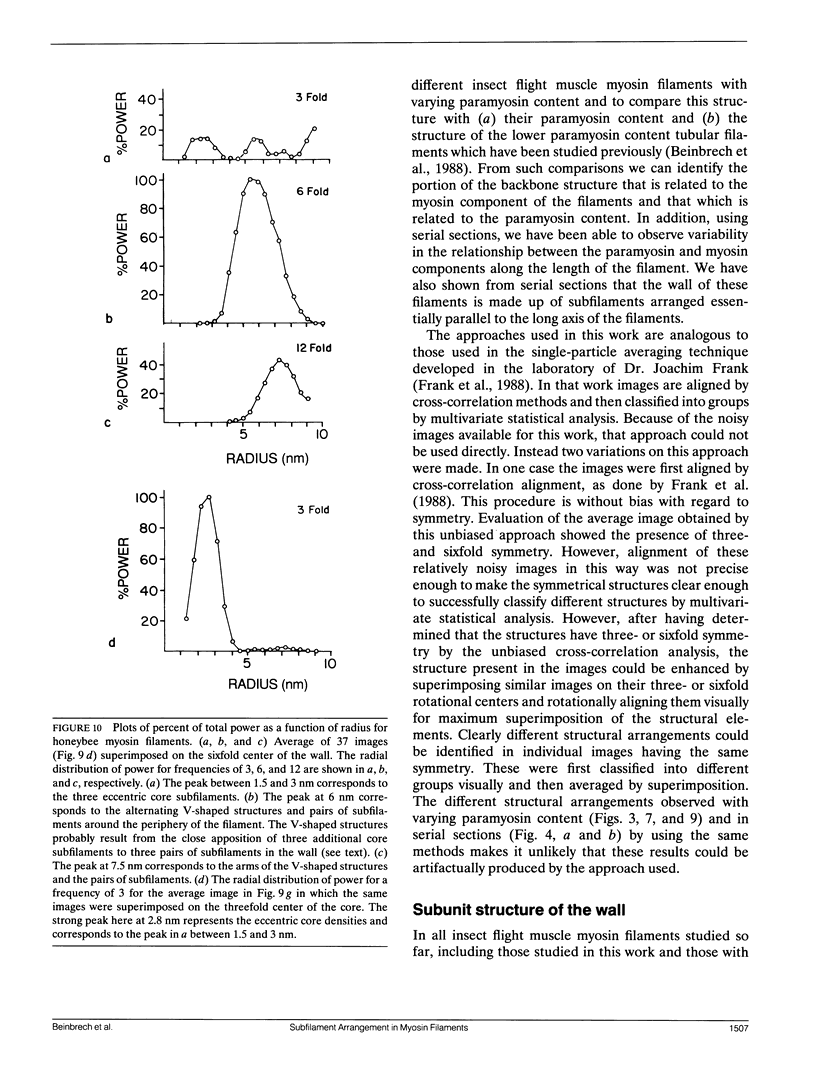
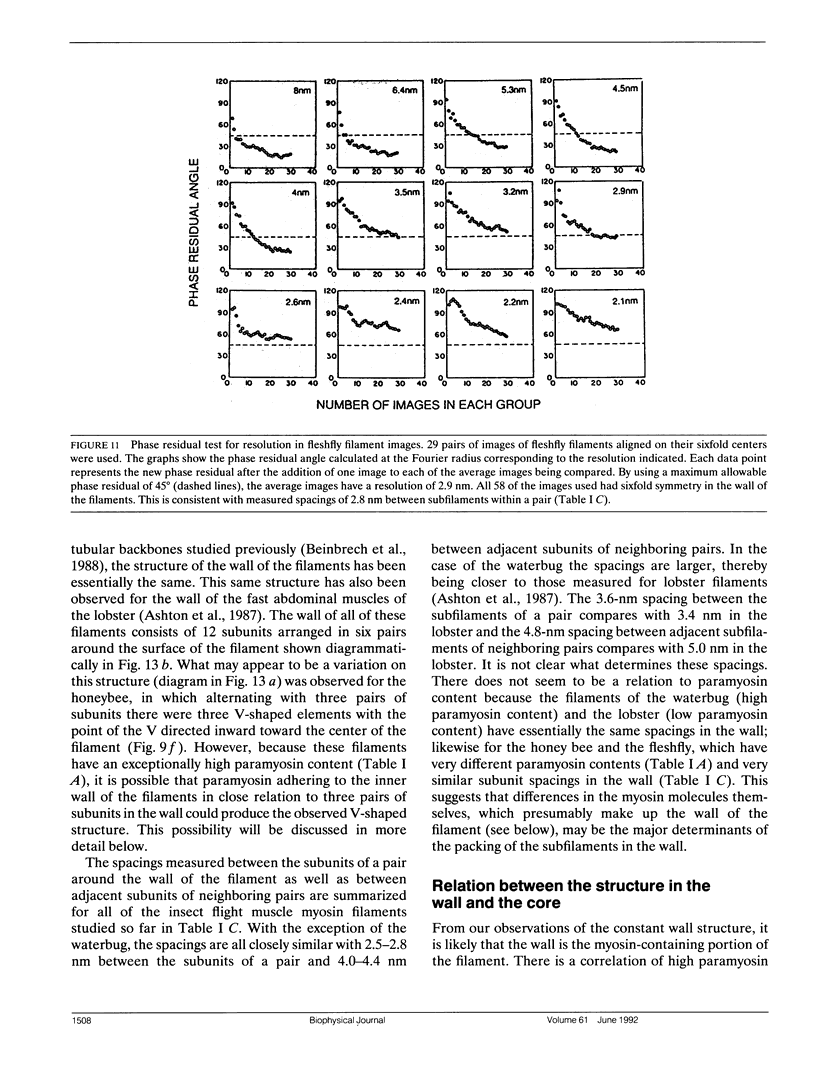
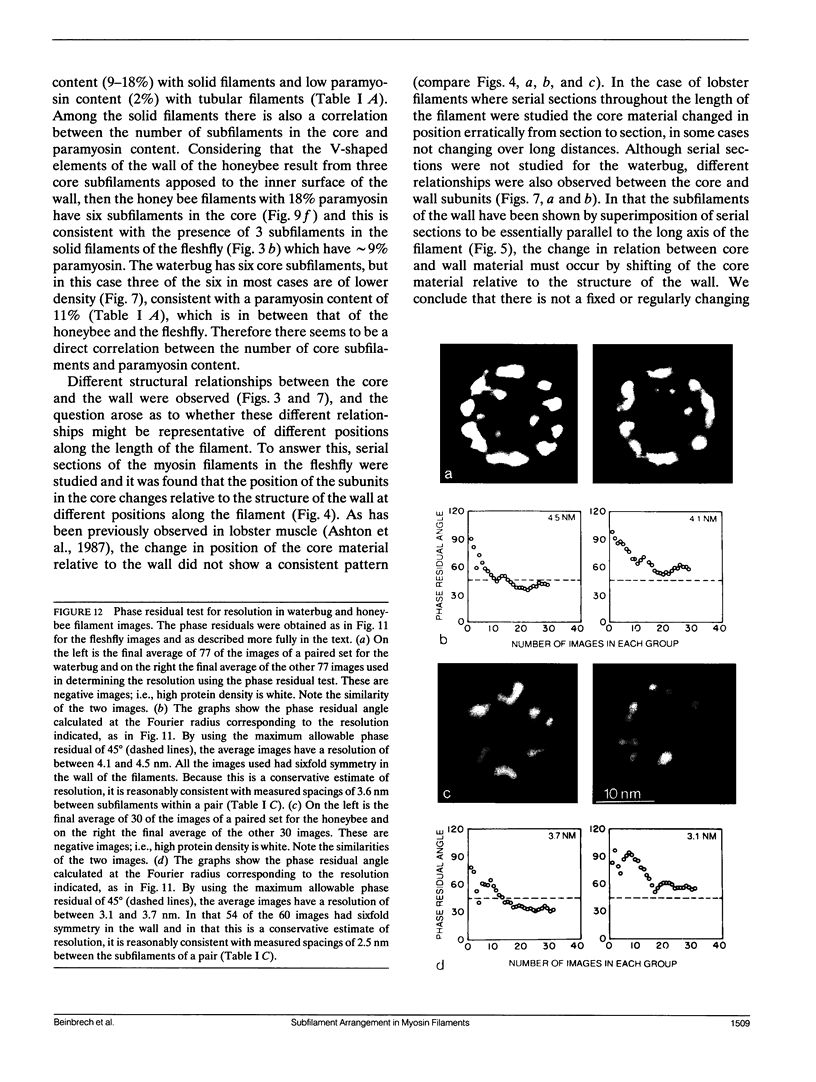
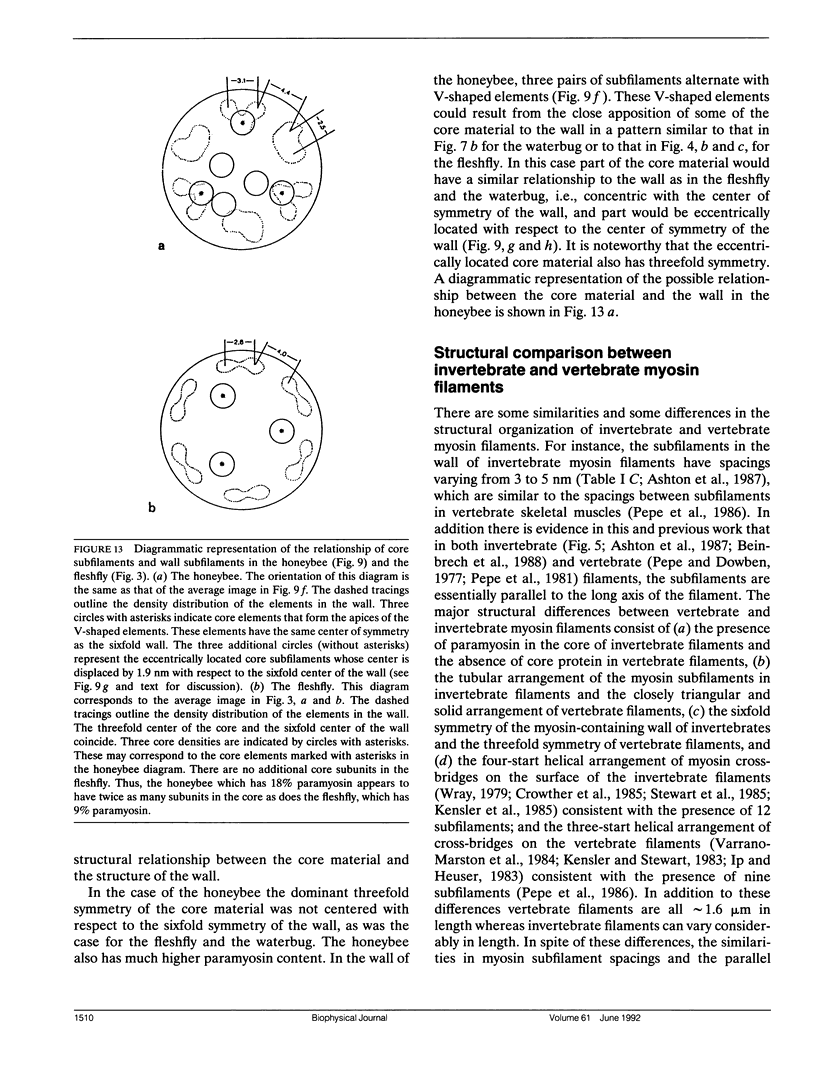


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton F. T., Beinbrech G., Pepe F. A. Subfilament organization in myosin filaments of the fast abdominal muscles of the lobster, Homarus americanus. Tissue Cell. 1987;19(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(87)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. T., Pepe F. A. The myosin filament. VIII. Preservation of subfilament organization. J Microsc. 1981 Jul;123(Pt 1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auber J. Particularités ultrastructurales des myofibrilles des muscles du vol chez des Lépidoptères. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jan 23;264(4):621–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auber J. Remarques sur la structure des fibrilles des muscles du vol d'insectes, au niveau de la strie M. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jun 19;264(25):2916–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccetti B. Nouvelles observations sur l'ultrastructure du myofilament. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Oct;13(3):245–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccetti B. Perplessita' e conferme sul problema della struttura dei filamenti muscolari miosinici. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1966 Sep 30;42(18):1181–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinbrech G., Ashton F. T., Pepe F. A. Invertebrate myosin filament: subfilament arrangement in the wall of tubular filaments of insect flight muscles. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90637-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. M., Elliott A. The structure of the paramyosin core in molluscan thick filaments. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Mar;2(1):65–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00712062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Luke B., Winkelman L. The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Amos L. A. Harmonic analysis of electron microscope images with rotational symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Padrón R., Craig R. Arrangement of the heads of myosin in relaxed thick filaments from tarantula muscle. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Berliner G. C., Casey D. L., Ortiz I. Purified thick filaments from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: evidence for multiple proteins associated with core structures. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1985–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank J., Radermacher M., Wagenknecht T., Verschoor A. Studying ribosome structure by electron microscopy and computer-image processing. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:3–35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank J., Verschoor A., Boublik M. Computer averaging of electron micrographs of 40S ribosomal subunits. Science. 1981 Dec 18;214(4527):1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.7313694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilëv V. P. The ultrastructure of myofilaments. II. Further investigation of the thick filaments of crab muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvarson M., Afzelius B. A. Filament organization in the body muscles of the arrowworm. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Feb;26(3):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle G. Diversity of striated muscle. Am Zool. 1967 Aug;7(3):435–449. doi: 10.1093/icb/7.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip W., Heuser J. Direct visualization of the myosin crossbridge helices on relaxed rabbit psoas thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 25;171(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Levine R. J., Stewart M. Electron microscopic and optical diffraction analysis of the structure of scorpion muscle thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):395–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Stewart M. Frog skeletal muscle thick filaments are three-stranded. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1797–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Elfvin M., Dewey M. M., Walcott B. Paramyosin in invertebrate muscles. II. Content in relation to structure and function. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):273–279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw M. C., Rowe A. J. Fraying of A-filaments into three subfilaments. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):412–414. doi: 10.1038/286412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura Y. Fine structure of the thick filament in molluscan catch muscle. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A., Ashton F. T., Dowben P., Stewart M. The myosin filament. VII Changes in internal structure along the length of the filament. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 15;145(2):421–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A., Ashton F. T., Street C., Weisel J. The myosin filament. X. Observation of nine subfilaments in transverse sections. Tissue Cell. 1986;18(4):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(86)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A., Dowben P. The myosin filament. V. Intermediate voltage electron microscopy and optical diffraction studies of the substructure. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):199–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K. Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. Screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):155–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reger J. F. A comparative study on striated muscle fibers of the first antenna and the claw muscle of the crab Pinnixia sp. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Sep;20(1):72–82. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reger J. F., Cooper D. P. A comparative study on the fine structure of the basalar muscle of the wing and the tibial extensor muscle of the leg of the lepidopteran Achalarus lyciades. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):531–542. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Ashton F. T., Lieberson R., Pepe F. A. The myosin filament. IX. Determination of subfilament positions by computer processing of electron micrographs. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of thick filaments from Limulus and scorpion muscle. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):402–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C., Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. II. Native filaments: isolation and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varriano-Marston E., Franzini-Armstrong C., Haselgrove J. C. The structure and disposition of crossbridges in deep-etched fish muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Aug;5(4):363–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00818256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelman L. Comparative studies of paramyosins. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1976;55(3B):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(76)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray J. S. Structure of the backbone in myosin filaments of muscle. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):37–40. doi: 10.1038/277037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]