Abstract
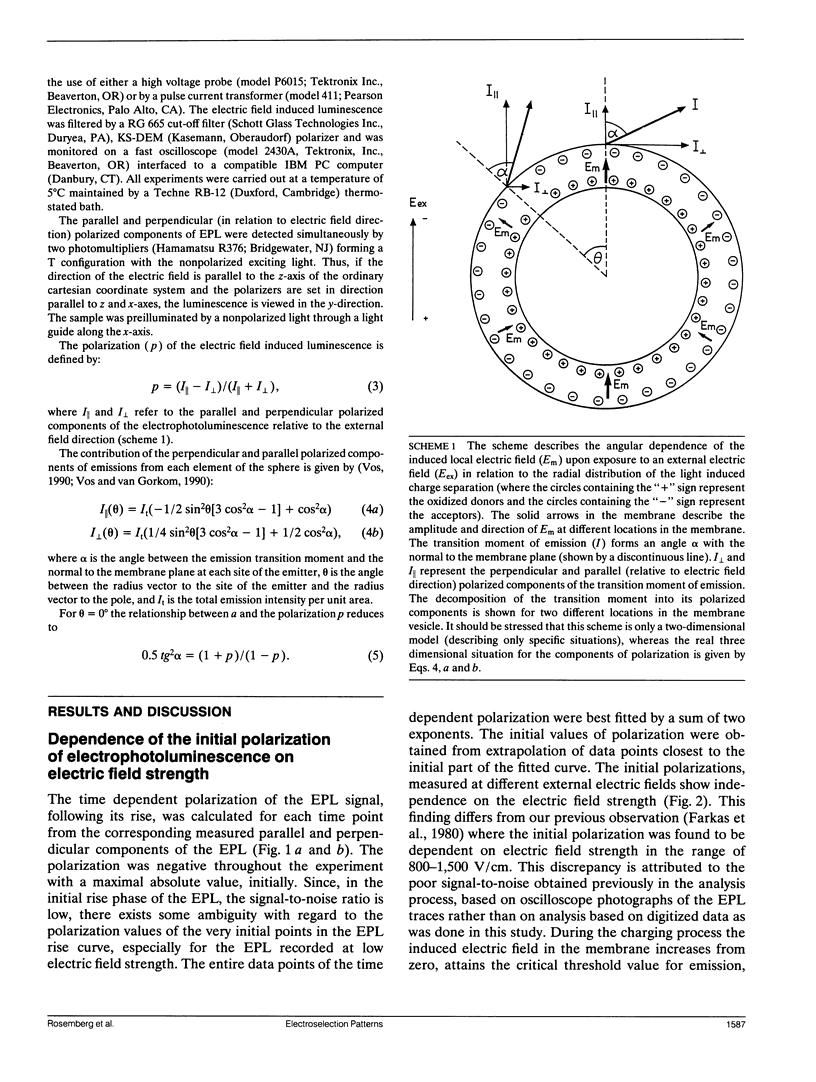
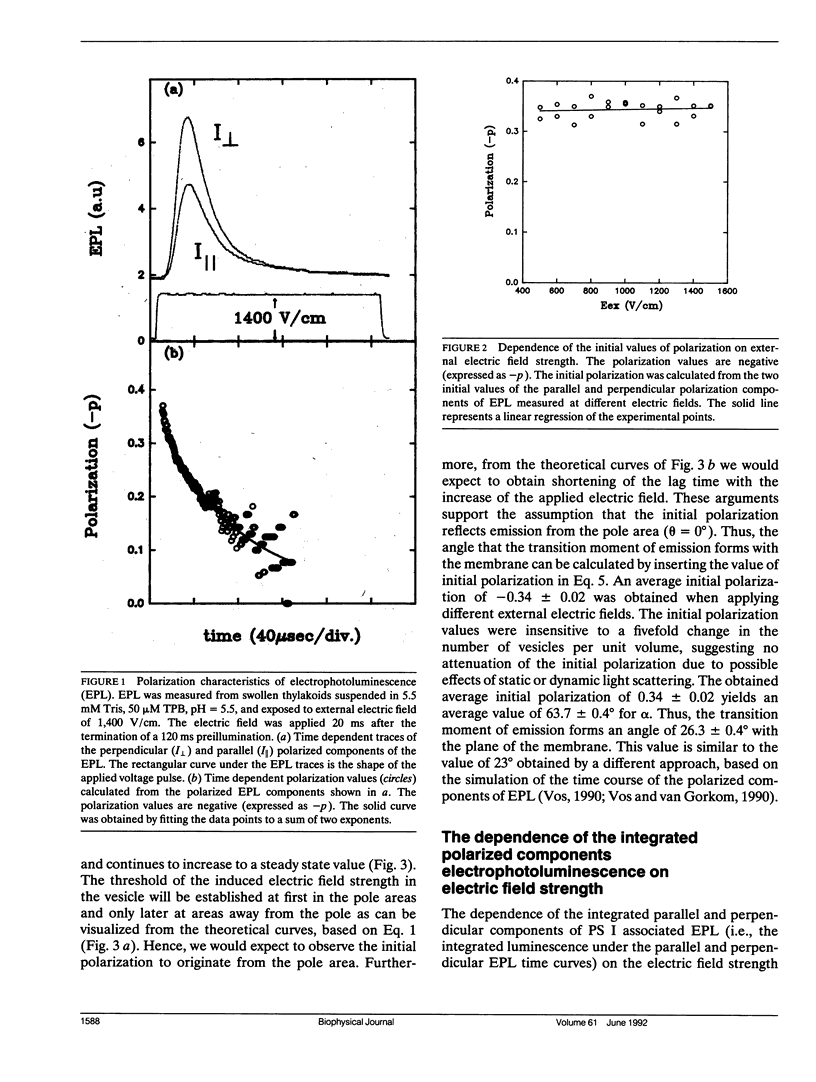
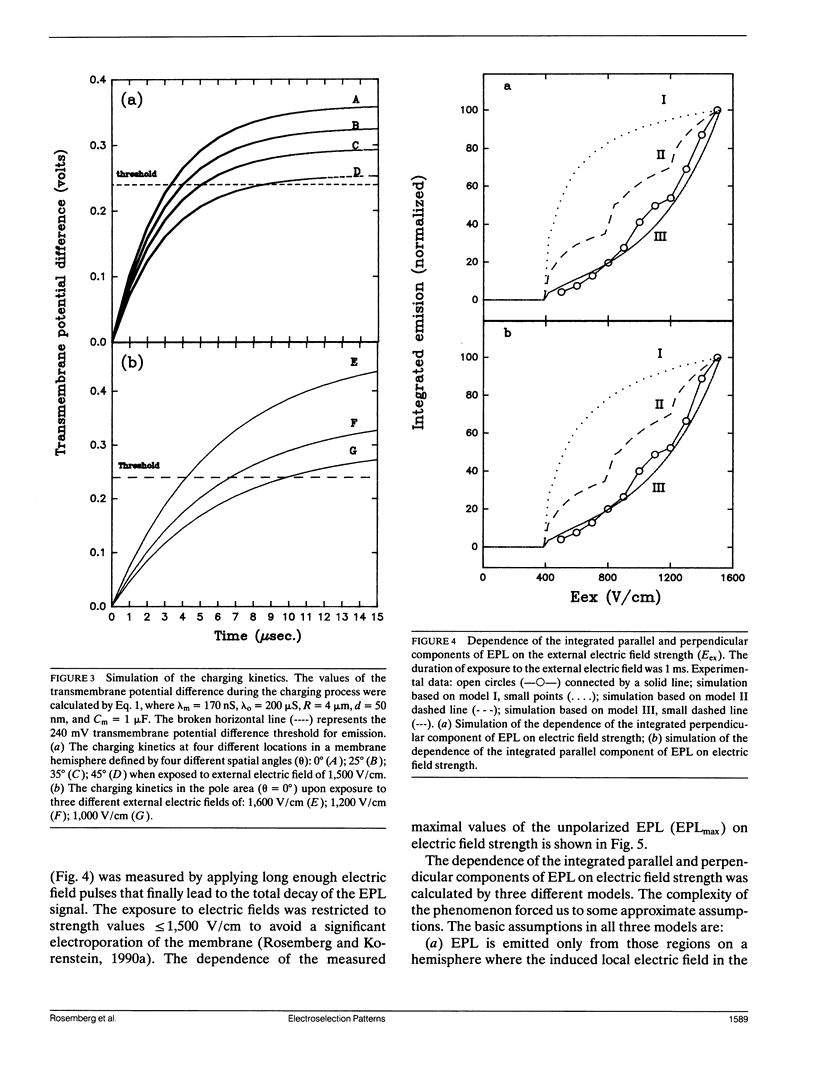
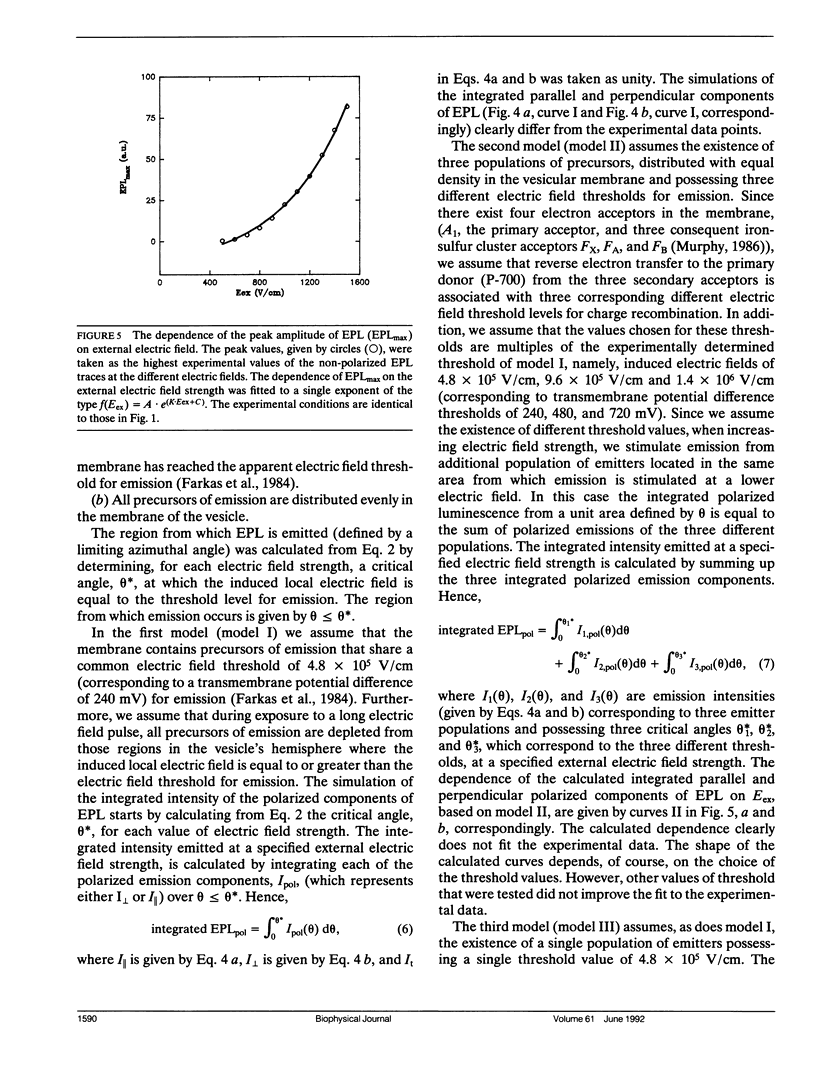
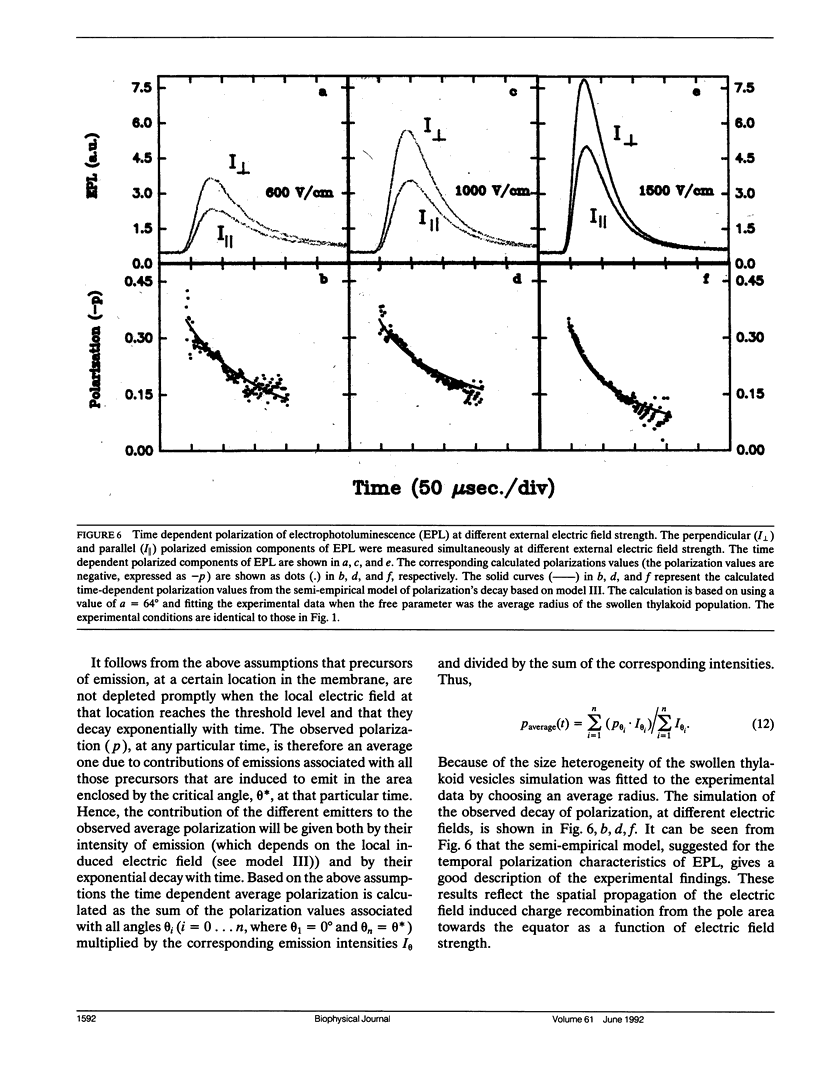
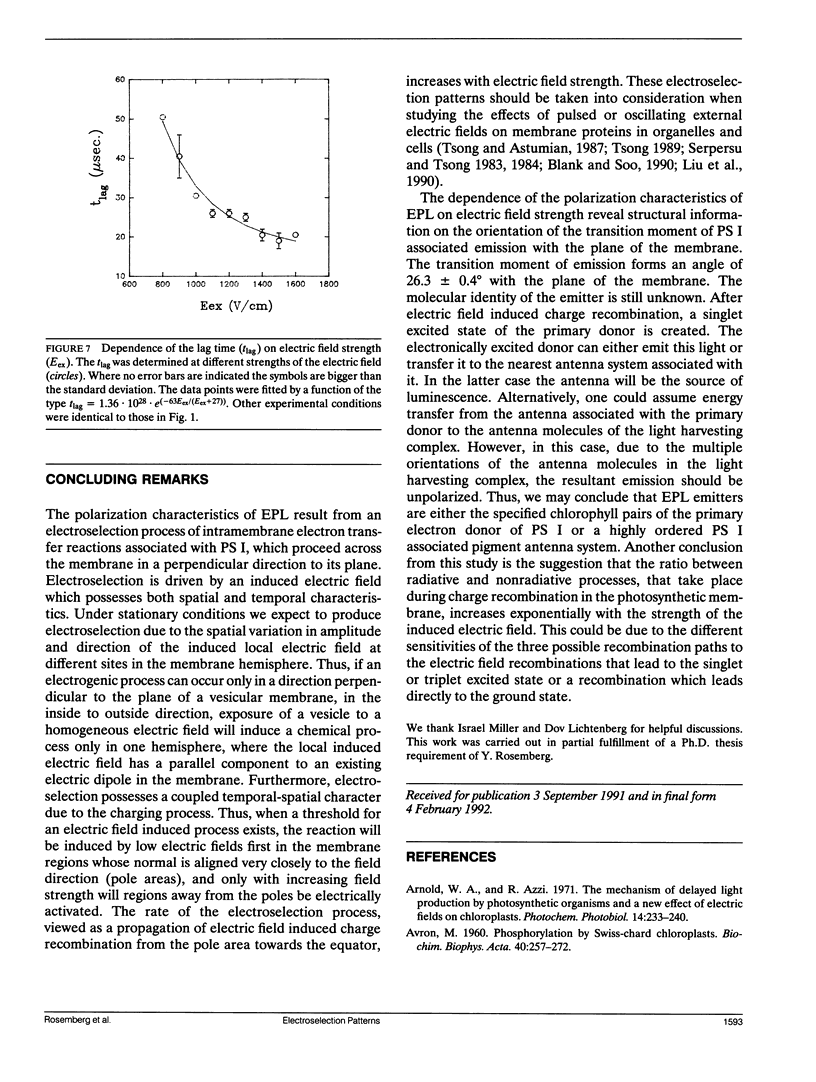
Electroselection processes of charge recombination are manifested in the study of electric field induced polarized emission from photosynthetic membrane vesicles. The study explores the coupled spatial-temporal characteristics of electric field induced charge recombination by examining the dependence of the integrated polarized emission and the time dependent polarization on electric field strength. The experimental results were fitted to theoretical models by computer simulations employing empirical parameters. Simulation of the dependence of the integrated polarized components of emission on electric field strength, suggests field-dependent increased ratio between radiative and nonradiative rates of charge recombination. The observation that the initial polarization values are independent of electric field strength supports the assumption that electric field induced emission originates from the pole area and then spreads away from it towards the equator. The propagation rate of this electric field induced charge recombination from the pole area towards the equator is reflected by the decay of polarization which increases upon raising the electric field strength. Simulation of the polarization's decay, based on a calculated angle of 26.3 ± 0.4° between the transition moment of emission and the plane of the membrane, establishes coupled temporal spatial patterns of electroselection in intramembrane electron transfer invoked by exposing preilluminated photosynthetic vesicles to a homogeneous electric field.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVRON M. Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:257–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfeld V., Miller I. R., Korenstein R. Electric field-induced lateral mobility of photosystem I in the photosynthetic membrane: A study by electrophotoluminescence. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):607–614. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82707-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos H., Vauquelin G., De Keyser J., De Backer J. P., Van Liefde I. Regional distribution of alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes in postmortem human brain. J Neurochem. 1992 Apr;58(4):1555–1560. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg B., Farkas D. L., Fluhler E. N., Lojewska Z., Loew L. M. Membrane potential induced by external electric field pulses can be followed with a potentiometric dye. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):833–837. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83410-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas D. L., Korenstein R., Malkin S. Electrophotoluminescence and the electrical properties of the photosynthetic membrane. I. Initial kinetics and the charging capacitance of the membrane. Biophys J. 1984 Feb;45(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84160-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D., Loew L. M., Webb W. W. Optical imaging of cell membrane potential changes induced by applied electric fields. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83467-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino M., Shigemori M., Itoh H., Nagayama K., Kinosita K., Jr Membrane conductance of an electroporated cell analyzed by submicrosecond imaging of transmembrane potential. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):209–220. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82212-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Ashikawa I., Saita N., Yoshimura H., Itoh H., Nagayama K., Ikegami A. Electroporation of cell membrane visualized under a pulsed-laser fluorescence microscope. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83181-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. S., Astumian R. D., Tsong T. Y. Activation of Na+ and K+ pumping modes of (Na,K)-ATPase by an oscillating electric field. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7260–7267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemberg Y., Korenstein R. A novel method for measuring membrane conductance changes by a voltage-sensitive optical probe. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80727-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemberg Y., Korenstein R. Electroporation of the photosynthetic membrane: A study by intrinsic and external optical probes. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82428-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serpersu E. H., Tsong T. Y. Activation of electrogenic Rb+ transport of (Na,K)-ATPase by an electric field. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7155–7162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serpersu E. H., Tsong T. Y. Stimulation of a ouabain-sensitive Rb+ uptake in human erthrocytes with an external electric field. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(3):191–201. doi: 10.1007/BF02332123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Astumian R. D. Electroconformational coupling and membrane protein function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1987;50(1):1–45. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(87)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y. Deciphering the language of cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


