Abstract
The paired oocyte cell-cell channel assay was used to investigate the mechanisms involved in the process of formation of gap junction channels. Single oocytes, injected with connexin-specific mRNAs, accumulate a pool of precursors from which cell-cell channels can form rapidly upon pairing. Several lines of evidence, including immunohistochemistry and surface labeling, indicate that part of this precursor pool is located in the cell membrane, probably in the form of closed hemichannels. The homophilic binding of hemichannels to each other can be mimicked by synthetic peptides representing the extracellular loop sequences of connexin32. The peptides specifically suppress channel formation. A crucial role is established for the six cysteines in the extracellular domains that are conserved in all vertebrate gap junction proteins. Change of any of these cysteines into serines results in absolute loss of function of the mutant connexin. The effects of thiol-specific reagents on channel formation suggest that docking and/or opening of channels involves disulfide exchange. Several of the variable amino acids in the extracellular loop sequences were found to determine specificity of connexin-connexin interactions.
Full text
PDF

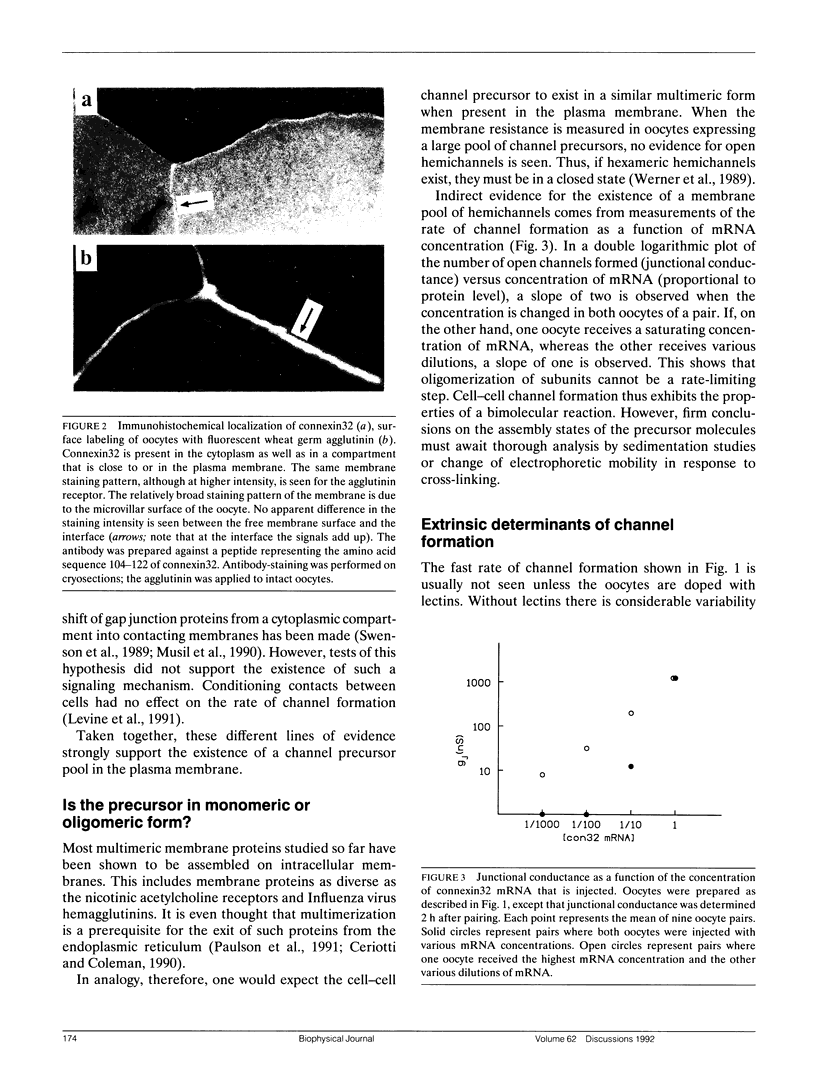
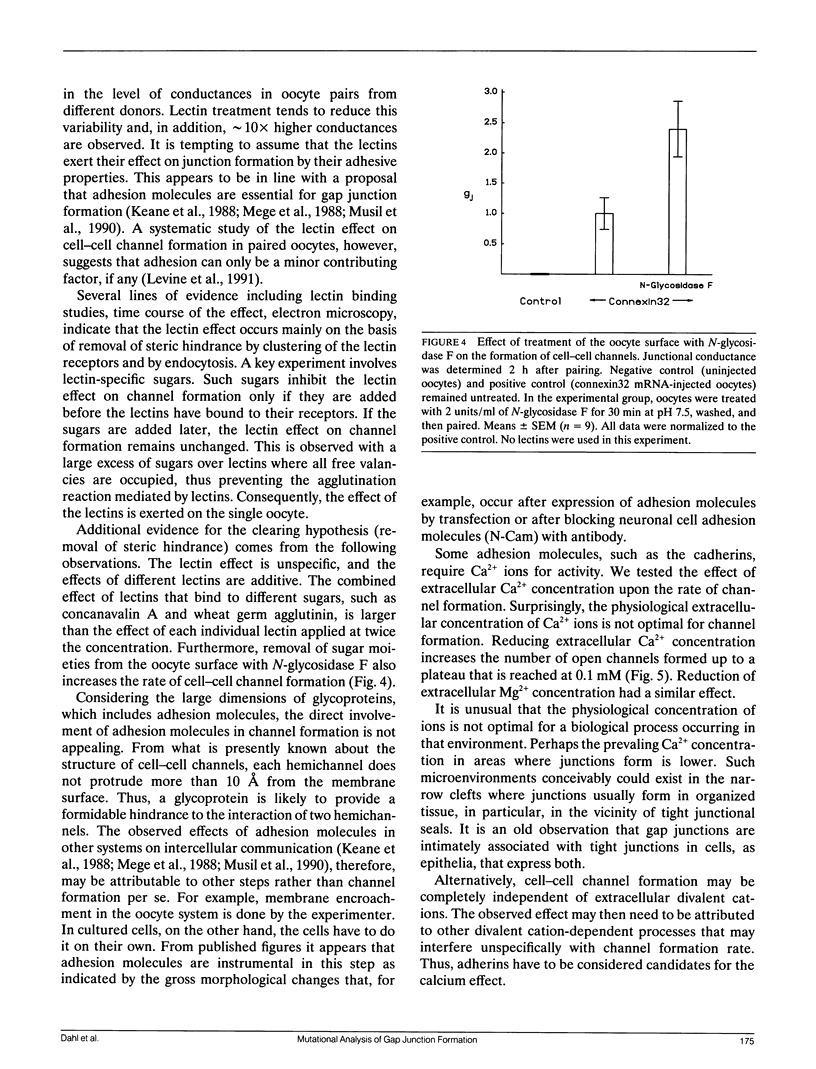
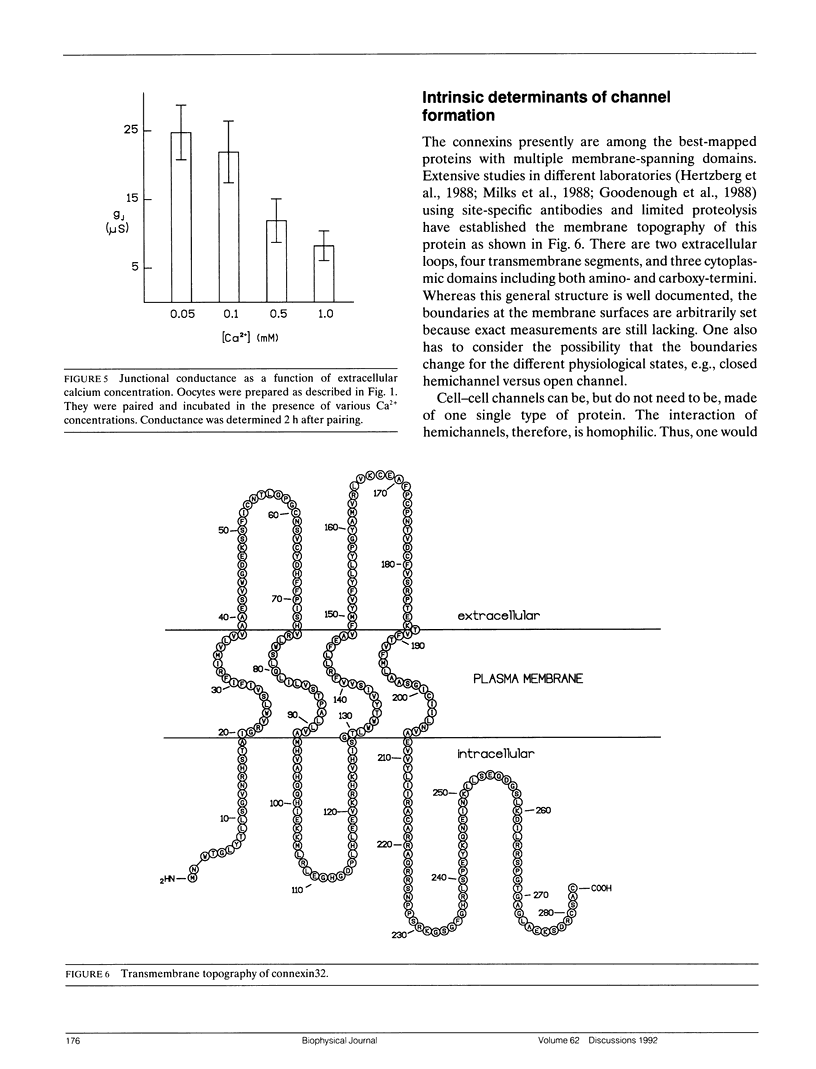
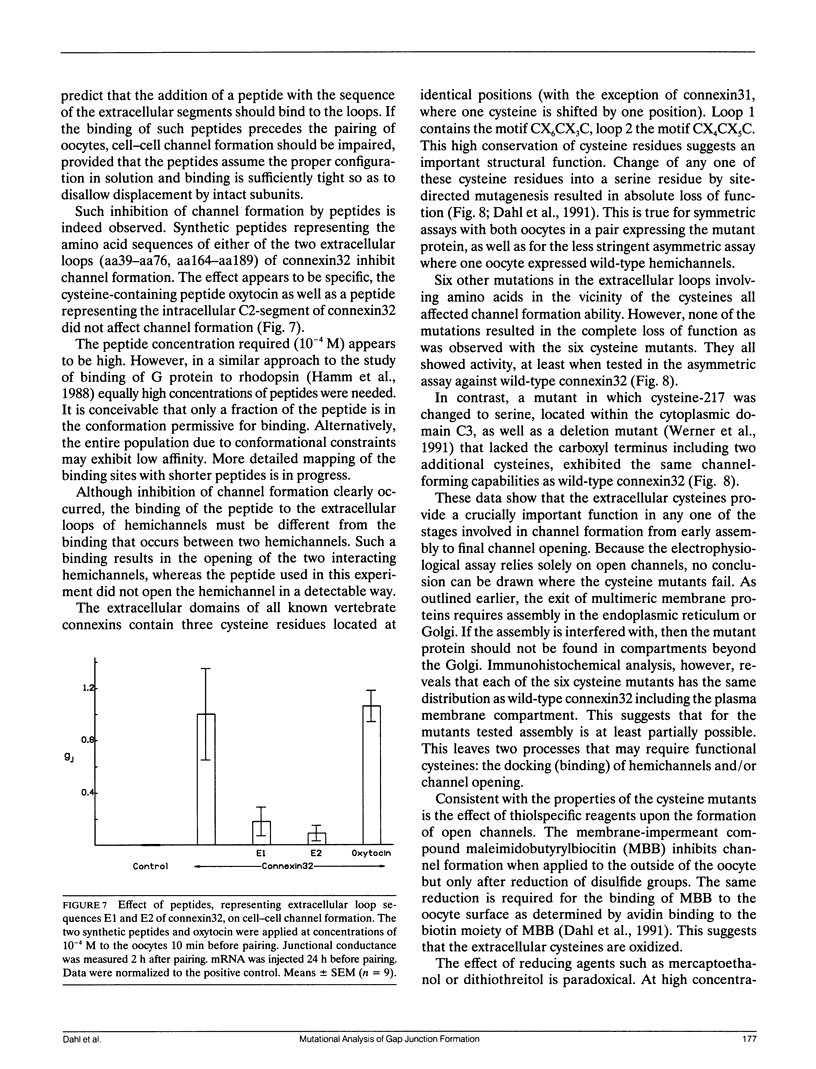


Images in this article
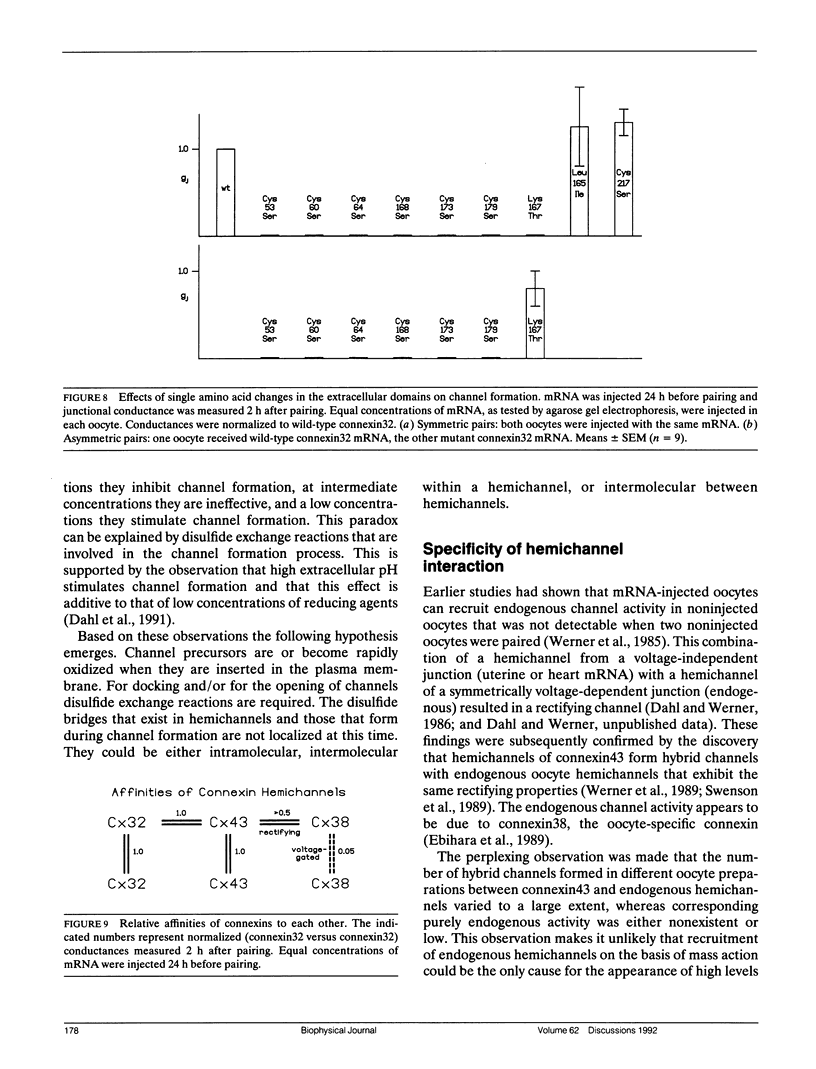
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abney J. R., Braun J., Owicki J. C. Lateral interactions among membrane proteins. Implications for the organization of gap junctions. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83233-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin family of gap junction proteins. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jul;116(3):187–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01868459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin43: a protein from rat heart homologous to a gap junction protein from liver. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2621–2629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriotti A., Colman A. Trimer formation determines the rate of influenza virus haemagglutinin transport in the early stages of secretion in Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):409–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao N. M., Young S. H., Poo M. M. Localization of cell membrane components by surface diffusion into a "trap". Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84721-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Levine E., Rabadan-Diehl C., Werner R. Cell/cell channel formation involves disulfide exchange. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):141–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Miller T., Paul D., Voellmy R., Werner R. Expression of functional cell-cell channels from cloned rat liver gap junction complementary DNA. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1290–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3035715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Beyer E. C., Swenson K. I., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Cloning and expression of a Xenopus embryonic gap junction protein. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1194–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.2466337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A., Paul D. L., Jesaitis L. Topological distribution of two connexin32 antigenic sites in intact and split rodent hepatocyte gap junctions. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1817–1824. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A., Koenig B., Hofmann K. P. Site of G protein binding to rhodopsin mapped with synthetic peptides from the alpha subunit. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):832–835. doi: 10.1126/science.3136547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Disher R. M., Tiller A. A., Zhou Y., Cook R. G. Topology of the Mr 27,000 liver gap junction protein. Cytoplasmic localization of amino- and carboxyl termini and a hydrophilic domain which is protease-hypersensitive. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19105–19111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane R. W., Mehta P. P., Rose B., Honig L. S., Loewenstein W. R., Rutishauser U. Neural differentiation, NCAM-mediated adhesion, and gap junctional communication in neuroectoderm. A study in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1307–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege R. M., Matsuzaki F., Gallin W. J., Goldberg J. I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Construction of epithelioid sheets by transfection of mouse sarcoma cells with cDNAs for chicken cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milks L. C., Kumar N. M., Houghten R., Unwin N., Gilula N. B. Topology of the 32-kd liver gap junction protein determined by site-directed antibody localizations. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2967–2975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M., Goodenough D. A. Differential phosphorylation of the gap junction protein connexin43 in junctional communication-competent and -deficient cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2077–2088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson H. L., Ross A. F., Green W. N., Claudio T. Analysis of early events in acetylcholine receptor assembly. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1371–1384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Equilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):77–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Jordan J. R., Beyer E. C., Paul D. L. Formation of gap junctions by expression of connexins in Xenopus oocyte pairs. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R., Levine E., Rabadan-Diehl C., Dahl G. Formation of hybrid cell-cell channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5380–5384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R., Levine E., Rabadan-Diehl C., Dahl G. Gating properties of connexin32 cell-cell channels and their mutants expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jan 22;243(1306):5–11. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R., Miller T., Azarnia R., Dahl G. Translation and functional expression of cell-cell channel mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):253–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01871226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]