Abstract
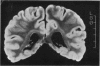
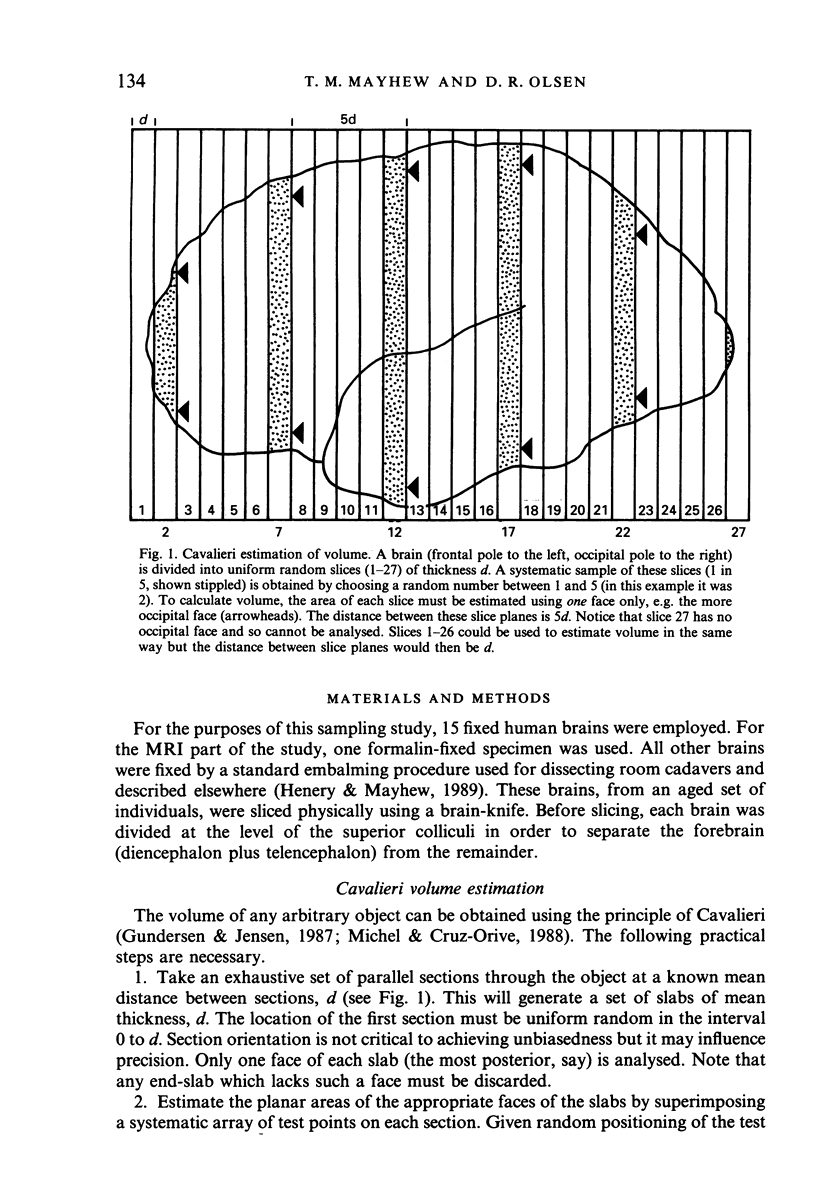
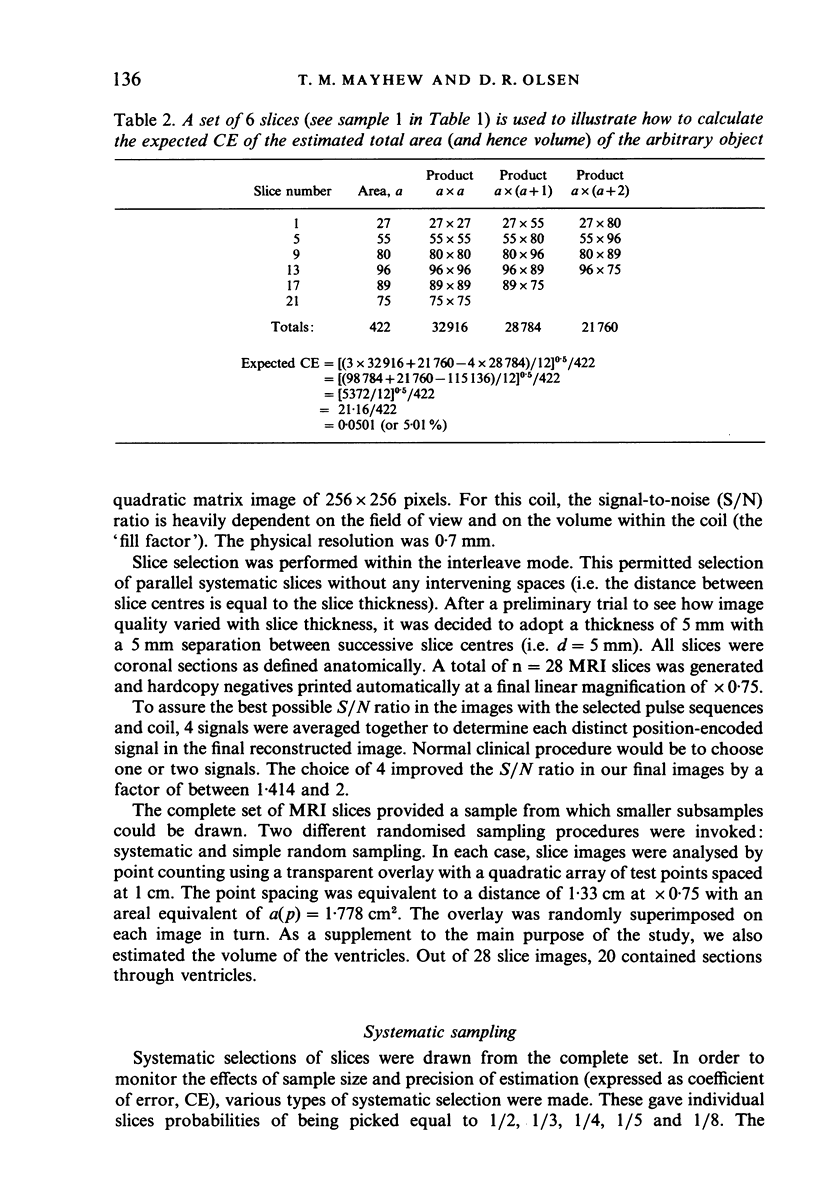
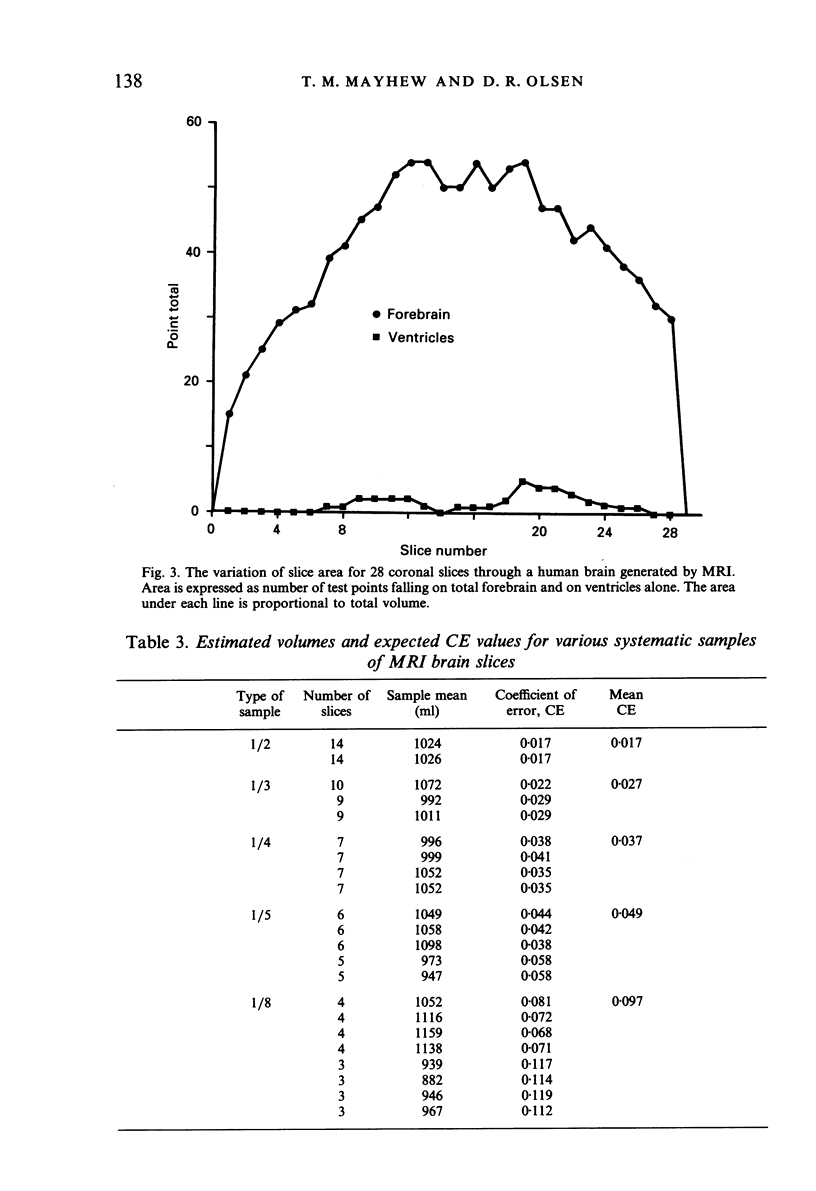
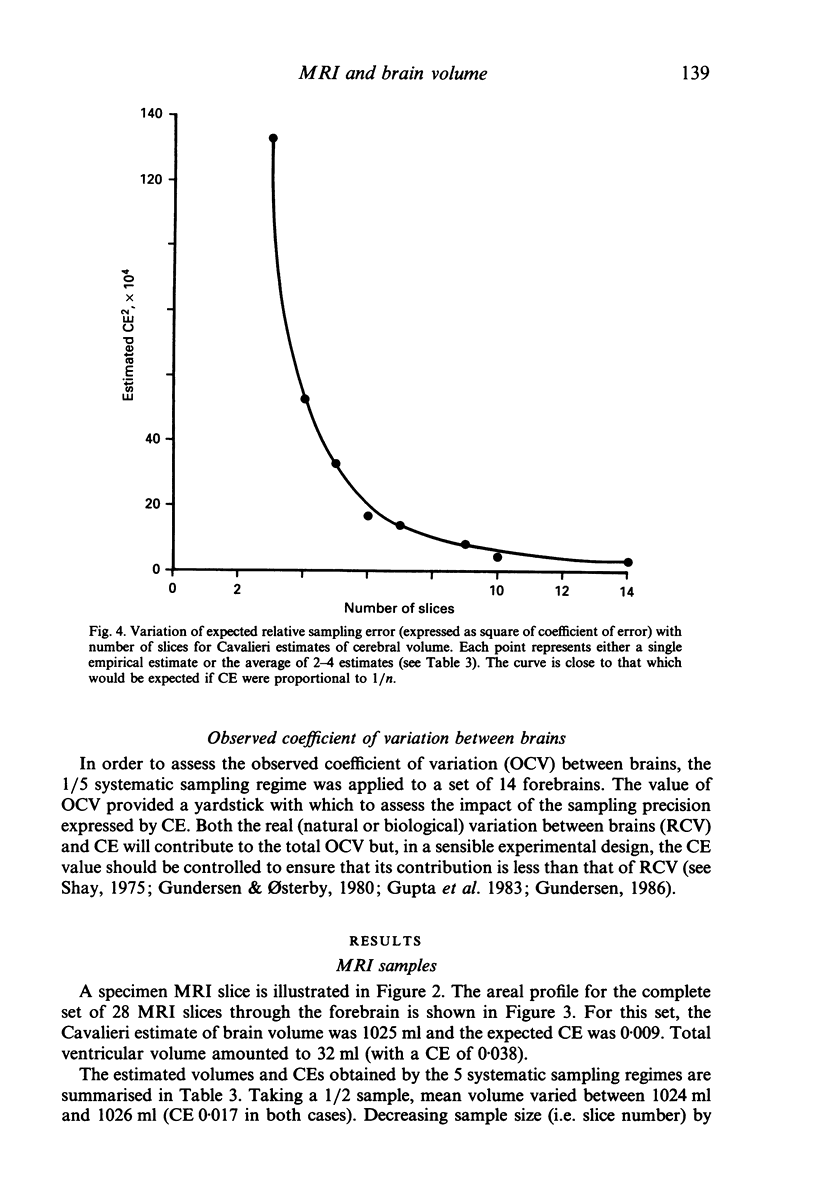
A complete set of parallel (coronal) slices through a fixed human forebrain was generated by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the Cavalieri principle, combined with point counting, was used to estimate brain volume. Alternative sampling schemes for estimating volume were then assessed by taking systematic and simple random selections of slices. Later, the brain was weighed and its fixed volume determined by fluid displacement. For the complete set of n = 28 MRI slices, the volume (1025 ml) was estimated with a coefficient of error (CE) of less than 1%. Decreasing the number of slices by systematic sampling increased the CE but this was still only 5% when just 5-6 slices were analysed. Estimated volumes varied from 947 ml to 1098 ml. Simple random sampling was less efficient (estimated volumes for 5-6 slices were 644-1187 ml). The forebrain actually weighed 1090 g and displaced 1060 ml of fluid. A set of 14 other brains was physically sliced in order to assess sampling errors in the context of observed brain-to-brain variation. It was found that 5-6 slices per brain is enough to yield efficient estimates of mean brain volume. The findings demonstrate the practicability of using MRI to estimate brain volumes unbiasedly and efficiently. The methods have great potential for noninvasive, longitudinal studies on in vivo brains and other organs.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashtari M., Zito J. L., Gold B. I., Lieberman J. A., Borenstein M. T., Herman P. G. Computerized volume measurement of brain structure. Invest Radiol. 1990 Jul;25(7):798–805. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199007000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley A. J., Gundersen H. J., Cruz-Orive L. M. Estimation of surface area from vertical sections. J Microsc. 1986 Jun;142(Pt 3):259–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb04282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler P. A., Casey C. E., Cameron G. G., Foster M. A., Knight C. H. Cyclic changes in composition and volume of the breast during the menstrual cycle, measured by magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990 Jul;97(7):595–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1990.tb02546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler P. A., Knight C. H., Cameron G. G., Foster M. A. Use of magnetic resonance imaging in the study of goat mammary glands in vivo. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 May;89(1):359–366. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0890359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Bagger P., Bendtsen T. F., Evans S. M., Korbo L., Marcussen N., Møller A., Nielsen K., Nyengaard J. R., Pakkenberg B. The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988 Oct;96(10):857–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Bendtsen T. F., Korbo L., Marcussen N., Møller A., Nielsen K., Nyengaard J. R., Pakkenberg B., Sørensen F. B., Vesterby A. Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988 May;96(5):379–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Jensen E. B. The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology and its prediction. J Microsc. 1987 Sep;147(Pt 3):229–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1987.tb02837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J. Stereology of arbitrary particles. A review of unbiased number and size estimators and the presentation of some new ones, in memory of William R. Thompson. J Microsc. 1986 Jul;143(Pt 1):3–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta M., Mayhew T. M., Bedi K. S., Sharma A. K., White F. H. Inter-animal variation and its influence on the overall precision of morphometric estimates based on nested sampling designs. J Microsc. 1983 Aug;131(Pt 2):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist H., Sjöström L., Tylén U. Adipose tissue volume determinations in women by computed tomography: technical considerations. Int J Obes. 1986;10(1):53–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew T. M., Mwamengele G. L., Dantzer V. Comparative morphometry of the mammalian brain: estimates of cerebral volumes and cortical surface areas obtained from macroscopic slices. J Anat. 1990 Oct;172:191–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew T. M., Mwamengele G. L., Dantzer V. Comparative morphometry of the mammalian brain: estimates of cerebral volumes and cortical surface areas obtained from macroscopic slices. J Anat. 1990 Oct;172:191–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel R. P., Cruz-Orive L. M. Application of the Cavalieri principle and vertical sections method to lung: estimation of volume and pleural surface area. J Microsc. 1988 May;150(Pt 2):117–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkenberg B., Boesen J., Albeck M., Gjerris F. Unbiased and efficient estimation of total ventricular volume of the brain obtained from CT-scans by a stereological method. Neuroradiology. 1989;31(5):413–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00343866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkenberg B., Gundersen H. J. Total number of neurons and glial cells in human brain nuclei estimated by the disector and the fractionator. J Microsc. 1988 Apr;150(Pt 1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkenberg B. Post-mortem study of chronic schizophrenic brains. Br J Psychiatry. 1987 Dec;151:744–752. doi: 10.1192/bjp.151.6.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regeur L., Pakkenberg B. Optimizing sampling designs for volume measurements of components of human brain using a stereological method. J Microsc. 1989 Jul;155(Pt 1):113–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1989.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]