Abstract
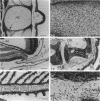
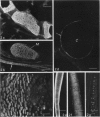
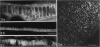
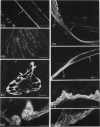
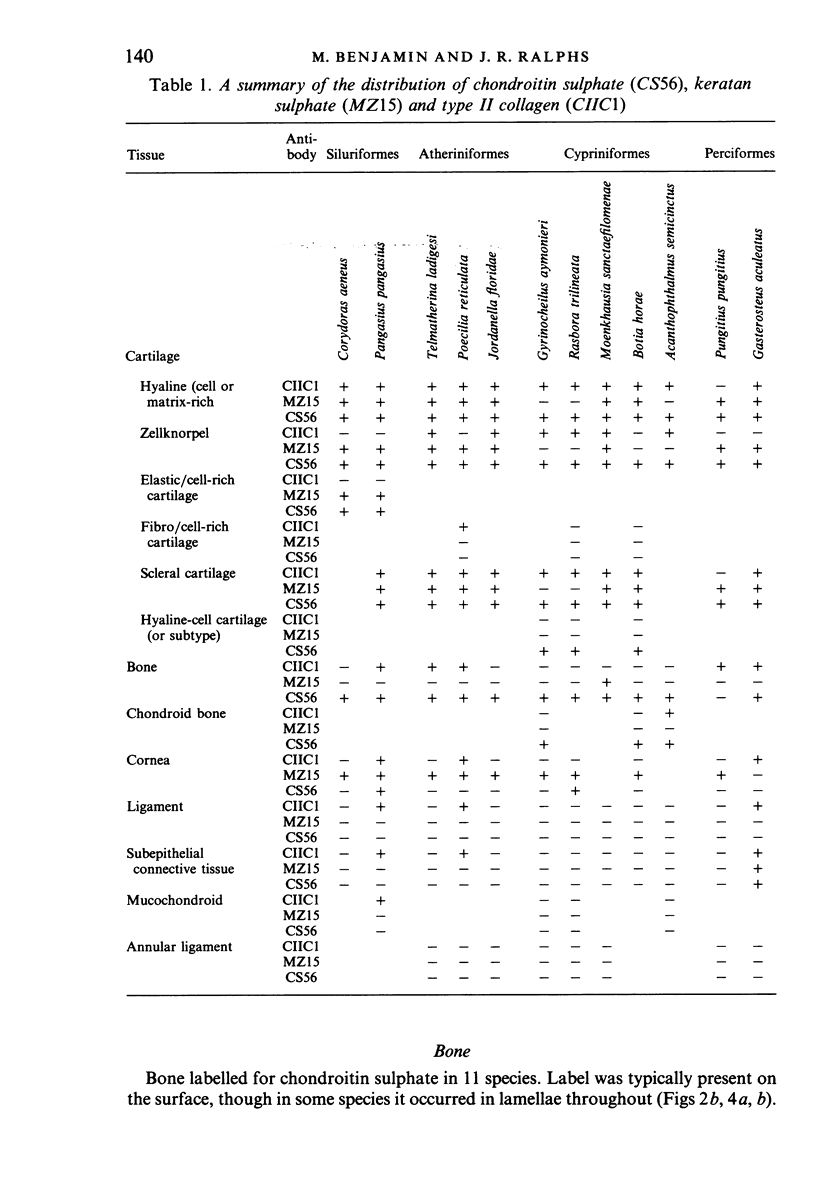
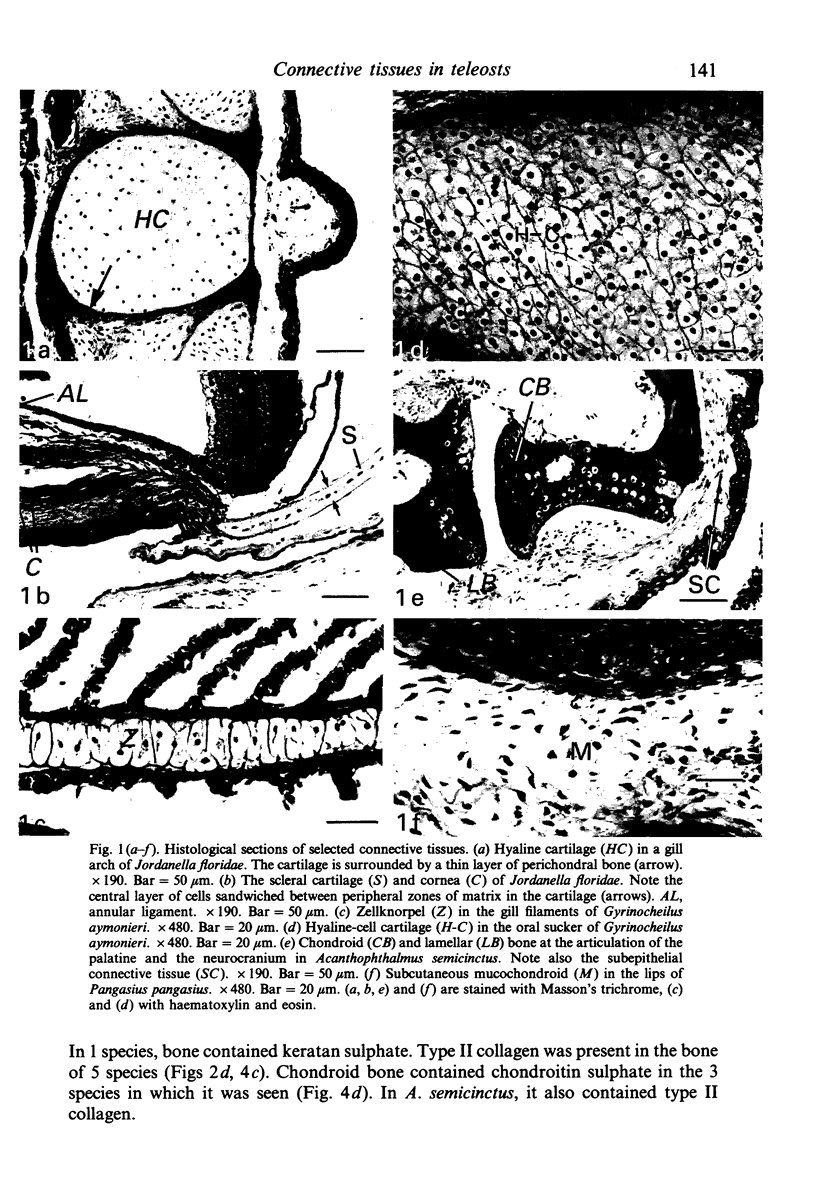
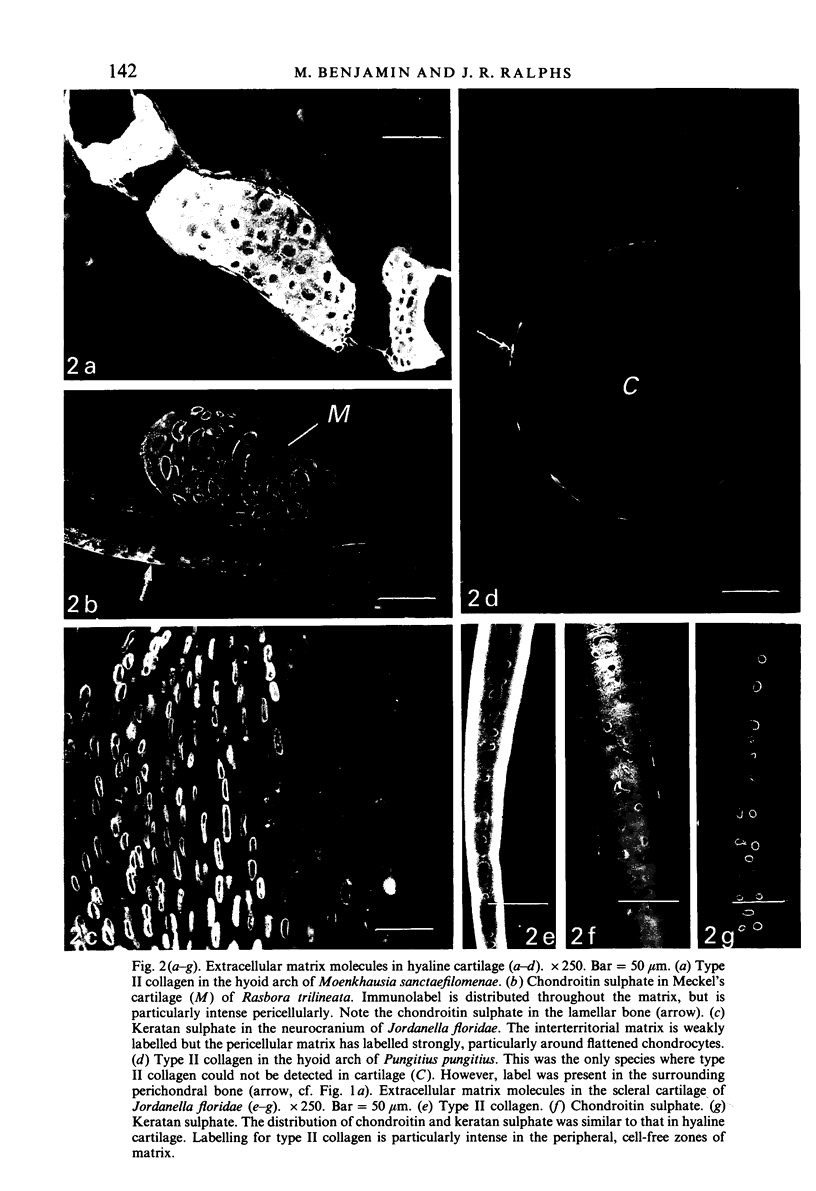
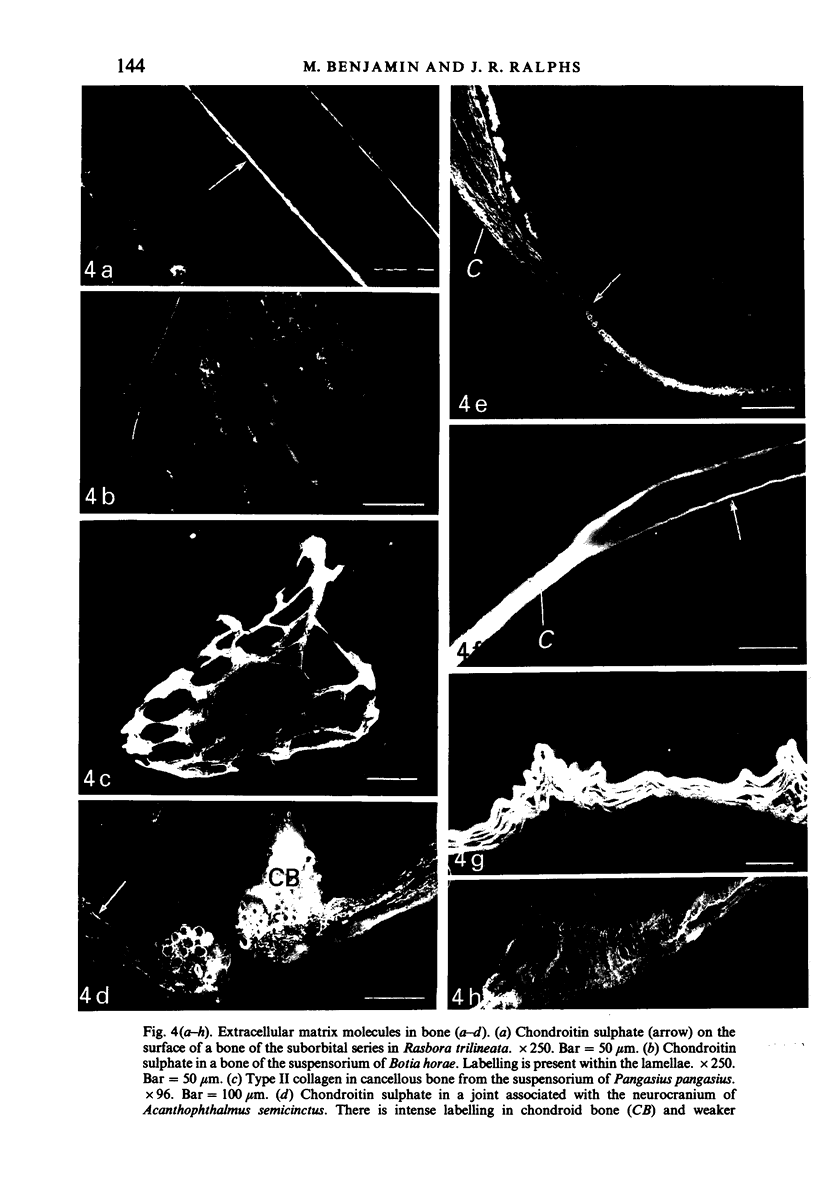
The distribution of extracellular matrix molecules (chondroitin and keratan sulphates, type II collagen) is described in cranial connective tissues of teleosts. Hyaline cartilage was similar to that in mammals and usually contained all 3 molecules. The more cellular cartilages that are not normally present in mammals were more variable in composition. Scleral cartilage closely resembled hyaline cartilage, Zellknorpel in the gill filaments resembled it in some species but not in others, and elastic/cell-rich and hyaline-cell cartilages were unlike hyaline cartilage. These variations may be related to functional or developmental differences between the tissues. Bone and chondroid bone also varied in composition between species. Whilst both tissues contained chondroitin sulphate, bone contained type II collagen in 5 of the 12 species examined. This suggests that cartilage components are more widespread in teleost bone than has previously been shown. Type II collagen also occurred in dense connective tissues of some species. Notably, where this molecule was present in one of these tissues, it was present in all.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avnur Z., Geiger B. Immunocytochemical localization of native chondroitin-sulfate in tissues and cultured cells using specific monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):811–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin M. Hyaline-cell cartilage (chondroid) in the heads of teleosts. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;179(3):285–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00326593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin M. Mucochondroid (mucous connective) tissues in the heads of teleosts. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;178(5):461–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00306053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin M. The cranial cartilages of teleosts and their classification. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:153–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin M. The development of hyaline-cell cartilage in the head of the black molly, Poecilia sphenops. Evidence for secondary cartilage in a teleost. J Anat. 1989 Jun;164:145–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Muir H. The distribution of different molecular species of collagen in fibrous, elastic and hyaline cartilages of the pig. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):595–602. doi: 10.1042/bj1510595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Characterization of the antibody response in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis, using monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):400–410. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Davidson R. S., McNamee K. C., Russell G., Goodwin D., Holborow E. J. Fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy: a study of the phenomenon and its remedy. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet H., Scudder P., Tang P. W., Hounsell E. F., Caterson B., Feizi T. The antigenic determinants recognized by three monoclonal antibodies to keratan sulphate involve sulphated hepta- or larger oligosaccharides of the poly(N-acetyllactosamine) series. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K. G., Koob T. J. Structural specialization in tendons under compression. Int Rev Cytol. 1989;115:267–293. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60632-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Ratcliffe A., Watt F. M. Two subpopulations of differentiated chondrocytes identified with a monoclonal antibody to keratan sulfate. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):53–59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., von der Mark K., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluorescence. I. Preparation of collagen type I and type II specific antibodies and their application to early stages of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H., Timpl R., Trelstad R. L. Immunofluorescent localization of collagen types I, II, and III in the embryonic chick eye. Dev Biol. 1977 Aug;59(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]