Abstract
Newly spliced mRNAs in mammalian cells are characterized by a complex of proteins at exon–exon junctions. This complex recruits Upf3 and Upf2, which function in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Both Upf proteins are detected on mRNA bound by the major nuclear cap-binding proteins CBP80/CBP20 but not mRNA bound by the major cytoplasmic cap-binding protein eIF4E. These and other data indicate that NMD targets CBP80-bound mRNA during a ‘pioneer’ round of translation, but whether nuclear eIF4E also binds nascent but dead-end transcripts is unclear. Here we provide evidence that nuclear CBP80 but not nuclear eIF4E is readily detected in association with intron-containing RNA and the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Consistent with this evidence, we demonstrate that RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf3X and Upf2 are detected in the nuclear fraction on CBP80-bound but not eIF4E-bound mRNA. Each of these proteins is also detected on CBP80-bound mRNA in the cytoplasmic fraction, indicating a presence on mRNA after export. The dynamics of mRNP composition before and after mRNA export are discussed.
Keywords: cap-binding proteins/CTD/exon junction complex/mRNP transport/Upf proteins
Introduction
In mammalian cells, the expression of protein-encoding genes requires a series of steps in which pre-mRNA is processed to mRNA in the nucleus before mRNA is translated into protein in the cytoplasm. These steps are subject to quality control to ensure that only completely processed mRNA is exported to the cytoplasm (reviewed in Maquat and Carmichael, 2001). An additional quality control, called mRNA surveillance or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), degrades mRNAs that prematurely terminate translation >50–55 nucleotides upstream of an exon–exon junction as a means to prevent the synthesis of potentially harmful truncated proteins (reviewed in Maquat, 1995, 2000, 2002; Li and Wilkinson, 1998; Culbertson, 1999; Hentze and Kulozik, 1999; Wilusz and Peltz, 2001). Beside translation, NMD in mammalian cells requires at least four proteins: Upf1, Upf2, Upf3/3X (related products of different genes that are also called Upf3a/b) and hSMG1/ATX (Sun et al., 1998; Lykke-Andersen et al., 2000; Mendell et al., 2000; Denning et al., 2001; Serin et al., 2001; Yamashita et al., 2001; K.M.Brumbaugh, D.M.Otterness, X.Li, F.Lejeune, R.S.Tibbetts, L.E.Maquat and R.T.Abraham, unpublished data). Studies of Upf orthologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae indicate that Upf1 interacts with eukaryotic release factors (eRFs) 1 and 3, Upf2 and Upf3 interact with eRF3 in a way that competes with the eRF3–eRF1 interaction, and all three proteins influence translation termination efficiency (Czaplinski et al., 1998; Maderazo et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2001). hSMG1/ATX, like its ortholog in Caenorhabditis elegans (Page et al., 1999), is a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase involved in the phosphorylation of Upf1 (Denning et al., 2001; Pal et al., 2001; Yamashita et al., 2001; K.M.Brumbaugh, D.M.Otterness, X.Li, F.Lejeune, R.S.Tibbetts, L.E.Maquat and R.T.Abraham, unpublished data).
Exon–exon junctions have been proposed to function in NMD via the ∼335 kDa exon junction complex (EJC) of proteins that is deposited ∼20–24 nucleotides upstream of junctions as a consequence of pre-mRNA splicing (Le Hir et al., 2000a,b, 2001a; Kataoka et al., 2001; Kim et al., 2001b; Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001). Components of this complex include REF/Aly, Y14, DEK, SRm160 and RNPS1. REF/Aly facilitates the nuclear export of mRNA by interacting with the mRNA export receptor TAP (Katahira et al., 1999; Lou and Reed, 1999; Bachi et al., 2000; Kataoka et al., 2000, 2001; Stutz et al., 2000; Zhou et al., 2000; Le Hir et al., 2001a; Rodrigues et al., 2001). Y14, which binds to mRNA that has undergone splicing (Kataoka et al., 2000) and interacts with REF/Aly and RNPS1 in vitro (Kataoka et al., 2001), has been proposed to provide a position-specific memory of the EJC in the cytoplasm since it is detected in association with both nuclear and newly exported cytoplasmic mRNA (Kim et al., 2001b). DEK has multiple functions that include interacting with SR proteins during splicing (McGarvey et al., 2000) as well as altering the superhelical density of DNA in chromatin (Alexiadis et al., 2000) and altering the transcription of certain genes (Faulkner et al., 2001). SRm160 co-activates pre-mRNA splicing (Blencowe et al., 1998; Kataoka et al., 2000; McGarvey et al., 2000) and promotes transcript 3′-end cleavage (McCracken et al., 2002). Notably, neither DEK nor SRm160 shuttle to the cytoplasm in assays using mammalian cell heterokaryons (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001; Y.Ishigaki, B.Blencowe and L.E.Maquat, unpublished data). RNPS1 functions in pre-mRNA splicing (Mayeda et al., 1999) and recently was shown to connect splicing and NMD mechanistically (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001): (i) RNPS1 and, to a lesser extent, Y14 tethered to the 3′-untranslated region of β-globin mRNA recapitulates the function of the EJC in NMD as does tethered Upf1, Upf2 or Upf3/3X (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2000, 2001); and (ii) FLAG-RNPS1 transiently expressed in HEK293 cells co-immunoprecipitates with Upf1, Upf2 and Upf3/3X (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001). Considering that Upf3/3X, RNPS1 and Y14 are mostly nuclear but shuttle, Upf2 is cytoplasmic but primarily perinuclear, and Upf1 is primarily cytoplasmic (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2000, 2001; Serin et al., 2001; J.T.Mendell and H.C.Dietz, personal communication), these data indicate that Upf3/3X joins the splicing-dependent mRNP complex in the nucleus by interacting either directly or indirectly with RNPS1 and, possibly, Y14 (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001). Extending the idea that Upf3/3X is recruited by the complex, Y14 has been shown to interact with REF/Aly, TAP and Upf3/3X independently of RNA, and Upf3X has been shown to map in vivo upstream of the exon–exon junction of two spliced mRNAs (Kim et al., 2001a). According to current thinking, Upf2 joins the complex during or immediately after export to the cytoplasm. Provided that translation terminates prematurely (i.e. >50–55 nucleotides upstream of an EJC-marked exon–exon junction), Upf1 subsequently interacts with the complex in a way that elicits NMD (Ishigaki et al., 2001; Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001).
Another important connection between splicing and NMD was elucidated recently with the finding that Upf2 and Upf3X can be detected on spliced mRNP immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody but not anti-eIF4E antibody (Ishigaki et al., 2001). This result implies that the two Upf proteins are recruited to newly synthesized mRNA that has yet to be translated. CBP80 is the mostly nuclear cap-binding protein that shuttles in association with mRNA to the cytoplasm (Visa et al., 1996; Shen et al., 2000; Ishigaki et al., 2001), where it is replaced by the mostly cytoplasmic cap-binding protein eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4E (reviewed in Gingras et al., 1999). CBP80-bound mRNA, rather than eIF4E-bound mRNA, was found to be the primary template for the first so-called ‘pioneer’ round of translation since it is the primary substrate of NMD (Ishigaki et al., 2001). The conclusion that CBP80-bound mRNA is targeted for NMD was based on several criteria: (i) nonsense-containing CBP80-bound mRNA is reduced in abundance to an extent that is comparable to nonsense-containing eIF4E-bound mRNA, and CBP80-bound mRNA is thought to be a precursor to eIF4E-bound mRNA; (ii) the nonsense-mediated reduction in the abundance of CBP80-bound mRNA is abrogated by either a suppressor tRNA that recognizes the nonsense codon as encoding an amino acid or a cycloheximide-induced block in translation; (iii) Upf2 and Upf3X are detected on CBP80-bound mRNA but not eIF4E-bound mRNA; and (iv) mRNA immunopurified using anti-Upf3/3X antibody is bound by CBP80 but not eIF4E (Ishigaki et al., 2001). These data indicate that NMD generally is confined to CBP80-bound mRNA, before CBP80 is replaced by eIF4E, and before Upf2 and Upf3X dissociate from the vicinity of splicing-generated exon–exon junctions (Ishigaki et al., 2001).
We aimed to gain a broader understanding of the structural rearrangements that typify CBP80- and eIF4E-bound transcripts as a consequence of pre-mRNA synthesis, pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export and mRNA translation. Here, we report the characterization of proteins bound to spliced mRNA immunopurified from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of Cos cells using anti-CBP80, anti-eIF4E or anti-Upf3/3X antibody under conditions that preserve RNP. In nuclear fractions, anti-CBP80 antibody and anti-Upf3/3X antibody, but not anti-eIF4E antibody, immunopurified RNPS1, Y14, SRm160 and REF/Aly, all of which are components of the EJC. Also present in the anti-CBP80 and anti-Upf3/3X immunopurifications of nuclear fractions were the NMD factors Upf3X and Upf2 and the mRNA export factor TAP. RNase treatment demonstrated that immunopurification of RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly and Upf2, but not CBP80, using anti-Upf3/3X antibody was independent of RNA, consistent with these proteins constituting the EJC and associating with Upf3/3X. Furthermore, immunopurification of RNPS1, Y14, Upf3X, Upf2 and, to a lesser extent, SRm160 and REF/Aly using anti-CBP80 antibody was dependent on RNA, suggesting that SRm160 and REF/Aly, in addition to being part of the EJC, may interact with CBP80. The immunopurification of TAP using anti-Upf3/3X antibody was also dependent on RNA, suggesting that TAP has a relatively weak association with the EJC or is present in association with non-EJC mRNA-binding proteins, or both. All EJC components were detected in cytoplasmic fractions immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody in a way that is RNase sensitive, indicating that they are exported with mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm before completely dissociating. Data demonstrating that Upf2 and Upf3X are exported to the cytoplasm in association with CBP80 and the EJC are consistent with the understanding that some mRNAs are subject to cytoplasmic NMD. The finding that eIF4E-bound transcripts that co-purify with nuclei are not bound by the EJC, together with the detection of significant levels of CBP80-bound pre-mRNA but not eIF4E-bound pre-mRNA, indicate that eIF4E replaces CBP80/CBP20 concomitant with or after dissociation of the EJC. In support of the idea that CBP80/CBP20 rather than eIF4E binds to nascent transcripts, antibody against the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II immunopurified CBP80 but not eIF4E.
Results
β-globin mRNA that co-purifies with nuclei is bound by CBP80 or eIF4E
CBP80 together with CBP20 comprise the major nuclear cap-binding complex that is added co-transcriptionally and functions in nuclear RNA processes such as pre-mRNA splicing and 3′ end formation (Izaurralde et al., 1994; Lewis and Izaurralde, 1997). Like CBP80 in Chirononomus tentans (Visa et al., 1996) and S.cerevisiae (Shen et al., 2000), mammalian CBP80 is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein (Ishigaki et al., 2001). Given that the bulk of cellular translation involves mRNA bound by the major cytoplasmic cap-binding protein, eIF4E, it makes sense that eIF4E replaces CBP80 at some point after mRNA export to the cytoplasm (reviewed in Gingras et al., 1999). However, the finding that a fraction of cellular eIF4E localizes to the nucleus (Lejbkowicz et al., 1992; Dostie et al., 2000) indicates that eIF4E could also have a nuclear function.
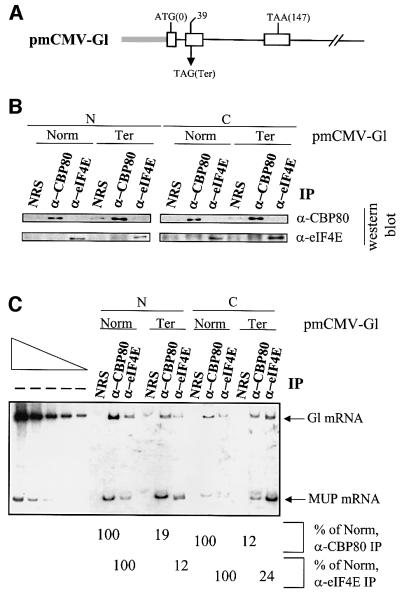
We first determined whether eIF4E that co-purifies with nuclei associates with mRNA. Cos cells were transiently transfected with two plasmids: a test pmCMV-Gl plasmid that produces β-globin (Gl) mRNA (Zhang et al., 1998; Figure 1A), and the reference phCMV-MUP plasmid that produces mRNA for the mouse major urinary protein (MUP; Belgrader and Maquat, 1994) and served to control for variations in the efficiencies of cell transfection and RNA recovery. After 40 h, cells were lysed, nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were generated, and immunopurifications were performed under conditions that preserve RNP (Ishigaki et al., 2001). Briefly, lysates first were cleared by incubation with protein A–agarose beads and subsequently incubated with rabbit anti-CBP80 antibody, rabbit anti-eIF4E antibody or, as a control for non-specific immunopurification, normal rabbit serum (NRS). After 90 min at 4°C, yeast RNA and protein A–agarose beads were added, and the incubation was continued for another 60 min. The beads were washed extensively, bound material was eluted with SDS-containing buffer, and protein and RNA were purified for analysis by western blotting and RT–PCR, respectively.
Fig. 1. CBP80 and eIF4E are bound to mRNA in both nuclear and cytoplasmic cell fractions. (A) Structure of the pmCMV-Gl test plasmids, which harbor either a nonsense-free Gl allele that terminates translation at codon 147 (Norm) or a Gl allele carrying a TAG nonsense codon at position 39 (Ter). (B) Cos cells were transiently transfected with a test pmCMV-Gl plasmid and the reference plasmid phCMV-MUP. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were then immunopurified under conditions that preserved RNP using either normal rabbit serum (NRS), anti-CBP80 antibody (α-CBP80) or anti-eIF4E antibody (α-eIF4E), and subjected to western blotting using anti-CBP80 antibody or anti-eIF4E antibody. Nuclear fractions were free of cytoplasm as evidenced by the absence of detectable reactivity with anti-eIF4A antibody (data not shown). For easy visualization, bands corresponding to antibody are not shown. (C) The levels of Gl and MUP mRNAs were quantitated in RNA prepared from each immunopurification using RT–PCR. The leftmost five lanes, which analyze decreasing amounts of RNA before immunopurification (– IP), demonstrate that the conditions of RT–PCR were quantitative. Numbers below the figure represent the level of Gl mRNA normalized to the level of MUP mRNA, where normalized levels of nonsense-free (Norm) mRNA in each anti-CBP80 and anti-eIF4E immunopurification of each fraction are defined as 100%. Results are representative of two independently performed experiments where the efficiency of NMD varied by no more than 12%. The immunopurification using anti-eIF4E and cytoplasmic sample was less efficient for the transfection using pmCMV-Gl Norm than for the transfection using pmCMV-Gl Ter, explaining the reduced levels of eIF4E detected by western blotting (B) and RNA detected by RT–PCR (C).
Results obtained using western blotting were consistent with previous findings (Ishigaki et al., 2001): anti-CBP80 antibody immunopurified only CBP80 in both cellular fractions, anti-eIF4E antibody immunopurified only eIF4E in both cellular fractions; and the control NRS did not immunopurify either protein in either cell fraction (Figure 1B). RT–PCR demonstrated that each antibody immunopurified Gl and MUP mRNAs and that, regardless of the cellular fraction or cap-binding protein, the level of nonsense-containing (Ter) Gl mRNA was reduced to an average of 17 ± 7% the level of nonsense-free (Norm) mRNA (Figure 1C). Therefore, eIF4E is associated with mRNA that co-purifies with nuclei.
CBP80 but not eIF4E is detectably bound to intron-containing Gl and SV40 T antigen pre-mRNAs
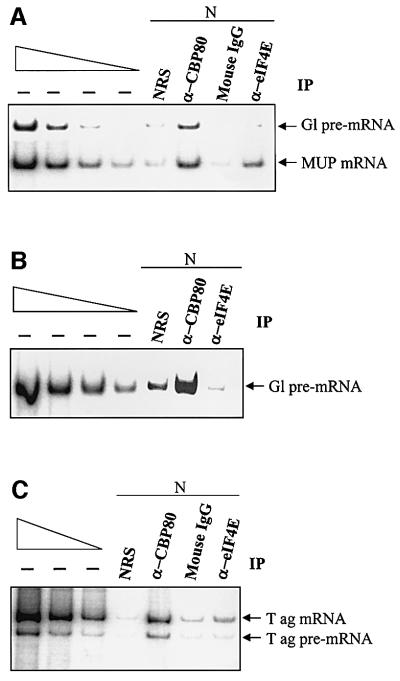
Since CBP80-bound but not eIF4E-bound mRNA was found to be associated with factors required for NMD, the reduction in the abundance of nonsense-containing eIF4E-bound mRNA was attributed to NMD that occurred prior to the exchange of CBP80 for eIF4E (Ishigaki et al., 2001). Therefore, intron-containing pre-mRNA may be bound primarily by CBP80 rather than eIF4E. Alternatively, it may be bound by CBP80 or eIF4E, but the latter is a dead-end product that fails to be spliced and, therefore, fails to recruit Upf3/3X and Upf2 (Ishigaki et al., 2001; see below). One way to determine whether eIF4E-bound mRNAs generally derive from CBP80-bound mRNAs or, alternatively, eIF4E binds to pre-mRNA is to identify the cap-binding protein on intron-containing RNA: if it is only CBP80, then eIF4E-bound RNA must derive from CBP80-bound RNA. To this end, the experiment described above was repeated. However, only nuclear fractions were prepared, and intron-containing Gl pre-mRNA was analyzed instead of Gl mRNA. Furthermore, the anti-eIF4E antibody derived from either rabbit or mouse. When mouse anti-eIF4E antibody was used, the level of non-specific immunopurification was controlled for using mouse IgG.
RT–PCR demonstrated that the levels of MUP mRNA immunopurified using either anti-CBP80 antibody or mouse anti-eIF4E antibody were higher than non-specific, i.e. higher than the levels immunopurified using NRS or mouse IgG, respectively (Figure 2A), consistent with previous findings (Ishigaki et al., 2001; Figure 1). In contrast, while the level of Gl pre-mRNA immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody was higher than non-specific, the level of Gl pre-mRNA immunopurified using mouse anti-eIF4E antibody was barely above non-specific (Figure 2A). The essential failure to detect eIF4E-bound Gl pre-mRNA was reproduced using rabbit anti-eIF4E antibody (Figure 2B). Therefore, CBP80 is readily detected in association with Gl pre-mRNA whereas eIF4E is not.
Fig. 2. CBP80 but not eIF4E is detectably bound to intron-containing pre-mRNA. (A) As in Figure 1, except that only nuclear fractions and Gl pre-mRNA rather than Gl mRNA were analyzed. Furthermore, mouse anti-eIF4E antibody was used instead of rabbit anti-eIF4E antibody and mouse IgG served to control for non-specific immunopurification using mouse anti-eIF4E antibody. (B) As in (A) except that rabbit anti-eIF4E antibody was used in place of mouse anti-eIF4E antibody and the analysis of MUP mRNA was omitted. (C) As in (A) except that SV40 pre-mRNA and mRNA were analyzed. Results are representative of other independently performed experiments, including those using rabbit anti-eIF4E antibody and NRS as a control. Taking the sum of Gl or SV40 pre-mRNA immunopurified by anti-CBP80 antibody and anti-eIF4E antibody in each panel as 100%, the amount of CBP80-bound pre-mRNA was 96 ± 6% and the amount of eIF4E-bound pre-mRNA was 4 ± 6%.
To determine if this result can be extended to another pre-mRNA, the immunopurification was repeated using untransfected Cos cells. RT–PCR was then used to assay the relative levels of SV40 T antigen (ag) pre-mRNA and mRNA. The level of SV40 T ag mRNA immunopurified using either anti-CBP80 or mouse anti-eIF4E antibody was higher than non-specific (Figure 2C). However, as was the case for Gl pre-mRNA, the level of SV40 T ag pre-mRNA immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody was significantly higher than non-specific, while the level immunopurified using mouse anti-eIF4E antibody was only slightly higher than non-specific (Figure 2C).
We conclude that the vast majority of Gl and SV40 T ag pre-mRNAs is bound by CBP80 rather than eIF4E, suggesting that eIF4E-bound mRNA derives primarily from transcripts initially bound by CBP80.
CBP80 but not eIF4E co-immunopurifies with the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II
Given that 5′ capping enzymes bind the phosphorylated C-terminal domain (CTD) of transcribing RNA poly merase II molecules (McCracken et al., 1997; Schroeder et al., 2000; Pei et al., 2001), and since proteins known to function in pre-mRNA splicing and 3′-end formation also associate with the CTD (reviewed in Hirose and Manley, 2000; Proudfoot, 2000), an additional way to determine whether CBP80-bound mRNA is generally a precursor to eIF4E-bound mRNA might be to determine whether CBP80 or eIF4E also co-immunopurify with the CTD. To test this idea, the nuclear fraction of untransfected Cos cells was immunopurified using anti-CTD antibody, and the presence of CBP80 and eIF4E was tested.
The results of western blotting indicate that anti-CTD antibody immunopurified CTD, as expected, and, remarkably, CBP80 but not eIF4E (Figure 3; data not shown for the analysis of larger amounts of immunopurified material). This finding is consistent with the finding that intron-containing pre-mRNA is bound by CBP80 rather than eIF4E (Figure 2) and offers additional support for a precursor–product relationship between CBP80-bound mRNA and eIF4E-bound mRNA. Another protein that failed to immunopurify with the CTD was Upf2 (Figure 3), which was chosen as a negative control based on its cytoplasmic localization (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2000; Serin et al., 2001).
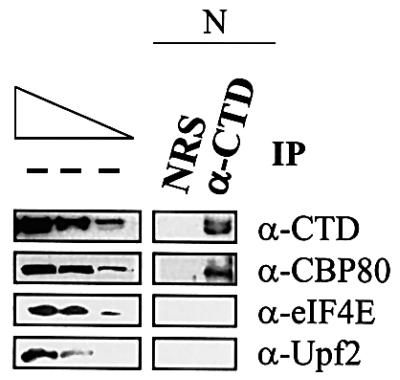
Fig. 3. CBP80 but neither eIF4E nor Upf2 immunopurifies with the CTD. The nuclear fraction of 32 × 106 untransfected Cos cells was immunopurified using either NRS or antibody to the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (α-CTD), and protein from either 8 × 105 cells (CTD) or 32 × 105 cells (CBP80, eIF4E and Upf2) was subjected to western blotting using anti-CTD, anti-CBP80, anti-eIF4E or anti-Upf2 antibody. The three leftmost lanes, which analyze 2-fold dilutions of nuclear protein from 1.6 × 105 cells (CTD and CBP80) or 6.4 × 105 cells (eIF4E and Upf2) before immunopurification (– IP), demonstrate that the conditions of western blotting were semi-quantitative. The two forms of CTD probably differ in the degree of phosphorylation (Dubois et al., 1994). Results are representative of 2–4 independently performed experiments, depending on the antibody used in western blotting.
Anti-CBP80 antibody, unlike anti-eIF4E antibody, co-immunopurifies with RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf2 and Upf3X in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions
To gain insight into the dynamics of mRNP remodeling before and after eIF4E replaces CBP80 at the mRNA cap, the immunopurifications were repeated using nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions from untransfected Cos cells and analyzed for a variety of proteins using western blotting. Initially, RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly and DEK, which are components of the mRNA EJC that is deposited as a consequence of pre-mRNA splicing in vitro, were analyzed. Remarkably, all components except DEK were detected in immunopurifications of both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions using anti-CBP80 antibody (Figure 4). The failure to detect DEK suggests that either it is not present in the complex in vivo or that conditions used in the immunopurification removed DEK. A similar conclusion was drawn from immunopurifications using unfractionated mammalian cells expressing FLAG-tagged proteins, where all tagged components of the EJC were detected except for DEK (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001). Our results indicate that RNPS1, Y14, SRm160 and REF shuttle to the cytoplasm, presumably in association with spliced mRNA (see below). Considering that SRm160 does not shuttle between the two nuclei of mammalian cell heterokaryons (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001; Y.Ishigaki, B.Blencowe and L.E.Maquat, unpublished data), detection of SRm160 in the cytoplasmic fraction by immunopurification using anti-CBP80 antibody suggests that SRm160 may have a limited trajectory in the cytoplasm. Consistent with our failure to detect eIF4E-bound pre-mRNA, no components of the EJC were detected in either cell fraction using anti-eIF4E antibody (Figure 4).

Fig. 4. Nuclear and cytoplasmic CBP80, unlike nuclear and cytoplasmic eIF4E, co-immunopurify with RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf3X and Upf2. Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of 32 × 106 untransfected Cos cells were immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody, anti-eIF4E antibody or, as a control, NRS. Immunopurified protein from 8 × 105 or 32 × 105 cells was then analyzed by western blotting using the antibodies specified. The three leftmost lanes, which analyze 2-fold dilutions of nuclear protein from 8 × 105 or 32 × 105 cells before immunopurification (– IP), demonstrate that the conditions of western blotting were semi-quantitative. Notably, Upf3 probably co-migrates with the heavy chain of anti-hUpf3/3X antibody and, therefore, was not assayable.
The mRNA export factor TAP and the NMD factors Upf2 and Upf3X were also detected in anti-CBP80 antibody immunopurifications of nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions but not anti-eIF4E immunopurifications of either fraction (Figure 4). The failure to detect either Upf protein using anti-eIf4E antibody is consistent with data demonstrating that eIF4E-bound mRNA is largely immune to NMD (Ishigaki et al., 2001). SMG1/ATX, the PIK-related protein kinase thought to be required for NMD because of its role in phosphorylating Upf1 (Denning et al., 2001; Yamashita et al., 2001; K.M.Brumbaugh, D.M.Otterness, X.Li, F.Lejeune, R.S.Tibbetts, L.E.Maquat and R.T.Abraham, unpublished data), was not detected in either anti-CBP80 or anti-eIF4E immunopurification (Figure 4). This suggests that, like Upf1, SMG1/ATX is not a stable component of mRNP, at least under the purification conditions used here.
Evidence that RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf2 and Upf3X are components of or associate with the EJC on CBP80-bound mRNA in mammalian cells
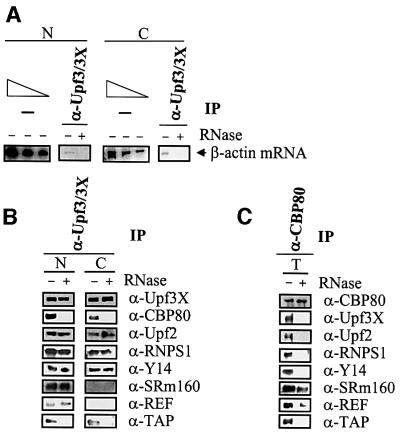
In order to determine if RNPS1, Y14, SRm160 and REF/Aly immunopurify with anti-CBP80 antibody as components of the EJC of mRNP, the immunopurifications were repeated using anti-Upf3/3X antibody or anti-CBP80 antibody either with or without the addition of RNase prior to the immunopurification step. Data demonstrating that Upf3/3X is recruited to mRNP by an EJC formed in vitro in mammalian cell extract (Kim et al., 2001a) or in vivo in intact mammalian cells using FLAG-tagged Upf3 produced by transient transfection (Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001) indicate that the EJC and CBP80 bind to distinct regions of mRNA. Therefore, components of or proteins recruited by the EJC would be expected to immunopurify with anti-Upf3/3X antibody both before and after RNase treatment, but with anti-CBP80 antibody only before and not after RNase treatment.
RNase treatment was shown to be effective by the disappearance of β-actin mRNA in immunopurified samples after exposure to RNase (Figure 5A; data not shown for the immunopurification using anti-CBP80 antibody). As expected, anti-Upf3/3X antibody immunopurified Upf3X in nuclear fractions with or without exposure to RNase (Figure 5B) and anti-CBP80 antibody immunopurified CBP80 in total cell extract with or without exposure to RNase (Figure 5C). Furthermore, anti-Upf3/3X antibody immunopurified CBP80 in both fractions only in the absence of RNase, but immunopurified Upf2, RNPS1 and Y14 in both fractions in the absence or presence of RNase (Figure 5B). These results, together with the finding that anti-CBP80 antibody immunopurified Upf3X, Upf2, RNPS1 and Y14 in total cell extract only in the absence of RNase (Figure 5C), indicate that Upf3X and Upf2 form a complex with the EJC that is conserved after mRNA export to the cytoplasm. SRm160 and REF/Aly immunopurified with anti-Upf3/3X antibody in the nuclear fraction with or without exposure to RNase (Figure 5B), as would be expected of EJC components. However, they failed to immunopurify with anti-Upf3/3X antibody in the cytoplasmic fraction (Figure 5B), and they immunopurified with anti-CBP80 antibody in a partially RNase-insensitive manner (Figure 5C). Considering that both proteins immunopurify with anti-CBP80 antibody in the cytoplasmic fraction (Figure 4), they may undergo a remodeling in the cytoplasm that provides a more direct connection to CBP80. The finding that TAP immunopurifies with anti-Upf3/3X antibody and anti-CBP80 antibody in an RNase-sensitive manner in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions (Figure 5B and C) does not preclude the possibility that it is recruited by the EJC. In fact, TAP could be only loosely associated with the EJC, making it susceptible to removal by RNase treatment. However, it is also possible that some TAP is recruited by the EJC and the majority is recruited by non-EJC mRNA-binding proteins (see Discussion).
Fig. 5. RNPS1, Y14, SRm160, REF/Aly and Upf2 co-immunopurify with Upf3X in an RNase-insensitive manner, while RNPS1, Y14, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf3X and Upf2 co-immunopurify with CBP80 in an RNase-sensitive manner. As in Figure 4 except that an additional immunopurification using anti-Upf3/3X was performed, total (T) lysate was immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody, RNase was added to half of each sample prior to immunopurification, RNA as well as protein were prepared, and western blot analyses of eIF4E and DEK were omitted. (A) RT–PCR quantitation of the level of β-actin mRNA before or after immunopurification using anti-Upf3/3X antibody in order to demonstrate the efficiency of RNase treatment. Prior to immununopurification, half of the sample was treated with RNase (+), and the other half was not treated with RNase (–). (B) Western blot analysis of protein immunopurified using anti-Upf3/3X antibody from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions. (C) Western blot analysis of protein immunopurified using anti-CBP80 antibody from total cell extract.
Discussion
This study aimed to characterize proteins associated with CBP80-bound and eIF4E-bound RNA in mammalian cells before and after export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Notably, endogenous proteins rather than proteins produced from introduced genes were assayed in order to avoid generating artifactual interactions attributable to expression at abnormal levels. Even though both CBP80 and eIF4E are present in nuclei (Ohno et al., 1990; Izaurralde et al., 1992; Lejbkowicz et al., 1992; Dostie et al., 2000) and eIF4E is detected in association with mRNA that co-purifies with nuclei (Figure 1), only CBP80 is readily detected in association with intron-containing pre-mRNA (Figure 2). The failure to detect appreciable amounts of eIF4E-bound pre-mRNA is consistent with data demonstrating that immunodepletion of CBP80 from HeLa cell extracts strongly reduces the efficiency of pre-mRNA splicing (Izaurralde et al., 1994). It is also consistent with the detection of CBP80 but not eIF4E in association with the CTD (Figure 3). We find that CBP80 and not eIF4E co-immunopurifies with components of the EJC (Figure 4). In verification that our conditions allow for the isolation of mRNP and, therefore, a characterization of its structure, we also demonstrate that immunopurification of components of the EJC using anti-CBP80 antibody is sensitive to RNase whereas immunopurification of these components using anti-Upf3/3X antibody is not (Figure 5). This result is expected of cap-bound CBP80 and distally bound components of the EJC, the latter of which recruits Upf3/3X. Our findings are consistent with data demonstrating that either FLAG-Upf3 or FLAG-Upf3X expressed transiently in 293T cells immunopurifies Y14 and REF/Aly independently of RNA (Kim et al., 2001b; RNPS1, SRm160 and Upf2 were not tested and, in contrast to our results, only Flag-Upf3 immunopurified TAP in a manner that was partially dependent on RNA). We conclude that eIF4E binds RNA after splicing and concomitant with or after removal of the EJC.
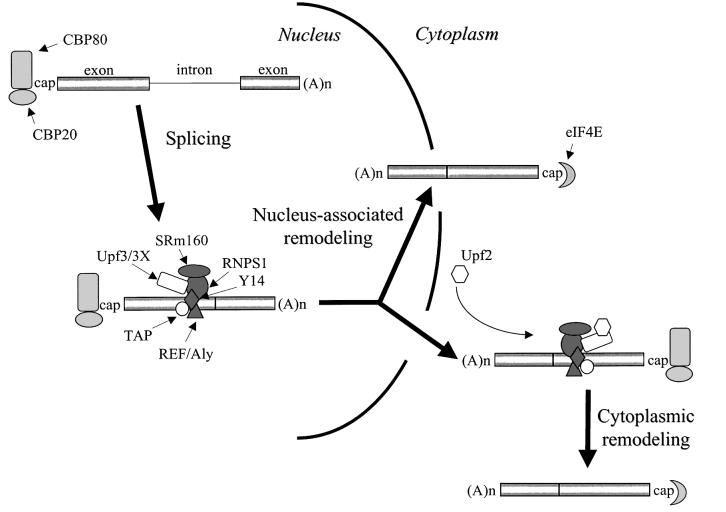
Given that CBP80-bound mRNA is the substrate for NMD and the NMD of some mRNA takes place in the cytoplasm, the replacement of CBP80 by eIF4E on mRNA subject to cytoplasmic NMD must take place in the cytoplasm at least some of the time (Ishigaki et al., 2001; Figure 6). However, the presence of eIF4E-bound mRNA in the nuclear fraction (Figure 1) indicates that the replacement of CBP80 by eIF4E on mRNA also takes place before mRNA release into the cytoplasm at least some of the time (Figure 6). In fact, replacement before release might typify mRNAs subject to nucleus-associated NMD. In theory, replacement before release could take place during transit across the nuclear pore, at a point when mRNA would co-purify with nuclei but have access to cytoplasmic ribosomes. In support of this possibility, mRNP in the insect C.tentans has been shown using electron microscopy to exit the nucleus 5′ end-first and associate with cytoplasmic ribosomes before its 3′ end transits the nuclear pore complex (Mehlin et al., 1992; Daneholt, 1997). Alternatively, since the EJC is not required for export (Huang and Steitz, 2001; Rodrigues et al., 2001), replacement could take place in the nucleoplasm.
Fig. 6. Model for the dynamics of mRNP structure in mammalian cells as a consequence of pre-mRNA capping, pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA export. In the nucleus, CBP80-bound pre-mRNA is spliced to generate CBP80-bound mRNA. This mRNA is bound by an EJC (dark gray shapes), consisting of RNPS1, Y14, SRm160 and REF/Aly, located 20–24 nucleotides upstream of the exon–exon junction. The EJC recruits the NMD factor Upf3/3X and the mRNA export factor TAP. Some mRNPs (possibly those subject to nucleus-associated NMD) undergo remodeling while associated with the nucleus (nucleus-associated remodeling). Other mRNPs (including those subject to cytoplasmic NMD) undergo remodeling after export to the cytoplasm (cytoplasmic remodeling). In both types of remodeling, CBP80 is replaced by eIF4E and the EJC is lost. Data indicate that the mostly perinuclear Upf2 protein is recruited by the EJC at a point when mRNA co-purifies with nuclei. In theory, recruitment could occur during mRNA export. However, if nucleus-associated remodeling takes place in the nucleoplasm, it is conceivable that an as yet undetected pool of Upf2 is nucleoplasmic. The single exon–exon junction exemplified is likely to typify all splicing-generated exon–exon junctions, regardless of position relative to the mRNA 3′ end.
Our data are consistent with a growing number of studies demonstrating that mRNP undergoes significant remodeling, in keeping with the requirements of mRNA export and NMD (Lou and Reed, 1999; Lou et al., 2001; Kataoka et al., 2000; Le Hir et al., 2000b, 2001a; Zhou et al., 2000; Kim et al., 2001a,b). RNPS1, Y14, SRm160 and REF/Aly, which are components of the EJC, and Upf2, Upf3X and TAP, which are recruited by the EJC either directly or indirectly (Le Hir et al., 2000a, 2001a,b; Ishigaki et al., 2001; Kim et al., 2001b; Lykke-Andersen et al., 2001), are detected on CBP80-bound mRNA in both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions (Figure 4). Therefore, each protein first binds directly or indirectly to mRNA either in the nucleoplasm or during mRNA export, and at least a fraction of each protein remains bound after export to the cytoplasm.
Studies of Xenopus oocytes indicate that Y14 and SRm160 remain associated with spliced mRNA after export, while RNPS1, REF/Aly and TAP fail to be detected on exported mRNA (Le Hir et al., 2001a). Differences in the behavior of RNPS1, REF/Aly and TAP between mammalian cells and Xenopus oocytes are not yet understood. The finding that these proteins are complexed with Y14, which remains bound to mRNA after export in Xenopus oocytes, suggests that there are bona fide differences between the fate of EJC components in mammalian cells and Xenopus oocytes. As another difference, Upf2 and Upf3X are associated with the EJC in both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of mammalian cells (Figures 4 and 5), whereas Upf3X is detected on mRNA only in Xenopus oocyte nuclei and Upf2 is detected on mRNA only in Xenopus oocyte cytoplasm (Le Hir et al., 2001a). Unlike mammalian cells, Xenopus oocytes do not support NMD (J.Zhang, E.Lund and L.E.Maquat, unpublished data), which may reflect the observed differences in mRNP.
Very recently, UAP56 and epitope-tagged Mago have also been shown to associate with the EJC. UAP56, a DEAD-box helicase and splicing factor, and Sub2p, its ortholog in S.cerevisiae, are linked to nuclear mRNA export via interactions with REF/Aly and Yra1p, respectively (Lou et al., 2001; Sträßer and Hurt, 2001). Mago joins the EJC by interacting with Y14 and has been shown to escort spliced mRNAs to the cytoplasm in Xenopus oocytes (Kataoka et al., 2001; Le Hir et al., 2001b). These studies join the growing number of observations that splicing, transport and translation are mechanistically linked through numerous steps of mRNP remodeling.
Data indicate that EJCs function in mRNA export (Lou and Reed, 1999; Zhou et al., 2000; Kim et al., 2001b; Le Hir et al., 2001a; reviewed in Reed and Magni, 2001; Reed and Hurt, 2002). However, EJCs are not the only means by which mRNA is exported, as exemplified by the export of intronless RNAs in pathways that involve the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins SRp20 and 9G8 (Huang and Steitz, 2001) and REF/Aly (Rodrigues et al., 2001). Given that spliced and unspliced mRNAs use TAP to reach the cytoplasm (Rodrigues et al., 2001), and considering that SRp20 and 9G8 have been shown to cross-link to polyadenylated RNA in both nuclear and cytoplasmic cell fractions (Huang and Steitz, 2001), it is conceivable that spliced mRNAs are bound by non-EJC proteins that recruit TAP for the purpose of export, possibly explaining at least in part the RNase sensitivity of TAP co-immunopurification with Upf3/3X (Figure 5B). Along similar lines, T-cell receptor-β mRNA was shown recently to harbor a novel cis-acting sequence distinct from an EJC that triggers NMD, presumably by recruiting Upf factors (Wang et al., 2002). Future studies that continue to characterize the nature of spliced mRNP should lend important insight into effectors of mRNA synthesis, transport and half-life.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and transfections
Monkey kidney Cos-7 cells were cultured and, where indicated, transfected as previously described (Ishigaki et al., 2001).
Cell fractionation, lysis and immunopurifications
Whole cells or nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of cells (3–4 × 107) were processed as previously described (Ishigaki et al., 2001). For all immunopurifications except those using anti-CTD antibody, samples were first cleared by incubation with end-over-end rotation in the presence of 50 µl of protein A–agarose beads (Boehringer Mannheim) in NET-2 buffer, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF; Sigma), 2 mM benzamidine (Sigma) and, when RNase was not used, 100 U of RNase inhibitor (Promega) for 30 min at 4°C followed by centrifugation at 10 000 g. Cleared samples were then rotated in the presence of either normal rabbit antiserum (NRS; Gibco-BRL) or mouse IgG (Sigma), anti-CBP80 antibody (Izaurralde et al., 1994), anti-eIF4E antibody (Morley and McKendrick, 1997; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or anti-hUpf3/3X antibody (Ishigaki et al., 2001) for 90 min at 4°C, after which 2 mg of yeast RNA (Sigma) and protein A–agarose beads were added. The incubation was continued for another 60 min at 4°C. The beads were washed 5–6 times with NET-2 buffer, suspended in 50 µl of SDS sample buffer (Ishigaki et al., 2001) that either did or, for the analysis of RNPS1 and Upf3 that co-migrated with antibody, did not contain 12% 2-mercaptoethanol, and split into two portions. In some experiments, RNase A (10 µg; Sigma) or, as a control, bovine serum albumin (BSA; 10 µg; New England Biolabs) was added to the beads and incubated for 30 min at 37°C before elution using SDS sample buffer. One portion (three-fifths) was used as a source of protein, which was analyzed by SDS–PAGE and western blotting. The other portion (two-fifths) was extracted with phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol, and precipitated using ethanol. Precipitates were dissolved in 20 µl of RQ1 DNase buffer (Promega), treated with 10 U of DNase I (Promega) for 30 min at 37°C, extracted, precipitated, dissolved in 20 µl of water, and used as a source of RNA for RT–PCR (Sun et al., 1998).
For immunopurifications using anti-CTD antibody and, as a control, NRS, the concentration of NaCl in NET-2 buffer was decreased from 300 to 50 mM.
Western blotting
Protein in immunopurifications (1–5 µl) was electrophoresed in 7.5% (for SMG1/ATX), 10% (for CBP80, Upf2, SRm160, TAP and CTD) or 12% (for eIF4E, Y14, REF, DEK, Upf3X and RNPS1) polyacrylamide. Protein was transferred to Hybond ECL nitrocellulose (Amersham), and probed with antibody against CBP80 (a gift from E.Izaurralde), eIF4E (a gift from S.Morley), Upf3/3X (Serin et al., 2001), Upf2 (Serin et al., 2001), RNPS1 (a gift from A.Mayeda), Y14 (a gift from G.Dreyfuss), SRm160 (a gift from B.J.Blencowe), DEK (a gift from G.Grosveld), REF/Aly (a gift from E.Izaurralde), TAP (a gift from E.Izaurralde), SMG1/ATX (a gift from R.T.Abraham) or CTD (a gift from D.Bentley). In the case of cellular fractionations, nuclear fractions were deemed free of cytoplasm by the absence of detectable reactivity with antibody against eIF4A (a gift from S.Morely; Lejbkowicz et al., 1992) and anti-PLCγ (a gift from R.T.Abraham). Reactivity to each primary antibody was detected using a 1:5000 dilution of anti-rabbit Ig, horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-linked whole antibody (Amersham; to detect CBP80, eIF4E, RNPS1, Y14, REF/Aly, TAP, Upf2, Upf3X, SMG1/ATX and CTD), anti-mouse Ig, HRP-linked whole antibody (Amersham; to detect eIF4E), or anti-mouse IgM peroxidase conjugate (Sigma; to detect SRm160). Reactivity of the secondary antibody was visualized by SuperSignal West Pico or West Femto Solution (Pierce).
RT–PCR
Gl or MUP mRNAs in immunopurifications (10 µl) were analyzed by RT–PCR as described (Ishigaki et al., 2001). Alternatively, Gl pre-mRNA was amplified using primers 5′ GCCTATTGGTCTATTTTCCC 3′ (sense) and 5′ CCTGAAGTTCTCAGGATC 3′ (antisense). To assay for RNase activity, endogenous Cos-cell β-actin mRNA was amplified using 5′ ATCTGGCACCACACCTTCTACAATGAGCTGCG 3′ (sense) and 5′ CGTCATACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTGC 3′ (antisense). Endogenous Cos cell SV40 T ag pre-mRNA and mRNA were amplified using primers 5′ TGCAAGGAGTTTCATCCTG 3′ (sense) and, respectively, 5′ AGAATCAGTAGTTTAACACAC 3′ and 5′ TGAGCA TAGTTATTAATAGCAG 3′ (antisense), in which case the annealing reaction was performed at 50°C for 40 s and a total of 23 cycles. The simultaneous analysis of serial dilutions of RNA ensured that RT–PCR was quantitative. RT–PCR products were quantitated by PhosphorImaging (Molecular Dynamics).
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Linda McKendrick for technical advice, Shang-Yi Chiu for comments on the manuscript, and Bob Abraham, David Bentley, Ben Blencowe, Gideon Dreyfuss, Gerard Grosveld, Elisa Izaurralde, Joe Lewis, Akila Mayeda and Simon Morley for antibodies. This work was supported by Public Health Service grants DK 33938 and GM 59614 from the National Institutes of Health. F.L. is partially supported by a post-doctoral fellowship from Fondation pour la Recherche Medicale.
References
- Alexiadis V., Waldmann,T., Andersen,J., Mann,M., Knippers,R and Gruss,C. (2000) The protein encoded by the proto-oncogene DEK changes the topology of chromatin and reduces the efficiency of DNA replication in a chromatin-specific manner. Genes Dev., 14, 1308–1312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachi A. et al. (2000) The C-terminal domain of TAP interacts with the nuclear complex and promotes export of specific CTE-bearing RNA substrates. RNA, 6, 136–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belgrader P. and Maquat,L.E. (1994) Nonsense but not missense mutations can decrease the abundance of nuclear mRNA for the mouse major urinary protein, while both types of mutations can facilitate exon skipping. Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 6326–6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B.J., Issner,R., Nickerson,J.A. and Sharp,P.A. (1998) A coactivator of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev., 12, 996–1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson M.R. (1999) RNA surveillance. Unforeseen consequences for gene expression, inherited genetic disorders and cancer. Trends Genet., 15, 74–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaplinski K., Ruiz-Echevarria,M.L., Paushkin,S.V., Han,X., Weng,Y., Perlick H.A., Dietz,H.C., Ter-Avanesyan,M.D. and Peltz,S.W. (1998) The surveillance complex interacts with the translation release factors to enhance termination and degrade aberrant mRNAs. Genes Dev., 12, 1665–1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. (1997) A look at messenger RNP moving through the nuclear pore. Cell, 88, 585–588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning G., Jamieson,L., Maquat,L.E., Thompson,E.A. and Fields,A.P. (2001) Cloning of a novel phosphoinositide kinase-related kinase: characterization of the human SMG-1 RNA surveillance protein. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 22709–22714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostie J., Lejbkowicz,F. and Sonenberg,N. (2000) Nuclear eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) colocalizes with splicing factors in speckles. J. Cell Biol., 148, 239–247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M.F., Nguyen,V.T., Dahmus,M.E., Pages,G., Pouyssegur,J. and Bensaude,O. (1994) Enhanced phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II upon serum stimulation of quiescent cells: possible involvement of MAP kinases. EMBO J., 13, 4787–4797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner N.E., Hilfinger,J.M. and Markovitz,D.M. (2001) Protein phosphatase 2A activates the HIV-2 promoter through enhancer elements that include the pets site. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 25804–25812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingras A.-C., Raught,B. and Sonenberg,N. (1999) eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 68, 913–963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M.W. and Kulozik,A.E. (1999) A perfect mRNA: RNA surveillance and nonsense-mediated decay. Cell, 96, 307–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose Y. and Manley,J.L. (2000) RNA polymerase II and the integration of nuclear events. Genes Dev., 14, 1415–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. and Steitz,J.A. (2001) Splicing factors SRp20 and 9G8 promote the nucleocytoplasmic export of mRNA. Mol. Cell, 7, 899–905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishigaki Y., Li,X., Serin,G. and Maquat,L.E. (2001) Evidence for a pioneer round of translation: mRNAs subject to nonsense-mediated decay in mammalian cells are bound by CBP80 and CBP20. Cell, 106, 607–617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Stepinski,J., Darzynkiewicz,E. and Mattaj,I.W. (1992) A cap binding protein that may mediate nuclear export of RNA polymerase II-transcribed RNAs. J. Cell Biol., 118, 1287–1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Lewis,J., McGuigan,C., Jankowska,M., Darzynkiewicz,E. and Mattaj,I.W. (1994) A nuclear cap binding protein complex involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Cell, 78, 657–668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira J., Sträßer,K., Podtelejnikov,A., Mann,M., Jung,J.U. and Hurt,E. (1999) The Mex67p-mediated nuclear mRNA export pathway is conserved from yeast to human. EMBO J., 18, 2593–2609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka N., Yong,J., Kim,V.N., Velazquez,F., Perkinson,R.A., Wang,F. and Dreyfuss,G. (2000) Pre-mRNA splicing imprints mRNA in the nucleus with a novel RNA-binding protein that persists in the cytoplasm. Mol. Cell, 6, 673–682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka N., Diem,M.D., Kim,V.N., Yong,J. and Dreyfuss,G. (2001) Magoh, a human homolog of Drosophila mago nashi protein, is a component of the splicing-dependent exon–exon junction complex. EMBO J., 20, 6424–6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim V.N., Kataoka,N. and Dreyfuss,G. (2001a) Role of nonsense-mediated decay factor Upf3 in the splicing-dependent exon–exon junction complex. Science, 293, 1832–1836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim V.N. Yong,J., Kataoka,N., Abel,L., Diem,M.D. and Dreyfuss,G. (2001b) The Y14 protein communicates to the cytoplasm the position of exon–exon junctions. EMBO J., 20, 2062–2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejbkowicz F., Goyer,C., Darveau,A., Neron,S., Lemieux,R. and Sonenberg,N. (1992) A fraction of the mRNA 5′ cap-binding protein, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E, localizes to the nucleus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 9612–9616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir H., Izaurralde,E., Maquat,L.E. and Moore,M.J. (2000a) The spliceosome deposits multiple proteins 20–24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon–exon junctions. EMBO J., 19, 6860–6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir H., Moore,M.J. and Maquat,L.E. (2000b) Pre-mRNA splicing alters mRNP composition: evidence for a stable association of proteins at exon–exon junctions. Genes Dev., 14, 1098–1108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir H., Gatfield,D., Izaurralde,E. and Moore,M.J. (2001a) The exon–exon junction complex provides a binding platform for factors involved in mRNA export and NMD. EMBO J., 17, 4987–4997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir H., Gatfield,D., Braun,I.C., Forler,D. and Izaurralde,E. (2001b) The protein Mago provides a link between splicing and mRNA localization. EMBO rep., 2, 1119–1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J.D. and Izaurralde,E. (1997) The role of the cap structure in RNA processing and nuclear export. Eur. J. Biochem., 247, 461–469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. and Wilkinson,M.F. (1998) Nonsense surveillance in lymphocytes? Immunity, 8, 135–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou M.J. and Reed,R. (1999) Splicing is required for rapid and efficient mRNA export in metazoans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 14937–14942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou M.J., Zhou,Z., Magni,K., Christoforides,C., Rappsilber,J., Mann,M. and Reed,R. (2001) Pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA export linked by direct interactions between UAP56 and Aly. Nature, 413, 644–647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykke-Andersen J., Shu,M.-D. and Steitz,J.A. (2000) Human Upf proteins target an mRNA for nonsense-mediated decay when bound downstream of a termination codon. Cell, 103, 1121–1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykke-Andersen J., Shu,M.-D. and Steitz,J.A. (2001) The protein RNPS1 communicates the position of exon–exon junctions to the mRNA surveillance machinery. Science, 293, 1836–1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderazo A.B., He,F., Mangus,D.A. and Jacobson,A. (2000) Upf1p control of nonsense mRNA translation is regulated by Nmd2p and Upf3p. Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 4591–4603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L.E. (1995) When cells stop making sense: effects of nonsense codons on RNA metabolism in vertebrate cells. RNA, 1, 453–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L.E. (2000) Nonsense-mediated RNA decay in mammalian cells: a splicing-dependent means to down-regulated the levels of mRNAs that prematurely terminate translation. In Sonenberg,N., Hershey,J.B.W. and Mathews,M.B. (eds), Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 849–868.
- Maquat L.E. (2002) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Curr. Biol., 11, R196–R197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L.E. and Carmichael,G.G. (2001) Quality control of mRNA function. Cell, 104, 173–176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Badolato,J., Kobayashi,R., Zhang,M.Q., Gardiner,E.M. and Krainer,A.R. (1999) Purification and characterization of human RNPS1: a general activator of pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J., 18, 4560–4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken S. et al. (1997) 5′-Capping enzymes are targeted to pre-mRNA by binding to the phosphorylated carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev., 11, 3306–3318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken S., Lambermon,M. and Blencowe,B.J. (2002) SRm160 splicing coactivator promotes transcript 3′-end cleavage. Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 148–160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarvey T. et al. (2000) The acute myeloid leukemia-associated protein DEK forms a splicing-dependent interaction with exon–exon product complexes. J. Cell Biol., 150, 309–320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlin H., Daneholt,B. and Skoglund,U. (1992) Translocation of a specific premessenger ribonucleoprotein particle through the nuclear pore studied with electron microscope tomography. Cell, 69, 605–613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell J.T., Medghalchi,S.M., Lake,R.G., Noensie,E.N. and Dietz,H.C. (2000) Novel Upf2p orthologues suggest a functional like between translation initiation and nonsense surveillance complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 8944–8957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S.J. and McKendrick,L. (1997) Involvement of stress-induced protein kinase and p38/RK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the enhanced phosphorylation of initiation factor 4E in NIH 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 17887–17893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Kataoka,N. and Simura,Y. (1990) A nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res., 18, 6989–6995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M.F., Carr,B., Anders,K.R, Grimson,A. and Anderson,P. (1999) SMG-2 is a phosphorylated protein required for mRNA surveillance in Caenorhabditis elegans and related to Upf1p of yeast. Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 5943–5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal M., Ishigaki,Y., Nagy,E. and Maquat,L.E. (2001) Evidence that phosphorylation of human Upf1 protein varies with intracellular location and is mediated by a wortmannin-sensitive and rapamycin-sensitive PI 3-kinase-related kinase signaling pathway. RNA, 7, 5–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Y., Hausmann,S., Ho,C.K., Schwer,B. and Shuman,S. (2001) The length, phosphorylation state and primary structure of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain dictate interactions with mRNA capping enzymes. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 28075–28082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. (2000) Connecting transcription to messenger RNA processing. Trends Biochem. Sci., 25, 290–293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. and Hurt,E. (2002) A conserved mRNA export machinery coupled to pre-mRNA splicing. Cell, 108, 523–531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. and Magni,K. (2001) A new view of mRNA export: separating the wheat from the chaff. Nat. Cell Biol., 3, E201–E204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues J.P., Rode,M., Gatfield,D., Blencowe,B.J., Carmo-Fonseca,M. and Izaurralde,E. (2001) REF proteins mediate the export of spliced and unspliced mRNAs from the nucleus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 1030–1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S.C., Schwer,B., Shuman,S. and Bentley,D.L. (2000) Dynamic association of capping activities with transcribing RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev., 14, 2435–2440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serin G., Gersappe,A., Black,J.D., Aronoff,R. and Maquat,L.E. (2001) Identification and characterization of human orthologues to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Upf2 protein and Upf3 protein (Caenorhabditis elegans SMG-4). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 209–223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen E.C., Stage-Zimmermann,T., Chui,P. and Silver,P.A. (2000) The yeast mRNA-binding protein Npl3p interacts with the cap-binding complex. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 23718–23724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sträßer K. and Hurt,E. (2001) Splicing factor Sub2p is required for nuclear mRNA export through its interaction with Yra1p. Nature, 413, 648–652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Bachi,A., Doerks,T., Braun,I.C., Seraphin,B., Wilm,M., Bork,P. and Izaurralde,E. (2000) REF, an evolutionary conserved family of hnRNP-like proteins, interacts with TAP/Mex67p and participates in mRNA nuclear export. RNA, 6, 638–650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Perlick,H.A., Dietz,H.C. and Maquat,L.E. (1998) A mutated human homologue to yeast Upf1 protein has a dominant-negative effect on the decay of nonsense-containing mRNAs in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 10009–10014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visa N., Izaurralde,E., Ferreira,J., Daneholt,B. and Mattaj,I.W. (1996) A nuclear cap-binding complex binds Balbiani ring pre-mRNA cotranscriptionally and accompanies the ribonucleoprotein particle during nuclear export. J. Cell Biol., 133, 5–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Gudikote,J.P., Olivas,O.R. and Wilkinson,M.F. (2002) Boundary-independent polar nonsense-mediated decay. EMBO rep., 3, 274–279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Czaplinski,K., Rao,Y. and Peltz,S.W. (2001) The role of Upf proteins in modulating the translation read-through of nonsense-containing transcripts. EMBO J., 20, 880–890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz C.J., Wang,W. and Peltz,S.W. (2001) Curbing the nonsense: the activation and regulation of mRNA surveillance. Genes Dev., 15, 2781–2785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita A., Ohnishi,T., Kashima,I., Taya,Y. and Ohno,S. (2001) Human SMG-1, a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase, associates with components of the mRNA surveillance complex and is involved in the regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev., 15, 2215–2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Sun,X., Qian,Y. and Maquat,L.E. (1998) Intron function in the nonsense-mediated decay of β-globin mRNA: indications that pre-mRNA splicing in the nucleus can influence mRNA translation in the cytoplasm. RNA, 4, 801–815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Lou,M.J., Staesser,K., Datahira,J., Hurt,E. and Reed,R. (2000) The protein Aly links pre-messenger-RNA splicing to nuclear export in metazoans. Nature, 407, 401–407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]