Abstract
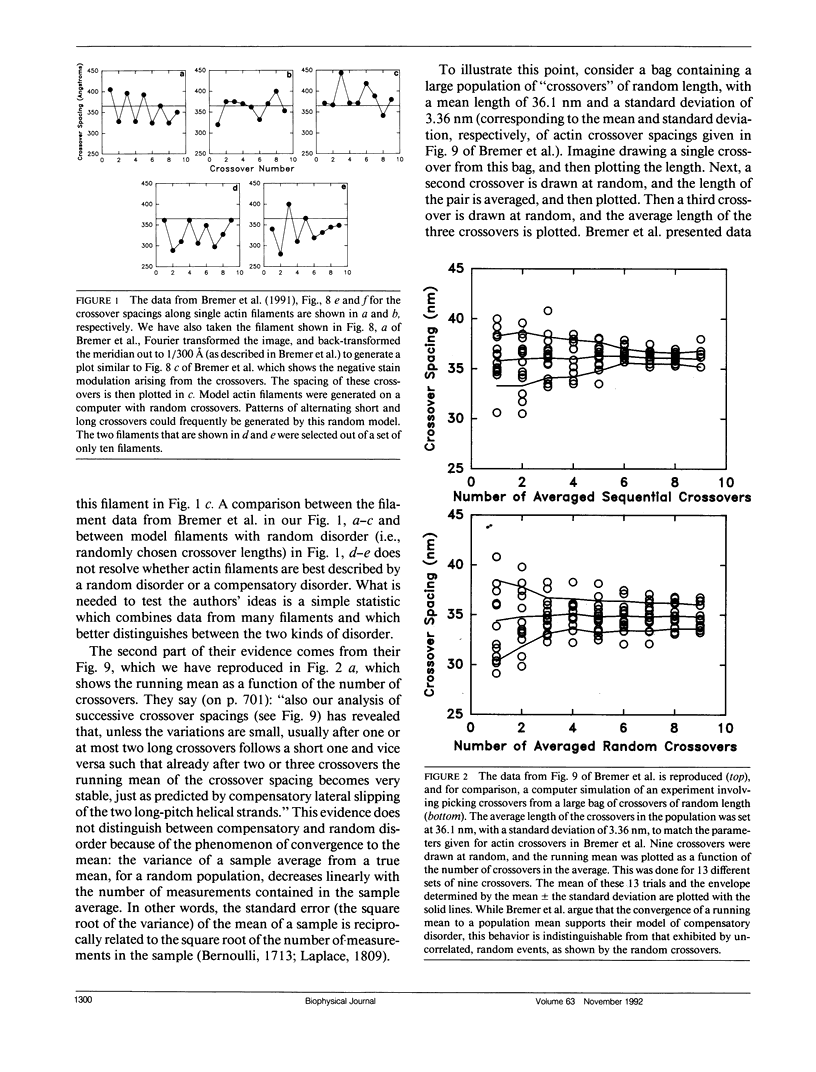
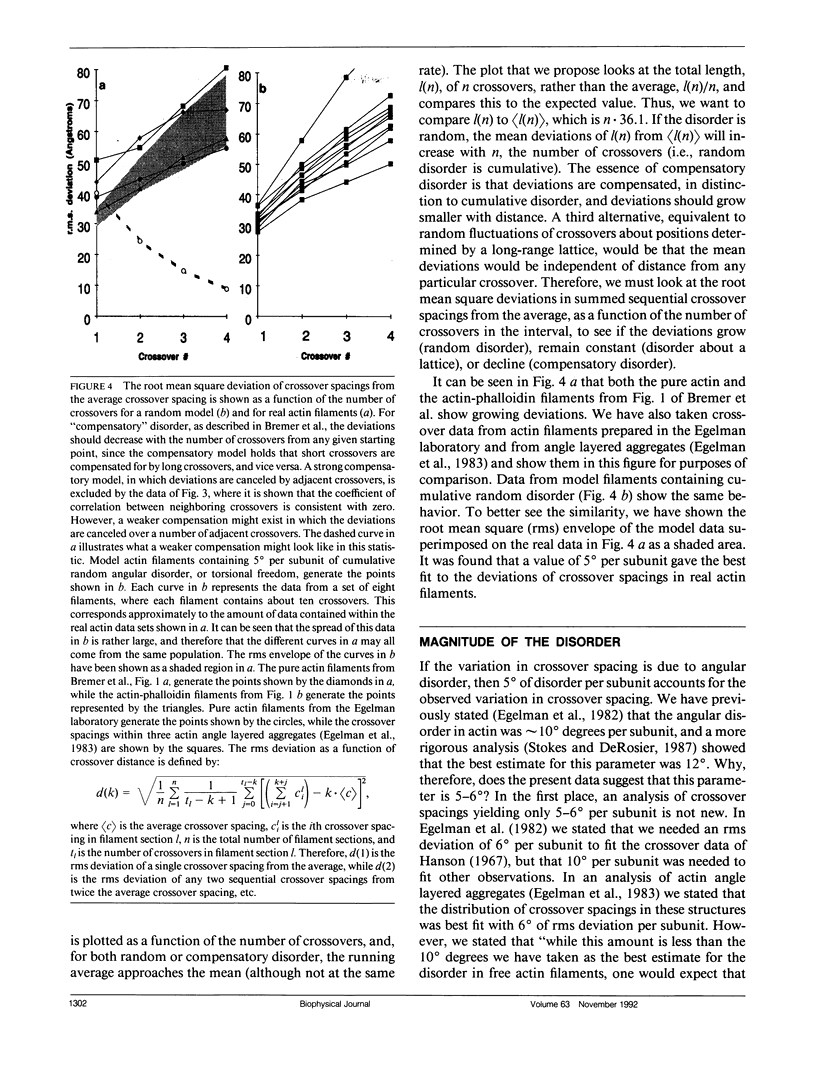
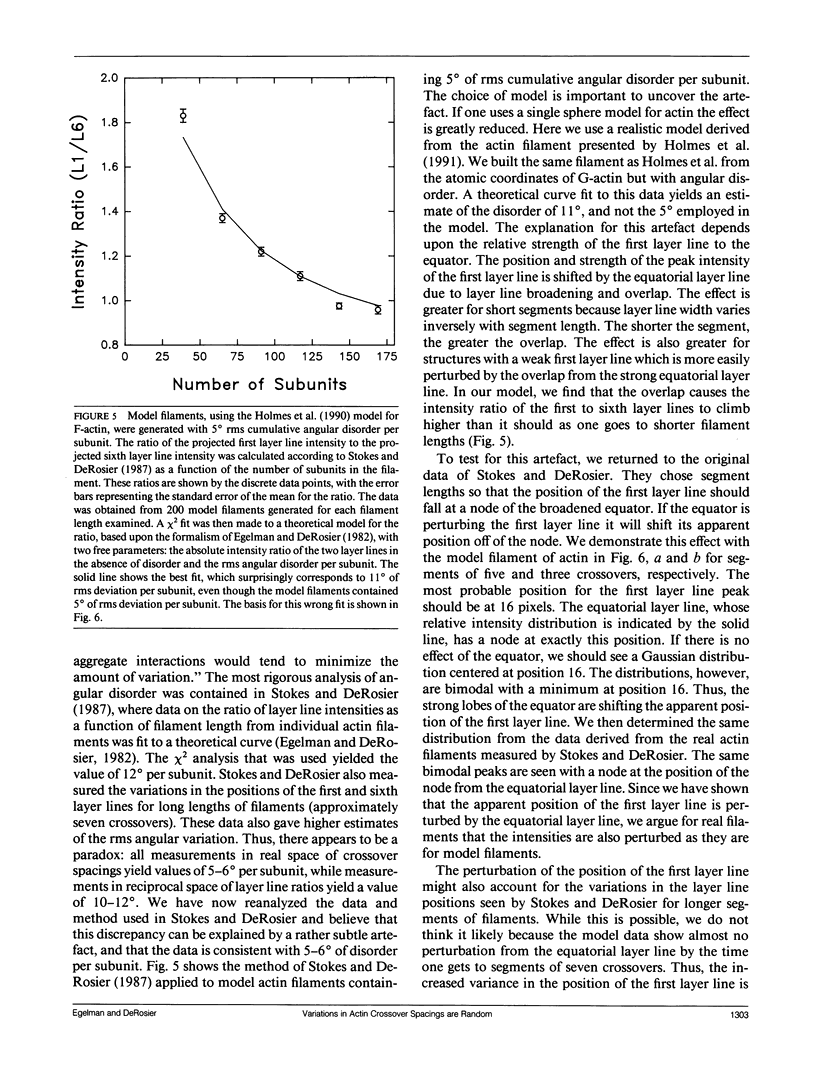
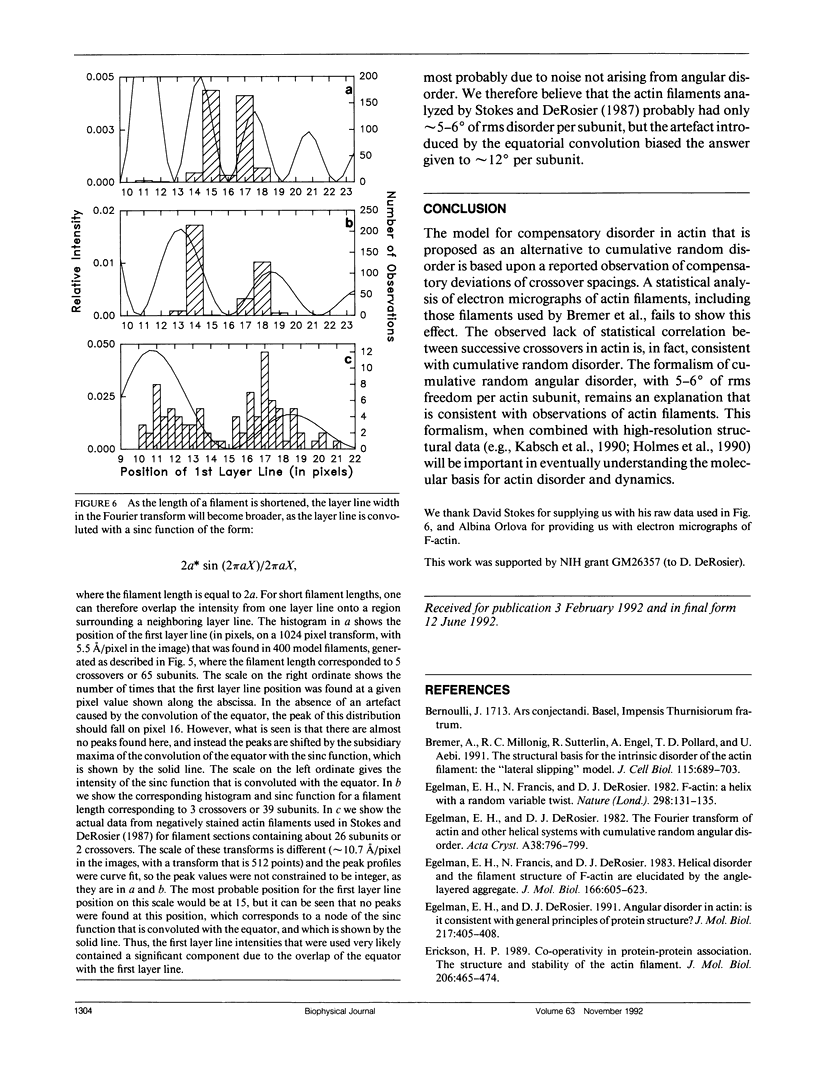
A recent paper by Bremer et al. (1991. J. Cell Biol. 115:689-703) has argued that the random angular disorder model for actin is wrong, and that the variations in crossover spacing observed in electron micrographs of F-actin filaments can be best explained by a compensatory disorder caused by the lateral slipping of the twin (or two-start) strands which comprise the actin filament. We have analyzed the images of F-actin presented in Bremer et al. and show that their data argues against compensatory disorder and in favor of random disorder, independent of the cause of the disorder. We also revise our estimate of the angular component and show that the magnitude of this disorder is about 5-6 degrees per subunit, which is less than the 10-12 degrees that we originally proposed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremer A., Millonig R. C., Sütterlin R., Engel A., Pollard T. D., Aebi U. The structural basis for the intrinsic disorder of the actin filament: the "lateral slipping" model. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):689–703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., DeRosier D. J. Angular disorder in actin: is it consistent with general principles of protein structure? J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90743-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Francis N., DeRosier D. J. F-actin is a helix with a random variable twist. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):131–135. doi: 10.1038/298131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Francis N., DeRosier D. J. Helical disorder and the filament structure of F-actin are elucidated by the angle-layered aggregate. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):605–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. Co-operativity in protein-protein association. The structure and stability of the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Popp D., Gebhard W., Kabsch W. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):44–49. doi: 10.1038/347044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., DeRosier D. J. The variable twist of actin and its modulation by actin-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1005–1017. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Oosawa F. Protein motors and Maxwell's demons: does mechanochemical transduction involve a thermal ratchet? Adv Biophys. 1990;26:97–134. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(90)90009-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


