Abstract
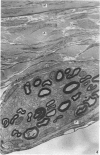
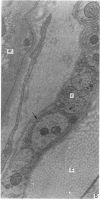
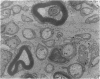
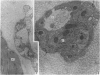
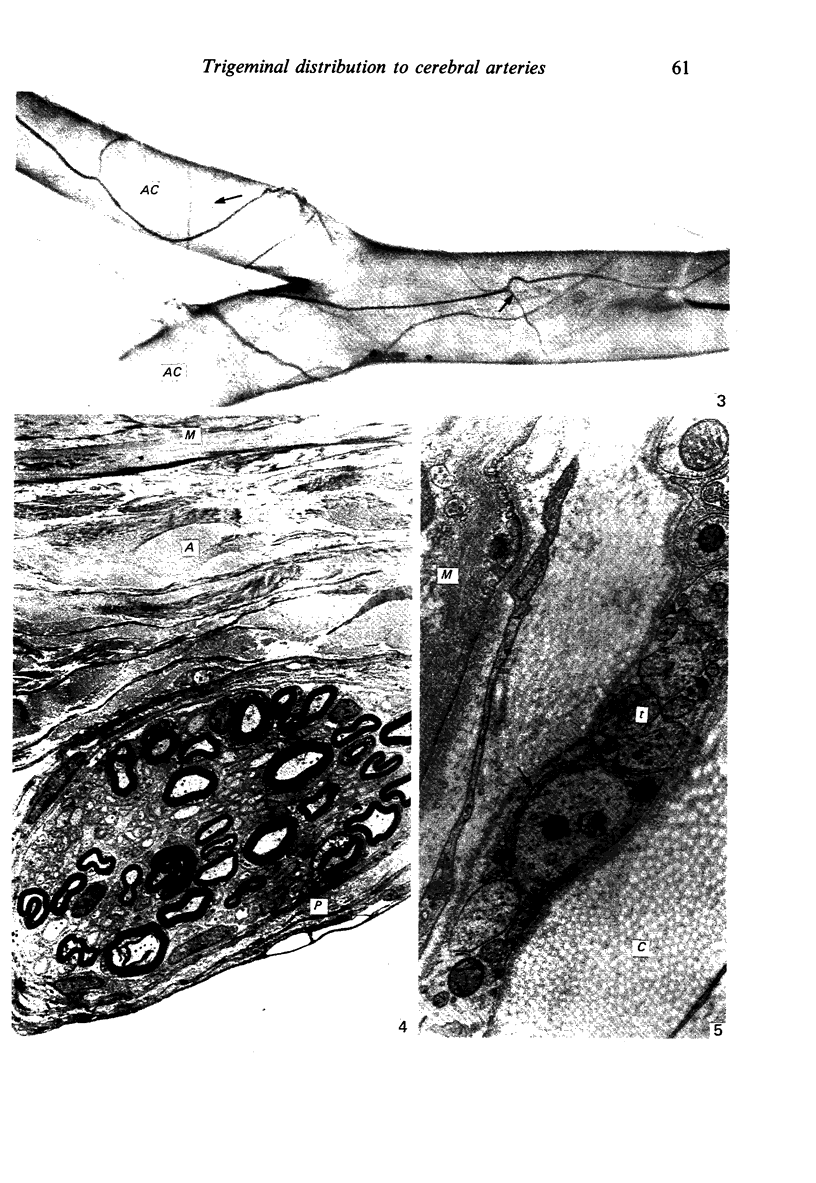
Wallerian degeneration was used to study the contributions of the first and second divisions of the trigeminal nerve to cerebral arterial innervation in the cynomolgus monkey. Animals were killed by intracardiac perfusion of fixative three to seven days after left ophthalmic or maxillary neurotomy or a combination of both, using three animals for each procedure. Cerebral arteries were dissected, removed and prepared for light and electron microscopy. The anterior vessels of the circle of Willis received nerve fibres, distributed via the internal carotid artery, from the ipsilateral ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve and a small maxillary contribution was also observed in some animals. The posterior vessels were supplied from the same trigeminal source but by a different route, the nerves moving onto the basilar artery bilaterally or unilaterally via the recurrent nerve of the cavernous plexus using the abducent nerve for access. From the basilar, fibres distributed to both posterior cerebral arteries. Augmentation of the vascular nerve supply apparently from branches of the vagus and/or hypoglossal nerves was noted but otherwise unexamined. Trigeminal terminals were found on all vessels of the circle of Willis and their distal branches throughout the thickness of the adventitia, often lying close to the media but never contacting smooth muscle cells. These observations are consistent with results from other studies employing neurohistochemical and tracer techniques in subprimates. Comparison of operated and control material failed to reveal any distinctive features of terminals attributable to a trigeminal source.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cuello A. C., Del Fiacco M., Paxinos G. The central and peripheral ends of the substance P-containing sensory neurones in the rat trigeminal system. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 8;152(3):499–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckles S. P., Buck S. H. Substance P in the cerebral vasculature: depletion by capsaicin suggests a sensory role. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 5;245(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90355-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., McCulloch J., Uddman R. Substance P: immunohistochemical localization and effect upon cat pial arteries in vitro and in situ. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:251–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Rosendal-Helgesen S., Uddman R. Substance P: localization, concentration and release in cerebral arteries, choroid plexus and dura mater. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00217397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Kellerth J. O., Nilsson G., Pernow B. Substance p: localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):889–890. doi: 10.1126/science.242075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura T., Okuno T., Nakakita K., Kamei I., Naka Y., Nakai K., Imai H., Komai N., Kimura H., Maeda T. A light and electron microscopic immunohistochemical study of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and substance P-containing nerve fibers along the cerebral blood vessels: comparison with aminergic and cholinergic nerve fibers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Sep;4(3):407–414. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. T., Beduk A., Saunders M. C. Origin of fibers innervating the basilar artery of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jul 31;58(2):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W. Headache. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jul;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Gillespie S. A., Norregaard T. V., Moskowitz M. A. Co-localization of retrogradely transported wheat germ agglutinin and the putative neurotransmitter substance P within trigeminal ganglion cells projecting to cat middle cerebral artery. J Comp Neurol. 1984 May 10;225(2):187–192. doi: 10.1002/cne.902250204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Han D. H., Moskowitz M. A. Pia arachnoid contains substance P originating from trigeminal neurons. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):803–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Liszczak T. M., King J. C., Moskowitz M. A. Immunoelectron microscopic study of substance P-containing fibers in feline cerebral arteries. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Mayberg M. R., Moskowitz M. A. Immunohistochemical evidence for a substance P-containing trigeminovascular pathway to pial arteries in cats. Brain Res. 1983 May 23;268(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. T., Peterfreund R. A., Sawchenko P. E., Corrigan A. Z., Rivier J. E., Vale W. W. Release of the predicted calcitonin gene-related peptide from cultured rat trigeminal ganglion cells. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):653–655. doi: 10.1038/308653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Matsumoto M., Shiosaka S., Hayakawa T., Yoneda S., Kimura K., Abe H., Tohyama M. Dual innervation of substance P-containing neuron system in the wall of the cerebral arteries. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 19;322(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Shiosaka S., Wanaka A., Yoneda S., Kimura K., Hayakawa T., Emson P. C., Tohyama M. Fine structure of peptidergic and catecholaminergic nerve fibers in the anterior cerebral artery and their interrelationship: an immunoelectron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1985 May 8;235(2):268–276. doi: 10.1002/cne.902350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg M. R., Zervas N. T., Moskowitz M. A. Trigeminal projections to supratentorial pial and dural blood vessels in cats demonstrated by horseradish peroxidase histochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Feb 10;223(1):46–56. doi: 10.1002/cne.902230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg M., Langer R. S., Zervas N. T., Moskowitz M. A. Perivascular meningeal projections from cat trigeminal ganglia: possible pathway for vascular headaches in man. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):228–230. doi: 10.1126/science.6166046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch J., Uddman R., Kingman T. A., Edvinsson L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: functional role in cerebrovascular regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5731–5735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norregaard T. V., Moskowitz M. A. Substance P and the sensory innervation of intracranial and extracranial feline cephalic arteries. Implications for vascular pain mechanisms in man. Brain. 1985 Jun;108(Pt 2):517–533. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.2.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskell G. L. Ocular fibres of the maxillary nerve in monkeys. J Anat. 1974 Nov;118(Pt 2):195–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskell G. L., Simons T. Trigeminal nerve pathways to the cerebral arteries in monkeys. J Anat. 1987 Dec;155:23–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Edvinsson L., Owman C., Sundler F. Perivascular substance P: occurrence and distribution in mammalian pial vessels. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(2):227–232. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Matsuyama T., Shiosaka S., Inagaki S., Senba E., Shimizu Y., Ishimoto I., Hayakawa T., Matsumoto M., Tohyama M. Overall distribution of substance P-containing nerves in the wall of the cerebral arteries of the guinea pig and its origins. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Apr 20;215(4):421–426. doi: 10.1002/cne.902150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]