Abstract
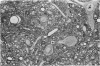
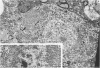
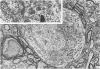
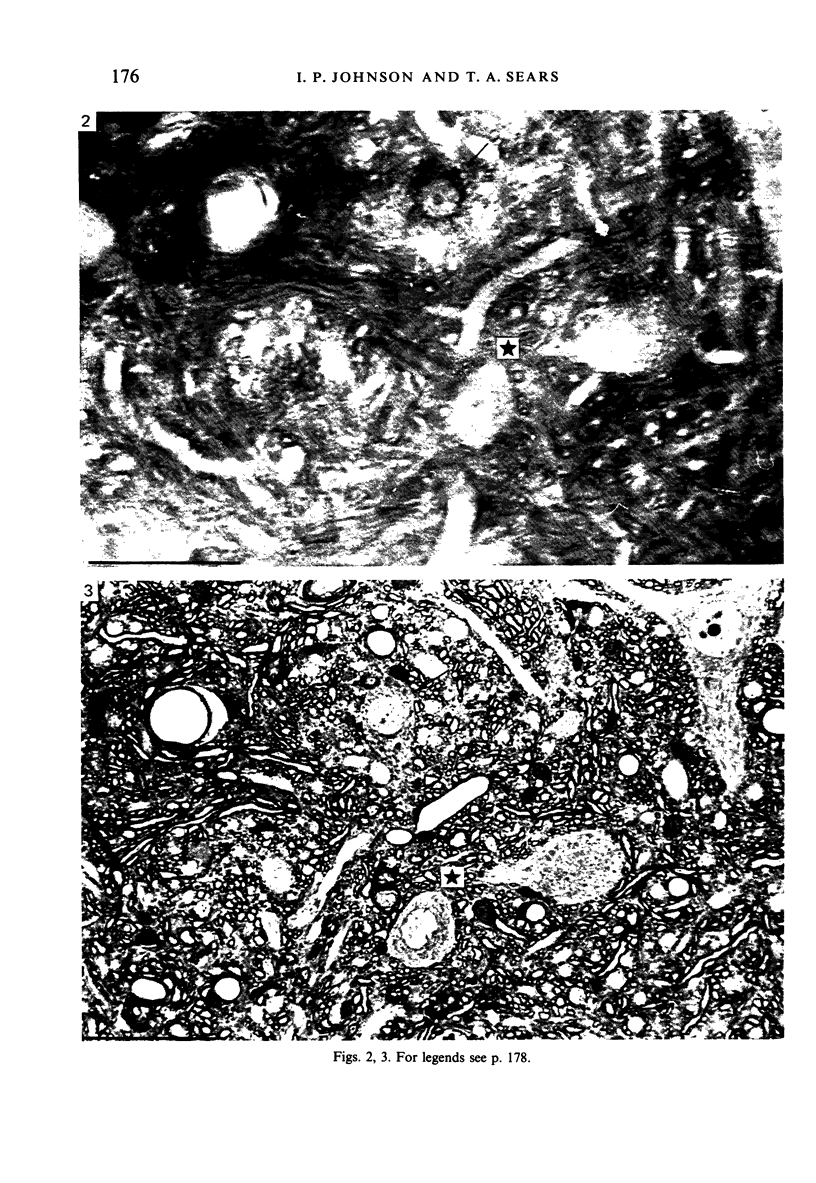
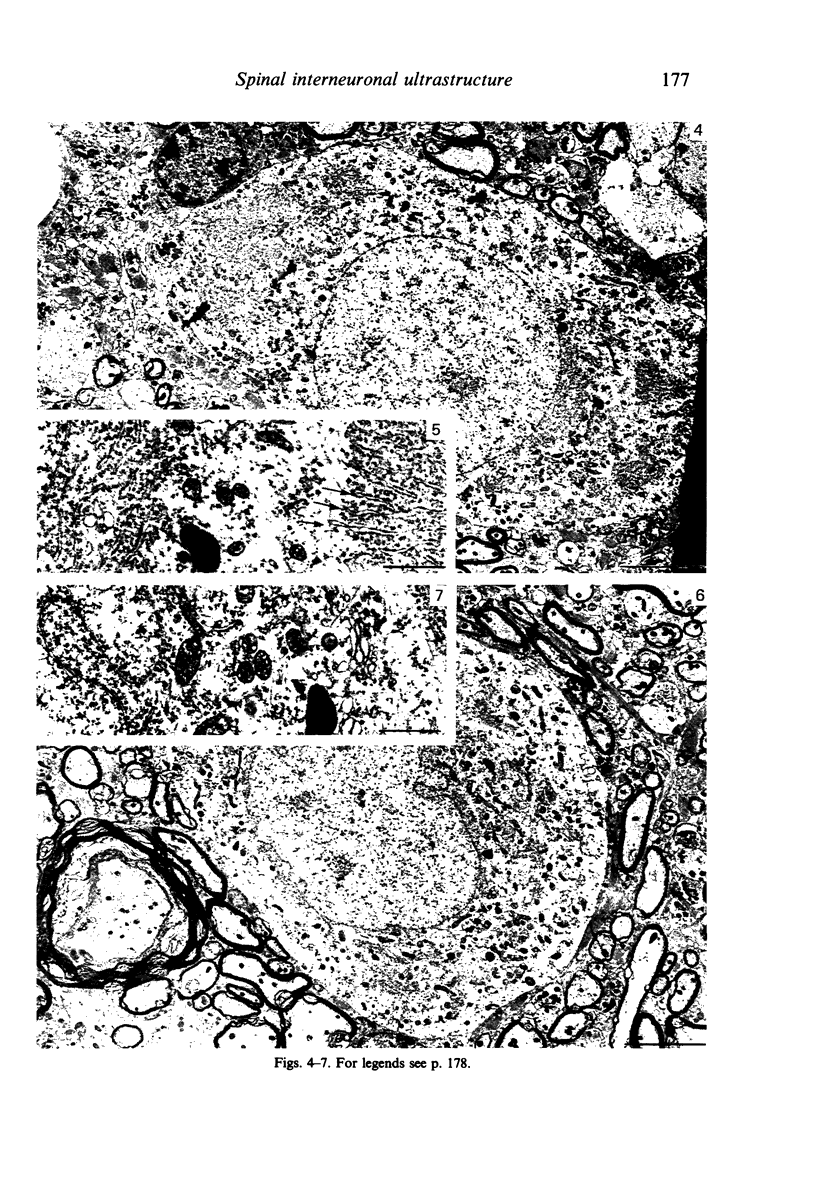
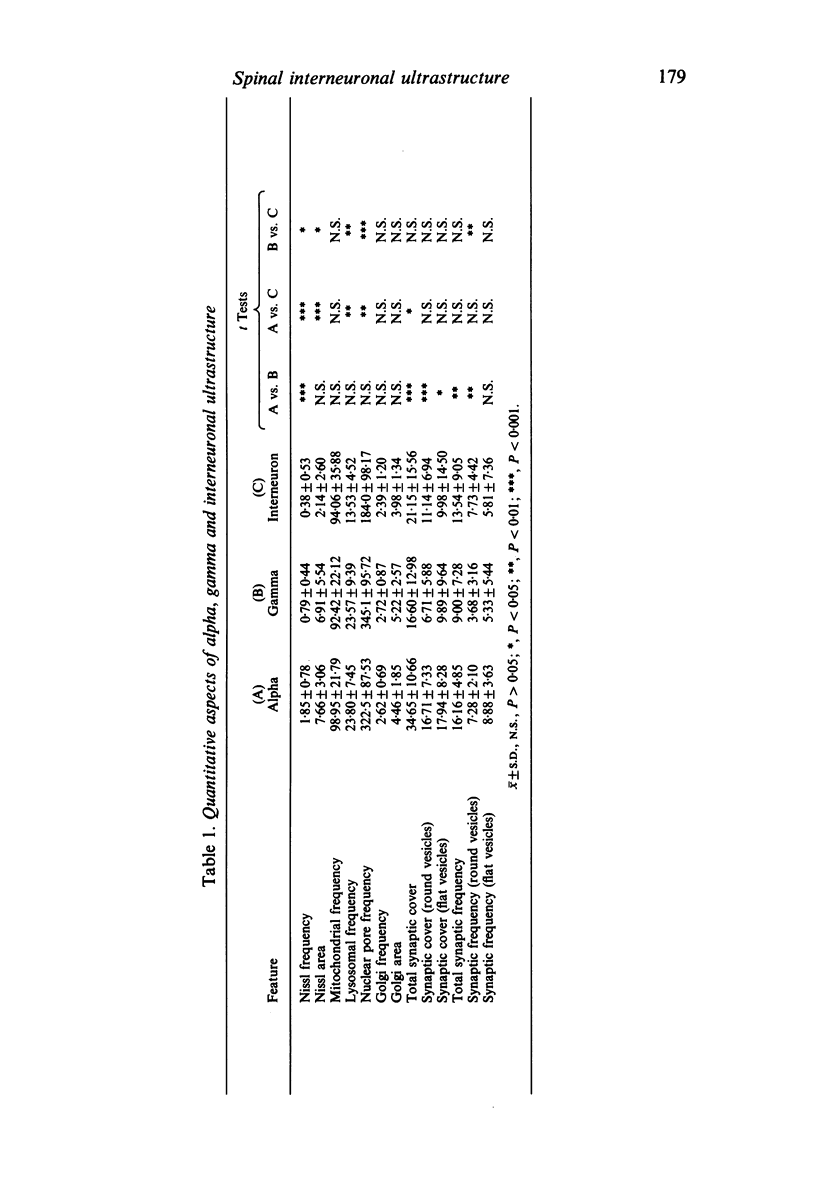
Alpha (greater than 40 microns) and gamma (less than 30 microns) motoneurons in inspiratory motor nuclei of the thoracic spinal cord of the adult cat were labelled retrogradely by the intramuscular injection of HRP. Small (less than 30 microns) unlabelled neurons within 200-300 microns of labelled motoneurons were analysed qualitatively and quantitatively with both the light and electron microscope. Most of these small unlabelled neurons had inconspicuous nucleoli, wrinkled nuclear membranes, low numbers of nuclear pores, and Nissl bodies which were either small or had the form of an amorphous perinuclear band. Such Nissl bodies were composed primarily of aggregates of polyribosomes within which short fragments of granular endoplasmic reticulum were distributed. Alpha and gamma motoneurons in contrast had prominent nucleoli, smooth-contoured nuclei, more nuclear pores and large, discrete Nissl bodies. Such Nissl bodies were composed primarily of several lamellae of granular endoplasmic reticulum with linear arrays of polyribosomes arranged between individual cisternae. Alpha motoneurons had most synaptic terminals on their cell bodies, gamma motoneurons had least and small unlabelled neurons had intermediate values. Synaptic terminals of the S-, F- T- and C-type were observed on alpha motoneurons, whereas only S- and F-types were observed on gamma motoneurons and small unlabelled neurons. Since they were unlabelled and differed morphologically from both alpha and gamma motoneurons, but were similar to small interneurons described elsewhere in the spinal cord and brain, it is suggested that the small unlabelled neurons located in the external intercostal and levator costae motor pools are interneurons. The functional significance of some of the morphological features which distinguish interneurons from motoneurons is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenteng K., Girdlestone D. Transneuronal transport of wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated horseradish peroxidase into trigeminal interneurones of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 15;258(3):387–396. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist A. Morphometric synaptology of gracilo-diencephalic relay cells: an electron microscopic study in the cat using retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Neurocytol. 1981 Aug;10(4):709–724. doi: 10.1007/BF01262599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. Direct observations on the contacts made between Ia afferent fibres and alpha-motoneurones in the cat's lumbosacral spinal cord. J Physiol. 1981;313:121–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Strick P. L., Kanda K., Kim C. C., Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):667–680. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa J. F., Engel W. K. Histochemistry of motor neurons and interneurons in the cat lumbar spinal cord. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):559–568. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradi S. Ultrastructure and distribution of neuronal and glial elements on the motoneuron surface in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the adult cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;332:5–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destombes J., Gogan P., Rouvière A. The fine structure of neurones and cellular relationships in the abducens nucleus in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Apr 2;35(2):249–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00236614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELFAN S. NEURONAL INTERDEPENDENCE. Prog Brain Res. 1964;11:238–260. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G., Wiksten B., Berkley K. J., Aldskogius H. The location of cerebellar-projecting neurons within the lumbosacral spinal cord in the cat. An anatomical study with HRP and retrograde chromatolysis. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Feb 1;204(4):336–348. doi: 10.1002/cne.902040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., SOMJEN G., CARPENTER D. O. FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL SIZE IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:560–580. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLINSHEAD W. H., KESWANI N. H. Localization of the phrenic nucleus in the spinal cord of man. Anat Rec. 1956 Aug;125(4):683–699. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091250403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Katz R., Storai B., Zytnicki D. Labelling of interneurones by retrograde transsynaptic transport of horseradish peroxidase from motoneurones in rats and cats. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Mar 9;45(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G. G., Nicholls J. G., Sears T. A. Central and proprioceptive influences on the activity of levator costae motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Lindström S., Wigström H. On the function of recurrent inhibition in the spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Oct;37(2):399–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00237722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E. Further indications for enhancement of retrograde transneuronal transport of WGA-HRP by synaptic activity. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 26;341(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lindström S. Morphological identification of Renshaw cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):428–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lindström S. Morphological identification of physiologically defined neurones in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1970 Jun 3;20(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lindström S. Morphology of interneurones mediating Ia reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):805–823. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson I. P. A quantitative ultrastructural comparison of alpha and gamma motoneurons in the thoracic region of the spinal cord of the adult cat. J Anat. 1986 Aug;147:55–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson I. P., Pullen A. H., Sears T. A. Target dependence of Nissl body ultrastructure in cat thoracic motoneurones. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 24;61(1-2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerbäck P. A. An ultrastructural study of cat lumbosacral gamma-motoneurons after retrograde labelling with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 15;240(3):256–264. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerbäck P. A. An ultrastructural study of serially sectioned Renshaw cells. III. Quantitative distribution of synaptic boutons. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 4;264(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerbäck P. A., Kellerth J. O. Light microscopic observations on cat Renshaw cells after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. II. The cell bodies and dendrites. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 22;240(4):368–376. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larnicol N., Rose D., Marlot D., Duron B. Anatomical organization of cat intercostal motor nuclei as demonstrated by HRP retrograde labelling. J Physiol (Paris) 1982 Aug;78(2):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limwongse V., DeSantis M. Coverage by axosomatic boutons varies directly with the diameter of the postsynaptic motor neuron in the trigeminal nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. 1980 May 5;189(1):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., Martin-Body R. L. Morphological properties of respiratory intercostal motoneurons in cats as revealed by intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jun 15;260(3):423–434. doi: 10.1002/cne.902600308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL G. A., WARWICK R. The phrenic nucleus of the macaque. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Oct;105(3):553–585. doi: 10.1002/cne.901050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M. Some aspects of interneuronal connections cat's spinal gray matter. J Comp Neurol. 1969 May;136(1):57–80. doi: 10.1002/cne.901360105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG-HANSEN R. ANATOMICAL DEMONSTRATION OF GAMMA MOTONEURONS IN THE CAT'S SPINAL CORD. Exp Neurol. 1965 Sep;13:71–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(65)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSCARSSON O. FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION OF THE SPINO- AND CUNEOCEREBELLAR TRACTS. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:495–522. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANES G. J. THE MOTOR POOLS OF THE SPINAL CORD. Prog Brain Res. 1964;11:93–119. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANES G. J. The motor cell columns of the lumbo-sacral spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Apr;94(2):313–363. doi: 10.1002/cne.900940209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHADE J. P., VAN HARREVELD A. Volume distribution of moto- and interneurons in the peroneus-tibialis neuron pool of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Dec;117:387–398. doi: 10.1002/cne.901170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. EFFERENT DISCHARGES IN ALPHA AND FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:295–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE FIBRE CALIBRE SPECTRA OF SENSORY AND MOTOR FIBRES IN THE INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:150–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAGUE J. M. Motor and propriospinal cells in the thoracic and lumbar ventral horn of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Aug;95(1):103–123. doi: 10.1002/cne.900950107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel M. E., Scheibel A. B. A structural analysis of spinal interneurons and Renshaw cells. UCLA Forum Med Sci. 1969;11:159–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Angaut P. The fine structure of the cerebellar central nuclei in the cat. I. Neurons and neuroglial cells. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Feb 28;16(4):410–430. doi: 10.1007/BF00233432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling P., Kuypers H. G. Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. 3. The propriospinal connections. Brain Res. 1968 Mar;7(3):419–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling P., Kuypers H. G. Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. II. The motoneuron plexus. Brain Res. 1967 Feb;4(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Cullheim S. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal gamma -motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):585–596. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal alpha-motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):571–583. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HARREVELD A., SCHADE J. P. Nerve cell destruction by asphyxiation of the spinal cord. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962 Jul;21:410–423. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196207000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra B., Kernell D. Sizes of soma and stem dendrites in intracellularly labelled alpha-motoneurones of the cat. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 12;204(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90590-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Keulen L. C. Axon trajectories of Renshaw cells in the lumbar spinal cord of the cat, as reconstructed after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1979 May 5;167(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]