Abstract
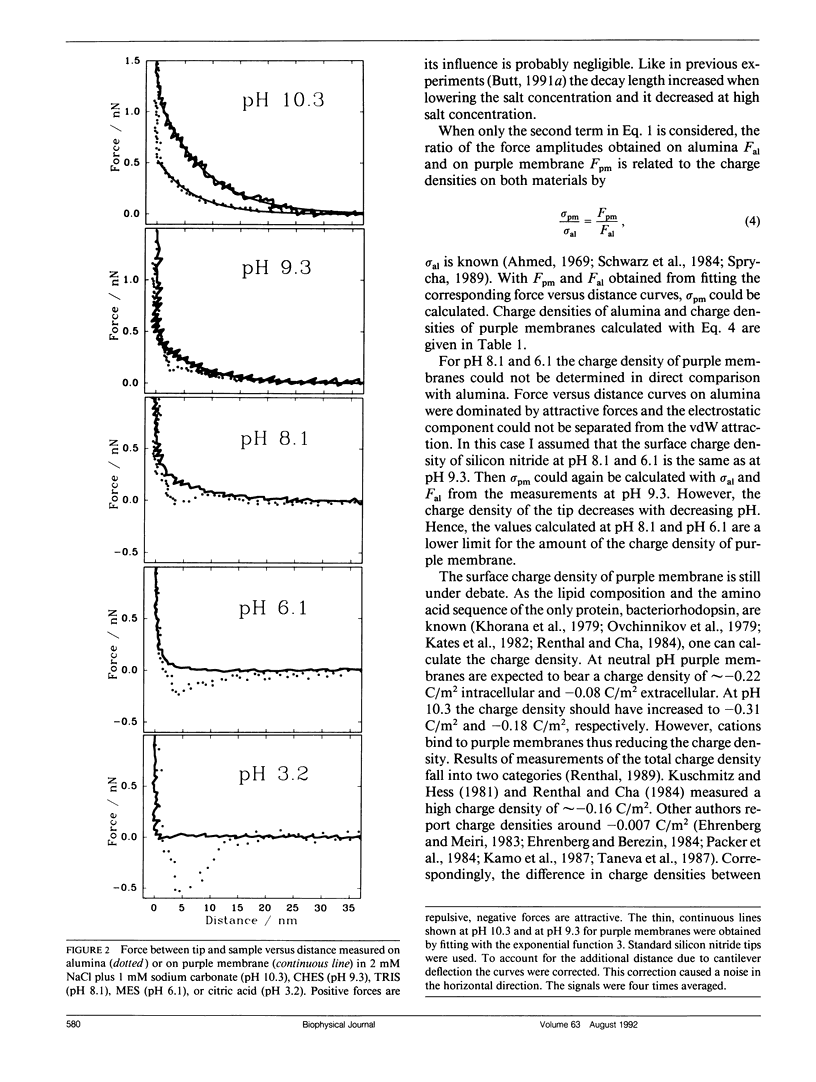
To show that local surface charge densities can be measured with a scanning force microscope purple membranes adsorbed to alumina were imaged in electrolyte solutions. Force versus distance curves were measured on purple membranes and on the bare alumina with standard silicon nitride tips. By comparing the electrostatic force measured on both substances, the surface charge density of purple membranes could be calculated from the known charge density of alumina. The charge density of purple membranes was estimated to be -0.05 C/m2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barabás K., Dér A., Dancsházy Z., Ormos P., Keszthelyi L., Marden M. Electro-optical measurements on aqueous suspension of purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84317-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette C. G., Muccio D. D., Finney T. K. pH dependence of bacteriorhodopsin thermal unfolding. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7431–7438. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J. Electrostatic interaction in atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82112-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeli C., Quintanilha A. T., Packer L. Surface charge changes in purple membranes and the photoreaction cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4707–4711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg B., Berezin Y. Surface potential on purple membranes and its sidedness studied by a resonance Raman dye probe. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keszthelyi L. Orientation of membrane fragments by electric field. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 6;598(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Gerber G. E., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Anderegg R. J., Nihei K., Biemann K. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Fujiwara M., Ikegami A. Anisotropic electric properties of purple membrane and their change during the photoreaction cycle. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):615–625. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84200-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuschmitz D., Hess B. On the ratio of the proton and photochemical cycles in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5950–5957. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Abdulaev N. G., Feigina M. Y., Kiselev A. V., Lobanov N. A. The structural basis of the functioning of bacteriorhodopsin: an overview. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Arrio B., Johannin G., Volfin P. Surface charge of purple membranes measured by laser Doppler velocimetry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papp E., Fricsovszky G., Meszéna G. Electrodichroism of purple membrane: ionic strength dependence. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):1089–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83737-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R., Cha C. H. Charge asymmetry of the purple membrane measured by uranyl quenching of dansyl fluorescence. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84245-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R. Surface charge density of purple membrane. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):581–583. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82852-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris BD, Stern JE, Rugar D, Mamin HJ. Contact electrification using force microscopy. Phys Rev Lett. 1989 Dec 11;63(24):2669–2672. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.2669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]