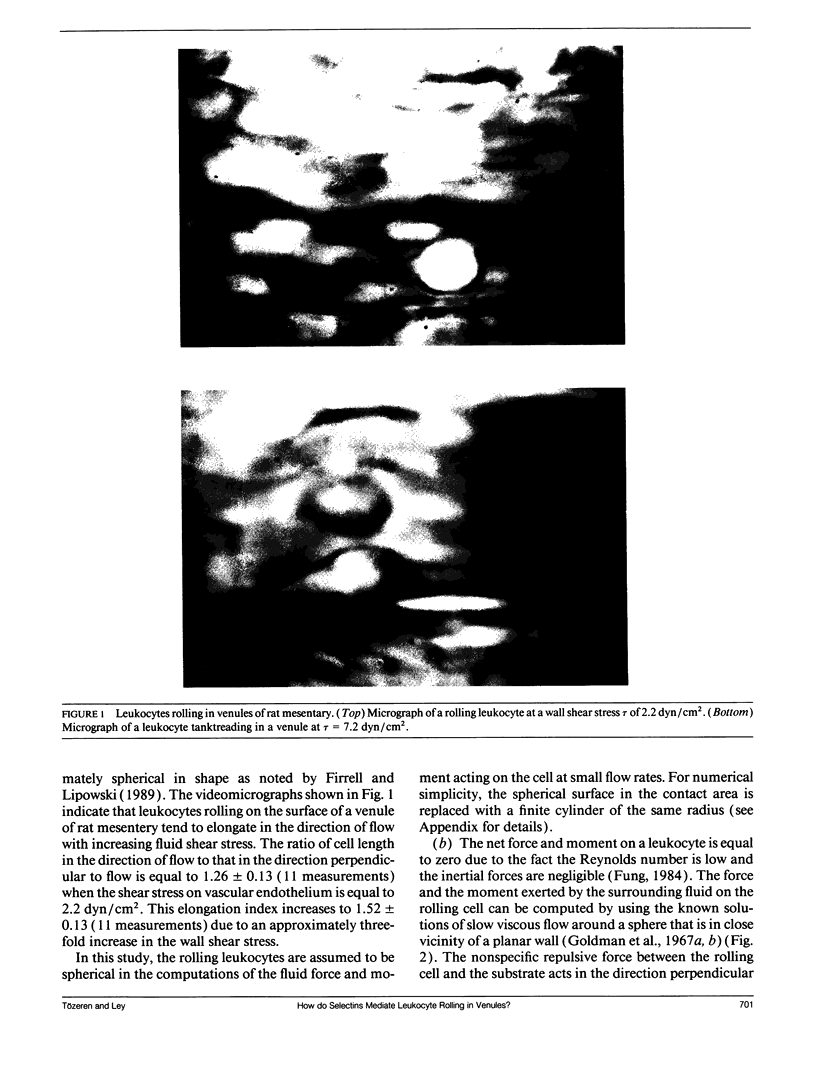
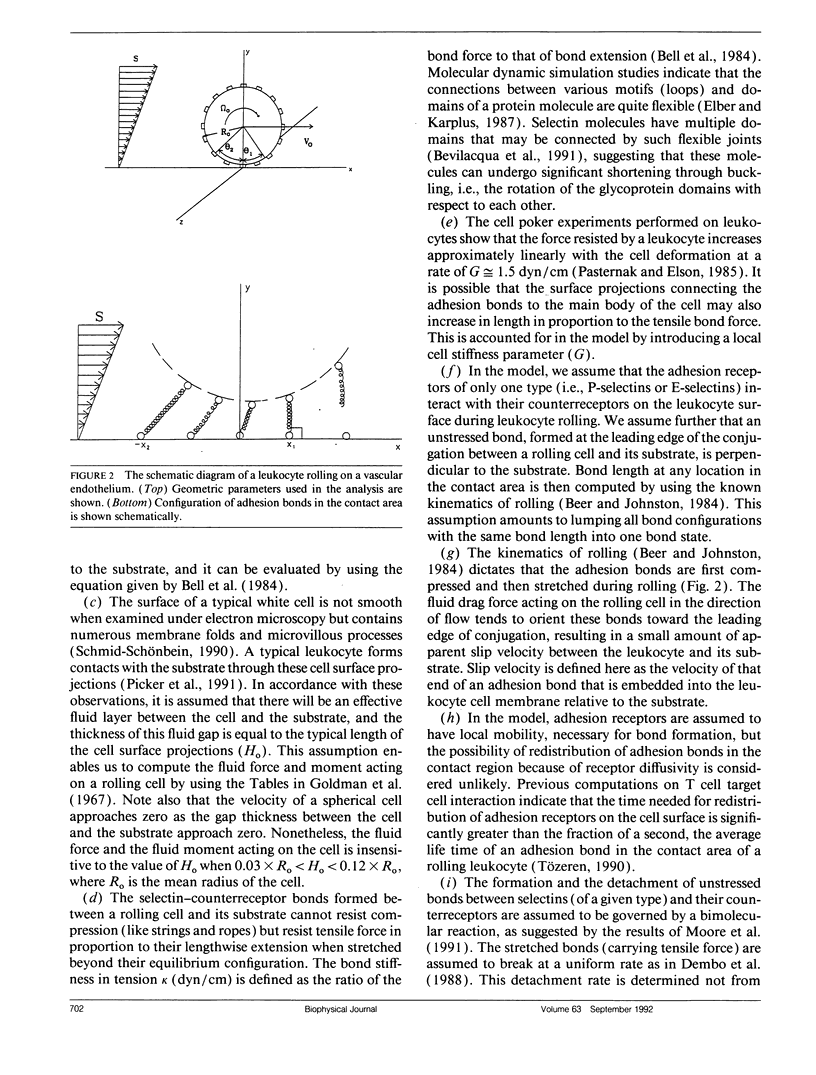
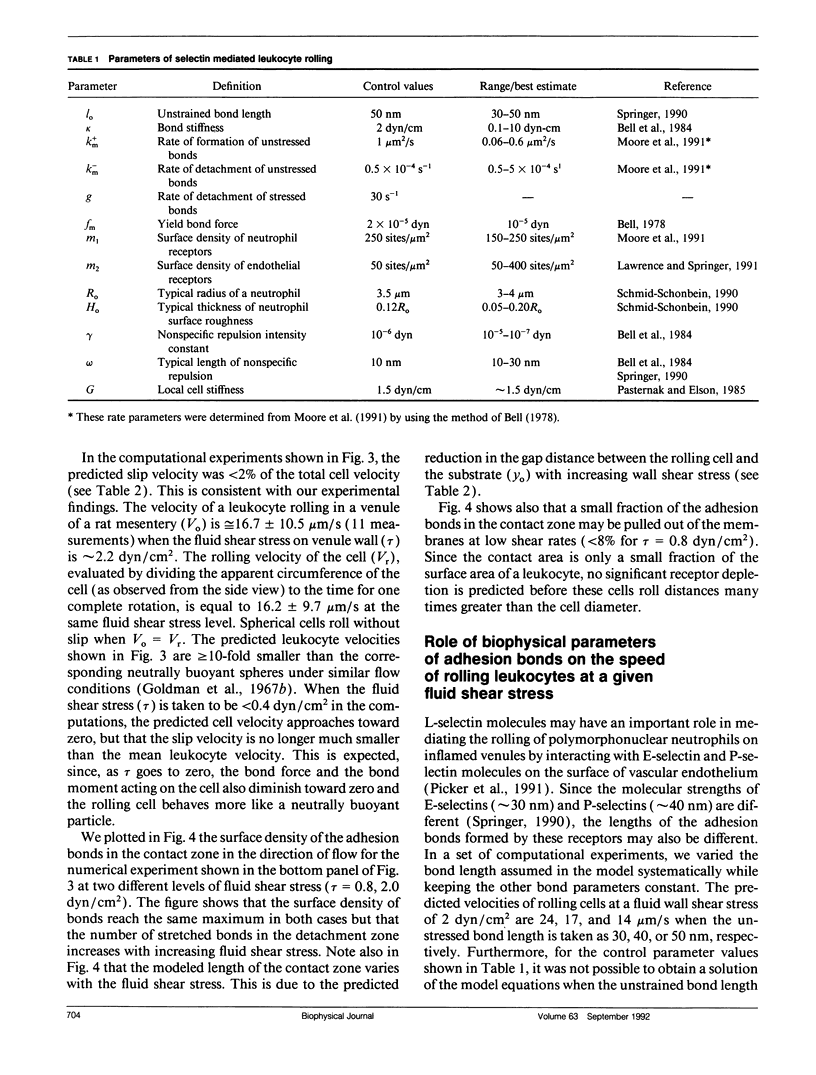
Abstract
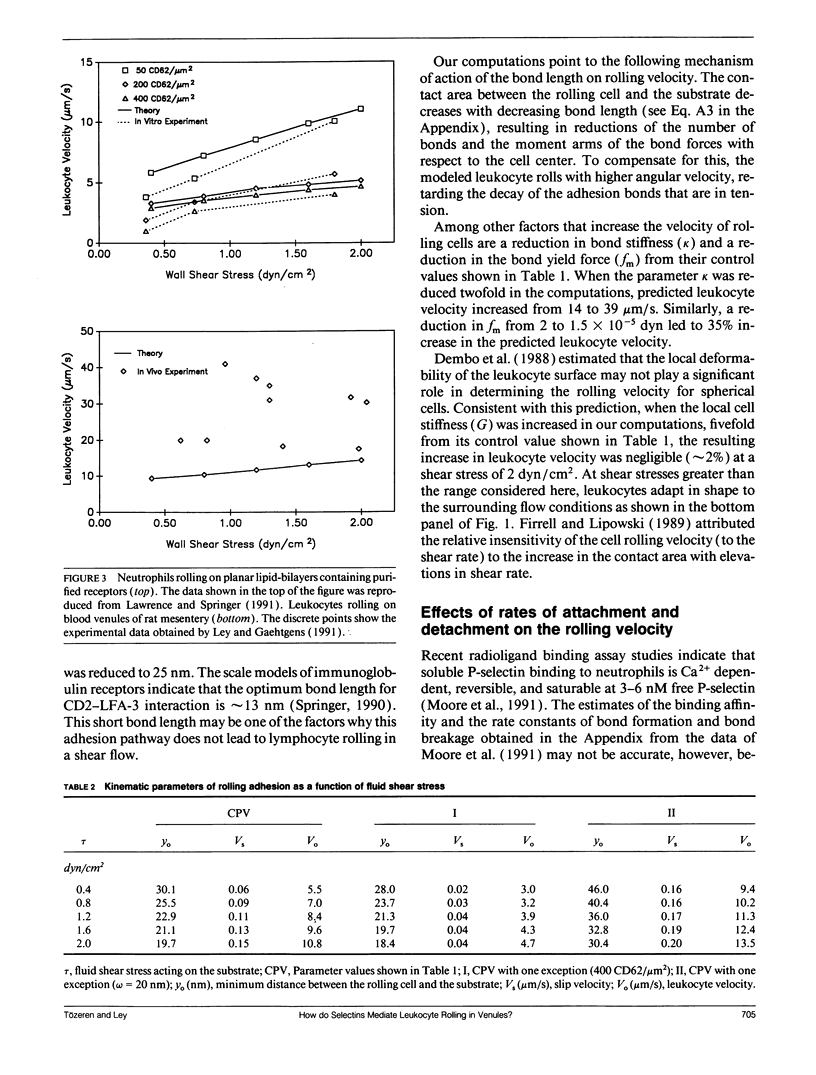
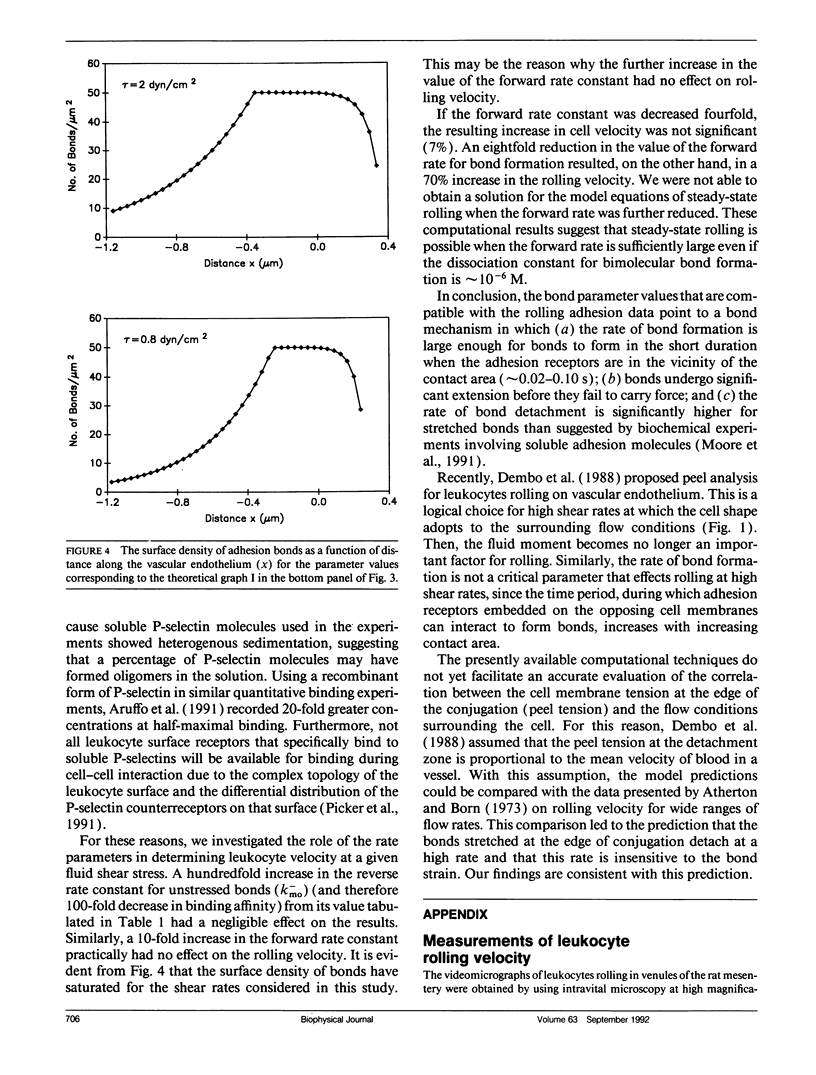
At the onset of inflammation, 20-80% of all leukocytes passing postcapillary venules roll along the endothelium. Recent blocking experiments with antibodies and soluble adhesion receptor molecules, as well as in vitro reconstitution experiments, suggest that leukocyte rolling is mediated by adhesion molecules that belong to the selectin family. What differentiates a selectin-counterreceptor interaction that leads to leukocyte rolling from others that mediate firm adhesion after static incubation but no adhesion when incubated under flow conditions? Here, we explore this question by introducing a quantitative biophysical model that is compatible with the laws of mechanics as applied to rolling leukocytes and the present biochemical and biophysical data on selectin mediated interactions. Our computational experiments point to an adhesion mechanism in which the rate of bond formation is high and the detachment rate low, except at the rear of the contact area where the stretched bonds detach at a high uniform rate. The bond length and bond flexibility play a critical role in enhancing leukocyte rolling at a wide range of fluid shear rates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbassi O., Lane C. L., Krater S., Kishimoto T. K., Anderson D. C., McIntire L. V., Smith C. W. Canine neutrophil margination mediated by lectin adhesion molecule-1 in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2107–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abney J. R., Scalettar B. A., Owicki J. C. Self diffusion of interacting membrane proteins. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):817–833. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82882-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Kolanus W., Walz G., Fredman P., Seed B. CD62/P-selectin recognition of myeloid and tumor cell sulfatides. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90570-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Dembo M., Bongrand P. Cell adhesion. Competition between nonspecific repulsion and specific bonding. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1051–1064. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84252-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M., Butcher E., Furie B., Furie B., Gallatin M., Gimbrone M., Harlan J., Kishimoto K., Lasky L., McEver R. Selectins: a family of adhesion receptors. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):233–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90174-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Hill T. L. Theoretical calculation methods for kinesin in fast axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):431–435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembo M., Torney D. C., Saxman K., Hammer D. The reaction-limited kinetics of membrane-to-surface adhesion and detachment. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):55–83. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elber R., Karplus M. Multiple conformational states of proteins: a molecular dynamics analysis of myoglobin. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):318–321. doi: 10.1126/science.3798113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Berk D., Leung A. Detachment of agglutinin-bonded red blood cells. I. Forces to rupture molecular-point attachments. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):838–848. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82296-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiebig E., Ley K., Arfors K. E. Rapid leukocyte accumulation by "spontaneous" rolling and adhesion in the exteriorized rabbit mesentery. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1991 May;10(2):127–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. I., Cook R. G., McEver R. P. Cloning of GMP-140, a granule membrane protein of platelets and endothelium: sequence similarity to proteins involved in cell adhesion and inflammation. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence M. B., Springer T. A. Leukocytes roll on a selectin at physiologic flow rates: distinction from and prerequisite for adhesion through integrins. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):859–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90393-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley K., Gaehtgens P. Endothelial, not hemodynamic, differences are responsible for preferential leukocyte rolling in rat mesenteric venules. Circ Res. 1991 Oct;69(4):1034–1041. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.4.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley K., Gaehtgens P., Fennie C., Singer M. S., Lasky L. A., Rosen S. D. Lectin-like cell adhesion molecule 1 mediates leukocyte rolling in mesenteric venules in vivo. Blood. 1991 Jun 15;77(12):2553–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T. The site of leucocyte emigration during inflammation. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1961 Apr;46:115–118. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1961.sp001522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P. Leukocyte interactions mediated by selectins. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
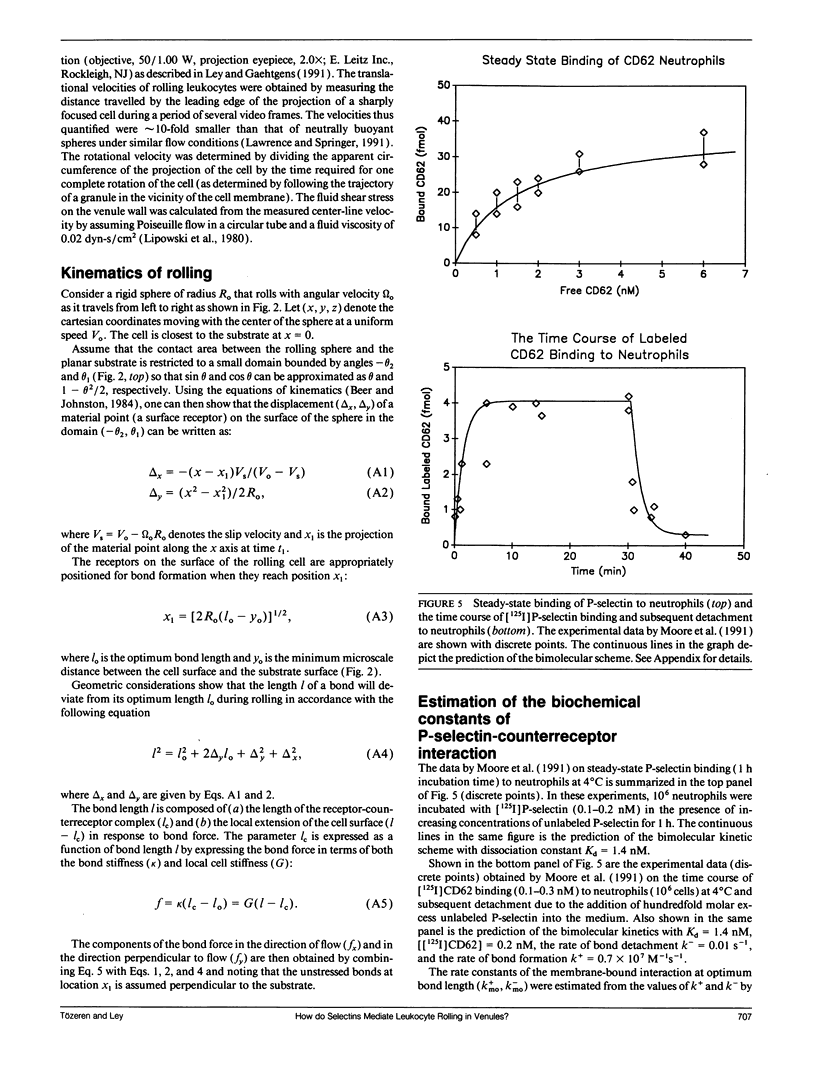
- Moore K. L., Varki A., McEver R. P. GMP-140 binds to a glycoprotein receptor on human neutrophils: evidence for a lectin-like interaction. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):491–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C., Elson E. L. Lymphocyte mechanical response triggered by cross-linking surface receptors. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):860–872. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Warnock R. A., Burns A. R., Doerschuk C. M., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. The neutrophil selectin LECAM-1 presents carbohydrate ligands to the vascular selectins ELAM-1 and GMP-140. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):921–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W. Leukocyte biophysics. An invited review. Cell Biophys. 1990 Oct;17(2):107–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02990492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Usami S., Skalak R., Chien S. The interaction of leukocytes and erythrocytes in capillary and postcapillary vessels. Microvasc Res. 1980 Jan;19(1):45–70. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Usami S., Skalak R., Chien S. The interaction of leukocytes and erythrocytes in capillary and postcapillary vessels. Microvasc Res. 1980 Jan;19(1):45–70. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozeren A. Cell-cell conjugation. Transient analysis and experimental implications. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):641–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82407-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozeren A., Sung K. L., Chien S. Theoretical and experimental studies on cross-bridge migration during cell disaggregation. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):479–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82841-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Andrian U. H., Chambers J. D., McEvoy L. M., Bargatze R. F., Arfors K. E., Butcher E. C. Two-step model of leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction in inflammation: distinct roles for LECAM-1 and the leukocyte beta 2 integrins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7538–7542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]