Abstract
We have used the atomic force microscope (AFM) to measure the local rigidity modulus at points on the surface of a section of hydrated cow tibia. These data are obtained either from contrast changes that occur as the contact force is altered, or from force versus distance curves obtained at fixed points. These two methods yield the same values for rigidity modulus (at a given point). At low resolution, the elastic morphology and topography mirror the features seen in optical and electron micrographs. At high resolution we see dramatic variations in elastic properties across distances as small as 50 nm.
Full text
PDF
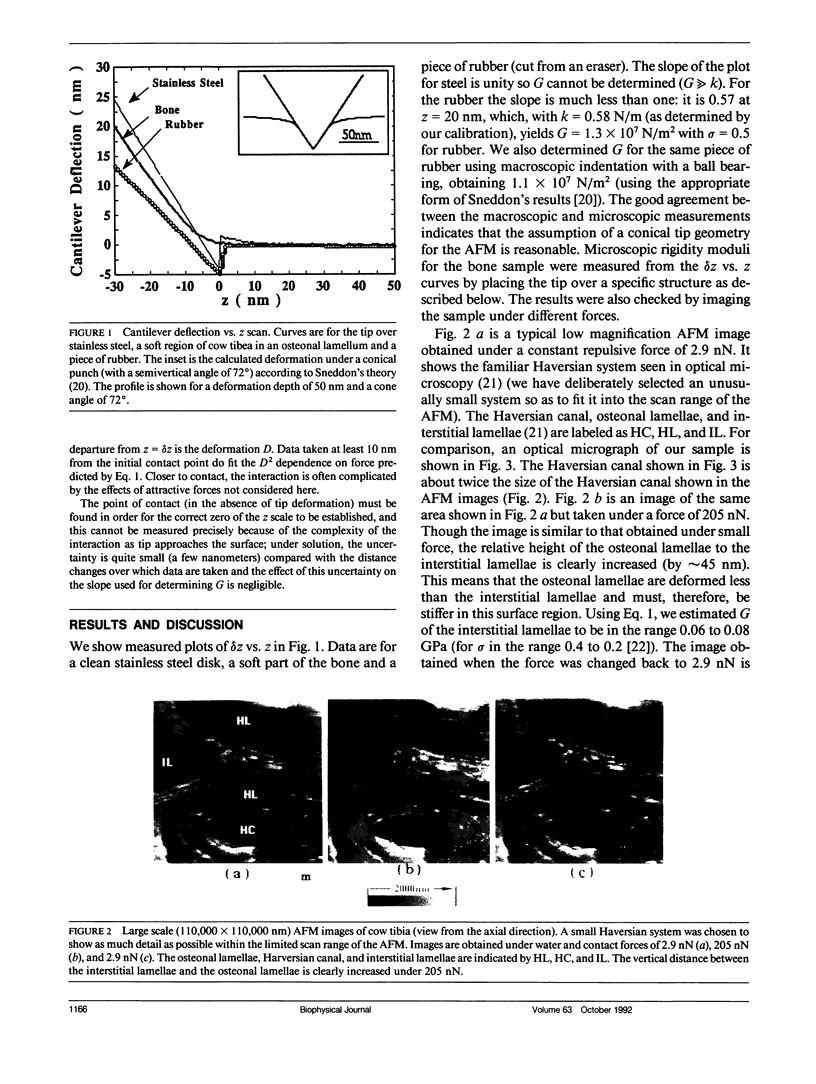
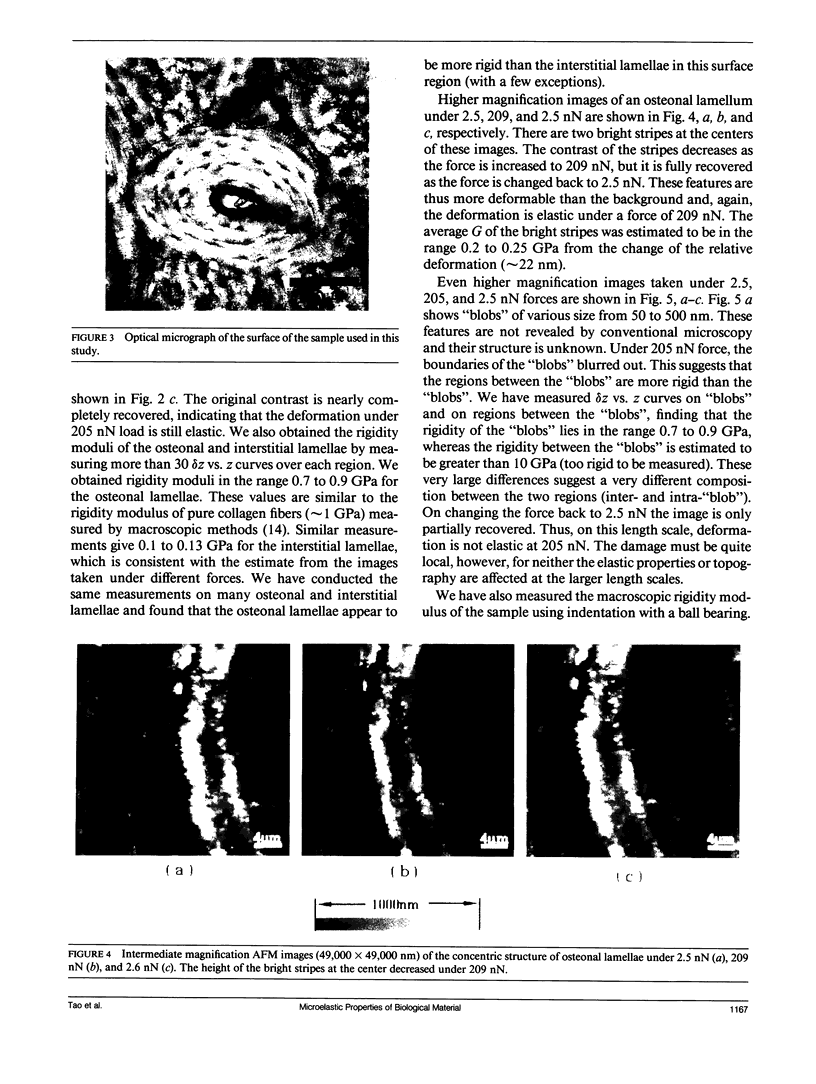


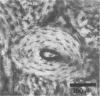
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham NA, Dominguez DD, Mowery RL, Colton RJ. Probing the surface forces of monolayer films with an atomic-force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Apr 16;64(16):1931–1934. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Miller A. Determination of the elastic constants of collagen by Brillouin light scattering. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley R., James D., Miller A., White J. W. Phonons and the elastic moduli of collagen and muscle. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):285–287. doi: 10.1038/267285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees S., Ahern J. M., Leonard M. Parameters influencing the sonic velocity in compact calcified tissues of various species. J Acoust Soc Am. 1983 Jul;74(1):28–33. doi: 10.1121/1.389723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees S., Tao N. J., Lindsay S. M. Studies of compact hard tissues and collagen by means of Brillouin light scattering. Connect Tissue Res. 1990;24(3-4):187–205. doi: 10.3109/03008209009152148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees S. Ultrasonic measurements of deer antler, bovine tibia and tympanic bulla. J Biomech. 1982;15(11):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mate CM, McClelland GM, Erlandsson R, Chiang S. Atomic-scale friction of a tungsten tip on a graphite surface. Phys Rev Lett. 1987 Oct 26;59(17):1942–1945. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.59.1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]