Abstract
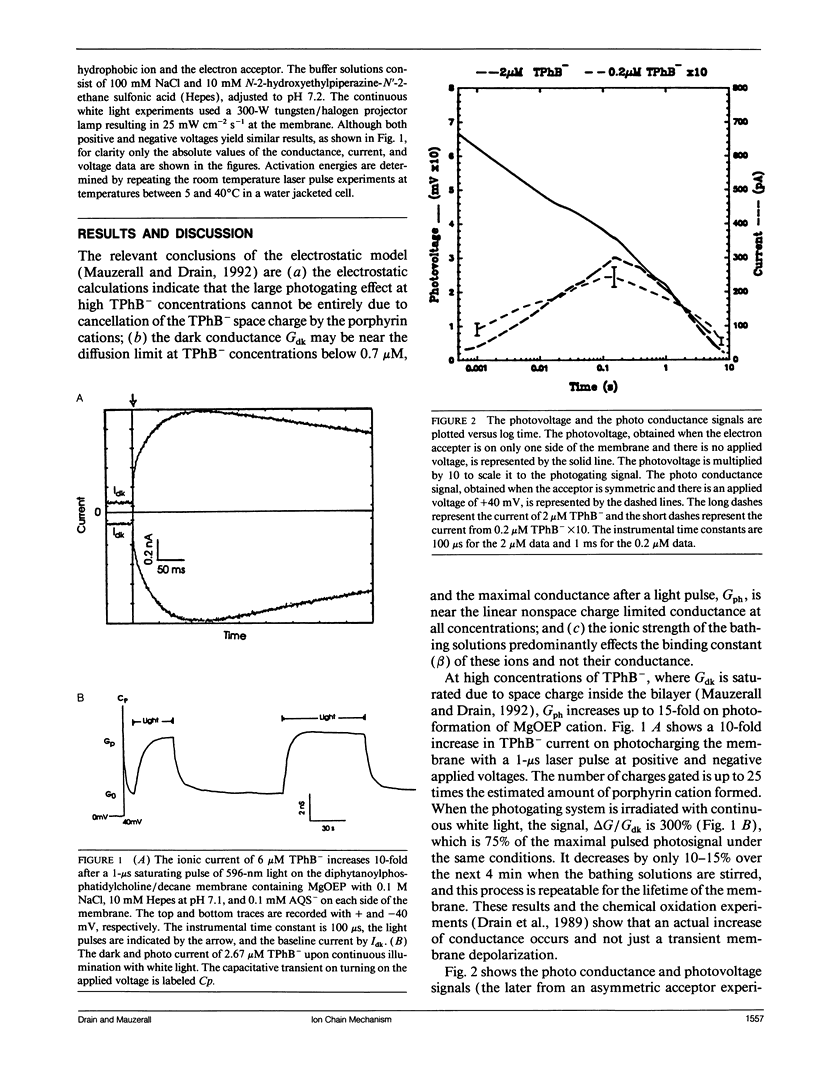
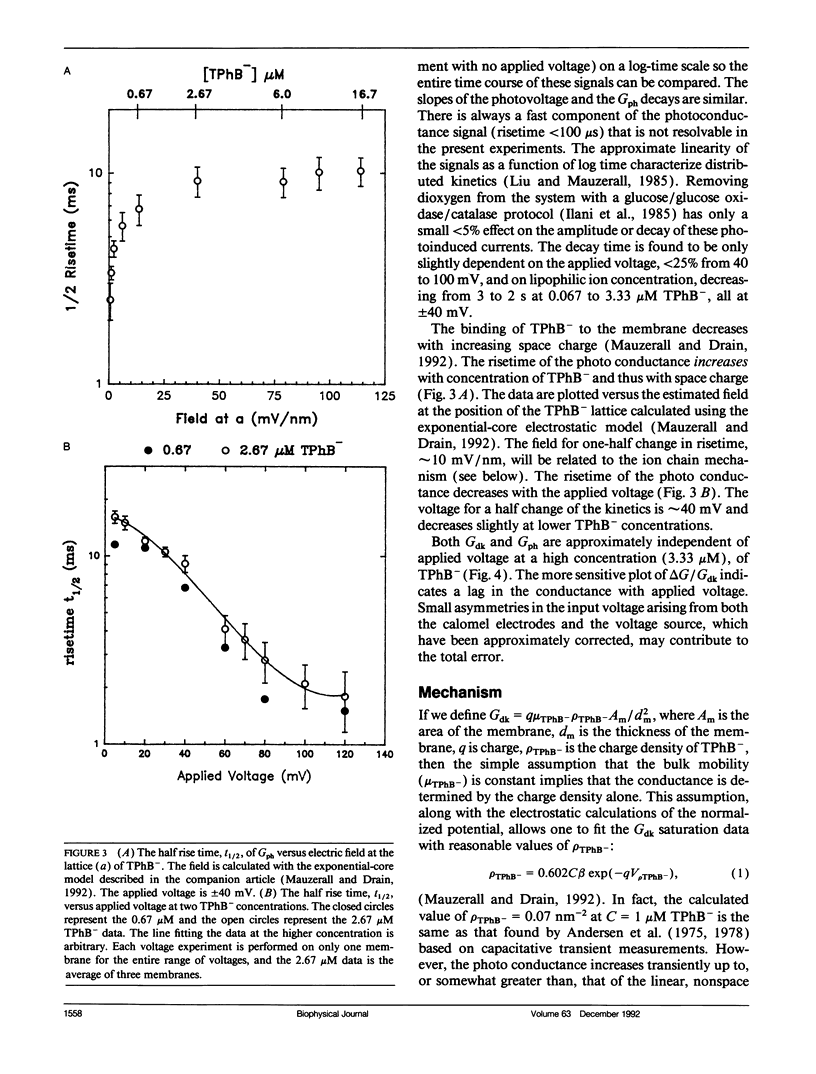
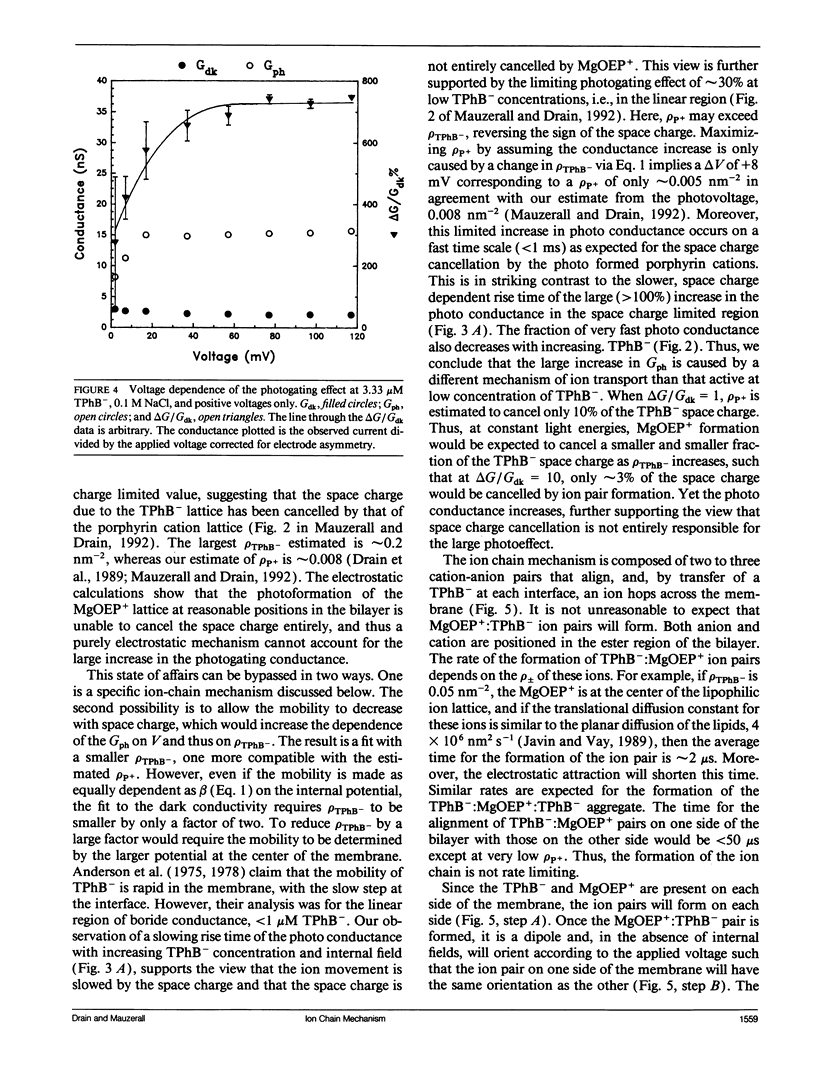
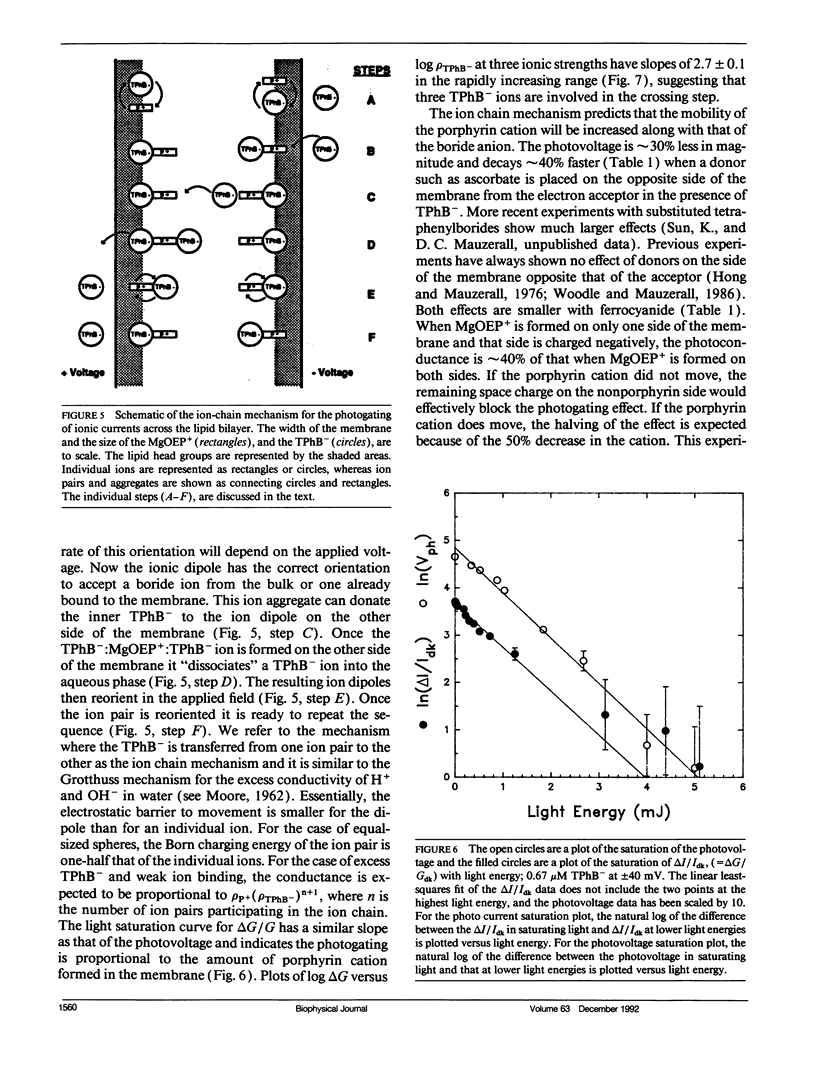
The photogating of hydrophobic ion currents across the lipid bilayer membrane allows the direct study of their kinetics by symmetrically forming charge within the membrane and across each interface, rather than across the membrane. We find that the photoinduced conductance continues to increase beyond the region where the tetraphenylboride charge density in the membrane exceeds the estimated porphyrin cation density. This photoconductance is proportional to the tetraphenylboride charge density raised to the second to third power. The risetime of the photogating effect increases with increasing concentration of tetraphenyl boride. The porphyrin cation mobility is increased when the tetraphenylboride anion is present, and low concentrations of tetraphenylphosphonium cation increase the dark conductivity while inhibiting the photoconductivity. The activation energy for both the porphyrin and phosphonium cation induced conductance is more positive than that of the tetraphenylboride conductance. From these results we conclude that in addition to some cancellation of space charge within the membrane, the mechanism of increased conductance involves the transport of these hydrophobic anions via an alternating anion-cation chain, analogous to the Grotthuss mechanism for excess proton conduction in water. This ion chain conductance can be viewed as an evolutionary prototype of an ion channel across the membrane. It also underscores the importance of the counter ion in the transport of large ions such as peptides across the lipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Feldberg S., Nakadomari H., Levy S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):35–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S., Fuchs M. Potential energy barriers to ion transport within lipid bilayers. Studies with tetraphenylborate. Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):795–830. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85856-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structural requirement for the rapid movement of charged molecules across membranes. Experiments with tetraphenylborate analogues. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82927-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drain C. M., Christensen B., Mauzerall D. Photogating of ionic currents across a lipid bilayer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6959–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. Hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Thermodynamic analysis of tetraphenylphosphonium binding to vesicles. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83663-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kadziauskas Y. P., Liberman E. A., Skulachev V. P., Topali V. P., Tsofina L. M., Vladimirova M. A. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. I. Submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B. H., Hubbell W. L., Flewelling R. F. Electrostatic interactions in membranes and proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:163–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilani A., Liu T. M., Mauzerall D. The effect of oxygen on the amplitude of photodriven electron transfer across the lipid bilayer-water interface. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):679–684. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83964-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Vaz W. L. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes measured by fluorescence and phosphorescence methods. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:471–513. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. M., Mauzerall D. Distributed kinetics of decay of the photovoltage at the lipid bilayer-water interface. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83755-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P., Benz R., Stark G., Bamberg E., Jordan P. C., Fahr A., Brock W. Relaxation studies of ion transport systems in lipid bilayer membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Nov;14(4):513–598. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000247x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauzerall D. C., Drain C. M. Photogating of ionic currents across lipid bilayers. Electrostatics of ions and dipoles inside the membrane. Biophys J. 1992 Dec;63(6):1544–1555. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81738-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickar A. D., Hobbs J. The influence of sterols on pentachlorophenol-induced charge transfer across lipid bilayers studied by alternating current methods. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. G., Seelig J. Electric charge effects on phospholipid headgroups. Phosphatidylcholine in mixtures with cationic and anionic amphiphiles. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7720–7728. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Ganz P. Nonclassical hydrophobic effect in membrane binding equilibria. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9354–9359. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J., Fischkoff S., Chance B., Cooper R. A. Fluorescent probe analysis of the lipid architecture of natural and experimental cholesterol-rich membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1589–1595. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodle M. C., Mauzerall D. Photoinitiated ion movements in bilayer membranes containing magnesium octaethylporphyrin. Biophys J. 1986 Sep;50(3):431–439. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83479-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodle M., Zhang J. W., Mauzerall D. Kinetics of charge transfer at the lipid bilayer-water interface on the nanosecond time scale. Biophys J. 1987 Oct;52(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83247-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


