Abstract
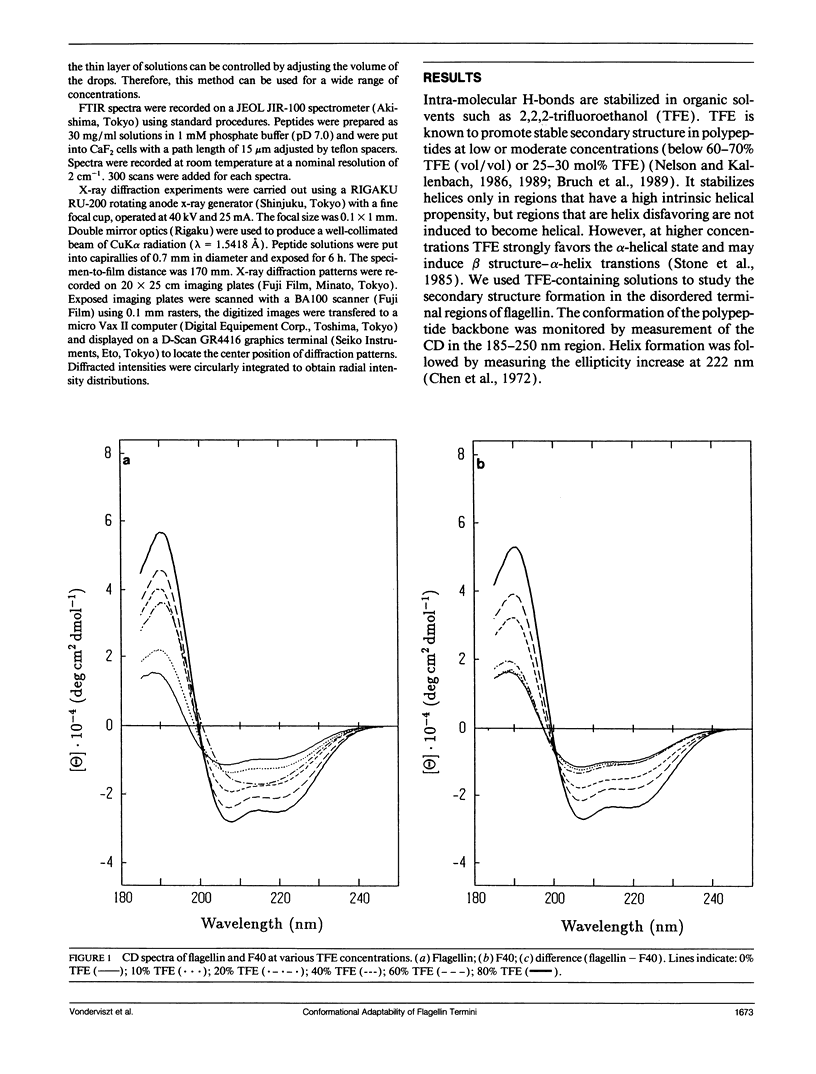
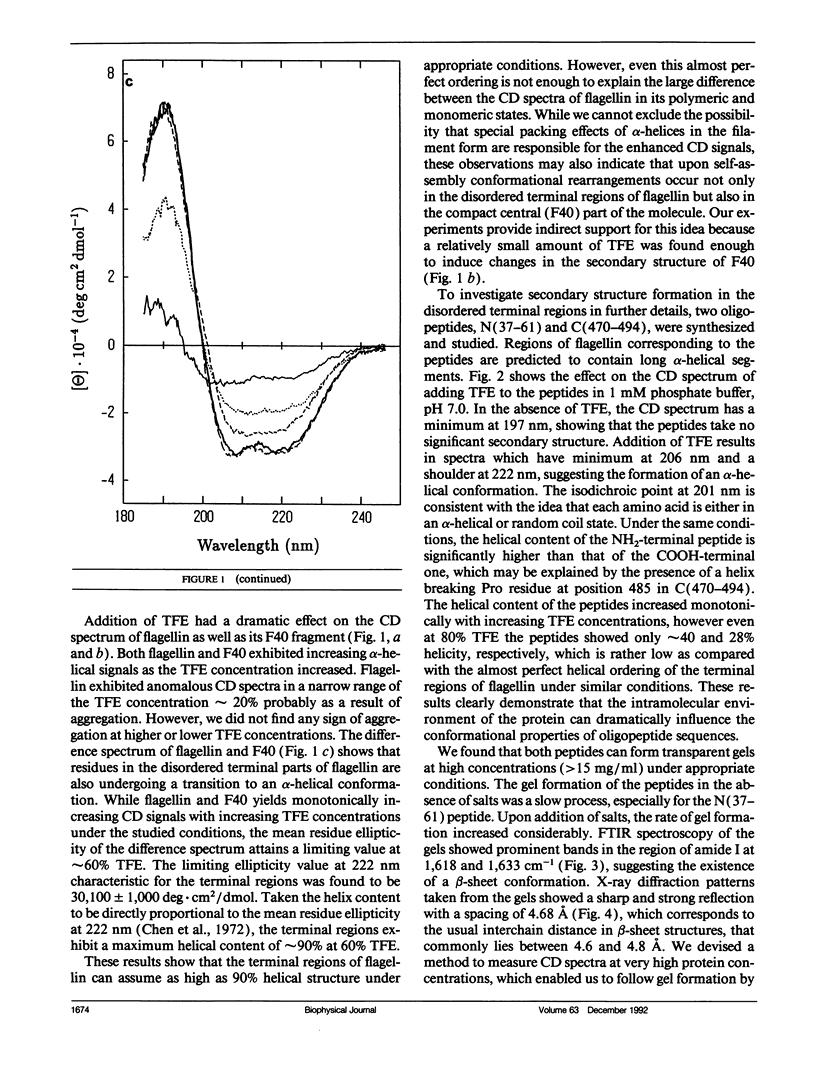
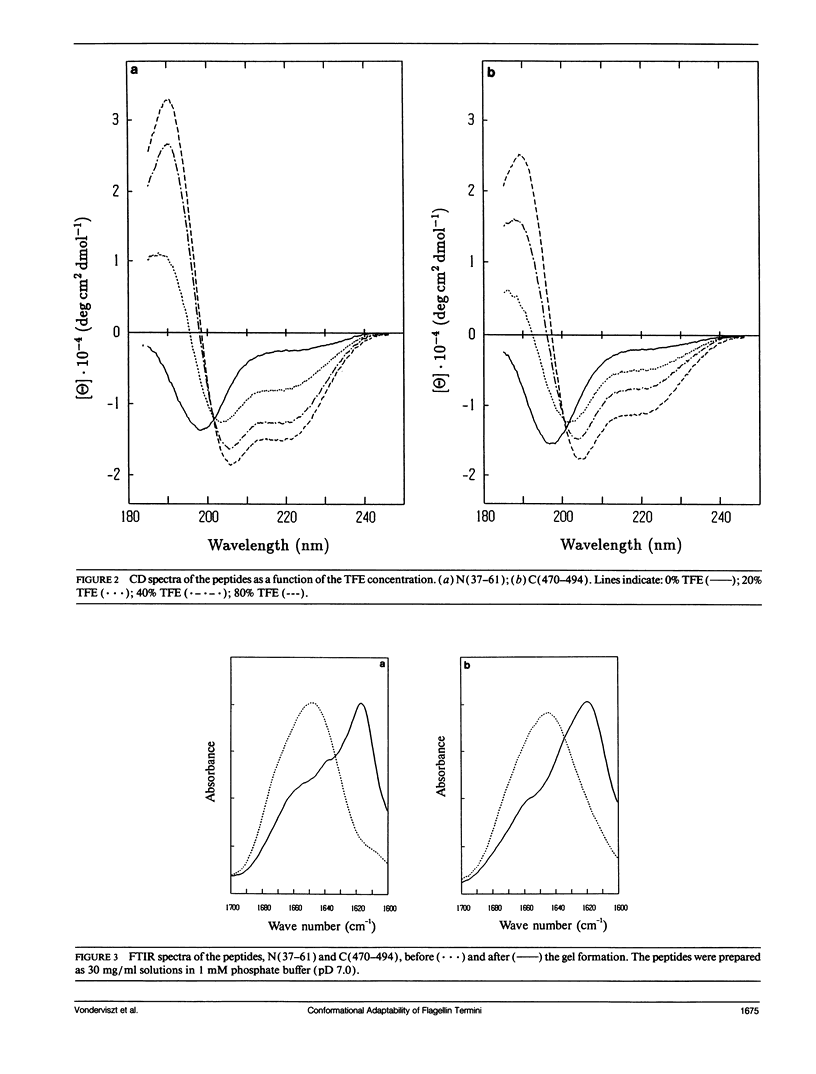
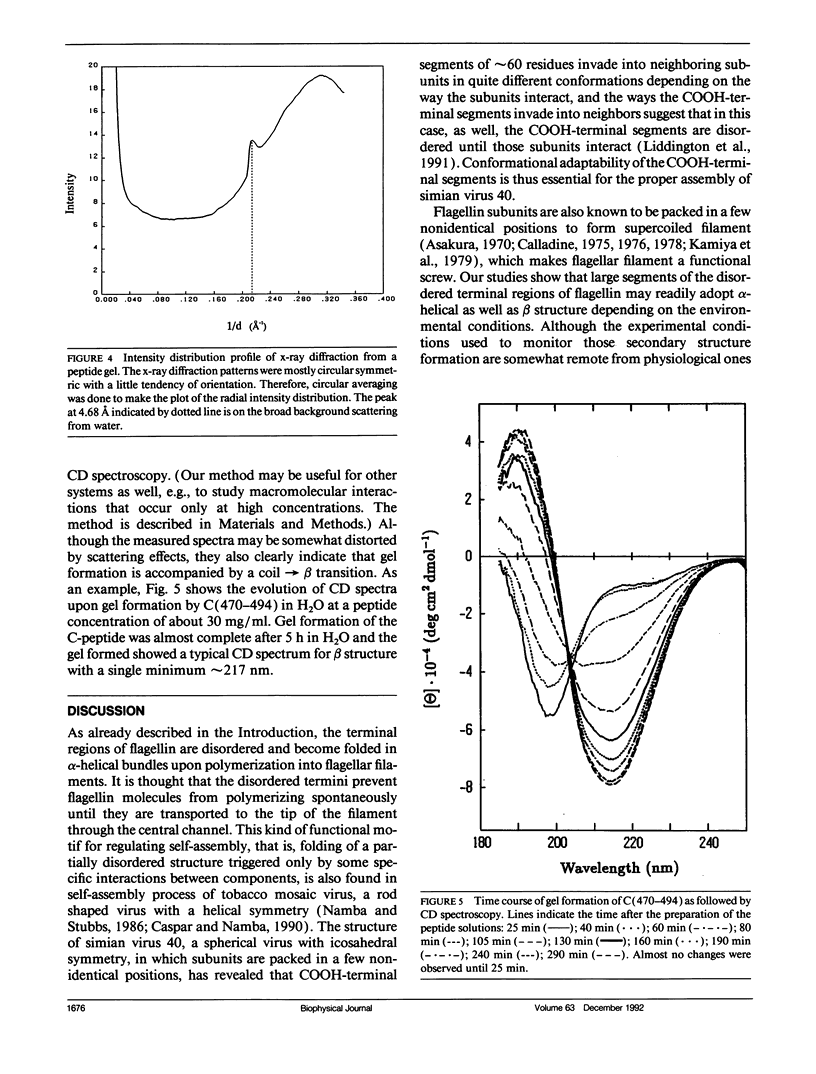
Secondary structure formation in the disordered terminal regions of flagellin were studied by circular dichroic (CD) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and x-ray diffraction. The terminal regions of flagellin are known to form alpha-helical bundles upon polymerization into flagellar filaments. We found from comparative CD studies of flagellin and its F40 tryptic fragment that a highly alpha-helical conformation can be induced and stabilized in the terminal regions in 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE) containing solutions, which is known to promote intra-molecular hydrogen bonding. Two oligopeptides, N(37-61) and C(470-494), each corresponding to a portion of terminal regions and predicted to have a high alpha-helix forming potential, were synthesized and studied. Both peptides were disordered in an aqueous environment, but they showed a strong tendency to assume alpha-helical structure in solutions containing TFE. On the other hand, peptides were found to form transparent gels at high concentrations (> 15 mg/ml) and all three methods confirmed that the peptides become ordered into a predominantly beta structure upon gel formation. Our results show that large segments of the disordered terminal regions of flagellin can adopt alpha-helical as well as beta structure depending on the environmental conditions. This high degree of conformational adaptability may be reflecting some unique characteristics of the flagellin termini, which are involved in self-assembly and polymorphism of flagellar filament.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asakura S. Polymerization of flagellin and polymorphism of flagella. Adv Biophys. 1970;1:99–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruch M. D., McKnight C. J., Gierasch L. M. Helix formation and stability in a signal sequence. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8554–8561. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Construction of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1975 May 8;255(5504):121–124. doi: 10.1038/255121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Design requirements for the construction of bacterial flagella. J Theor Biol. 1976 Apr;57(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Namba K. Switching in the self-assembly of tobacco mosaic virus. Adv Biophys. 1990;26:157–185. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(90)90011-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov O. V., Kostyukova A. S., Pyatibratov M. G. Architectonics of a bacterial flagellin filament subunit. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., DeRosier D. J., Macnab R. M. Flagellar hook and hook-associated proteins of Salmonella typhimurium and their relationship to other axial components of the flagellum. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):819–832. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Asakura S., Wakabayashi K., Namba K. Transition of bacterial flagella from helical to straight forms with different subunit arrangements. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):725–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyukova A. S., Pyatibratov M. G., Filimonov V. V., Fedorov O. V. Flagellin parts acquiring a regular structure during polymerization are disposed on the molecule ends. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddington R. C., Yan Y., Moulai J., Sahli R., Benjamin T. L., Harrison S. C. Structure of simian virus 40 at 3.8-A resolution. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):278–284. doi: 10.1038/354278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Stubbs G. Structure of tobacco mosaic virus at 3.6 A resolution: implications for assembly. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3952490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Yamashita I., Vonderviszt F. Structure of the core and central channel of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):648–654. doi: 10.1038/342648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. W., Kallenbach N. R. Persistence of the alpha-helix stop signal in the S-peptide in trifluoroethanol solutions. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5256–5261. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. W., Kallenbach N. R. Stabilization of the ribonuclease S-peptide alpha-helix by trifluoroethanol. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):211–217. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone A. L., Park J. Y., Martenson R. E. Low-ultraviolet circular dichroism spectroscopy of oligopeptides 1-95 and 96-168 derived from myelin basic protein of rabbit. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6666–6673. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uratani Y., Asakura S., Imahori K. A circular dichroism study of Salmonella flagellin: evidence for conformational change on polymerization. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderviszt F., Kanto S., Aizawa S., Namba K. Terminal regions of flagellin are disordered in solution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderviszt F., Uedaira H., Kidokoro S., Namba K. Structural organization of flagellin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90149-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


