Abstract
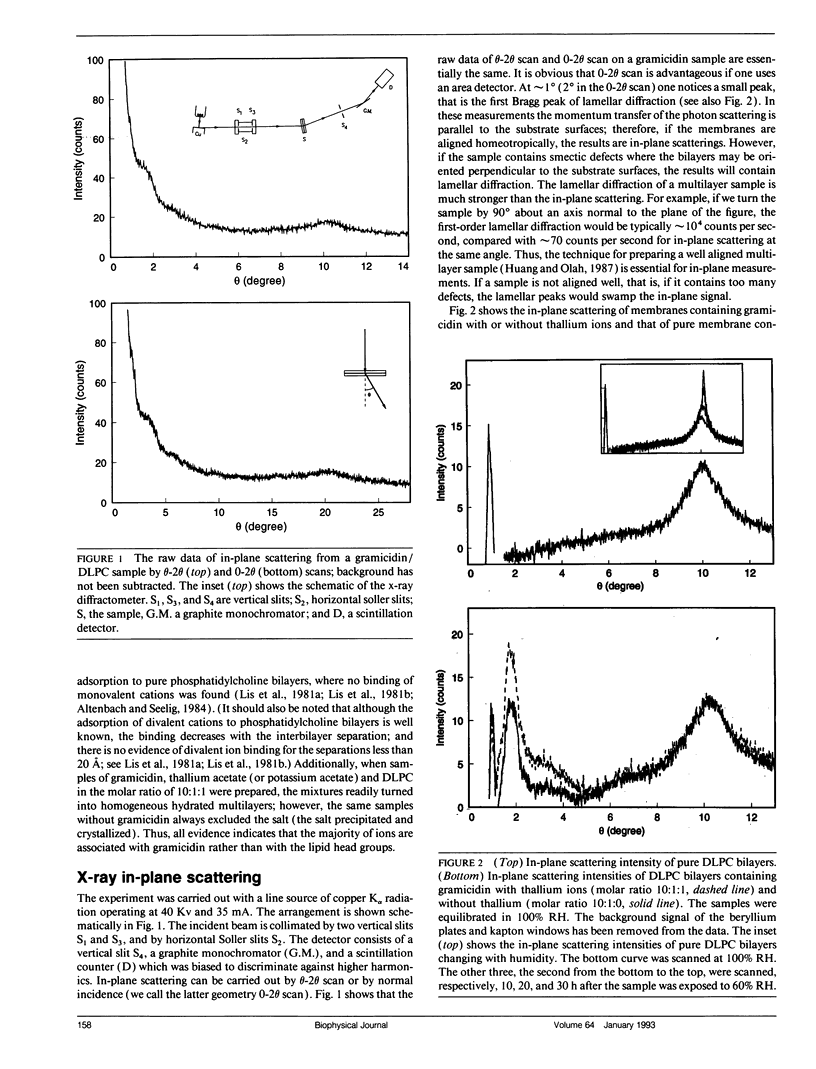
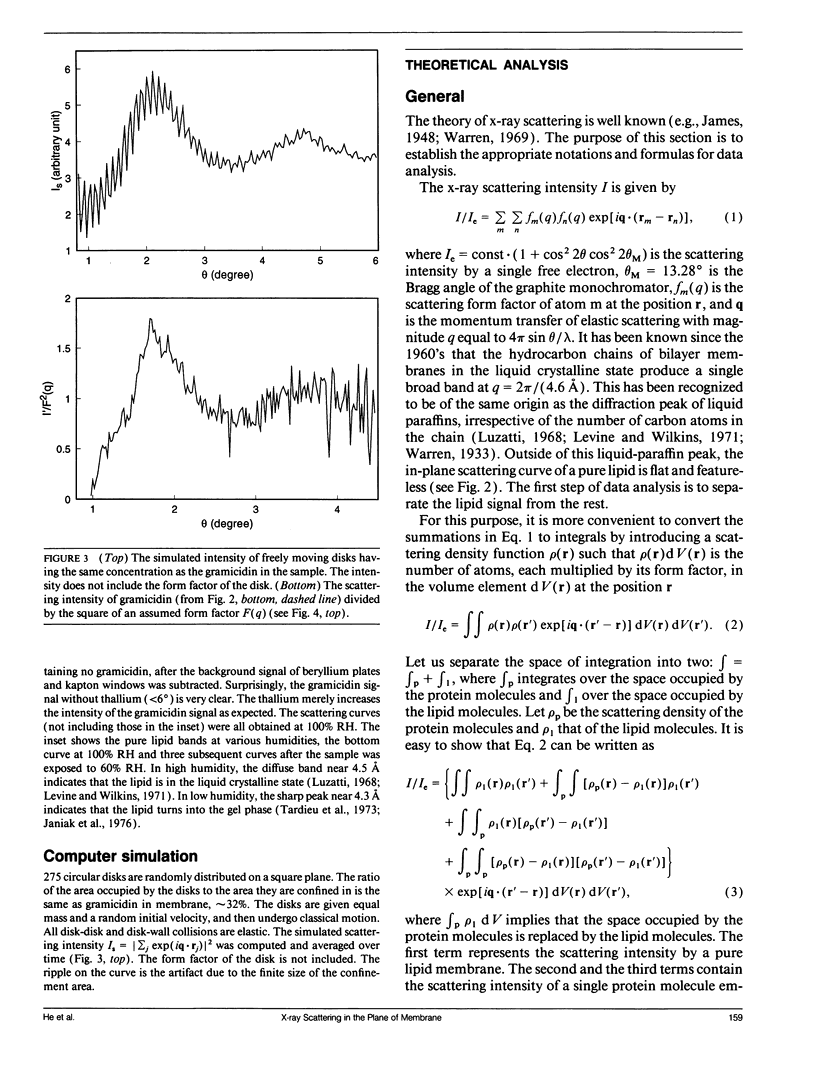
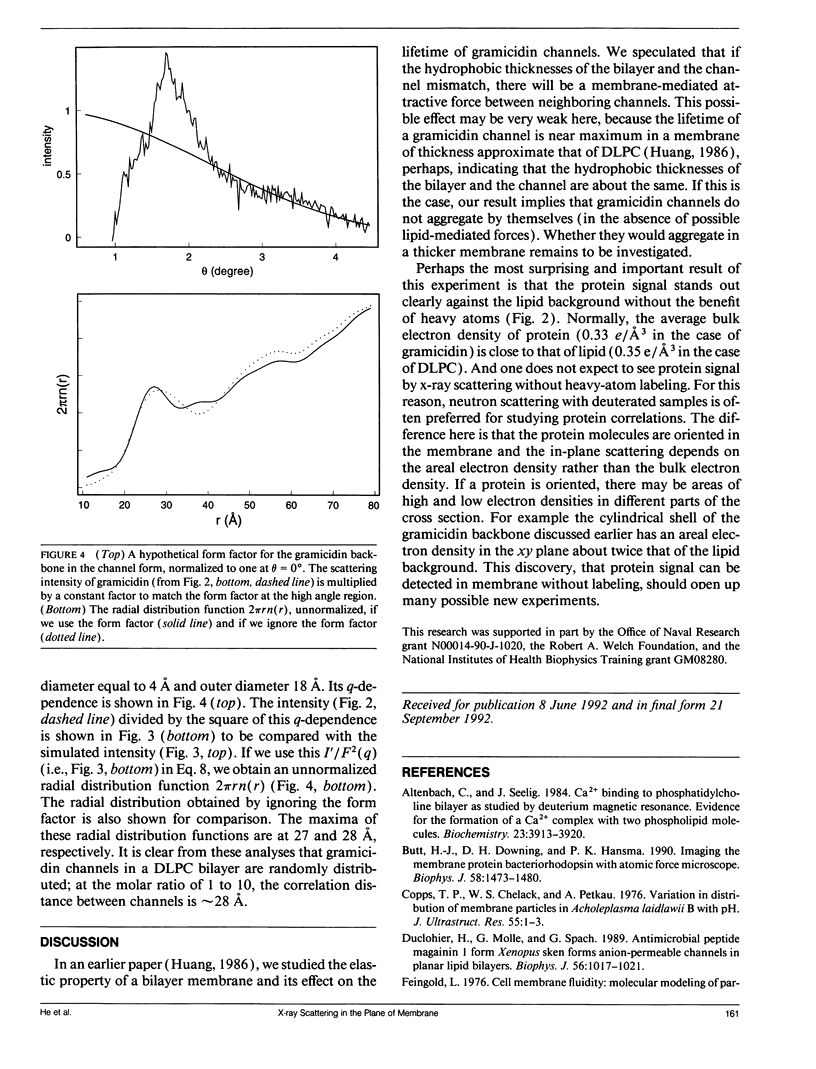
We demonstrate a technique for measuring x-ray (or neutron) scattering with the momentum transfer confined in the plane of membrane, for the purpose of studying lateral organization of proteins and peptides in membrane. Unlike freeze-fracture electron microscopy or atomic force microscopy which requires the membrane to be frozen or fixed, in-plane x-ray scattering can be performed with the membrane maintained in the liquid crystalline state. As an example, the controversial question of whether gramicidin forms aggregates in membrane was investigated. We used dilauroylphosphatidylcholine (DLPC) bilayers containing gramicidin in the molar ratio of 10:1. Very clear scattering curves reflecting gramicidin channel-channel correlation were obtained, even for the sample containing no heavy atoms. Thallium ions bound to gramicidin channels merely increase the magnitude of the scattering curve. Analysis of the data shows that the channels were randomly distributed in the membrane, similar to a computer simulation of freely moving disks in a plane. We suggest that oriented proteins may provide substantial x-ray contrast against the lipid background without requiring heavy-atom labeling. This should open up many possible new experiments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbach C., Seelig J. Ca2+ binding to phosphatidylcholine bilayers as studied by deuterium magnetic resonance. Evidence for the formation of a Ca2+ complex with two phospholipid molecules. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3913–3920. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copps T. P., Chelack W. S., Petkau A. Variation in distribution of membrane particles in Acholeplasma laidlawii B with pH. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Apr;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duclohier H., Molle G., Spach G. Antimicrobial peptide magainin I from Xenopus skin forms anion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82746-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold L. Cell membrane fluidity: molecular modeling of particle aggregations seen in electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. W. Deformation free energy of bilayer membrane and its effect on gramicidin channel lifetime. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83550-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. W., Olah G. A. Uniformly oriented gramicidin channels embedded in thick monodomain lecithin multilayers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):989–992. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83427-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. W., Wu Y. Lipid-alamethicin interactions influence alamethicin orientation. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82144-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., de Kruijff B. Proposed Mechanism for H(II) Phase Induction by Gramicidin in Model Membranes and Its Relation to Channel Formation. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(88)83072-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacapère J. J., Stokes D. L., Chatenay D. Atomic force microscopy of three-dimensional membrane protein crystals. Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):303–308. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81600-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Alvarez O. Voltage-dependent channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):77–150. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. D., Wasserman Z. R., DeGrado W. F. Synthetic amphiphilic peptide models for protein ion channels. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1177–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.2453923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Wilkins M. H. Structure of oriented lipid bilayers. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):69–72. doi: 10.1038/newbio230069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., Lis W. T., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P. Adsorption of divalent cations to a variety of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1771–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P. Binding of divalent cations of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers and its effect on bilayer interaction. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1761–1770. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Analysis of freeze-fracture electron micrographs by a computer-based technique. Biophys J. 1976 Jun;16(6):613–625. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85716-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oiki S., Danho W., Madison V., Montal M. M2 delta, a candidate for the structure lining the ionic channel of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olah G. A., Huang H. W., Liu W. H., Wu Y. L. Location of ion-binding sites in the gramicidin channel by X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 20;218(4):847–858. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L. T., Chan S. I., Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Pair distribution functions of bacteriorhodopsin and rhodopsin in model bilayers. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84337-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L. T., Edelman J., Chan S. I. Statistical mechanics of lipid membranes. Protein correlation functions and lipid ordering. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):863–871. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84232-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. P., Hui S. W., Stewart T. P. Correlative statistical analysis and computer modelling of intramembraneous particle distributions in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spisni A., Pasquali-Ronchetti I., Casali E., Lindner L., Cavatorta P., Masotti L., Urry D. W. Supramolecular organization of lysophosphatidylcholine-packaged Gramicidin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 13;732(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G., Strässle M., Takácz Z. Temperature-jump and voltage-jump experiments at planar lipid membranes support an aggregational (micellar) model of the gramicidin A ion channel. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(1):23–37. doi: 10.1007/BF01870893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. The sting. Melittin forms channels in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84719-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Ravikumar K. The gramicidin pore: crystal structure of a cesium complex. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):182–187. doi: 10.1126/science.2455344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


