Abstract
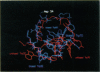
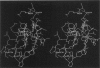
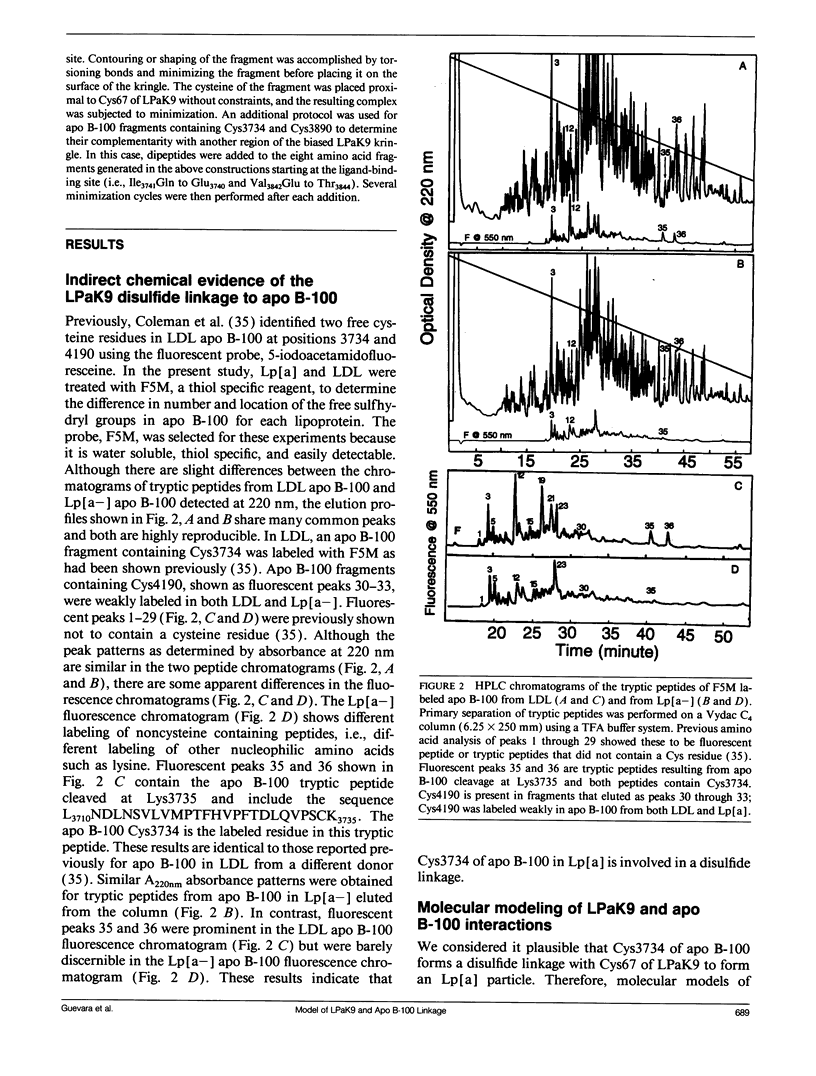
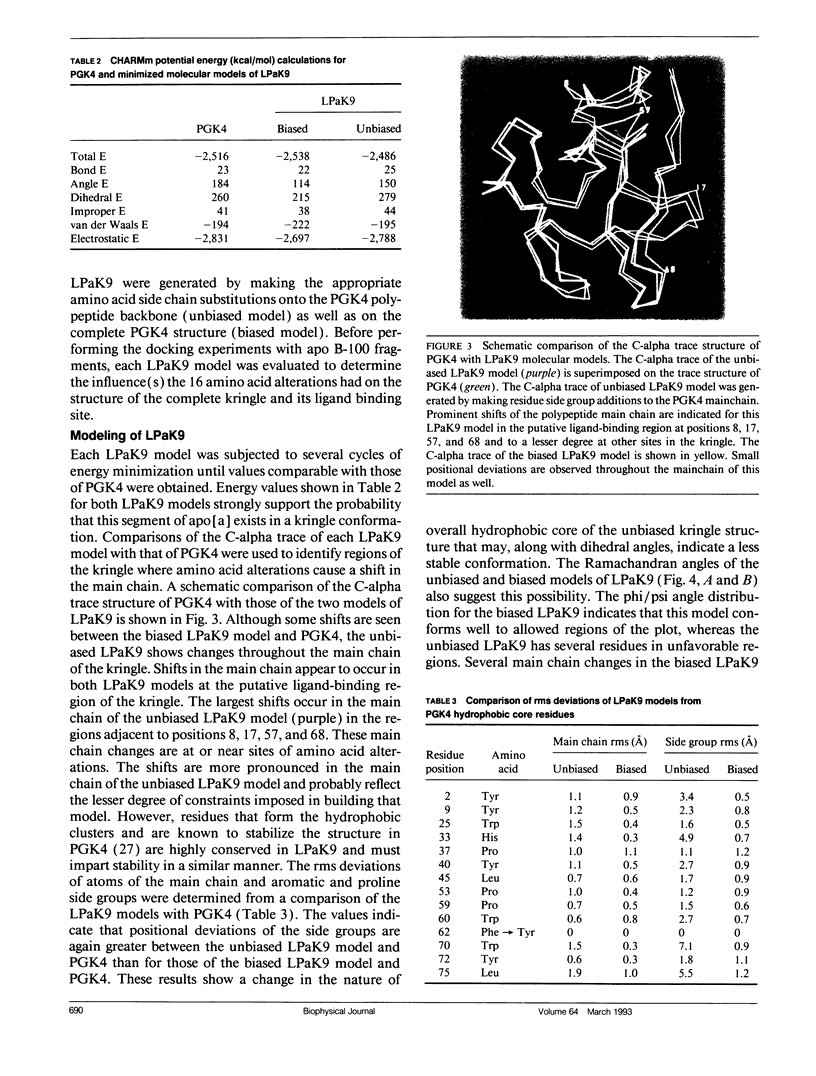
The protein component of human lipoprotein[a] consists primarily of two apolipoproteins, apo[a] and apo B-100, linked through a cystine disulfide(s). In the amino acid sequence of apo bd, Cys4057 located within a plasminogen kringle 4-like repeat sequence (3991-4068) is believed to form a disulfide bond with a specific cysteine residue in apo B-100. Our fluorescence-labeling experiments and molecular modeling studies have provided evidence for possible interactions between this apo[a] kringle type and apo B-100. The fluorescent probe, fluorescein-5-maleimide, was used in parallel experiments to label free sulfhydryl moieties in lipoprotein[a] and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). In apo B-100 of LDL, Cys3734 was labeled with the probe, but this site was not labeled in autologous lipoprotein[a]. The result strongly implicates Cys3734 of apo B-100 as the residue forming the disulfide linkage with Cys4057 of apo[a]. To explore possible noncovalent interactions between apo B-100 and apo[a], the crystallographic coordinates for plasminogen kringle 4 were used to generate molecular models of the apo[a] kringle-repeat sequence (3991-4068, LPaK9), the only plasminogen kringle 4 type repeat in apo[a] having an extra cysteine residue not involved in an intramolecular disulfide bond. The Cys4057 residue (henceforth designated as Cys67 in the LPaK9 sequence) is believed to form an intermolecular disulfide bond with a cysteine of apo B-100. In computer graphics molecular models of LPaK9, Cys67 is located on the surface of the kringle near the lysine ligand binding site. Selected segments of the LDL apo B-100 sequence that contain free sulfhydryl cysteines were subjected to energy minimization and docking with the ligand binding site and adjacent regions of the LPaK9 model. In the docking experiments, apo B-100 segment 3732-3745 (PSCKLDFREIQIYK) displayed the best fit and the largest number of van der Waals contacts with models of LPaK9. Other apo B-100 peptides with sulfhydryl cysteine were found to be less compatible when minimized with this kringle. These results support and extend previously suggested mechanisms for a complex interaction between apo[a] and apo B-100 that involve more than a simple covalent disulfide bond.
Full text
PDF




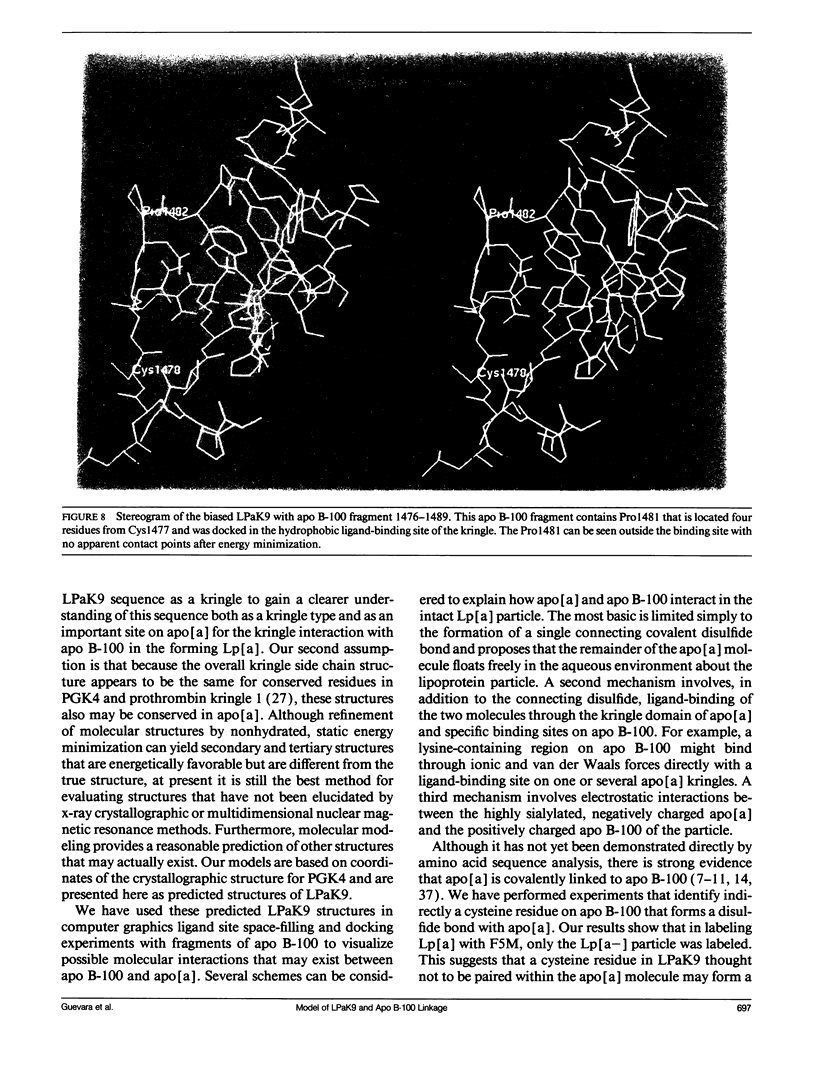



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong V. W., Walli A. K., Seidel D. Isolation, characterization, and uptake in human fibroblasts of an apo(a)-free lipoprotein obtained on reduction of lipoprotein(a). J Lipid Res. 1985 Nov;26(11):1314–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. D., Kim T. W., Gotto A. M., Jr, Yang C. Y. Determination of cysteine on low-density lipoproteins using the fluorescent probe, 5-iodoacetamidofluoresceine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 19;1037(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90111-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing G. L., Gaubatz J. W., Nava M. L., Burdick B. J., Bocan T. M., Guyton J. R., Weilbaecher D., DeBakey M. E., Lawrie G. M., Morrisett J. D. Quantitation and localization of apolipoproteins [a] and B in coronary artery bypass vein grafts resected at re-operation. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):593–603. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 1986 Oct;74(4):758–765. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Fless G. M., Kohr W. J., McLean J. W., Xu Q. T., Miller C. G., Lawn R. M., Scanu A. M. Partial amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein(a) shows that it is homologous to plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3224–3228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Garoff H., Renkonen O., Simons K. Protein and carbohydrate composition of Lp(a)lipoprotein from human plasma. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 15;11(17):3229–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00767a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Chari M. V., Nava M. L., Guyton J. R., Morrisett J. D. Isolation and characterization of the two major apoproteins in human lipoprotein [a]. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jan;28(1):69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Heideman C., Gotto A. M., Jr, Morrisett J. D., Dahlen G. H. Human plasma lipoprotein [a]. Structural properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4582–4589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guevara J., Jr, Knapp R. D., Honda S., Northup S. R., Morrisett J. D. A structural assessment of the apo[a] protein of human lipoprotein[a]. Proteins. 1992 Feb;12(2):188–199. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler G., Harnoncourt F., Paschke E., Mirtl W., Pfeiffer K. H., Kostner G. M. Lipoprotein Lp(a). A risk factor for myocardial infarction. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):398–401. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.4.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G., Lee D. M., Singh S. Identification of the thiol ester linked lipids in apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulichak A. M., Tulinsky A., Ravichandran K. G. Crystal and molecular structure of human plasminogen kringle 4 refined at 1.9-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10576–10588. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulichak A. M., Tulinsky A. Structure of the lysine-fibrin binding subsite of human plasminogen kringle 4. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Dec;1(6):673–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai A., Miyahara T., Fujimoto N., Matsuda M., Kameyama M. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Feb;59(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. H., Tulinsky A. Three-dimensional structure of the kringle sequence: structure of prothrombin fragment 1. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):3977–3982. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., Beisiegel U. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):579–592. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seman L. J., Breckenridge W. C. Isolation and partial characterization of apolipoprotein (a) from human lipoprotein (a). Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;64(10):999–1009. doi: 10.1139/o86-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri T. P., Tulinsky A., Skrzypczak-Jankun E., Park C. H. Structure of bovine prothrombin fragment 1 refined at 2.25 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Gorges R., Kostner G. M., Paltauf F., Hermetter A. Sulfhydryl-selective fluorescence labeling of lipoprotein(a) reveals evidence for one single disulfide linkage between apoproteins(a) and B-100. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 26;30(47):11245–11249. doi: 10.1021/bi00111a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu V. N., McConathy W. J. Lipoprotein(a) binding to other apolipoprotein B containing lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5919–5924. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu V. N., Zioncheck T. F., Lawn R. M., McConathy W. J. Interaction of apolipoprotein(a) with apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5480–5485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulinsky A., Park C. H., Mao B., Llinás M. Lysine/fibrin binding sites of kringles modeled after the structure of kringle 1 of prothrombin. Proteins. 1988;3(2):85–96. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulinsky A., Park C. H., Skrzypczak-Jankun E. Structure of prothrombin fragment 1 refined at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):885–901. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Weber W. Protein composition of Lp(a) lipoprotein from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. P., Padmanabhan K., Tulinsky A., Mulichak A. M. The refined structure of the epsilon-aminocaproic acid complex of human plasminogen kringle 4. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10589–10594. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Weng S. A., Kim T. W., Chen S. H., Pownall H. J., Sharp P. M., Liu S. W., Li W. H., Gotto A. M., Jr Structure of apolipoprotein B-100 of human low density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):96–108. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Kim T. W., Weng S. A., Lee B. R., Yang M. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Isolation and characterization of sulfhydryl and disulfide peptides of human apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye S. Q., Trieu V. N., Stiers D. L., McConathy W. J. Interactions of low density lipoprotein2 and other apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins with lipoprotein(a). J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6337–6343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki Z., Tercé F., Seman L. J., Theolis R. T., Breckenridge W. C., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L. The linkage with apolipoprotein (a) in lipoprotein (a) modifies the immunochemical and functional properties of apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8474–8481. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenker G., Költringer P., Boné G., Niederkorn K., Pfeiffer K., Jürgens G. Lipoprotein(a) as a strong indicator for cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 1986 Sep-Oct;17(5):942–945. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.5.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M. H., Kelley R. F., Padmanabhan K., Tulinsky A., Westbrook M. L., Kossiakoff A. A. Crystal structure of the kringle 2 domain of tissue plasminogen activator at 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):270–279. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]