Abstract
It recently has been demonstrated that magnetic resonance imaging can be used to map changes in brain hemodynamics produced by human mental operations. One method under development relies on blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) contrast: a change in the signal strength of brain water protons produced by the paramagnetic effects of venous blood deoxyhemoglobin. Here we discuss the basic quantitative features of the observed BOLD-based signal changes, including the signal amplitude and its magnetic field dependence and dynamic effects such as a pronounced oscillatory pattern that is induced in the signal from primary visual cortex during photic stimulation experiments. The observed features are compared with the results of Monte Carlo simulations of water proton intravoxel phase dispersion produced by local field gradients generated by paramagnetic deoxyhemoglobin in nearby venous blood vessels. The simulations suggest that the effect of water molecule diffusion is strong for the case of blood capillaries, but, for larger venous blood vessels, water diffusion is not an important determinant of deoxyhemoglobin-induced signal dephasing. We provide an expression for the apparent in-plane relaxation rate constant (R2*) in terms of the main magnetic field strength, the degree of the oxygenation of the venous blood, the venous blood volume fraction in the tissue, and the size of the blood vessel.
Full text
PDF


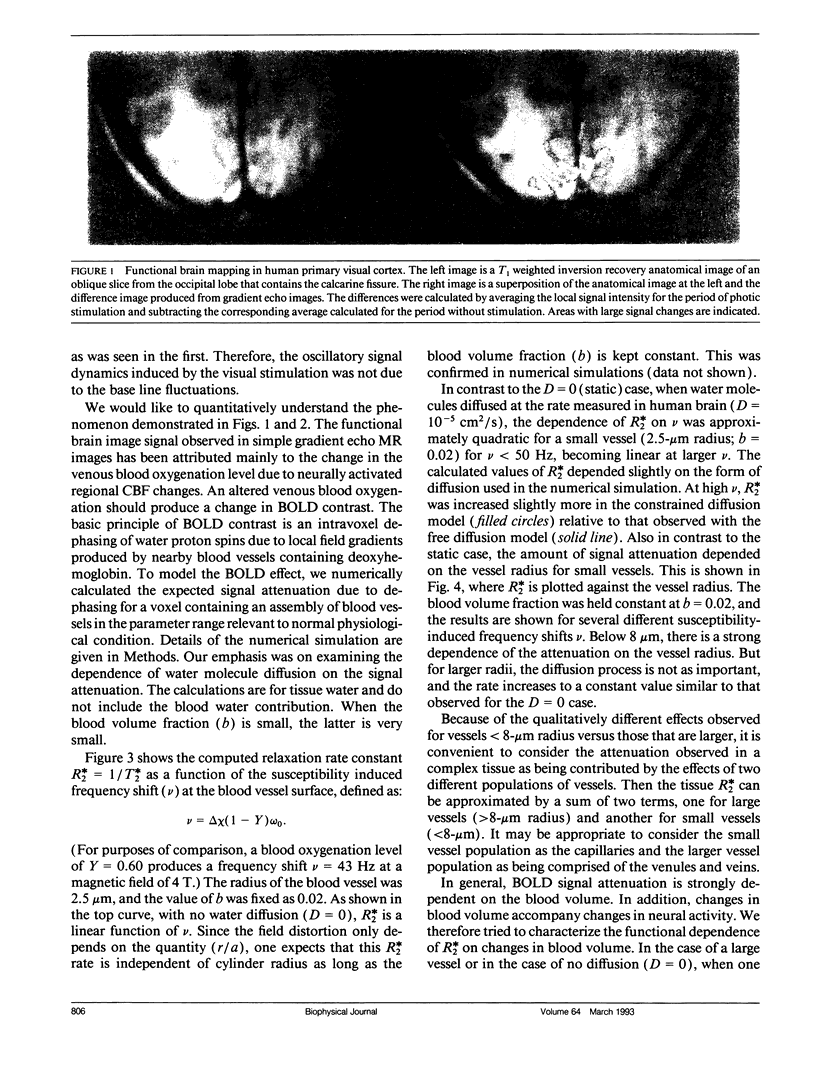
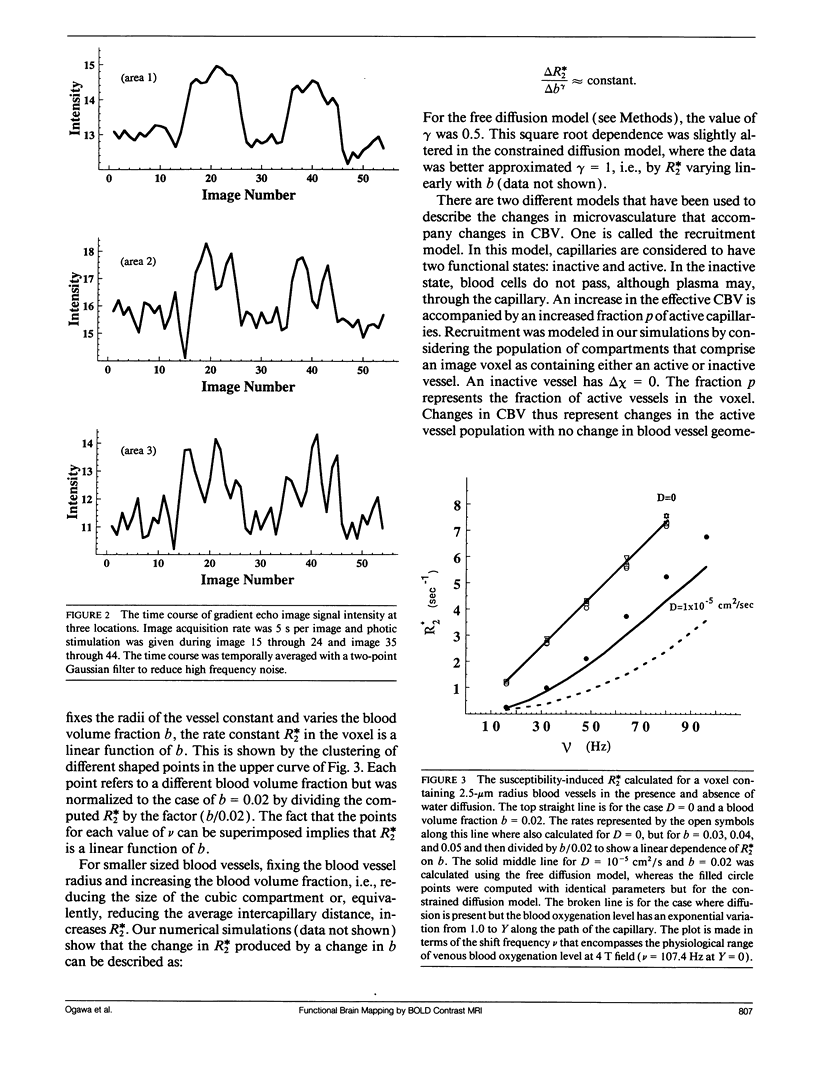
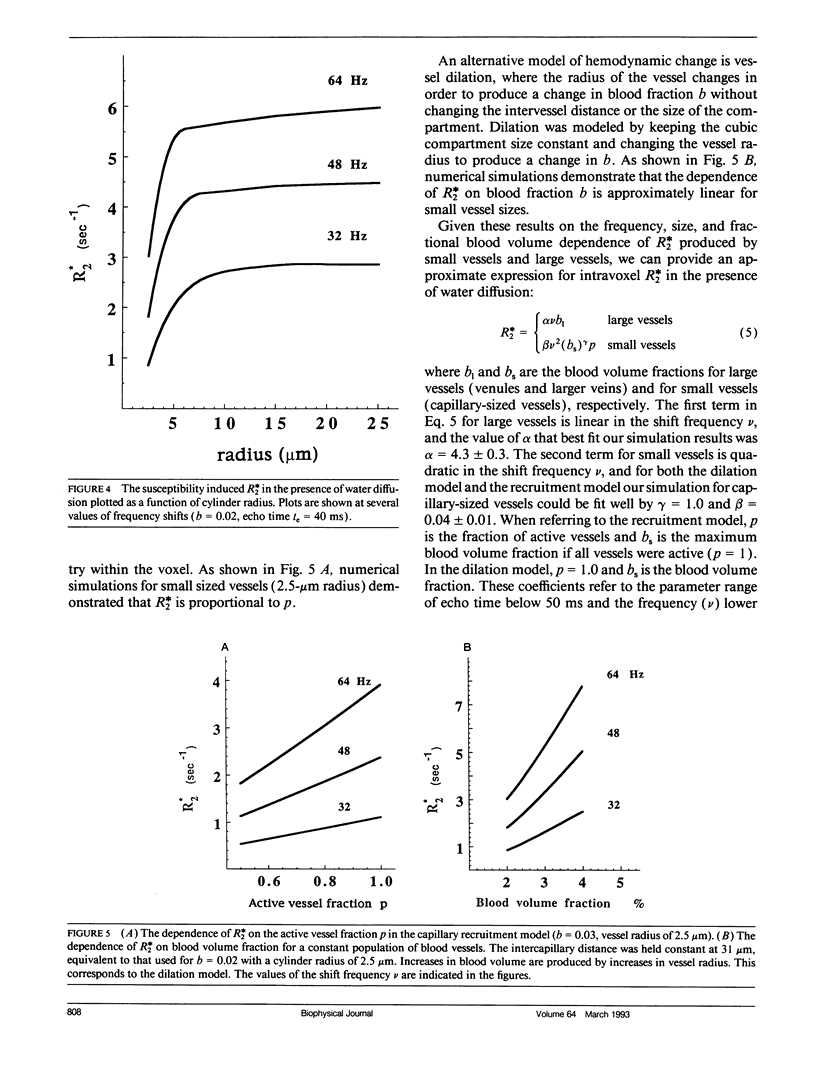
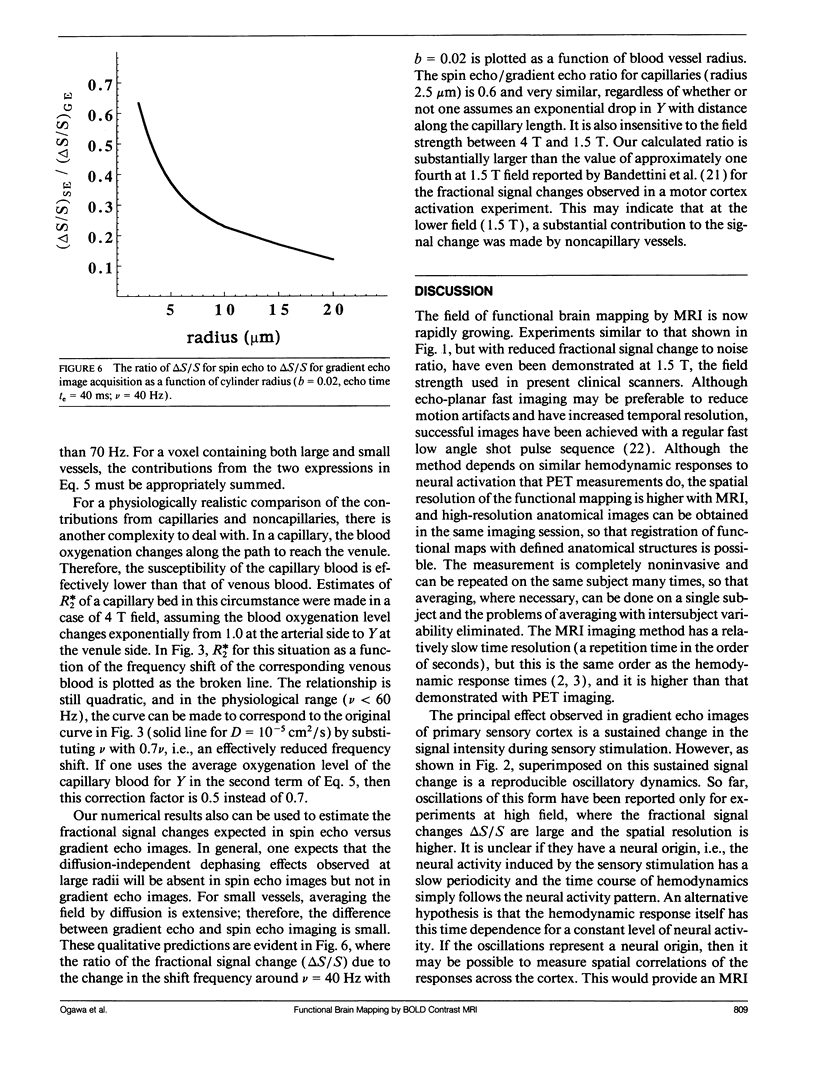



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandettini P. A., Wong E. C., Hinks R. S., Tikofsky R. S., Hyde J. S. Time course EPI of human brain function during task activation. Magn Reson Med. 1992 Jun;25(2):390–397. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910250220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belliveau J. W., Kennedy D. N., Jr, McKinstry R. C., Buchbinder B. R., Weisskoff R. M., Cohen M. S., Vevea J. M., Brady T. J., Rosen B. R. Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):716–719. doi: 10.1126/science.1948051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisel C. R., Ackerman J. L., Buxton R. B., Garrido L., Belliveau J. W., Rosen B. R., Brady T. J. MR contrast due to microscopically heterogeneous magnetic susceptibility: numerical simulations and applications to cerebral physiology. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Feb;17(2):336–347. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Focal physiological uncoupling of cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism during somatosensory stimulation in human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1140–1144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E., Mintun M. A., Dence C. Nonoxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.3260686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frahm J., Bruhn H., Merboldt K. D., Hänicke W. Dynamic MR imaging of human brain oxygenation during rest and photic stimulation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1992 Sep-Oct;2(5):501–505. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880020505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frostig R. D., Lieke E. E., Ts'o D. Y., Grinvald A. Cortical functional architecture and local coupling between neuronal activity and the microcirculation revealed by in vivo high-resolution optical imaging of intrinsic signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6082–6086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Frostig R. D., Siegel R. M., Bartfeld E. High-resolution optical imaging of functional brain architecture in the awake monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11559–11563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund M. M., Ojemann G. A., Hochman D. W. Optical imaging of epileptiform and functional activity in human cerebral cortex. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):668–671. doi: 10.1038/358668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P., Henkelman R. M. On the transverse relaxation rate enhancement induced by diffusion of spins through inhomogeneous fields. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Feb;17(2):348–356. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910170207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong K. K., Belliveau J. W., Chesler D. A., Goldberg I. E., Weisskoff R. M., Poncelet B. P., Kennedy D. N., Hoppel B. E., Cohen M. S., Turner R. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity during primary sensory stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5675–5679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bihan D., Turner R. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using spin echoes. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Jun;19(2):221–227. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910190206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Lee T. M., Kay A. R., Tank D. W. Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9868–9872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Lee T. M. Magnetic resonance imaging of blood vessels at high fields: in vivo and in vitro measurements and image simulation. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Oct;16(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Lee T. M., Nayak A. S., Glynn P. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of rodent brain at high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Apr;14(1):68–78. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Tank D. W., Menon R., Ellermann J. M., Kim S. G., Merkle H., Ugurbil K. Intrinsic signal changes accompanying sensory stimulation: functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L., Coryell C. D. The Magnetic Properties and Structure of Hemoglobin, Oxyhemoglobin and Carbonmonoxyhemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1936 Apr;22(4):210–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.22.4.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlik G., Rackl A., Bing R. J. Quantitative capillary topography and blood flow in the cerebral cortex of cats: an in vivo microscopic study. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 9;208(1):35–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. R., Belliveau J. W., Vevea J. M., Brady T. J. Perfusion imaging with NMR contrast agents. Magn Reson Med. 1990 May;14(2):249–265. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



