Abstract
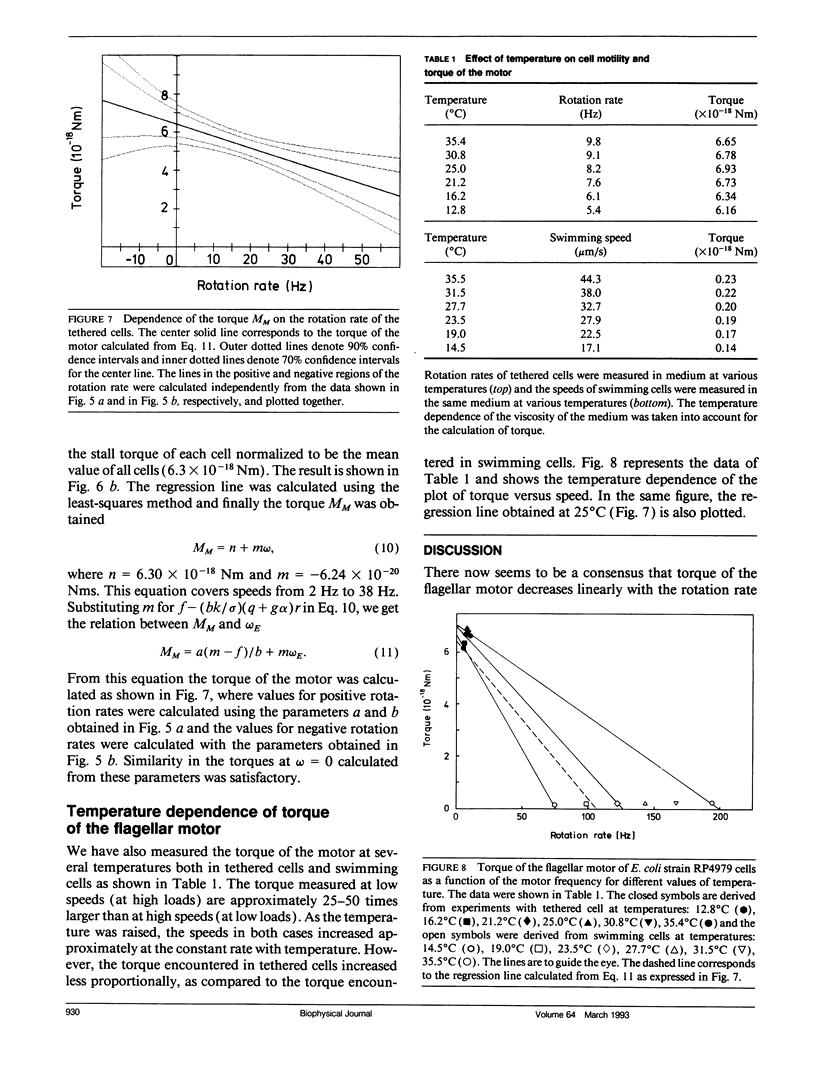
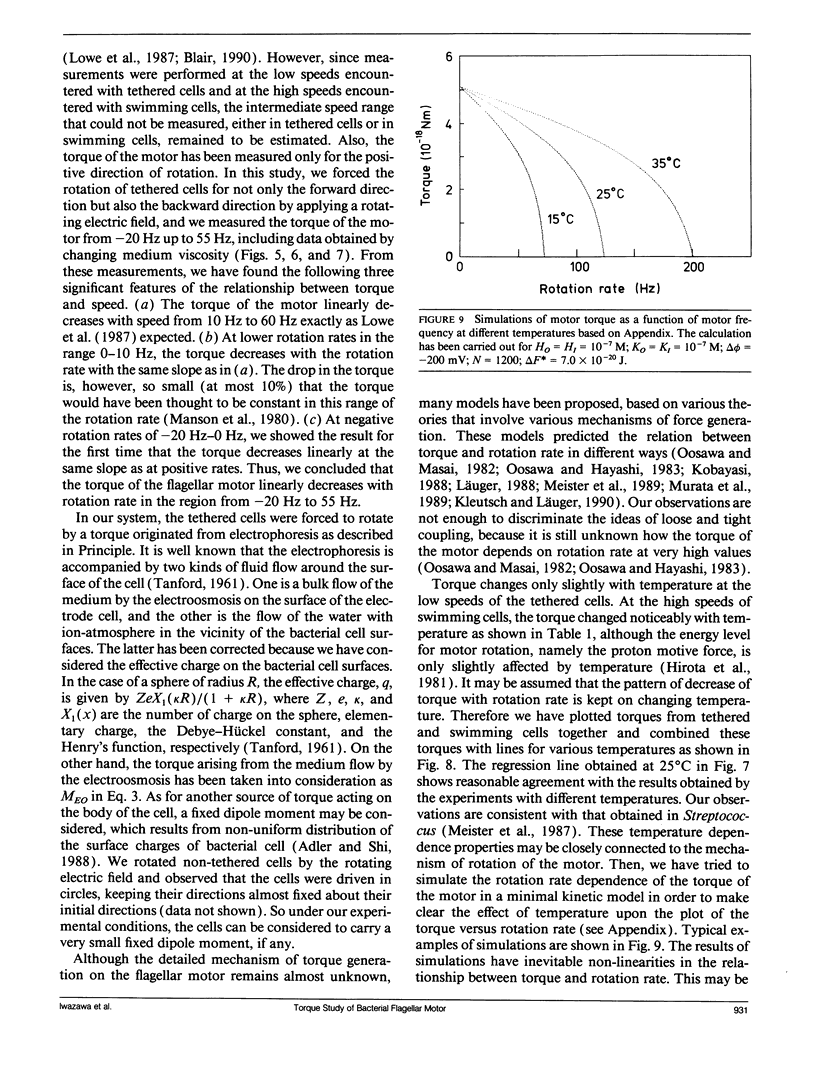
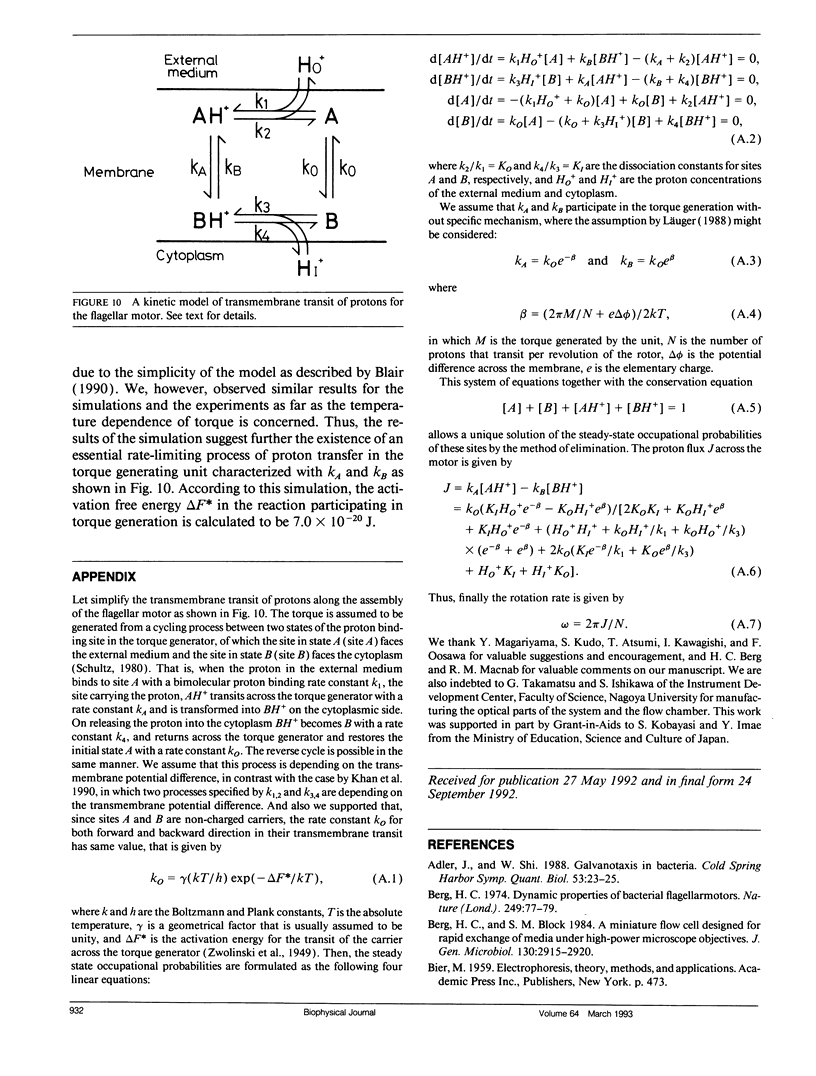
Bacterial flagella are driven by a rotary motor that is energized by an electrochemical ion gradient across the cell membrane. In this study the torque generated by the flagellar motor was measured in tethered cells of a smooth-swimming Escherichia coli strain by using rotating electric fields to determine the relationship between the torque and speed over a wide range. By measuring the electric current applied to the sample cell and combining the data obtained at different viscosities, the torque of the flagellar motor was estimated up to 55 Hz, and also at negative rotation rates. By this method we have found that the torque of the flagellar motor linearly decreases with rotation rate from negative through positive rate of rotation. In addition, the dependence of torque upon temperature was also investigated. We showed that torque at the high speeds encountered in swimming cells had a much steeper dependence on temperature that at the low speeds encountered in tethered cells. From these results, the activation energy of the proton transfer reaction in the torque-generating unit was calculated to be about 7.0 x 10(-20) J.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Shi W. Galvanotaxis in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):23–25. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Dynamic properties of bacterial flagellar motors. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):77–79. doi: 10.1038/249077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F. The bacterial flagellar motor. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Imae Y. Na+-driven flagellar motors of an alkalophilic Bacillus strain YN-1. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10577–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Matsuura S., Mochizuki N., Mutoh N., Imae Y. Use of lipophilic cation-permeable mutants for measurement of transmembrane electrical potential in metabolizing cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):399–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.399-405.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Matsukura H., Kobayasi S. Sodium-driven flagellar motors of alkalophilic Bacillus. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:582–592. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Aizawa S. The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109–172. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Humayun I. Energy transduction in the bacterial flagellar motor. Effects of load and pH. Biophys J. 1990 Apr;57(4):779–796. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82598-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayasi S., Maeda K., Imae Y. Apparatus for detecting rate and direction of rotation of tethered bacterial cells. Rev Sci Instrum. 1977 Apr;48(4):407–410. doi: 10.1063/1.1135033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Torque and rotation rate of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83065-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P. M., Berg H. C. Energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsura S., Shioi J., Imae Y. Motility in Bacillus subtilis driven by an artificial protonmotive force. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Berg H. C. The stall torque of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):413–419. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83230-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Caplan S. R., Berg H. C. Dynamics of a tightly coupled mechanism for flagellar rotation. Bacterial motility, chemiosmotic coupling, protonmotive force. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82889-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Lowe G., Berg H. C. The proton flux through the bacterial flagellar motor. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):643–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Yano M., Shimizu H. A model for bacterial flagellar motor: free energy transduction and self-organization of rotational motion. J Theor Biol. 1989 Aug 22;139(4):531–559. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(89)80069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Shimada K., Asakura S. Cinemicrographic analysis of the movement of flagellated bacteria. I. The ratio of the propulsive velocity to the frequency of bodily rotation. J Mechanochem Cell Motil. 1975;3(2):87–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


