Abstract
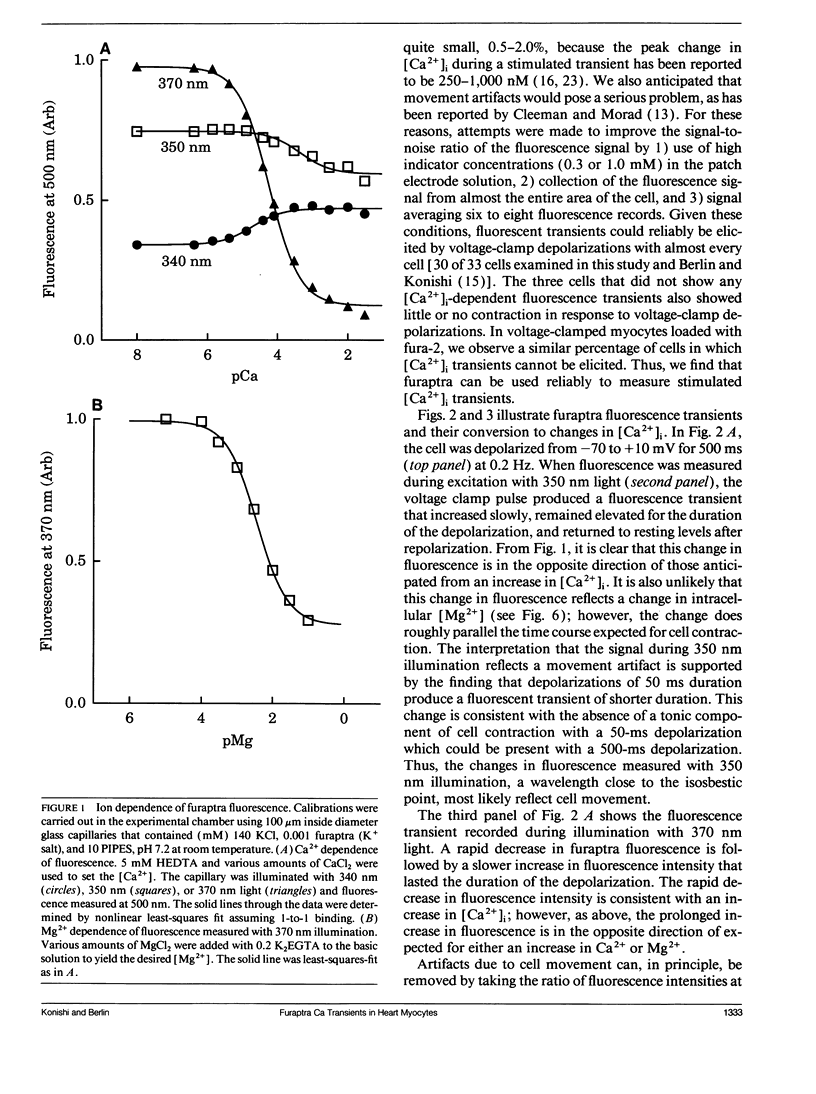
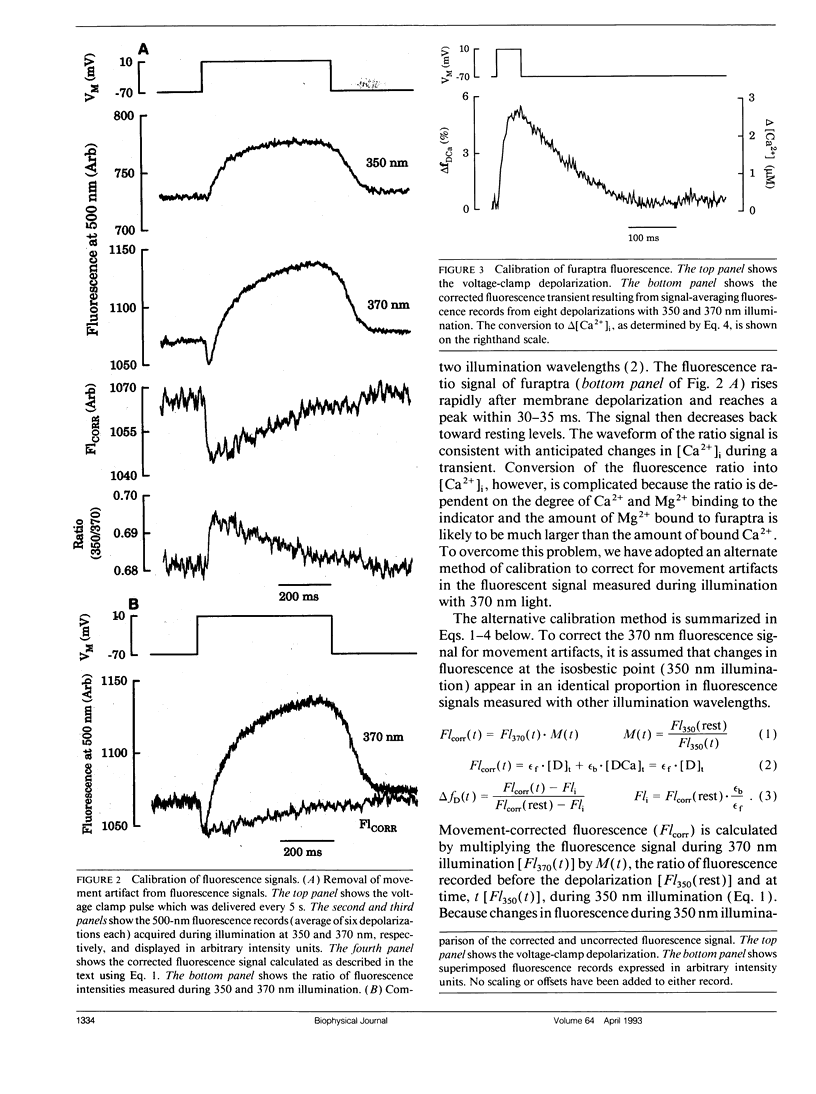
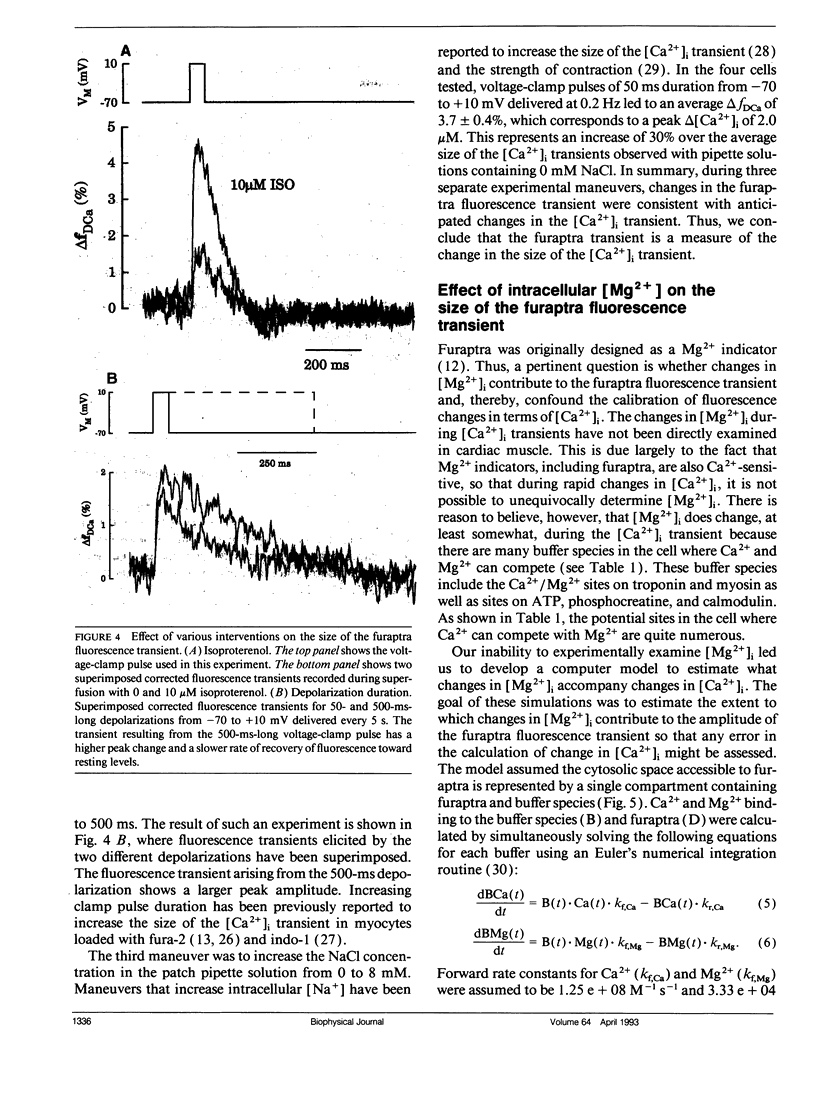
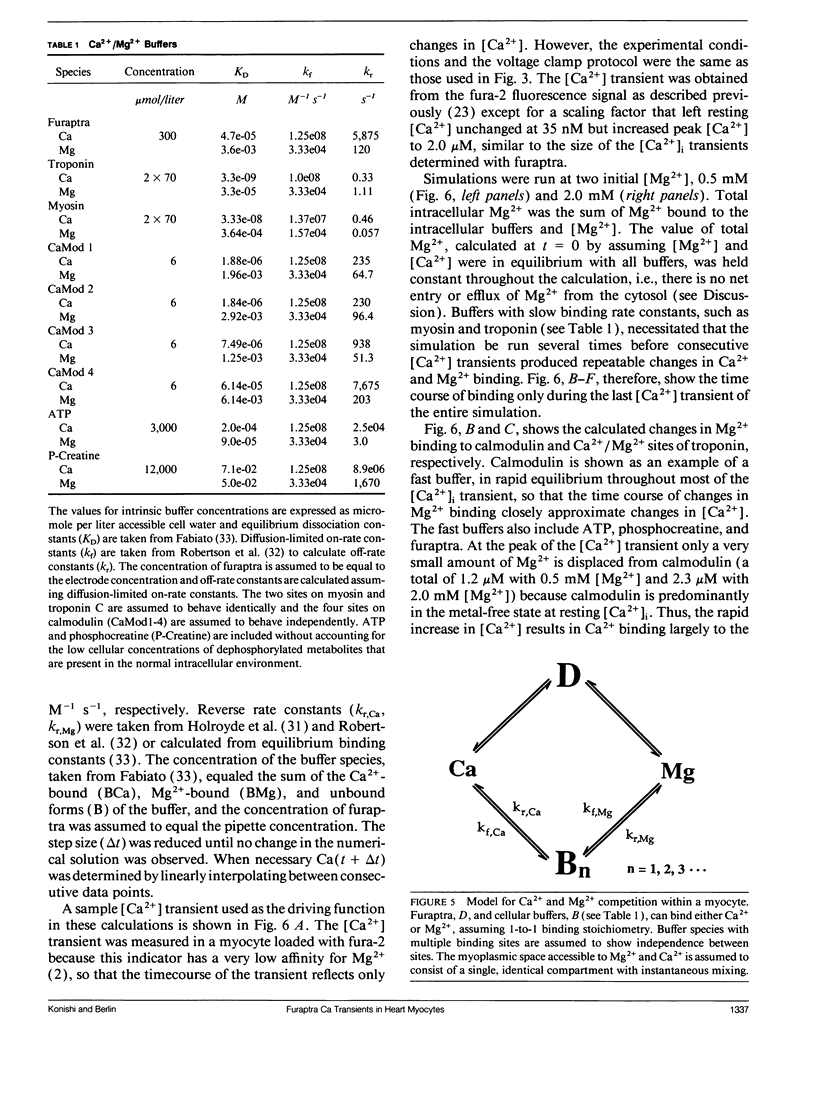
Intracellular calcium ion ([Ca2+]i) transients were measured in single rat ventricular myocytes with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. Cells were voltage clamped with a single patch electrode containing the K+ salt of furaptra and fluorescence at 500 nm was measured during illumination with 350 and 370 nm light. Depolarizing voltage-clamp pulses elicited [Ca2+]-dependent fluorescent transients in 30 of 33 cells tested. The peak change in [Ca2+]i elicited by 50-ms depolarizations from -70 to +10 mV was 1.52 +/- 0.25 microM (mean +/- SEM, n = 7). The size of the [Ca2+]i transient increased in response to 10 microM isoproterenol, prolongation of the depolarization, and increasing pipette [Na+]. Because furaptra is sensitive to Ca2+ and Mg2+, changes in [Mg2+]i during the [Ca2+]i transient could not be measured. Instead, a single-compartment model was developed to simulate changes in [Mg2+] during [Ca2+] transients. The simulations predicted that a 2 microM [Ca2+] transient was accompanied by a slow increase in [Mg2+] (14-29 microM), which became larger as basal [Mg2+] increased (0.5-2.0 mM). The [Mg2+] transient reached a peak approximately 1 s after the peak of the [Ca2+] transient with the slow changes in [Mg2+] dominated by competition at the Ca2+/Mg2+ sites of Troponin. These changes in [Mg2+], however, were so small and slow that they were unlikely to affect the furaptra fluorescence signal at the peak of the [Ca2+]i transient. The [Ca2+]i transient reported by furaptra appears to be larger than that reported by other Ca2+ indicators; however, we conclude this larger transient is at least as accurate as [Ca2+]i transients reported by the other indicators.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R. Calcium transients in aequorin-injected frog cardiac muscle. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):509–513. doi: 10.1038/273509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Optical measurements of intracellular pH and magnesium in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:105–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. Cellular origins of the transient inward current in cardiac myocytes. Role of fluctuations and waves of elevated intracellular calcium. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):115–126. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Lederer W. J., Berlin J. R. Intracellular Ca transients in rat cardiac myocytes: role of Na-Ca exchange in excitation-contraction coupling. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C944–C954. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., McGuigan J. A. Estimation of the upper limit of the free magnesium concentration measured with Mg-sensitive microelectrodes in ferret ventricular muscle: (1) use of the Nicolsky-Eisenman equation and (2) in calibrating solutions of the appropriate concentration. Magnesium. 1988;7(3):154–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Intracellular diffusion, binding, and compartmentalization of the fluorescent calcium indicators indo-1 and fura-2. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R. Use of calcium-regulated photoproteins as intracellular Ca2+ indicators. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:164–203. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Effect of membrane potential changes on the calcium transient in single rat cardiac muscle cells. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1419–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2446391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Intracellular calcium in cardiac myocytes: calcium transients measured using fluorescence imaging. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1987;42:201–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. A novel experimental chamber for single-cell voltage-clamp and patch-clamp applications with low electrical noise and excellent temperature and flow control. Pflugers Arch. 1986 May;406(5):536–539. doi: 10.1007/BF00583378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleemann L., Morad M. Role of Ca2+ channel in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in the rat: evidence from Ca2+ transients and contraction. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:283–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. The quantitative relationship between twitch tension and intracellular sodium activity in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:251–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. M., Bers D. M. The effect of temperature and ionic strength on the apparent Ca-affinity of EGTA and the analogous Ca-chelators BAPTA and dibromo-BAPTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Wier W. G. Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Effects of caffeine on the intracellular [Ca2+] transient, membrane currents, and contraction. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):417–433. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holroyde M. J., Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Solaro R. J., Potter J. D. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on cardiac troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11688–11693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Indo-1 binding to protein in permeabilized ventricular myocytes alters its spectral and Ca binding properties. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81597-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaguma Y., Kurobe N., Shinohara H., Kato K. Sensitive immunoassay for rat parvalbumin: tissue distribution and developmental changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 2;1075(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90076-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Maylie J., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Simultaneous monitoring of changes in magnesium and calcium concentrations in frog cut twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):585–608. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenlohr H. L., Metcalfe J. C., Morris P. G., Rodrigo G. C., Smith G. A. Ca2+ transient, Mg2+, and pH measurements in the cardiac cycle by 19F NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9017–9021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Szucs G., Schneider M. F. Simultaneous recording of calcium transients in skeletal muscle using high- and low-affinity calcium indicators. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):971–988. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83178-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers monitored with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):271–301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort A. A., Lakatta E. G. Calcium-dependent mechanical oscillations occur spontaneously in unstimulated mammalian cardiac tissues. Circ Res. 1984 Apr;54(4):396–404. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.4.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusuoka H., Koretsune Y., Chacko V. P., Weisfeldt M. L., Marban E. Excitation-contraction coupling in postischemic myocardium. Does failure of activator Ca2+ transients underlie stunning? Circ Res. 1990 May;66(5):1268–1276. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.5.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Altschuld R. A., Stokes B. T. Quantitation of intracellular free calcium in single adult cardiomyocytes by fura-2 fluorescence microscopy: calibration of fura-2 ratios. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Kitakaze M., Koretsune Y., Yue D. T., Chacko V. P., Pike M. M. Quantification of [Ca2+]i in perfused hearts. Critical evaluation of the 5F-BAPTA and nuclear magnetic resonance method as applied to the study of ischemia and reperfusion. Circ Res. 1990 May;66(5):1255–1267. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.5.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Freudenrich C. C., Lieberman M. Cellular magnesium and Na/Mg exchange in heart cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:273–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Steenbergen C., Levy L. A., Raju B., London R. E. Cytosolic free magnesium levels in ischemic rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5622–5627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju B., Murphy E., Levy L. A., Hall R. D., London R. E. A fluorescent indicator for measuring cytosolic free magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C540–C548. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., McClellan G., Gonzalez-Serratos H., Somlyo A. P. Electron probe X-ray microanalysis of post-tetanic Ca2+ and Mg2+ movements across the sarcoplasmic reticulum in situ. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6801–6807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Yue D. T. Intracellular calcium transients underlying the short-term force-interval relationship in ferret ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- duBell W. H., Houser S. R. Voltage and beat dependence of Ca2+ transient in feline ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):H746–H759. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.3.H746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


