Abstract
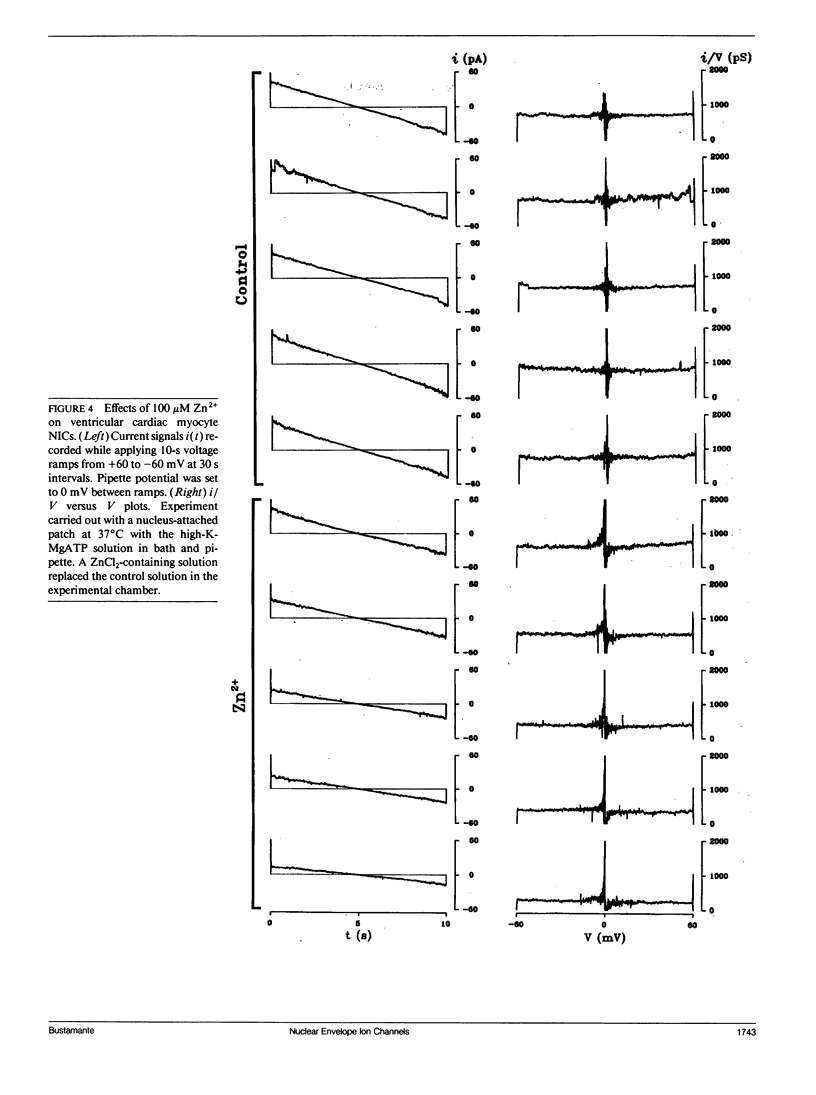
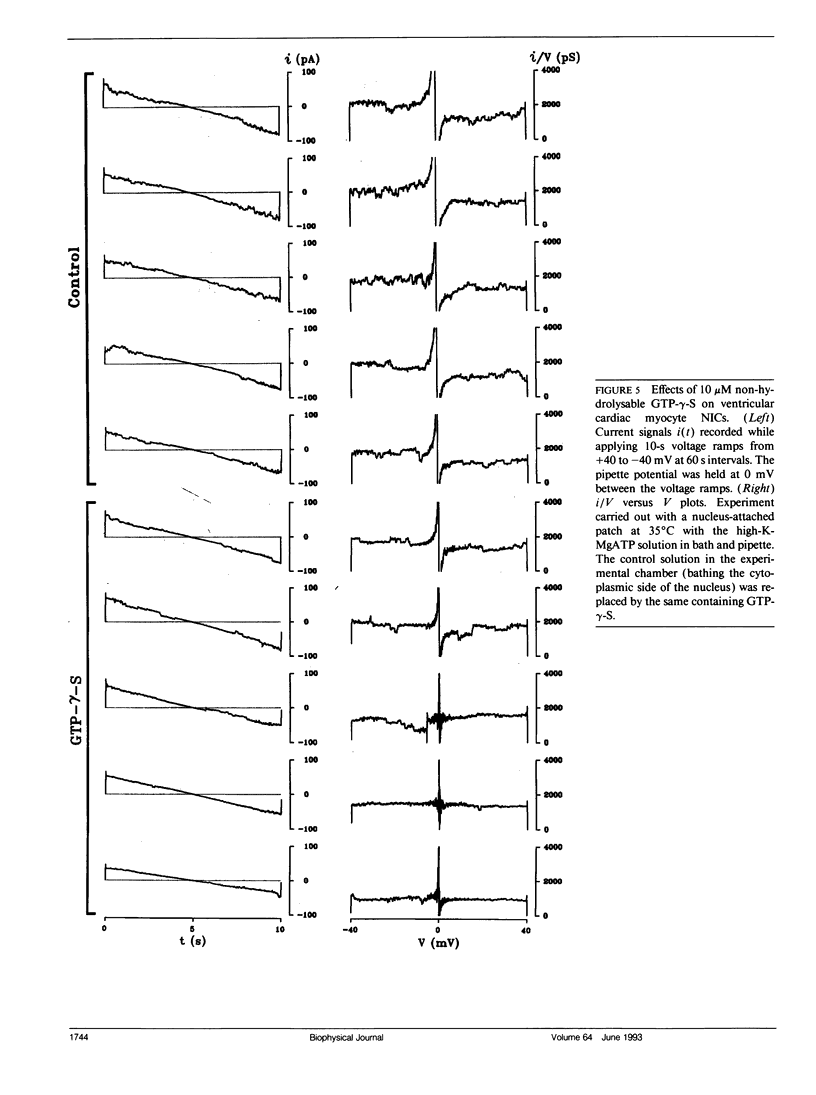
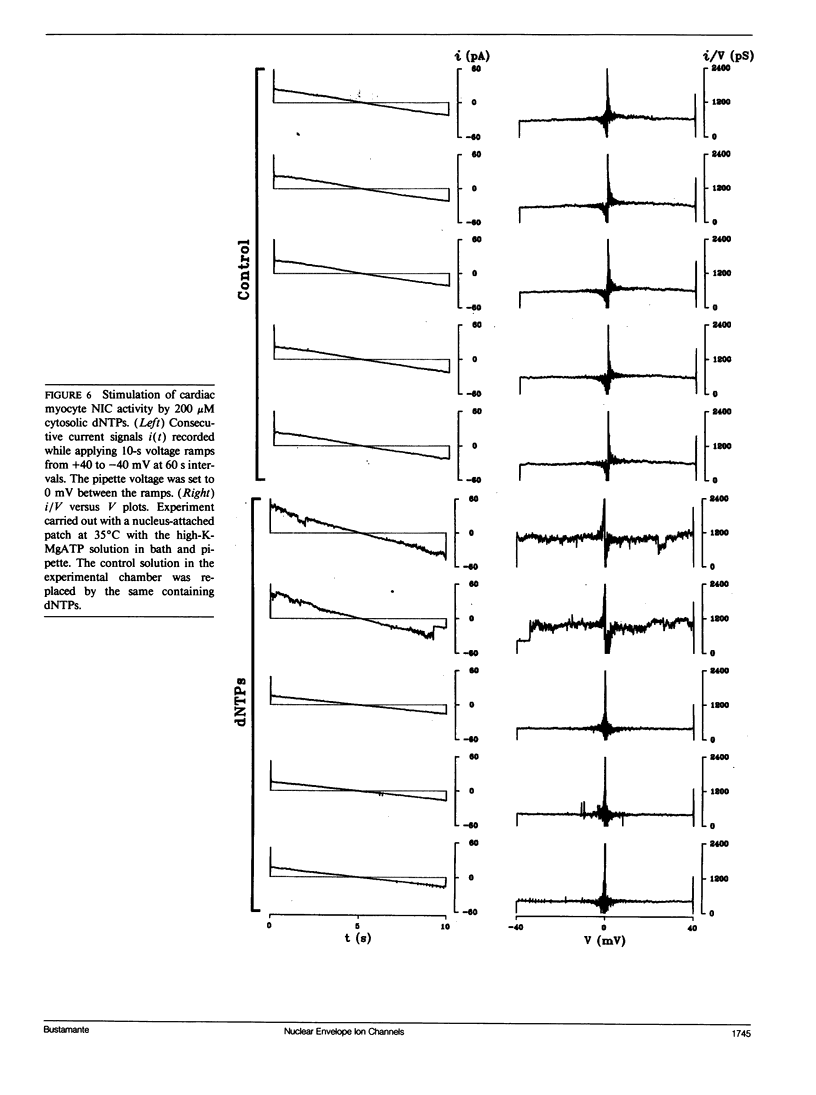
Flow of small ions across the nuclear envelope (NE) is thought to occur without restriction through large diameter nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). However, investigations with electron and fluorescence microscopy, and with patch-clamp and microelectrode electrophysiology, suggest that in many animal and plant cell types small ions move through a barrier having the signature of large conductance nuclear ion channels (NICs). As nucleocytoplasmic transport and gene activity are regulated by cytoplasmic signals and as it has recently been shown by this investigator that cardiac NICs are sensitive to cAMP-dependent processes (1), it was considered relevant to further investigate the effects of various cytosolic signals on NIC activity. Ion species substitution demonstrated that K+ is the major species responsible for NIC currents. The Na-channel blocker tetrodotoxin (TTX, 100 microM) and the Ca-channel blocker diltiazem (100 microM) had no effect, indicating no relation of NICs to Na- or Ca-channels in transit to the cell surface membrane. Zn2+ (100 microM) blocked NIC activity, suggesting a dual role in nucleocytoplasmic transport and gene function. GTP did not produce measurable effect. However, its nonhydrolyzable analogue GTP-gamma-S (10 microM) suppressed NIC activity, suggesting a role for GTP hydrolysis in NIC function. Deoxynucleotides (dNTPs, 200 microM) produced a transient increase in NIC activity, pointing to a modulation of NIC function by nucleic acid substrates. These results indicate a role for NICs in mediating: (a) control of gene activity by transduction and other cytosolic signals, and (b) nuclear demands and response to such signals.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Marr R. S., Gerace L. Nuclear protein import in permeabilized mammalian cells requires soluble cytoplasmic factors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):807–816. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Probing the structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;2(3):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. Single-channel dose-response studies in single, cell-attached patches. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):660–670. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82095-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman A. L., Delannoy M. R., Wilson K. L. GTP hydrolysis is required for vesicle fusion during nuclear envelope assembly in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):281–294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. The nuclear envelope and nuclear transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):514–520. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O. A system for the automated data-acquisition of fast transient signals in excitable membranes. Int J Biomed Comput. 1988 May-Jun;22(3-4):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(88)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O. An inexpensive inverted microscope for patch-clamp and other electrophysiological studies at the cellular level. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jul;418(6):608–610. doi: 10.1007/BF00370578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O., Jachimowicz D. Cryopreservation of human heart cells. Cryobiology. 1988 Oct;25(5):394–408. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(88)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O. Nuclear ion channels in cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Aug;421(5):473–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00370259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O., Watanabe T., McDonald T. F. Nonspecific proteases: a new approach to the isolation of adult cardiocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;60(7):997–1002. doi: 10.1139/y82-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante J. O., Watanabe T., McDonald T. F. Single cells from adult mammalian heart: isolation procedure and preliminary electrophysiological studies. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;59(8):907–910. doi: 10.1139/y81-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Century T. J., Fenichel I. R., Horowitz S. B. The concentrations of water, sodium and potassium in the nucleus and cytoplasm of amphibian oocytes. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jul;7(1):5–13. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I. Control of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):424–429. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. The nuclear membrane. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):942–947. doi: 10.1126/science.1439805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C. Protein structure: plugging the nuclear pore. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):512–514. doi: 10.1038/346512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C. Transport across the nuclear envelope: enigmas and explanations. Bioessays. 1991 May;13(5):213–218. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes A. M., Morales M. C., Handa V., Moore J. A., Alvarez M. R. Nuclear size and DNA content in rat cardiac myocytes during growth, maturation and aging. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Jul;23(7):833–839. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Diacumakos E. G. The electrophysiological mapping of compartments within a mammalian cell. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):86–103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakes D. J., Berezney R. Molecular cloning of matrin F/G: A DNA binding protein of the nuclear matrix that contains putative zinc finger motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6186–6190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanover J. A. The nuclear pore: at the crossroads. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2288–2295. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1312045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Adams P. R. Subcellular calcium transients visualized by confocal microscopy in a voltage-clamped vertebrate neuron. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2154851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Connor J. A. Stimulus-induced nuclear Ca2+ signals in fura-2-loaded amphibian neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:416–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw J. E., Carragher B. O., Milligan R. A. Architecture and design of the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90635-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. B., Paine P. L. Cytoplasmic exclusion as a basis for asymmetric nucleocytoplasmic solute distributions. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):151–153. doi: 10.1038/260151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnik M., Aebi U. Toward a more complete 3-D structure of the nuclear pore complex. J Struct Biol. 1991 Dec;107(3):291–308. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(91)90054-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANNO Y., LOEWENSTEIN W. R. A STUDY OF THE NUCLEUS AND CELL MEMBRANES OF OOCYTES WITH AN INTRA-CELLULAR ELECTRODE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Jun;31:149–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Ashman R. F., Loewenstein W. R. Nucleus and cell membrane conductance in marine oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Aug;39(1):184–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Signal transduction and gene control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90075-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R., KANNO Y. Some electrical properties of the membrane of a cell nucleus. Nature. 1962 Aug 4;195:462–464. doi: 10.1038/195462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R., KANNO Y. The electrical conductance and potential across the membrane of some cell nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:421–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R., Kanno Y., Ito S. Permeability of nuclear membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):708–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of a nuclear membrane: changes during normal development and changes induced by growth hormone. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):909–910. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke A. J., Behensky C., Weiger T., Matzke M. A. A large conductance ion channel in the nuclear envelope of a higher plant cell. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 4;302(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80290-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke A. J., Weiger T. M., Matzke M. A. Detection of a large cation-selective channel in nuclear envelopes of avian erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzanti M., DeFelice L. J., Cohn J., Malter H. Ion channels in the nuclear envelope. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):764–767. doi: 10.1038/343764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzanti M., DeFelice L. J., Smith E. F. Ion channels in murine nuclei during early development and in fully differentiated adult cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(2):189–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01870532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam S. C., Hockberger P. E. Divalent ions released from stainless steel hypodermic needles reduce neuronal calcium currents. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Jan;420(1):106–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00378649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. An N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive cytosolic factor necessary for nuclear protein import: requirement in signal-mediated binding to the nuclear pore. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):547–557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Baeuerle P. A., Lührmann R. Nuclear import-export: in search of signals and mechanisms. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90135-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L. Nucleocytoplasmic movement of fluorescent tracers microinjected into living salivary gland cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):652–657. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przywara D. A., Bhave S. V., Bhave A., Wakade T. D., Wakade A. R. Stimulated rise in neuronal calcium is faster and greater in the nucleus than the cytosol. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):217–222. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.2004666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. G proteins in cellular control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabares L., Mazzanti M., Clapham D. E. Chloride channels in the nuclear membrane. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jul;123(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01993962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu T., Wier W. G. High temporal resolution video imaging of intracellular calcium. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waybill M. M., Yelamarty R. V., Zhang Y. L., Scaduto R. C., Jr, LaNoue K. F., Hsu C. J., Smith B. C., Tillotson D. L., Yu F. T., Cheung J. Y. Nuclear calcium gradients in cultured rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):E49–E57. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.1.E49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J., Spiro D., Loewenstein W. R. Ultrastructure and permeability of nuclear membranes. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):107–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wonderlin W. F., French R. J. Ion channels in transit: voltage-gated Na and K channels in axoplasmic organelles of the squid Loligo pealei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4391–4395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong I., Lohman T. M. Allosteric effects of nucleotide cofactors on Escherichia coli Rep helicase-DNA binding. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):350–355. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]