Abstract
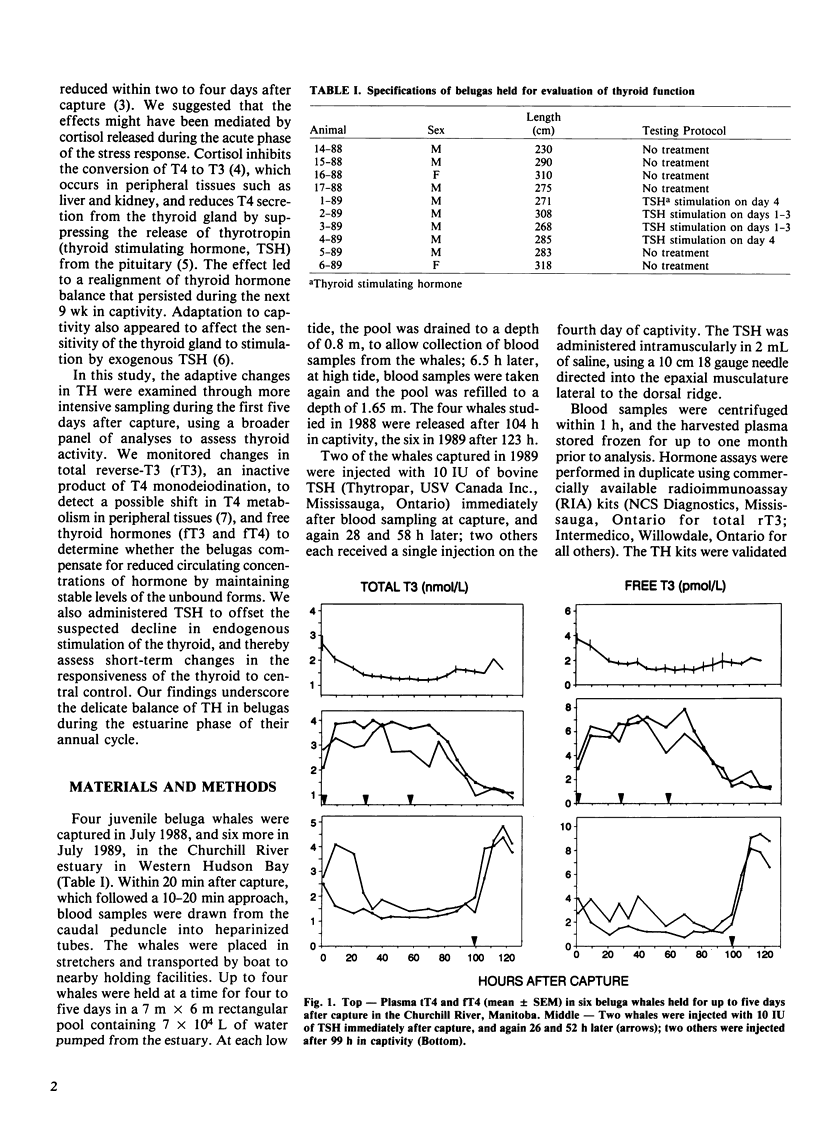
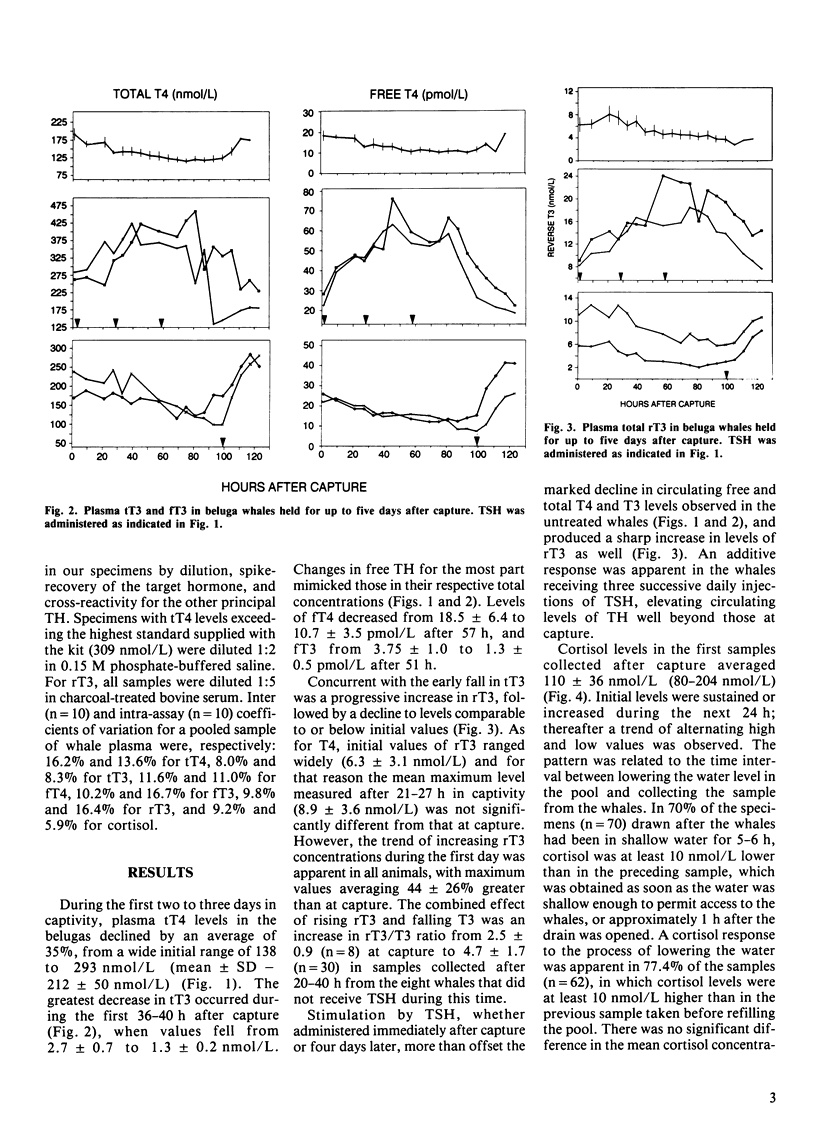
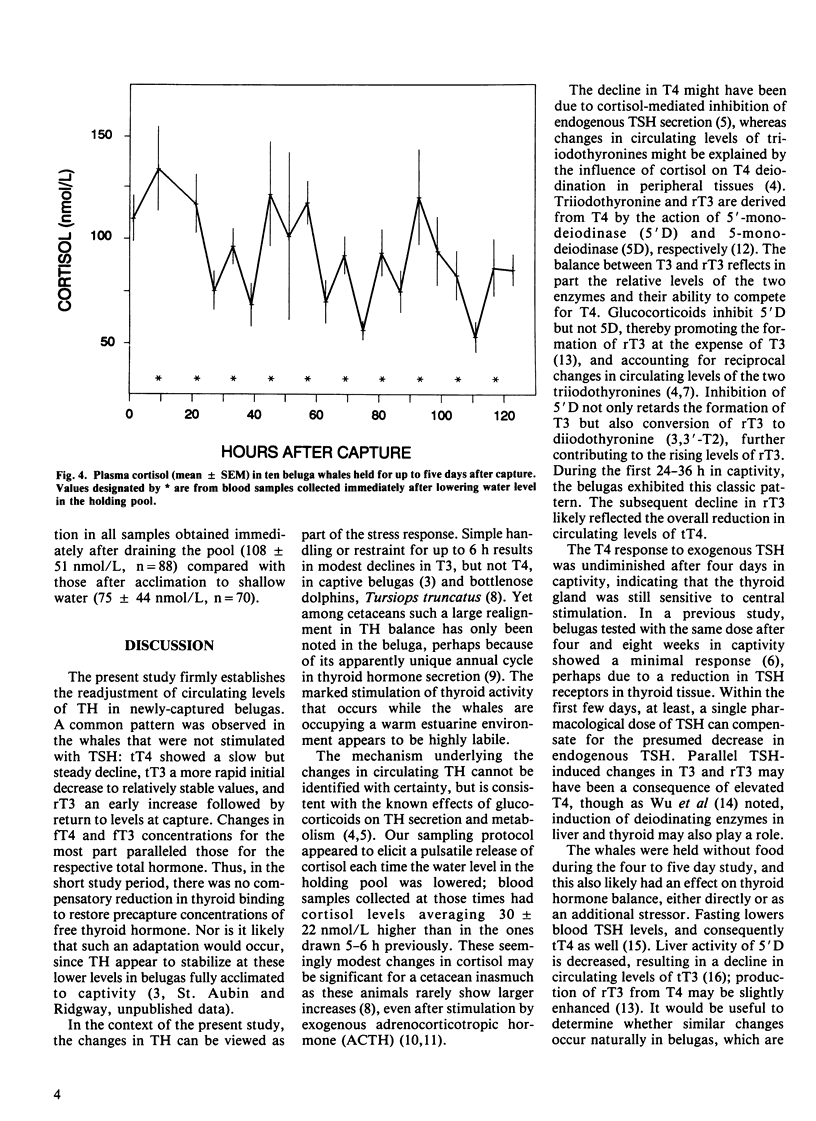
Ten beluga whales, Delphinapterus leucas, were captured in the Churchill River, Manitoba, held for up to five days, and then released. Blood samples were obtained immediately after capture and at 6-7 h intervals thereafter to monitor changes in circulating levels of thyroid hormones (TH). In six of the whales, total and free thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) declined steadily, whereas reverse-T3 (rT3) showed a transient increase during the first 24-36 h, followed by a decrease to below initial values. The changes in TH may have been due to glucocorticoid-mediated reduction in endogenous thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), and inhibition of 5'-monodeiodinase in peripheral tissue. Two whales were given 10 IU of bovine TSH immediately after capture, and again one and two days later, resulting in successive increases in all TH, which remained elevated for at least 24 h after the last injection. Thereafter, circulating levels declined as in the untreated whales. Two whales receiving a single TSH injection on the fourth day responded with an increase in plasma TH comparable to that observed following the first TSH injection in the other two animals. Average (+/- SD) circulating level of rT3 at capture was 6.3 +/- 3.1 nmol/L, which is higher than reported for any other mammal and was significantly correlated with the naturally elevated levels of T4 that occur in belugas occupying estuaries during the summer.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balsam A., Ingbar S. H. The influence of fasting, diabetes, and several pharmacological agents on the pathways of thyroxine metabolism in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):415–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI109143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. C., Nunes M. T., Hell N. S., Maciel R. M. The role of glucocorticoids in the stress-induced reduction of extrathyroidal 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine generation in rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):1033–1038. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Chopra U., Smith S. R., Reza M., Solomon D. H. Reciprocal changes in serum concentrations of 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in systemic illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1043–1049. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Williams D. E., Orgiazzi J., Solomon D. H. Opposite effects of dexamethasone on serum concentrations of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3) and 3,3'5-triiodothyronine (T3). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Nov;41(5):911–920. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-5-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kock M. D., Clark R. K., Franti C. E., Jessup D. A., Wehausen J. D. Effects of capture on biological parameters in free-ranging bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis): evaluation of normal, stressed and mortality outcomes and documentation of postcapture survival. J Wildl Dis. 1987 Oct;23(4):652–662. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-23.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P., Vigas M., Kvetnanský R., Földes O., Culman J. Immediate increase of thyroid hormone release during acute stress in rats: effect of biogenic amines rather than that of TSH? Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Dec;104(4):443–449. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1040443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlov M. M., Mukhlia A. M., Kulikov N. A. Gormonal'nye pokazateli u del'fina Turpsiops truncatus v norme i v dinamike éksperimental'nogo stressa. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol. 1988 Jul-Aug;24(4):557–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Lum S. M., Wilber J. F., Kaptein E. M., Nicoloff J. T. Dynamics of serum thyrotropin and thyroid hormone changes in fasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 May;56(5):883–888. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-5-883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Aubin D. J. Stimulation of thyroid hormone secretion by thyrotropin in beluga whales, Delphinapterus leucas. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jul;51(3):409–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilber J. F., Utiger R. D. The effect of glucocorticoids on thyrotropin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2096–2103. doi: 10.1172/JCI106176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Reggio R., Florsheim W. H. Characterization of thyrotropin-induced increase in iodothyronine monodeiodinating activity in mice. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):901–908. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y. The effect of fasting on thyroidal T4-5' monodeiodinating activity in mice. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1990 Feb;122(2):175–180. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1220175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


