Abstract
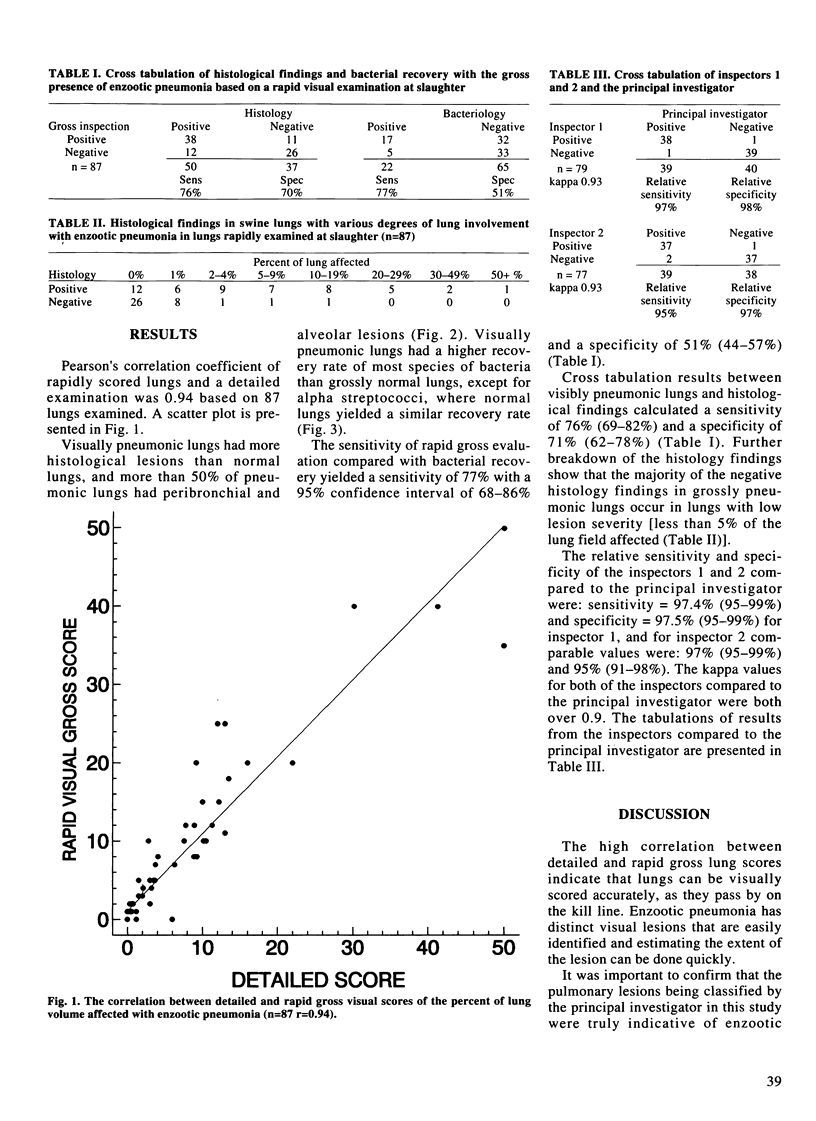
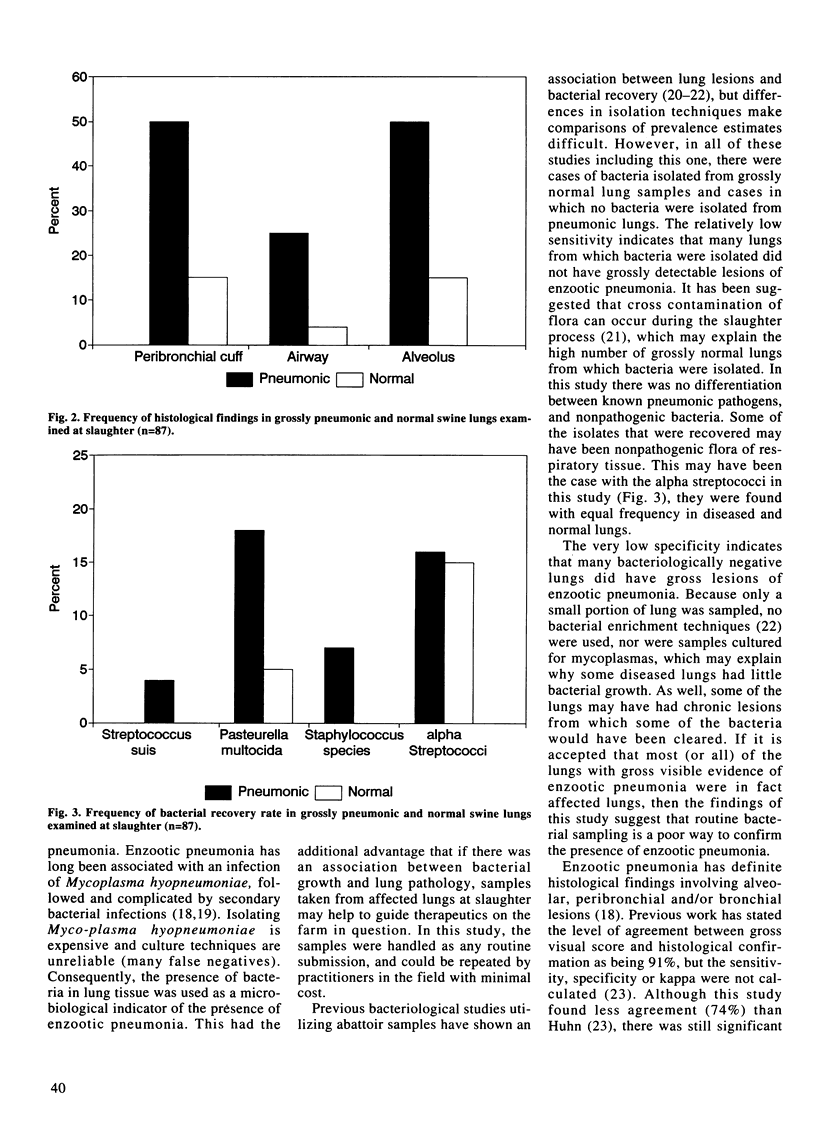
A rapid gross visual appraisal of enzootic pneumonia lesions was made of 87 lungs at a local abattoir and the lungs were then set aside and examined in more detail. A sample of pulmonary tissue was taken from each lung and submitted for bacterial and histological examination. The principal investigator who had performed the gross and detailed lung scores was then used to assess the agreement of two inspectors who were scoring lung lesions in the abattoir. The Pearson's correlation coefficient between grossly scored lungs and scores derived from a detailed examination was 0.94. Using histological examination as the gold standard, rapid gross examination had a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 71%. Using bacterial recovery as a gold standard yielded a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 51%. The sensitivity and specificity of inspectors 1 and 2 compared to the principal investigator were: sensitivity = 97.5% and specificity = 97.4% for inspector 1, and 97% and 98% for inspector 2. The kappa values for both of the inspectors compared to the principal investigator were 0.95 suggesting that designated lay inspectors consistently agreed with the principal investigator.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardo T. M., Dohoo I. R., Donald A. Effect of ascariasis and respiratory diseases on growth rates in swine. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Apr;54(2):278–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohoo I. R. Animal productivity and health information network. Can Vet J. 1988 Mar;29(3):281–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. J., Penny R. H., Mulley R. Enzootic pneumonia of pigs: the incidence of pneumonic lesions seen in an abattoir in New South Wales. Aust Vet J. 1971 Oct;47(10):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1971.tb02027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn R. G. Swine enzootic pneumonia: incidence and effect on rate of body weight gain. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Jun;31(6):1097–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist J. O. Animal health and environment in the production of fattening pigs. A study of disease incidence in relation to certain environmental factors, daily weight gain and carcass classification. Acta Vet Scand Suppl. 1974;(51):1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. B., Hilley H. D., Leman A. D. Comparison of methods for assessing the prevalence and extent of pneumonia in market weight Swine. Can Vet J. 1985 Dec;26(12):381–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. B., Pijoan C., Hilley H. D., Rapp V. Microorganisms associated with pneumonia in slaughter weight swine. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Apr;49(2):129–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne A. D., Saunders J. R., K-Sebunya T. An abattoir survey of the incidence of pneumonia in Saskatchewan swine and an investigation of the microbiology of affected lungs. Can Vet J. 1981 Apr;22(4):82–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pijoan C., Lastra A., Ramirez C., Leman A. D. Isolation of toxigenic strains of Pasteurella multocida from lungs of pneumonic swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Sep 1;185(5):522–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straw B. E., Tuovinen V. K., Bigras-Poulin M. Estimation of the cost of pneumonia in swine herds. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1989 Dec 15;195(12):1702–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


