Abstract
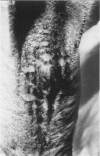
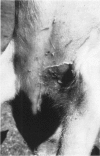
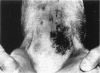
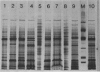
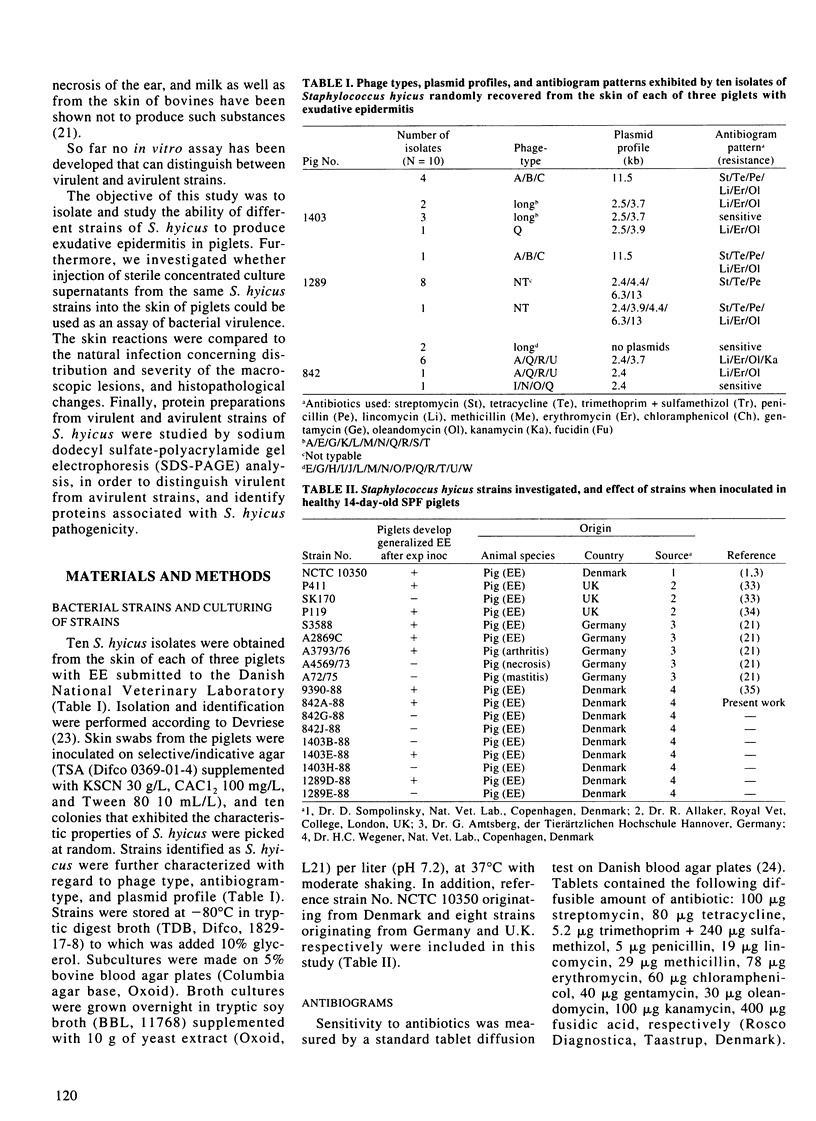
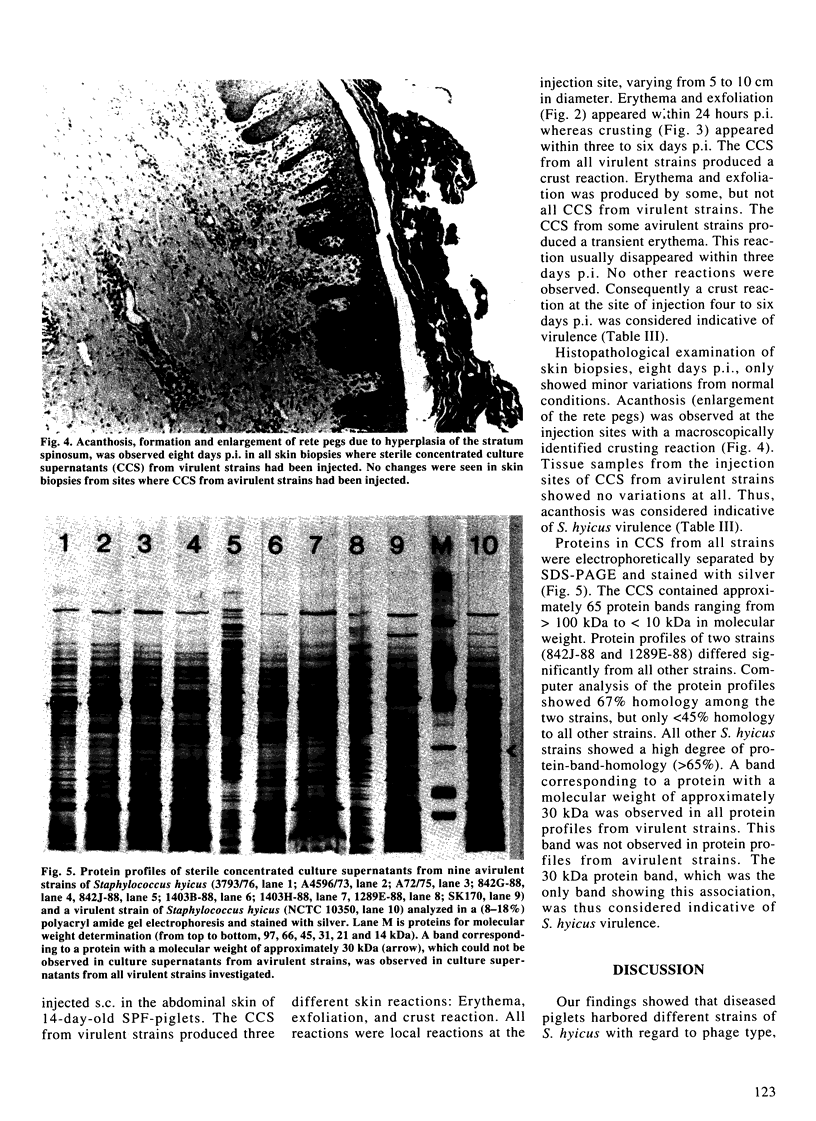
Staphylococcus hyicus strains with different phage types, plasmid profiles, and antibiotic resistance patterns were isolated from piglets with exudative epidermitis. The strains could be divided into virulent strains, producing exudative epidermitis, and avirulent strains, producing no dermal changes when injected in experimental piglets. The results showed that both virulent and avirulent strains were present simultaneously on diseased piglets. This constitutes a diagnostic problem. Concentrated culture supernatants from nine virulent strains injected in the skin of healthy piglets produced a crusting reaction in all piglets. Acanthosis was observed in the histopathological examination of the crustaceous skin. Concentrated culture supernatants from nine avirulent strains produced no macroscopic or microscopic skin changes. Protein profiles from all virulent strains and seven out of nine avirulent strains showed a high degree of protein band homology. An approximately 30 kDa protein present in all concentrated culture supernatants capable of producing skin changes, could not be detected in samples that did not produce skin changes. No other protein showed a similar association. It is concluded that crusting reaction of piglet skin is a suitable indicator of virulence in S. hyicus in relation to exudative epidermitis, and that virulent strains produce a 30 kDa protein, absent in concentrated culture supernatants from avirulent strains. This 30 kDa protein might be an exfoliative toxin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaker R. P., Lloyd D. H., Smith I. M. Prevention of exudative epidermitis in gnotobiotic piglets by bacterial interference. Vet Rec. 1988 Dec 3;123(23):597–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amtsberg G., Hazem S. Vergleichende experimentelle Untersuchungen zum Nachweis der Pathogenität von Staphylococcus hyicus des Schweines bzw. von Staphylococcus epidermis Biotyp 2 des Rindes an gnotobiotischen Ferkeln und Kaninchen. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1978 Aug 1;91(15):299–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amtsberg G. Nachweis von Exfoliation auslösenden Substanzen in Kulturen von Staphylococcus hyicus des Schweines und Staphylococcus epidermidis Biotyp 2 des Rindes. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1979 May;26(4):257–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amtsberg G. Tierexperimentelle Untersuchungen zur Pathogenese des lokalen und generalisierten Nässenden Ekzems sowie der durch Staphylococcus hyicus verursachten Polyarthritis der Schweine. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1978 Nov 5;85(11):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amtsberg G. Vergleichende biochemische und serologische Untersuchungen an Staphylokokken von Schweinen und Rindern unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Staphylococcus hyicus bzw. Staphylococcus epidermidis Biotyp 2. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1979 Mar;26(2):137–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheville N. F., Tappe J., Ackermann M., Jensen A. Acute fibrinopurulent blepharitis and conjunctivitis associated with Staphylococcus hyicus, Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus sp. in chickens and turkeys. Vet Pathol. 1988 Sep;25(5):369–375. doi: 10.1177/030098588802500506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirino-Trejo M., Wheler C. Saskatchewan. Conjunctivitis associated with Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus in an ostrich. Can Vet J. 1989 Sep;30(9):759–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Derycke J. Staphylococcus hyicus in cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 May;26(3):356–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus hyicus. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):787–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Thelissen M. Staphylococcus hyicus in donkeys. Vet Rec. 1986 Jan 18;118(3):76–76. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.3.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Vlaminck K., Nuytten J., De Keersmaecker P. Staphylococcus hyicus in skin lesions of horses. Equine Vet J. 1983 Jul;15(3):263–265. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1983.tb01786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D., Todd J. N., Larkin M. Exudative epidermitis of pigs. The serological identification and distribution of the associated staphylococcus. Br Vet J. 1970 May;126(5):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J. Genetic analysis of extracellular toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Ecuyer C. Exudative epidermitis in pigs. Bacteriological studies on the causative agent. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1967 Oct;31(10):243–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Ecuyer C. Exudative epidermitis in pigs. Clinical studies and preliminary transmission trials. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1966 Jan;30(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onet G. E., Pommer J. L. Staphylococcus hyicus abortion in a sow. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):362–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. E., Jr, King R. E., Kloos W. E. Isolation of Staphylococcus hyicus subsp hyicus from a pig with septic polyarthritis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Feb;41(2):274–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Contribution of electron microscopy in the study of the interactions between pathogenic bacteria and their host cells. J Struct Biol. 1990 Jul-Sep;104(1-3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90072-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Tanabe T., Kuramoto M., Tanaka K., Hashimoto T., Saito H. Isolation of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus and its exfoliative activity in the piglet. Vet Microbiol. 1991 May;27(3-4):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuker G., Bertschinger H. U. Staphylococcus hyicus: Kulturell-biochemische Charakterisierung, serologische Typisierung und Pathogenitätsnachweis im Tierversuch. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1976 Nov;23(9):733–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ferguson J. L., Ward L. R. Characterization of plasmids conferring resistance to gentamicin and apramycin in strains of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 204c isolated in Britain. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Dec;97(3):419–426. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERDAHL N. R., GRACE O. D., TWIEHAUS M. J. PORCINE EXUDATIVE EPIDERMITIS: CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIAL AGENT. Am J Vet Res. 1965 May;26:617–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. L., Owens W. E. Prevalence of staphylococcal species in four dairy herds. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Jan;46(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saxe M. J., Notley C. M. Experiences with the typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci and micrococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Jul;241(1):46–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]