Abstract
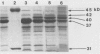
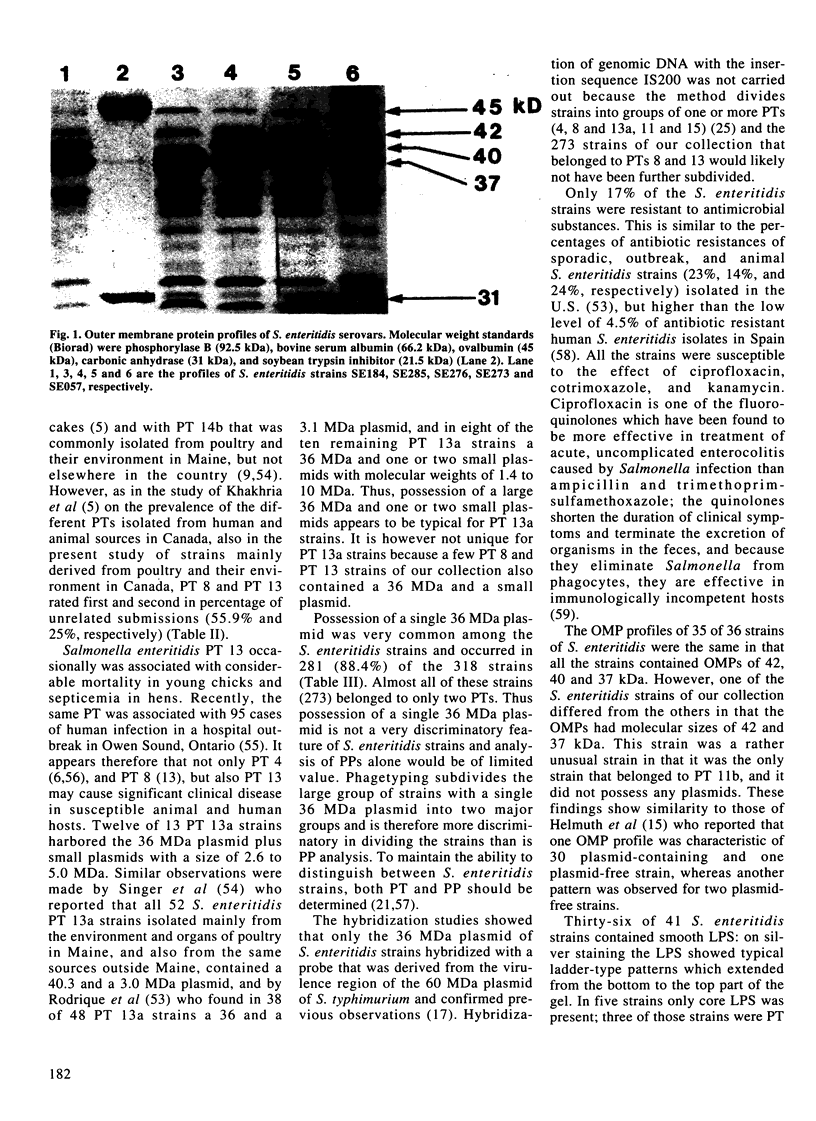
A study was conducted to characterize 318 Salmonella enteritidis strains that were mainly isolated from poultry and their environment in Canada. Biotype, phagetype (PT), plasmid profile (PP), hybridization with a plasmid-derived virulence sequence probe, antibiotic resistance, outer membrane proteins (OMPs), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) profiles were determined. Relationships of these properties to one another, and their diagnostic and pathogenic significance were assessed. Biotyping indicated that failure to ferment rhamnose was sometimes useful as a marker for epidemiologically related strains. Phagetyping was the most effective method for subdividing S. enteritidis; it distinguished 12 PTs. Phagetype 13 was occasionally associated with septicemia and mortality in chickens. The strains belonged to 15 PPs. A 36 megadalton (MDa) plasmid was found in 97% of the strains. Only the 36 MDa plasmid hybridized with the probe. Seventeen percent of the strains were drug resistant; all strains were sensitive to ciprofloxacin. Thirty-five of 36 strains possessed the same OMP profile, and 36 of 41 strains contained smooth LPS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asperilla M. O., Smego R. A., Jr, Scott L. K. Quinolone antibiotics in the treatment of Salmonella infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Sep-Oct;12(5):873–889. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.5.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. M., Old D. C. The usefulness of biotyping in studying the epidemiology and phylogeny of salmonellae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):81–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Musser J. M., Helmuth R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Frerichs W. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Ferris K., McWhorter A. C., Wells J. G., Cravioto A. Toward a population genetic analysis of Salmonella: genetic diversity and relationships among strains of serotypes S. choleraesuis, S. derby, S. dublin, S. enteritidis, S. heidelberg, S. infantis, S. newport, and S. typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of the Repliscan system for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):695–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.695-699.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullas L. R., Ryu J. I. Salmonella typhimurium LT2 strains which are r- m+ for all three chromosomally located systems of DNA restriction and modification. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):471–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.471-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Row B., Threlfall E. J., Ward L. R. Conversion of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 to phage type 7 involves loss of lipopolysaccharide with concomitant loss of virulence. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Rowe B. Antibodies to lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane proteins of Salmonella enteritidis PT4 are not involved in protection from experimental infection. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Dec 1;68(3):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90380-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowden J. M., Chisholm D., O'Mahony M., Lynch D., Mawer S. L., Spain G. E., Ward L., Rowe B. Two outbreaks of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection associated with the consumption of fresh shell-egg products. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):47–52. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003034x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowden J. M., Lynch D., Joseph C. A., O'Mahony M., Mawer S. L., Rowe B., Bartlett C. L. Case-control study of infections with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 in England. BMJ. 1989 Sep 23;299(6702):771–773. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6702.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. L. Outer membrane protein profiles of Yersinia ruckeri. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jan;26(1-2):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90049-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost J. A., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Acquisition of a drug resistance plasmid converts Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 to phage type 24. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Oct;103(2):243–248. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant R. B., Di Mambro L. Antimicrobial resistance and resistance plasmids in Salmonella from Ontario, Canada. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1266–1273. doi: 10.1139/m77-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A. Virulence plasmids of Salmonella typhimurium and other salmonellae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Montenegro M. A., Steinbeck A., Seiler A., Pietzsch O. Molekularbiologische Methoden zur epidemiologischen Feincharakterisierung von Krankheitserregern am Beispiel von Salmonella enteritidis aus Geflügel. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1990 Dec 1;103(12):416–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Stubbs A. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Phage typing of Salmonella enteritidis in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2817–2823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2817-2823.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hof H. Epidemiologie der Salmonellose im Wandel. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1991 Apr 5;116(14):545–547. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1063646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hospital outbreak of Salmonella enteriditis infection--Ontario. Can Commun Dis Rep. 1992 May 1;18(8):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Hamaoka T., Suzuki S., Nakamura M., Murayama S. Y., Arai T., Terakado N., Danbara H. Lipopolysaccharide alteration mediated by the virulence plasmid of Salmonella. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelln R. A., Lintott L. G. Construction of plasmid-free derivatives of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 using temperature-sensitive mutants of pKZ1 for displacement of the resident plasmid, pSLT. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):438–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00633852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakhria R., Duck D., Lior H. Distribution of Salmonella enteritidis phage types in Canada. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Feb;106(1):25–32. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister S. A. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broilers and broiler breeders. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):350–350. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinetti G., Altwegg M. rRNA gene restriction patterns and plasmid analysis as a tool for typing Salmonella enteritidis. Res Microbiol. 1990 Nov-Dec;141(9):1151–1162. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro M. A., Morelli G., Helmuth R. Heteroduplex analysis of Salmonella virulence plasmids and their prevalence in isolates of defined sources. Microb Pathog. 1991 Dec;11(6):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Dwyer D. M., Hoge C. W., Stubbs A. D., Tilghman D., Groves C., Israel E., Libonati J. P. Changing clonal patterns of Salmonella enteritidis in Maryland: evaluation of strains isolated between 1985 and 1990. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1301–1303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1301-1303.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Sato S., Ohya T., Suzuki S., Ikeda S. Possible relationship of a 36-megadalton Salmonella enteritidis plasmid to virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):831–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.831-833.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl P., Lintermans P., Marin M., Couturier M. Epidemiological study of Salmonella enteritidis strains of animal origin in Belgium. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Feb;106(1):11–16. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Curtiss R., 3rd, Gulig P. A., Gyles C. L. Hybridization studies with a DNA probe derived from the virulence region of the 60 Mdal plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Vet Res. 1989 Oct;53(4):378–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Gyles C. L. Relation of plasmids to virulence and other properties of salmonellae from avian sources. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):844–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Gyles C. L. Tagging and elimination of plasmids in Salmonella of avian origin. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Sep;18(1):73–87. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Irwin R. J., Forsberg C. M., Clarke R. C., Oggel J. The prevalence of Salmonella enteritidis and other Salmonella spp. among Canadian registered commercial layer flocks. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Apr;106(2):259–270. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Irwin R. J., Messier S., Finley G. G., Oggel J. The prevalence of Salmonella enteritidis and other Salmonella sp. among Canadian registered commercial chicken broiler flocks. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):201–211. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Johnson R. P., Forsberg C. M., Irwin R. J. Salmonella enteritidis and other Salmonella in laying hens and eggs from flocks with Salmonella in their environment. Can J Vet Res. 1992 Jul;56(3):226–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M. J., Rivera N., Castillo J., Rubio M. C., Gómez-Lus R. Molecular and epidemiological study of Salmonella clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):927–932. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.927-932.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Kuo T. T., MacPhee D. G. The effect of defined lipopolysaccharide core defects upon antibiotic resistances of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue D. C., Cameron D. N., Puhr N. D., Brenner F. W., St Louis M. E., Wachsmuth I. K., Tauxe R. V. Comparison of plasmid profiles, phage types, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella enteritidis isolates in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):854–857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.854-857.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue D. C., Tauxe R. V., Rowe B. International increase in Salmonella enteritidis: a new pandemic? Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):21–27. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp C. R., Rowe B. A mechanised microtechnique for salmonella serotyping. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jun;33(6):595–597. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.6.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. T., Opitz H. M., Gershman M., Hall M. M., Muniz I. G., Rao S. V. Molecular characterization of Salmonella enteritidis isolates from Maine poultry and poultry farm environments. Avian Dis. 1992 Apr-Jun;36(2):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Burnens A. P., Threlfall E. J., Chowdry N., Goldsworthy M. Genetic relationships among strains of Salmonella enteritidis in a national epidemic in Switzerland. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Apr;108(2):213–220. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Goldsworthy M., Threlfall E. J. Molecular phylogenetic typing of pandemic isolates of Salmonella enteritidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Jan 1;69(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90620-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telzak E. E., Budnick L. D., Greenberg M. S., Blum S., Shayegani M., Benson C. E., Schultz S. A nosocomial outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis infection due to the consumption of raw eggs. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):394–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terakado N., Hamaoka T., Danbara H. Plasmid-mediated serum resistance and alterations in the composition of lipopolysaccharides in Salmonella dublin. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):2089–2093. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-2089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ward L. R. Subdivision of Salmonella enteritidis phage types by plasmid profile typing. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Jun;102(3):459–465. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003017x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Shivaprasad H. L., Baker R. C., Rowe B. Egg transmission after infection of hens with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 9;125(24):600–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., de Sa J. D., Rowe B. A phage-typing scheme for Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):291–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]