Abstract
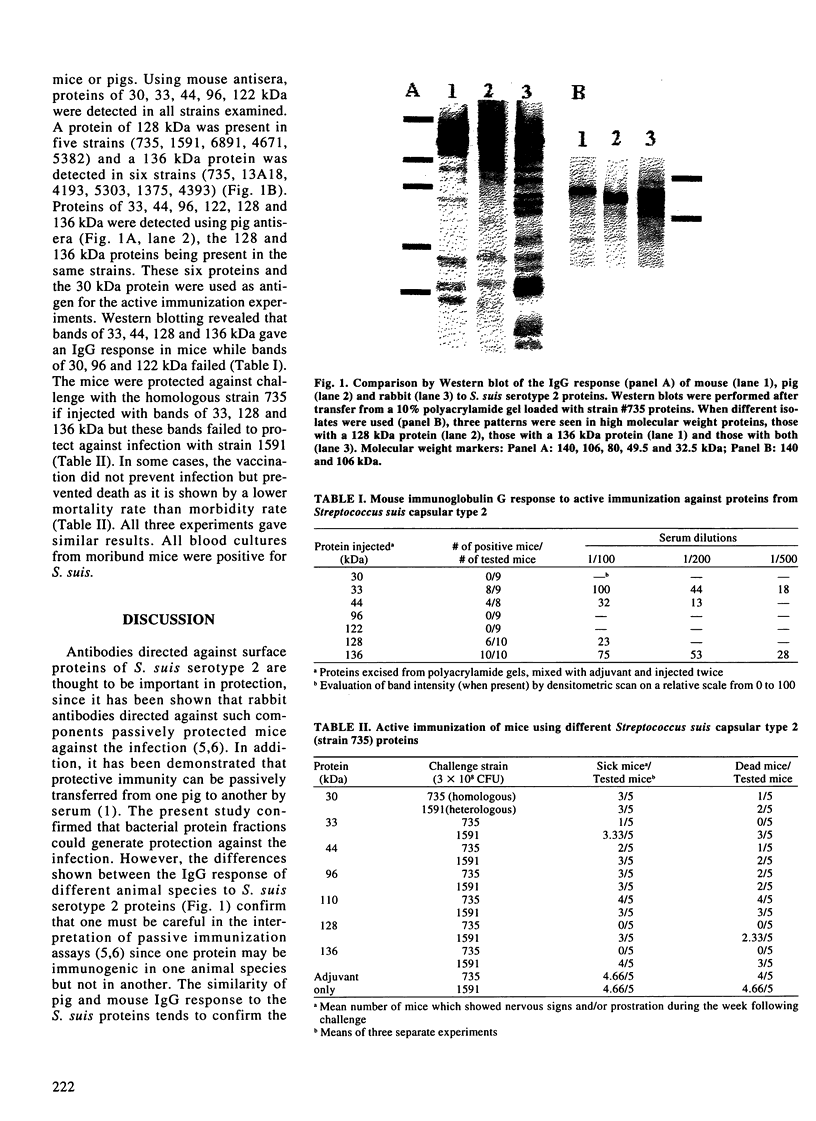
The aim of this study was to compare the IgG response of different animal species to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 proteins and to evaluate the immunogenic potential of these proteins in the mouse experimental model of infection. The protein profiles of ten different S. suis capsular type 2 isolates were compared by Western blotting using antisera produced in mice, rabbits and pigs against the reference strain. Strains were grown overnight in Todd-Hewitt broth, harvested by centrifugation, processed in a French press cell and digested with lysozyme. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was then performed and proteins transferred to nitrocellulose. The rabbit antiserum recognized seventeen common immunoreactive proteins, of which, proteins of 33, 44, 96, 122 kDa were present in all strains. Two, 128 and 136 kDa proteins were recognized by swine serum in many strains. An additional protein of 30 kDa was recognized by the mouse antiserum. These seven proteins, originating from the reference strain, were excised directly from polyacrylamide gels, mixed with incomplete Freund's adjuvant and given to groups of five mice on days 0 and 10. Immunoglobulin G response to each protein was monitored on day 20 using Western blots. Mice were then experimentally infected on day 21. Results indicated that vaccination with proteins of 33, 44, 128 and 136 kDa resulted in an IgG response and protection against the challenge with the reference strain, but gave only a partial protection against another virulent S. suis serotype 2 strain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudoin M., Higgins R., Harel J., Gottschalk M. Studies on a murine model for evaluation of virulence of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 isolates. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Plummer F. A., Stephens R. S. Bacterial antigenic variation, host immune response, and pathogen-host coevolution. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2273–2276. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2273-2276.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D., Clifton-Hadley F., Tai J. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. V. An immunogenic polysaccharide from Streptococcus suis type 2 with particular reference to vaccination against streptococcal meningitis in pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Oct;85(2):275–285. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Dubreuil D. Production and characterization of two Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 mutants. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90094-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M. An update on Streptococcus suis identification. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Jul;2(3):249–252. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt M. E., Enright M. R., Alexander T. J. Immunisation of pigs with live cultures of Streptococcus suis type 2. Res Vet Sci. 1988 Nov;45(3):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt M. E., Enright M. R., Alexander T. J. Protective effect of sera raised against different fractions of Streptococcus suis type 2. J Comp Pathol. 1990 Jul;103(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(08)80138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka Y., Haritani M., Mori M., Kishima M., Sugimoto C., Nakazawa M., Yamamoto K. Experimental infections of mice and pigs with Streptococcus suis type 2. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Dec;53(6):1043–1049. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson I. D., Blackmore D. K. Experimental studies on the comparative infectivity and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis type 2. II. Porcine and human isolates in laboratory animals. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Dec;105(3):479–484. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K. R., Morton R. J., Mosier D. A., Fulton R. W., Confer A. W. Comparison of the Pasteurella haemolytica A1 envelope proteins obtained by two cell disruption methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.664-667.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., Jellema M. L., Smith H. E. Identification of two proteins associated with virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3156–3162. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3156-3162.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E., Blakemore W. F., Alexander T. J. A murine model of Streptococcus suis type 2 meningitis in the pig. Res Vet Sci. 1988 Nov;45(3):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E. Relationship between intracellular survival in macrophages and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis type 2 isolates. Microb Pathog. 1990 Mar;8(3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90046-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]