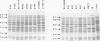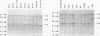Abstract
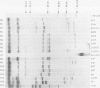
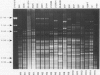
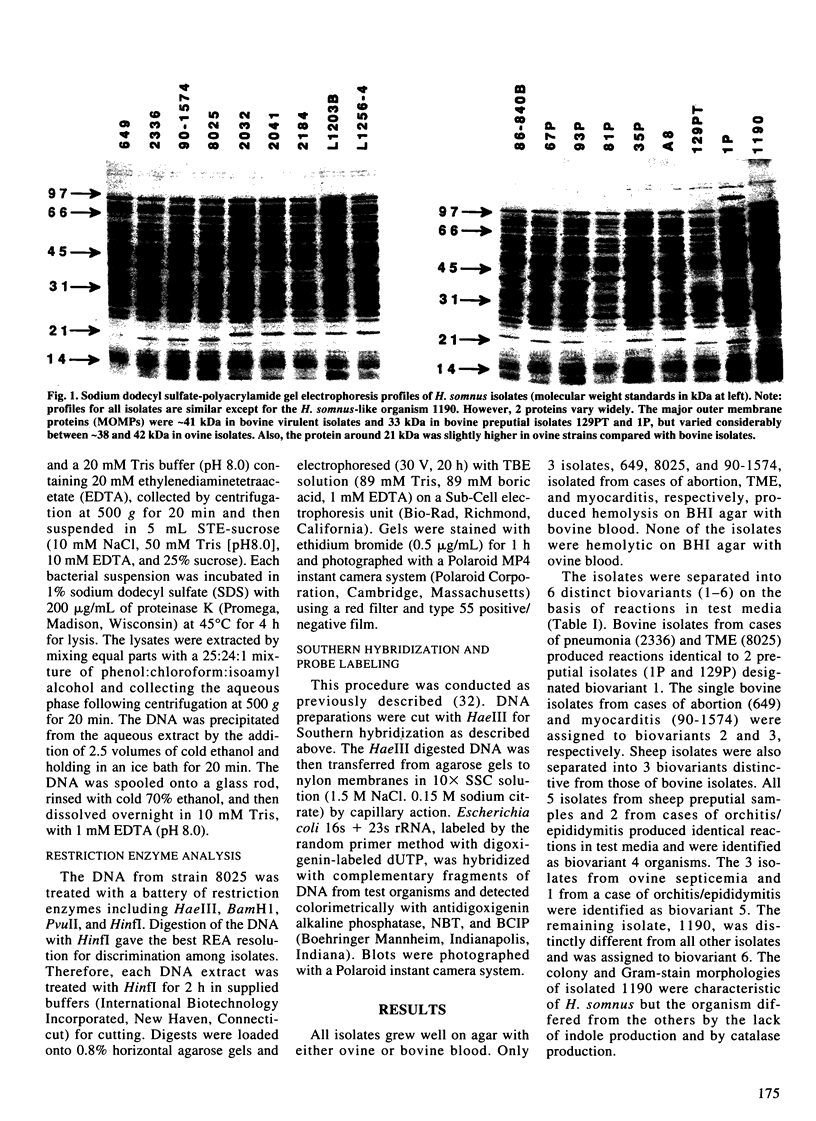
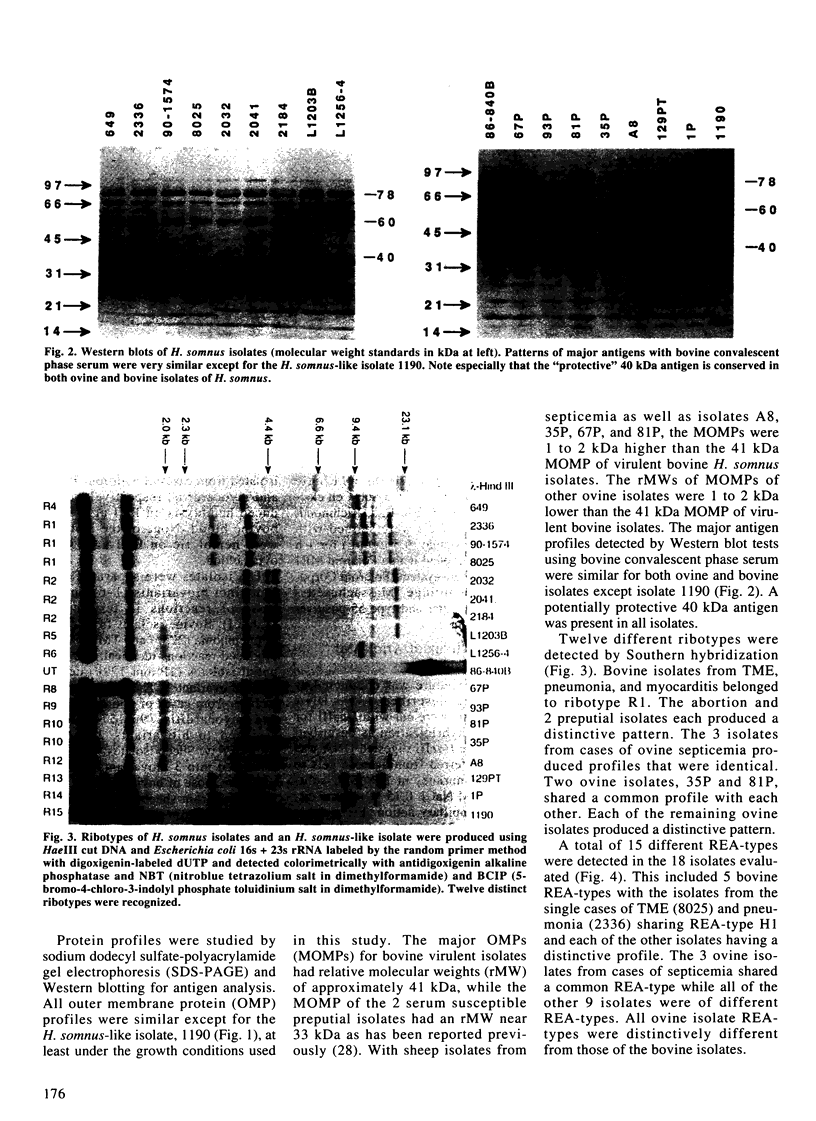
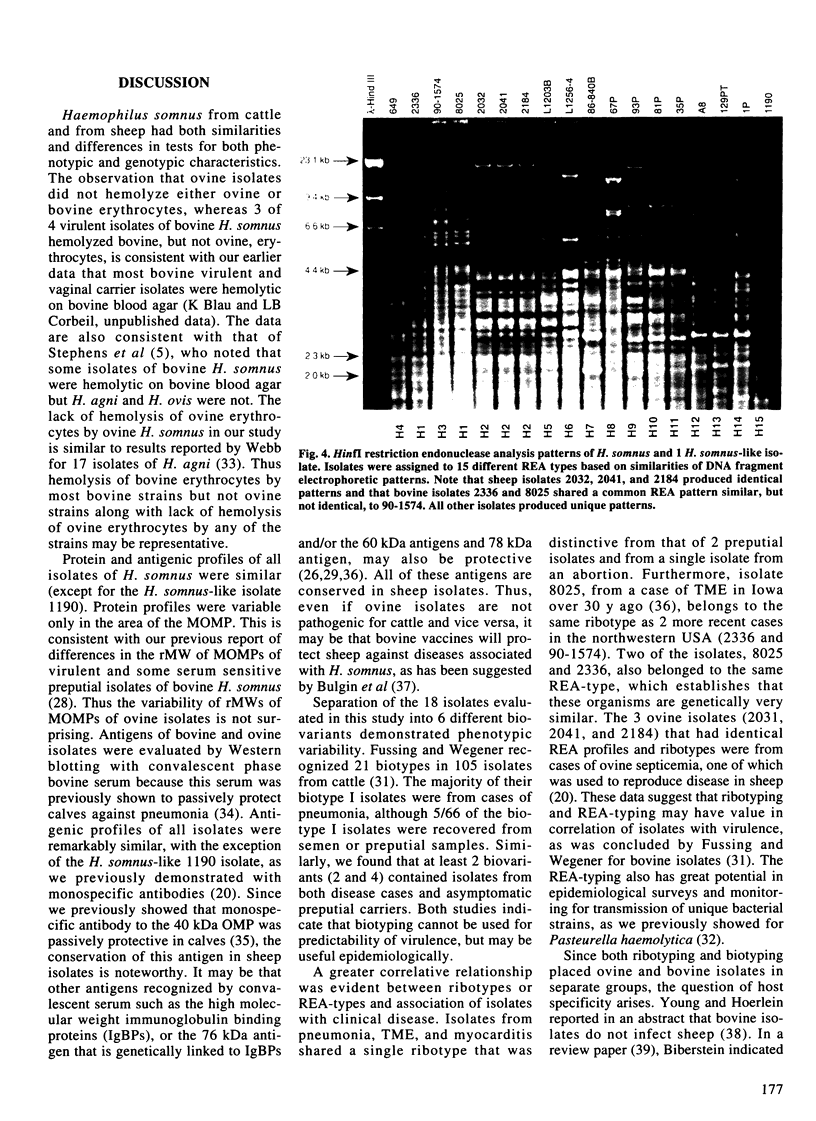
Bacterial isolates (including 17 Haemophilus somnus isolates and an H. somnus-like isolate) from asymptomatic or diseased cattle and sheep, were evaluated for markers associated with virulence and host predilection. The isolates were separated into 6 distinct biovariants, 3 for sheep and 3 for cattle, based on reactions in a battery of 21 test media. Three bovine isolates associated with disease caused hemolysis of bovine blood. The rest of the isolates did not hemolyze either bovine or ovine erythrocytes. Protein profiles of all H. somnus isolates were similar with the exception of the major outer membrane proteins (MOMPs). The MOMPs of isolates associated with disease in cattle had a relative molecular weight of approximately 41 kDa compared with 33 kDa for the MOMPs of isolates from asymptomatic cattle. The MOMPs from sheep isolates were either slightly higher or lower than the 41 kDa MOMPs of bovine isolates. Major antigens detected by Western blotting were similar in all isolates except the H. somnus-like isolate. An immunodominant 40 kDa antigen was conserved in all H. somnus isolates. Antibodies to this antigen have previously been found to be protective in cattle and may also be protective for sheep. Marked differences between cattle and sheep isolates were revealed by use of restriction enzyme analysis, which separated the isolates into 12 ribotypes and 15 unique DNA profiles. Thus, cattle and sheep isolates in this collection had distinctive differences in biochemical reactions, MOMP profiles, and DNA analyses. Such differences have potential value for epidemiological studies and may also be used to evaluate host specificity of H. somnus isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. J., Anderson T. D., Slife L. N., Stevenson G. W. Microscopic lesions associated with the isolation of Haemophilus somnus from pneumonic bovine lungs. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball H. J., Kennedy S., Ellis W. A. Experimental reproduction of ovine vulvitis with bacteria of the haemophilus/histophilus group. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Jan;50(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90057-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulgin M. S., Anderson B. C. Association of sexual experience with isolation of various bacteria in cases of ovine epididymitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Feb 15;182(4):372–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulgin M. S. Epididymitis in rams and lambs. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1990 Nov;6(3):683–690. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30840-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. P., Guiney D. G., Corbeil L. B. Two linked genes for outer membrane proteins are absent in four non-disease strains of Haemophilus somnus. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1895–1902. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Blau K., Prieur D. J., Ward A. C. Serum susceptibility of Haemophilus somnus from bovine clinical cases and carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.192-198.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fussing V., Wegener H. C. Characterization of bovine Haemophilus somnus by biotyping, plasmid profiling, REA-patterns and ribotyping. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Jun;279(1):60–74. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80492-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability of antibodies against 78- and 40-kilodalton outer membrane antigens of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2307–2316. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2307-2316.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groom S. C., Little P. B., Rosendal S. Virulence differences among three strains of Haemophilus somnus following intratracheal inoculation of calves. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):349–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guichon P. T., Pritchard J., Jim G. K. Haemophilus somnus myocarditis in a feedlot steer. Can Vet J. 1988 Dec;29(12):1012–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris F. W., Janzen E. D. The Haemophilus somnus disease complex (Hemophilosis): A review. Can Vet J. 1989 Oct;30(10):816–822. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Martin J. R., Larouche Y., Goyette G. Mastitis Caused by Haemophilus somnus in a Dairy Cow. Can Vet J. 1987 Mar;28(3):117–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski M. D., Ward A. C., Hunter D. L., Wesley I. V. Use of DNA analysis of Pasteurella haemolytica biotype T isolates to monitor transmission in bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis canadensis). J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):831–835. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.831-835.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., BIBERSTEIN E. L., HOWARTH J. A., FRAZIER L. M., DUNGWORTH D. L. Infectious meningo-encephalitis in cattle, caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., FRAZIER L. M., THEILEN G. H., BIBERSTEIN E. L. A septicemic disease of lambs caused by Hemophilus agni (new species). Am J Vet Res. 1958 Jul;19(72):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania S. A., Gogolewski R. P., Corbeil L. B. Characterization of a 78-kilodalton outer membrane protein of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.237-244.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees V. W., Meek A. H., Rosendal S. Epidemiology of Haemophilus somnus in young rams. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Jun;54(3):331–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees V. W., Yates W. D., Corbeil L. B. Ovine Haemophilus somnus: experimental intracisternal infection and antigenic comparison with bovine Haemophilus somnus. Can J Vet Res. 1994 Jul;58(3):202–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. B., Barnum D. A., McEntee K. E. Hemophilus somnus in the reproductive tracts of slaughtered cows: location and frequency of isolations and lesions. Vet Pathol. 1983 Sep;20(5):515–521. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Dahlgren R. R., Rinker H. B. Observations on septicemia of cattle caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Pathol Vet. 1968;5(3):212–216. doi: 10.1177/030098586800500303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaley R. S., White W. E. Histophilus ovis infection in sheep in Western Victoria. Aust Vet J. 1977 Mar;53(3):124–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1977.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A. Morphological, biochemical, antigenic, and cytochemical relationships among Haemophilus somnus, Haemophilus agni, Haemophilus haemoglobinophilus, Histophilus ovis, and Actinobacillus seminis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):728–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.728-737.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Slee K. J., Poulton P., Larcombe M., Kosior E. Investigation of purulent vaginal discharge in cows, with particular reference to Haemophilus somnus. Aust Vet J. 1986 Jun;63(6):182–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb02969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. L., LeaMaster B. R. Prevalence of Histophilus ovis and Actinobacillus seminis in the genital tract of sheep. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1928–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R. F. Bacteriological characteristics of Histophilus ovis and its relationship to similar bacteria. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Jul;35(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Dorrance L. A., Yarnall M., Corbeil L. B. Immunoglobulin-binding activity among pathogenic and carrier isolates of Haemophilus somnus. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):639–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.639-642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Paisley L. G., Gogolewski R. P., Evermann J. F., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Experimental abortion and the systemic immune response to "Haemophilus somnus" in cattle. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):555–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.555-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dreumel A. A., Kierstead M. Abortion associated with Hemophilus somnus infection in a bovine fetus. Can Vet J. 1975 Dec;16(12):367–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]