Abstract
Helicobacter genus-specific PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis can detect and speciate the helicobacters that colonize the lower bowel of laboratory mice. The method's sensitivity is comparable to that of species-specific PCR and may detect unnamed Helicobacter species. This approach should prove useful for commercial and research murine facilities.
A number of the Helicobacter species that colonize the murine lower bowel may confound experimental data because of their association with typhlocolitis, hepatitis, and hepatic neoplasia in susceptible murine strains (3, 6-11, 13-15, 24, 25, 27). Screening of laboratory mice for lower bowel colonization is particularly desirable, because Helicobacter species are transmitted by the fecal-oral route (16, 28) and are prevalent in commercial and research animal facilities (9, 18, 22, 28). Testing can be performed using culture or PCR; however, the former is labor-intensive and the latter requires multiple PCRs for species identification. As denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of PCR products (PCR-DGGE) generated with genus-specific primers has been used successfully to detect and speciate the bacteria of a targeted genus (12, 21), we sought to develop this method for the identification of Helicobacter species in the lower bowel of laboratory mice.
Primer 1067R that targets the 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) of the Helicobacter genus was designed by comparing the 16S rDNA sequences of 73 lower bowel Helicobacter species and 25 other colonic bacterial species (2, 26). This primer was used in combination with a reversed and GC-clamped version of primer H676 (18) (Table 1). Hot-start PCR using this primer pair was performed on a PCR Sprint thermal cycler (Hybaid, Ashford, Middlesex, United Kingdom), using a 50-μl reaction mixture containing 67 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), 16.6 mM (NH4)2SO4, 0.45% Triton X-100, 0.01 mg of gelatin, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 200 nM concentrations of each nucleotide triphosphate, 20 pmol of each primer, 1.1 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Biotech International, Belmont, Western Australia, Australia), and 10 to 30 ng of template DNA. Thermal cycling consisted of 94°C for 5 min, 30 cycles of 94°C for 10 s, 62°C for 10 s, 72°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 2 min. DNA template was obtained from bacterial cultures using the Puregene DNA isolation kit (Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, Minn.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The specificity of the PCR was confirmed by the amplification of template DNA from Helicobacter hepaticus (ATCC 51448), Helicobacter rodentium (ATCC 700285), Helicobacter muridarum (ATCC 49282), Helicobacter bilis (ATCC 51630), Helicobacter trogontum (ATCC 700114), and two laboratory strains of Helicobacter ganmani, but not 13 other colonic bacteria, including Campylobacter fetus and Campylobacter coli.
TABLE 1.
Primer sequences used in Helicobacter genus-specific and species-specific PCRs
| Target | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helicobacter genus | GC658F | CGC CCC CCG CGC CCC GCG CCC GGC CCG CCG CCC CCG CCC TGG GAG AGG TAG GTG GAA T | Riley et al. (18)a |
| 1067R | GCC GTG CAG CAC CTG TTT TCA | This paper | |
| H. rodentium and H. ganmanib | D86 | GTC CTT AGT TGC TAA CTA TT | Shen et al. (23) |
| D87 | AGA TTT GCT CCA TTT CAC AA | Shen et al. (23) | |
| H. bilis | H276f | CTA TGA CGG GTA TCC GGC | Riley et al. (18) |
| Hbr | TCT CCC ATA CTC TAG AAA AGT | Riley et al. (18) | |
| H. hepaticus | B38 | GCA TTT GAA ACT GTT ACT CTG | Shames et al. (22) |
| B39 | CTG TTT TCA AGC TCC CC | Shames et al. (22) | |
| H. muridarumc | Hmur | ACA GAA GTG GCA CTC CCA | This paper |
GC658F is a GC-clamped and reversed version of H676r.
Primer set will amplify 16S rDNA from both species (19).
Primer used in combination with H276f.
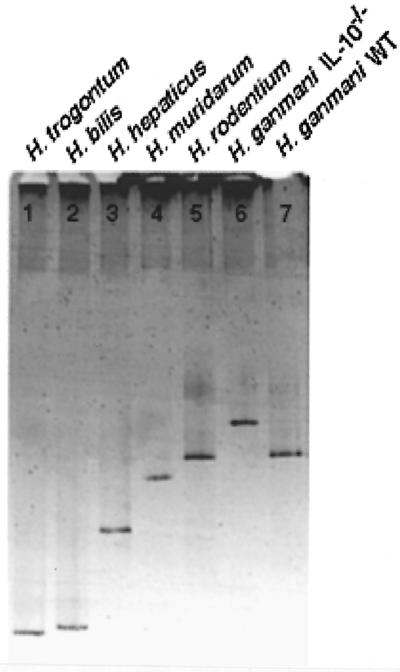
DGGE of the Helicobacter genus-specific PCR product on a 6% polyacrylamide gel (acrylamide-bisacrylamide, 37.5:1) containing a 41-to-48% gradient of urea and formamide (100% is 7 M urea and 40% deionized formamide) was performed for 16 h at 75 V and 60°C (Bio-Rad, Hercules, Calif.). Bands were visualized with ethidium bromide staining. PCR products were directly sequenced using the ABI PRISM Ready Reaction DyeDeoxy Terminator cycle sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, Calif.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The results of PCR-DGGE with American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and laboratory helicobacter strains are shown in Fig. 1. Band positions were generally species specific; however, those of H. rodentium and a laboratory strain of H. ganmani isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice were practically indistinguishable due to the very high degree of sequence homology in the amplified region. It is noteworthy that laboratory strains of H. ganmani isolated from interleukin-10-deficient (IL-10−/−) and wild-type C57BL/6 mice had differing gel positions as a result of a 2-base difference in their 16S rDNA sequence (T versus G at position 971 and A versus G at position 1045; Escherichia coli 16S rDNA numbering).
FIG. 1.
Results of Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE for ATCC and laboratory strains of Helicobacter species. Lane 1, H. trogontum, lane 2, H. bilis; lane 3, H. hepaticus; lane 4, H. muridarum; lane 5, H. rodentium; lane 6, H. ganmani isolated from IL-10−/− C57BL/6 mice; lane 7, H. ganmani isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
The sensitivity of Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE was determined by assessing the detection of Helicobacter species in spiked murine fecal samples and by direct comparison with species-specific PCR. Equal portions of a murine fecal sample were spiked with serial dilutions of cultured H. hepaticus, and DNA was extracted according to the animal tissue protocol of the Puregene DNA isolation kit (Gentra). The limit of detection of PCR-DGGE was 107 H. hepaticus organisms per g of feces. The sensitivity of Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE was also directly compared with PCRs specific for individual Helicobacter species by using fresh fecal samples from 13 12-week-old C57BL/6 cagemates obtained from the same supplier. Primer sequences and references for these PCRs are given in Table 1. PCR for H. muridarum used a 2.5 mM MgCl2 concentration, and thermal cycling consisted of 94°C for 4 min, 35 cycles of 94°C for 10 s, 58°C for 10 s, 72°C for 30 s, and finally 72°C for 2 min. Combining the results, all of the mice were colonized with H. bilis and H. ganmani but not the other Helicobacter species. PCR-DGGE detected H. ganmani in 92% and H. bilis in 100% of mice, while species-specific PCRs were 92% sensitive for the same organisms, suggesting that the sensitivities of both methods were comparable and consistent with previous reports (1, 17, 22).
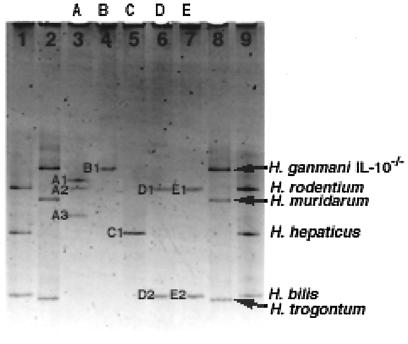
In order to examine the utility of Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE for the identification of colonizing Helicobacter species, the method was applied to eight mice housed in different cages in four rooms of our animal facility. These mice were between 2 and 12 months of age and had originated from three Australian suppliers. The resulting DGGE gel is shown in Fig. 2. Bands were excised from the gel and DNA obtained using the “crush and soak” method (20) was amplified and sequenced. The results of comparing these sequences with the BLAST database (2) are shown in Table 2. For six of the mice, the bands matched the gel position and sequence of the ATCC and laboratory strains of Helicobacter species. As noted previously, bands representing one strain of H. ganmani had an identical gel position to H. rodentium. One mouse did not have detectable helicobacter colonization. Interestingly, two bands derived from the remaining mouse (cage A) did not match the gel position of known standards; sequencing showed that one (band A1) was closely related to H. rodentium (23) and the second (band A3) was 98.3% homologous to 16S rDNA from a helicobacter previously isolated from dog stomach (5). The presence of unnamed Helicobacter species in the colony is not surprising, as a significant number of murine helicobacters have not yet been named (4).
FIG. 2.
Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE results for Animal Facility mice. Lanes 1 and 9, marker containing H. rodentium, H. hepaticus, and H. bilis; lanes 2 and 8, marker containing H. ganmani of IL-10−/− mice, H. muridarum, and H. trogontum; lane 3, cage A mouse; lane 4, cage B mouse; lane 5, cage C mouse; lane 6, cage D mouse; lane 7, cage E mouse. (Results for cages F, G, and H are not shown.)
TABLE 2.
Combined results of Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE and sequencing
| Cage | Strain | Age (mos) | Helicobacter species |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | BALB/c | 9 | HSU96299(23) H. ganmania HSU51874(5) |
| B | C57BL/6 IL10−/− | 8 | H. ganmanib |
| C | BALB/c | 12 | H. hepaticus |
| D | C57BL/6 | 2 | H. ganmania |
| H. bilis | |||
| E | BALB/c | 5 | H. ganmania |
| H. bilis | |||
| F | BALB/c | 12 | H. hepaticus |
| G | BALB/c | 11 | Negative |
| H | BALB/c | 12 | H. hepaticus |
Laboratory strain of H. ganmani with 971G/1045G (E. coli numbering).
Laboratory strain of H. ganmani with 971T/1045A (E. coli numbering).
To accurately apply this method to the screening of laboratory mice, PCR standards representing the range of Helicobacter species and the strains present in a given colony must first be developed. Once established, however, Helicobacter spp. may be identified in a single PCR and the presence of a novel species may be detected. Murine fecal samples may be stored at room temperature for up to a week without affecting the outcome of PCR for Helicobacter species (1). In addition, recent studies of the prevalence of Helicobacter species in animal facilities and their rates of transmission to helicobacter-free sentinels suggest that the results obtained from just a few mice are likely to reflect the colonization status of their cagemates (16, 28). With appropriate standards, Helicobacter genus-specific PCR-DGGE could also be adapted for the screening of other laboratory animals, e.g., gerbils, ferrets, and rats.
REFERENCES
- 1.Beckwith, C. S., C. L. Franklin, R. R. Hook, C. L. Beschwilliford, and L. K. Riley. 1997. Fecal PCR assay for diagnosis of Helicobacter infection in laboratory rodents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:1620-1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benson, D. A., I. Karsch-Mizrachi, D. J. Lipman, J. Ostell, B. A. Rapp, and D. L. Wheeler. 2000. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:15-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chin, E. Y., C. A. Dangler, J. G. Fox, and D. B. Schauer. 2000. Helicobacter hepaticus infection triggers inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor alpha beta mutant mice. Comp. Med. 50:586-594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dewhirst, F. E., J. G. Fox, E. N. Mendes, B. J. Paster, C. E. Gates, C. A. Kirkbride, and K. A. Eaton. 2000. “Flexispira rappini” strains represent at least 10 Helicobacter taxa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50:1781-1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eaton, K. A., F. E. Dewhirst, B. J. Paster, N. Tzellas, B. E. Coleman, J. Paola, and R. Sherding. 1996. Prevalence and varieties of Helicobacter species in dogs from random sources and pet dogs: animal and public health implications. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34:3165-3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fox, J. G., P. L. Gorelick, M. C. Kullberg, Z. M. Ge, F. E. Dewhirst, and J. M. Ward. 1999. A novel urease-negative Helicobacter species associated with colitis and typhlitis in IL-10-deficient mice. Infect. Immun. 67:1757-1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fox, J. G., X. Li, L. Yan, R. J. Cahill, R. Hurley, R. Lewis, and J. C. Murphy. 1996. Chronic proliferative hepatitis in A/JCr mice associated with persistent Helicobacter hepaticus infection: a model of helicobacter-induced carcinogenesis. Infect. Immun. 64:1548-1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fox, J. G., L. L. Yan, F. E. Dewhirst, B. J. Paster, B. Shames, J. C. Murphy, A. Hayward, J. C. Belcher, and E. N. Mendes. 1995. Helicobacter bilis sp. nov., a novel Helicobacter species isolated from bile, livers, and intestines of aged, inbred mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:445-454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Franklin, C. L., P. L. Gorelick, L. K. Riley, F. E. Dewhirst, R. S. Livingston, J. M. Ward, C. S. Beckwith, and J. G. Fox. 2001. Helicobacter typhlonius sp. nov., a novel murine urease-negative Helicobacter species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:3920-3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Franklin, C. L., L. K. Riley, R. S. Livingston, C. S. Beckwith, C. L. Beschwilliford, and R. R. Hook. 1998. Enterohepatic lesions in scid mice infected with Helicobacter bilis. Lab. Anim. Sci. 48:334-339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Franklin, C. L., L. K. Riley, R. S. Livingston, C. S. Beckwith, R. R. Hook, C. L. Besch-Williford, R. Hunziker, and P. L. Gorelick. 1999. Enteric lesions in SCID mice infected with “Helicobacter typhlonicus,” a novel urease-negative Helicobacter species. Lab. Anim. Sci. 49:496-505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Heilig, H. G., E. G. Zoetendal, E. E. Vaughan, P. Marteau, A. D. Akkermans, and W. M. de Vos. 2002. Molecular diversity of Lactobacillus spp. and other lactic acid bacteria in the human intestine as determined by specific amplification of 16S ribosomal DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68:114-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jiang, H. Q., N. Kushnir, M. C. Thurnheer, N. A. Bos, and J. J. Cebra. 2002. Monoassociation of SCID mice with Helicobacter muridarum, but not four other enterics, provokes IBD upon receipt of T cells. Gastroenterology 122:1346-1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kullberg, M. C., J. M. Ward, P. L. Gorelick, P. Caspar, S. Hieny, A. Cheever, D. Jankovic, and A. Sher. 1998. Helicobacter hepaticus triggers colitis in specific-pathogen-free interleukin-10 (IL-10)-deficient mice through an IL-12- and gamma interferon-dependent mechanism. Infect. Immun. 66:5157-5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li, X. T., J. G. Fox, M. T. Whary, L. L. Yan, B. Shames, and Z. B. Zhao. 1998. SCID/NCr mice naturally infected with Helicobacter hepaticus develop progressive hepatitis, proliferative typhlitis, and colitis. Infect. Immun. 66:5477-5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Livingston, R. S., L. K. Riley, C. L. Beschwilliford, R. R. Hook, and C. L. Franklin. 1998. Transmission of Helicobacter hepaticus infection to sentinel mice by contaminated bedding. Lab. Anim. Sci. 48:291-293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahler, M., H. G. Bedigian, B. L. Burgett, R. J. Bates, M. E. Hogan, and J. P. Sundberg. 1998. Comparison of four diagnostic methods for detection of Helicobacter species in laboratory mice. Lab. Anim. Sci. 48:85-91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riley, L. K., C. L. Franklin, R. R. Hook, and C. Beschwilliford. 1996. Identification of murine helicobacters by PCR and restriction enzyme analyses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34:942-946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Robertson, B. R., J. L. O'Rourke, P. Vandamme, S. On, and A. Lee. 2001. Helicobacter ganmani sp. nov., a urease-negative anaerobe isolated from the intestines of laboratory mice. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1881-1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Isolation of DNA fragments from polyacrylamide gels, p. 6.46-6.48. In C. Nolan (ed.), Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed., vol. 1. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, N.Y. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Satokari, R. M., E. E. Vaughan, A. D. Akkermans, M. Saarela, and W. M. De Vos. 2001. Bifidobacterial diversity in human feces detected by genus-specific PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:504-513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shames, B., J. G. Fox, F. Dewhirst, L. L. Yan, Z. L. Shen, and N. S. Taylor. 1995. Identification of widespread Helicobacter hepaticus infection in feces in commercial mouse colonies by culture and PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:2968-2972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shen, Z., J. G. Fox, F. E. Dewhirst, B. J. Paster, C. J. Foltz, L. Yan, B. Shames, and L. Perry. 1997. Helicobacter rodentium sp. nov., a urease-negative Helicobacter species isolated from laboratory mice. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:627-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shomer, N. H., C. A. Dangler, R. P. Marini, and J. G. Fox. 1998. Helicobacter bilis/Helicobacter rodentium co-infection associated with diarrhea in a colony of scid mice. Lab. Anim. Sci. 48:455-459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shomer, N. H., C. A. Dangler, M. D. Schrenzel, and J. G. Fox. 1997. Helicobacter bilis-induced inflammatory bowel disease in SCID mice with defined flora. Infect. Immun. 65:4858-4864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Thompson, J. D., D. G. Higgins, and T. J. Gibson. 1994. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:4673-4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ward, J. M., J. G. Fox, M. R. Anver, D. C. Haines, C. V. George, M. J. Collins, P. L. Gorelick, K. Nagashima, M. A. Gonda, R. V. Gilden, J. G. Tully, R. J. Russell, R. E. Benveniste, B. J. Paster, F. E. Dewhirst, J. C. Donovan, L. M. Anderson, and J. M. Rice. 1994. Chronic active hepatitis and associated liver tumors in mice caused by a persistent bacterial infection with a novel Helicobacter species. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 86:1222-1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Whary, M. T., J. H. Cline, A. E. King, K. M. Hewes, D. Chojnacky, A. Salvarrey, and J. G. Fox. 2000. Monitoring sentinel mice for Helicobacter hepaticus, H. rodentium, and H. bilis infection by use of polymerase chain reaction analysis and serologic testing. Comp. Med. 50:436-443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]