Abstract
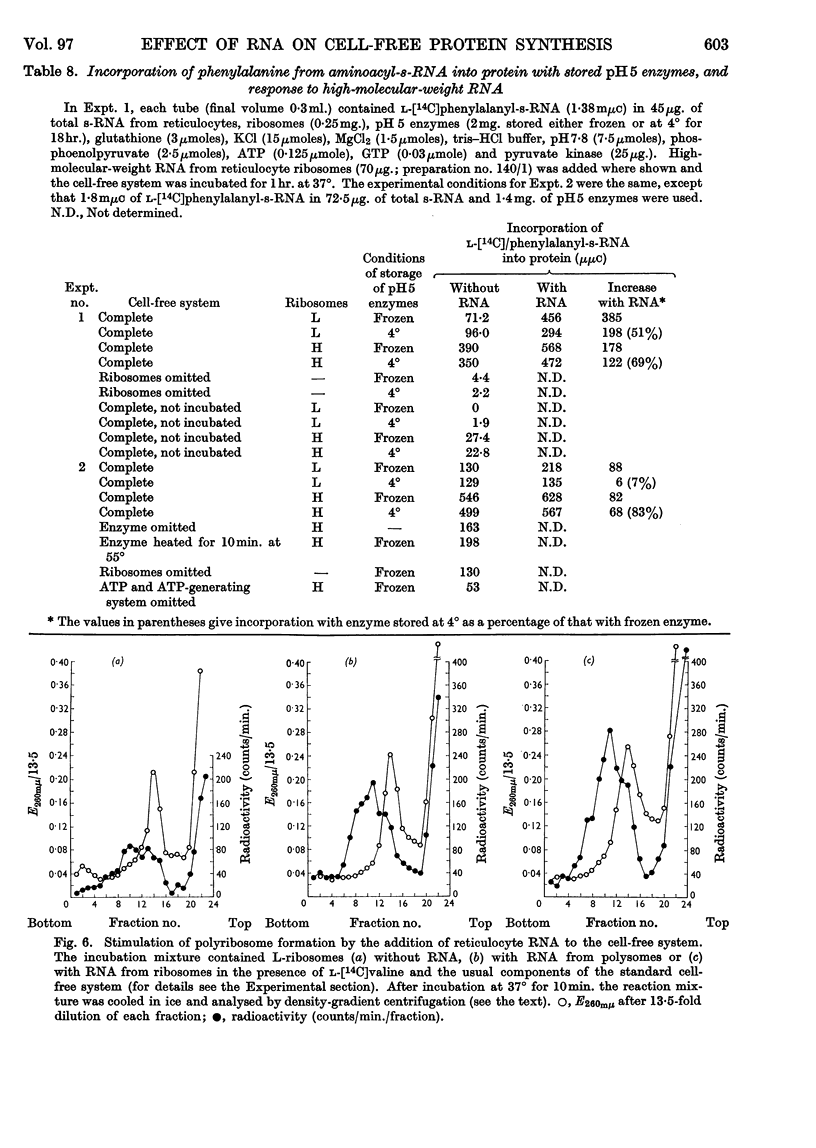
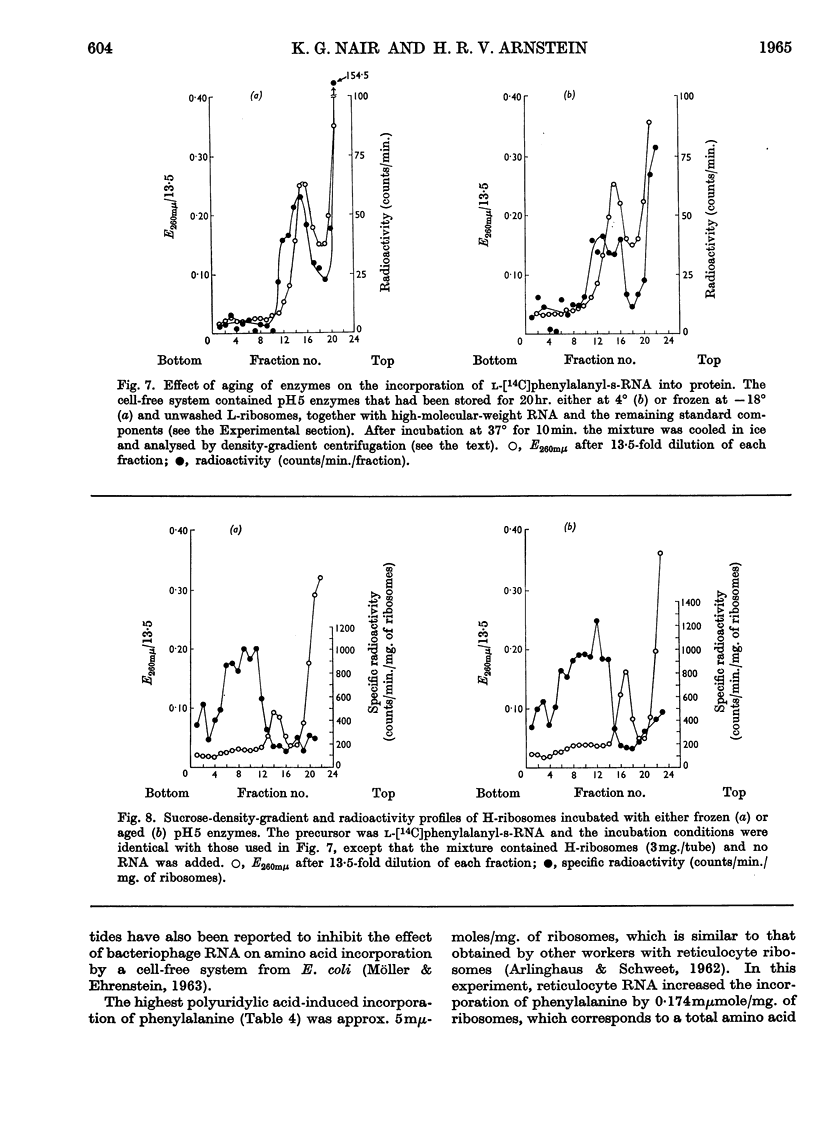
1. The effect of high-molecular-weight RNA from reticulocyte polyribosomes (messenger RNA) on protein synthesis by subcellular fractions derived from reticulocytes, reported by Arnstein, Cox & Hunt (1964), has now been studied in detail. Optimum response of the cell-free system requires 30–50mm-K+ and approx. 5mm-Mg2+ in the pH range 7·4–7·6. 2. RNA stimulates the incorporation into protein of both free amino acids and of aminoacyl residues from s-RNA. Stimulation by either RNA or polyuridylic acid is dependent on a labile factor or enzyme, which is present in the `pH5 fraction' and may be concerned with the formation of new polysomes. Quantitatively the response of the cell-free system to RNA is similar to that of polyuridylic acid, and there appears to be competition between messenger RNA and polyuridylic acid or polyadenylic acid.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNSTEIN H. R., COX R. A., HUNT J. A. Function of polyuridylic acid and ribonucleic acid in protein biosynthesis by ribosomes from mammalian reticulocytes. Nature. 1962 Jun 16;194:1042–1044. doi: 10.1038/1941042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Hunt J. A. The function of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid from rabbit reticulocytes in haemoglobin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):648–661. doi: 10.1042/bj0920648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRETSCHER M. S., GRUNBERG-MANAGO M. Polyribonucleotide-directed protein synthesis using an E. coli cell-free system. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:283–284. doi: 10.1038/195283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTONI G. L., GELBOIN H. V., LUBORSKY S. W., RICHARDS H. H., SINGER M. F. Studies on soluble ribonucleic acid of rabbit liver. II. Preparation and properties of rabbit-liver soluble RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 17;61:354–367. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARLWOOD P. A. Applications of radioactively labeled marker proteins in density gradient ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1963 Mar;5:226–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A., ARNSTEIN H. R. THE ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM RABBIT-RETICULOCYTE RIBOSOMES. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:574–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0890574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S. M., WEINSTEIN I. B. LACK OF FIDELITY IN THE TRANSLATION OF SYNTHETIC POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:988–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER R. S., WAHBA A. J., BASILIO C., MILLER R. S., LENGYEL P., SPEYER J. F. Synthetic polynucleotides and the amino acid code. VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2087–2094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. M., RICH A. MECHANISM OF POLYRIBOSOME ACTION DURING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Nature. 1963 Jul 27;199:318–322. doi: 10.1038/199318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDESTY B., HUTTON J. J., ARLINGHAUS R., SCHWEET R. POLYRIBOSOME FORMATION AND HEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1078–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER W. J., VON EHRENSTEIN G. Inhibition of cell free protein synthesis by homopolynucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 22;11:325–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90565-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OFENGAND J., HASELKORN R. Viral RNA-dependent incorporation of amino acids into protein by cell-free extracts of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jan 24;6:469–474. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90377-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EHRENSTEIN G., LIPMANN F. Experiments on hemoglobin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jul 15;47:941–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.7.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


