Abstract
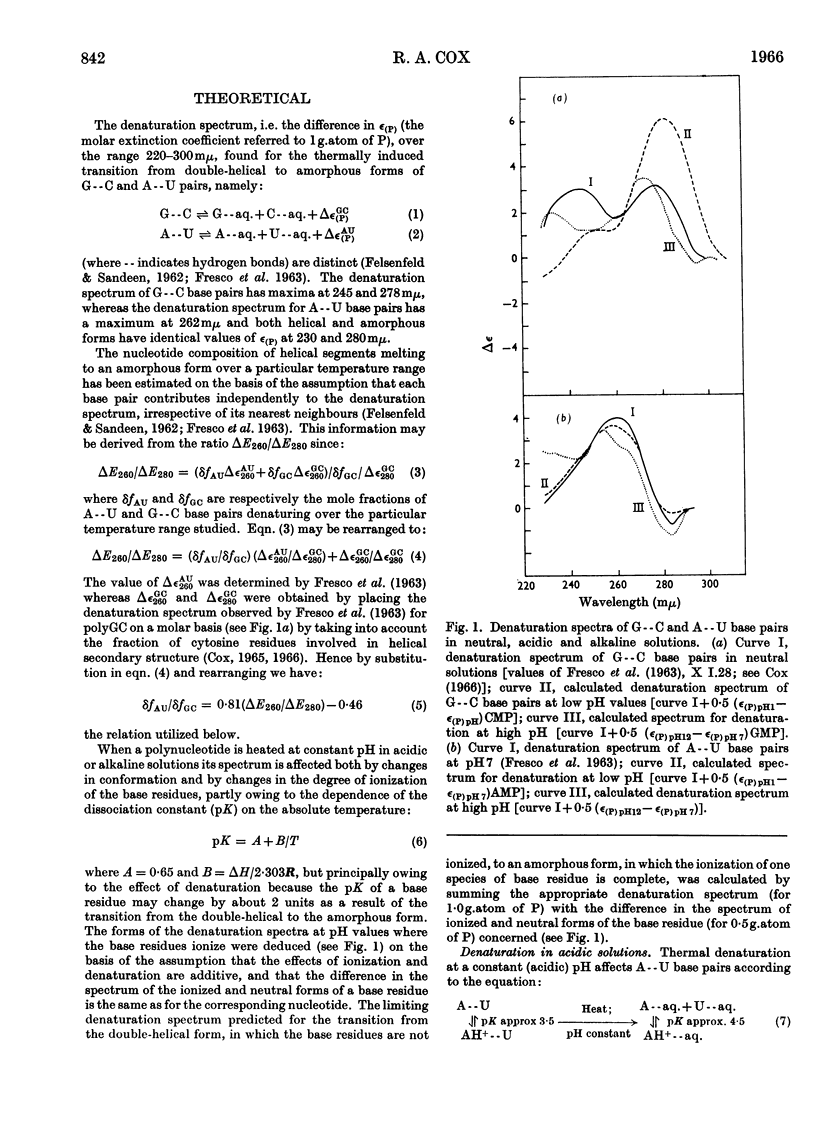
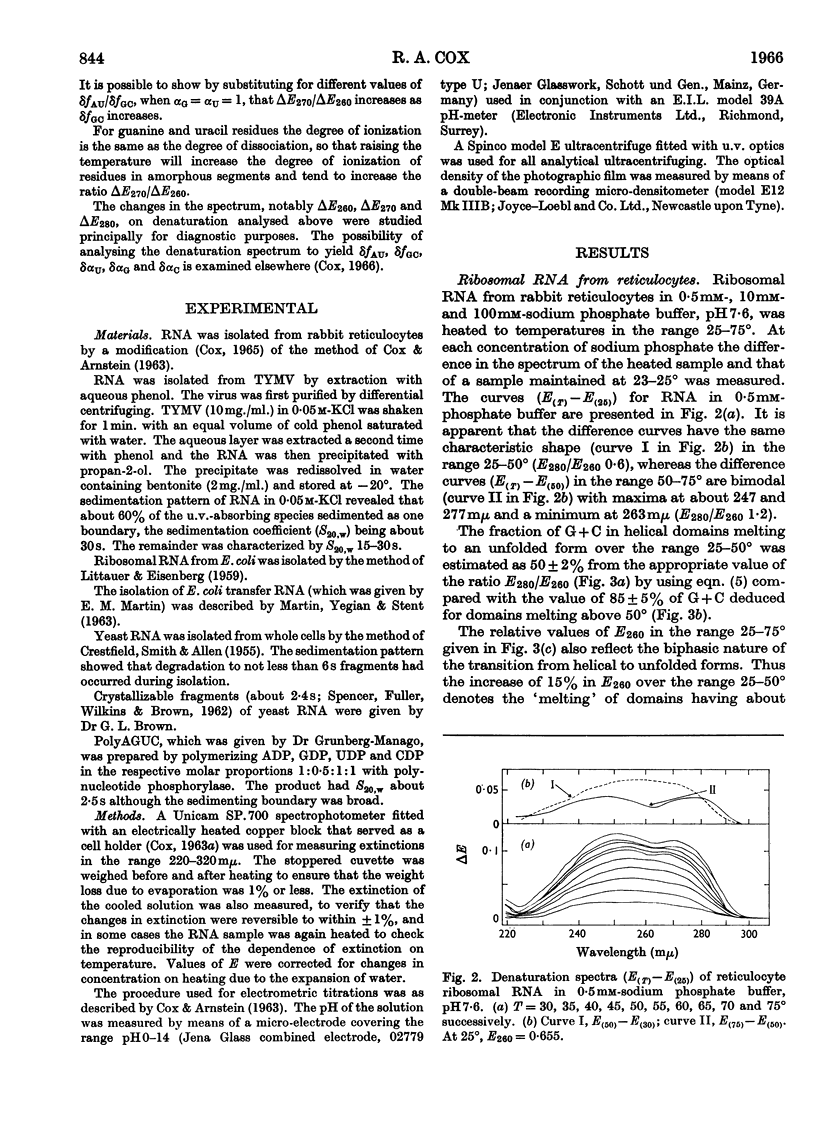
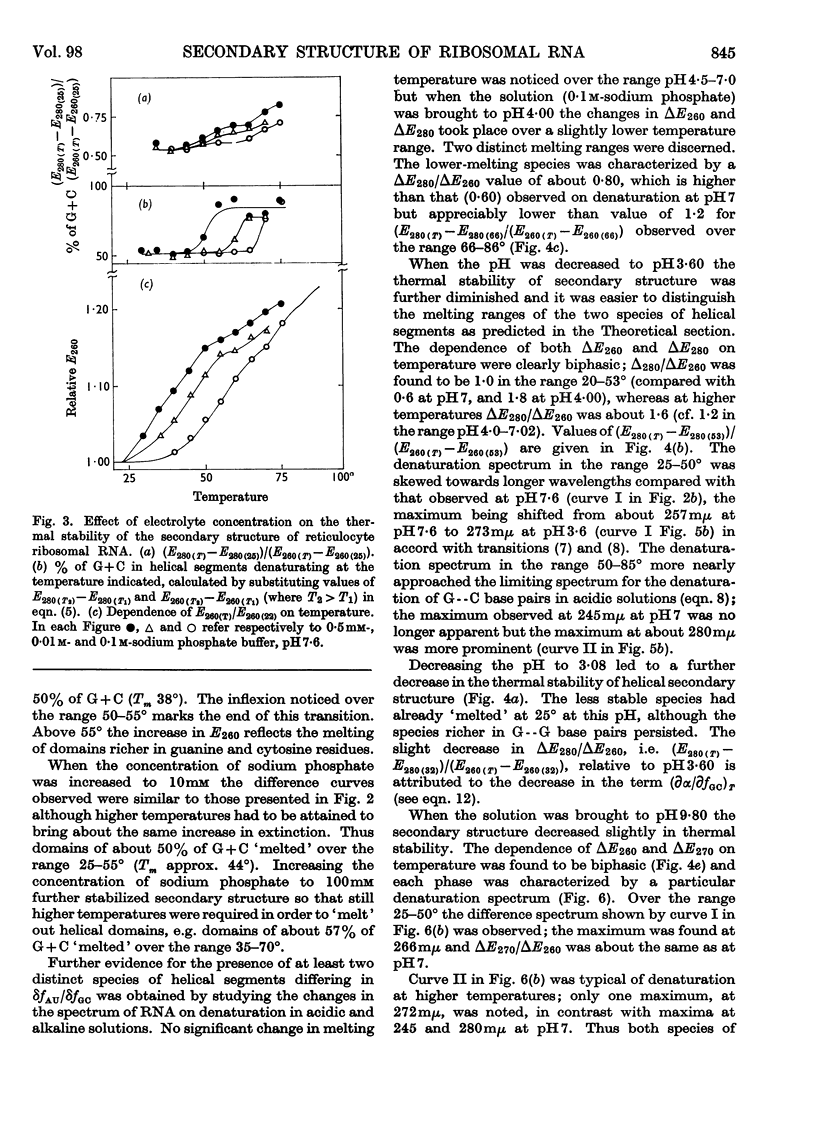
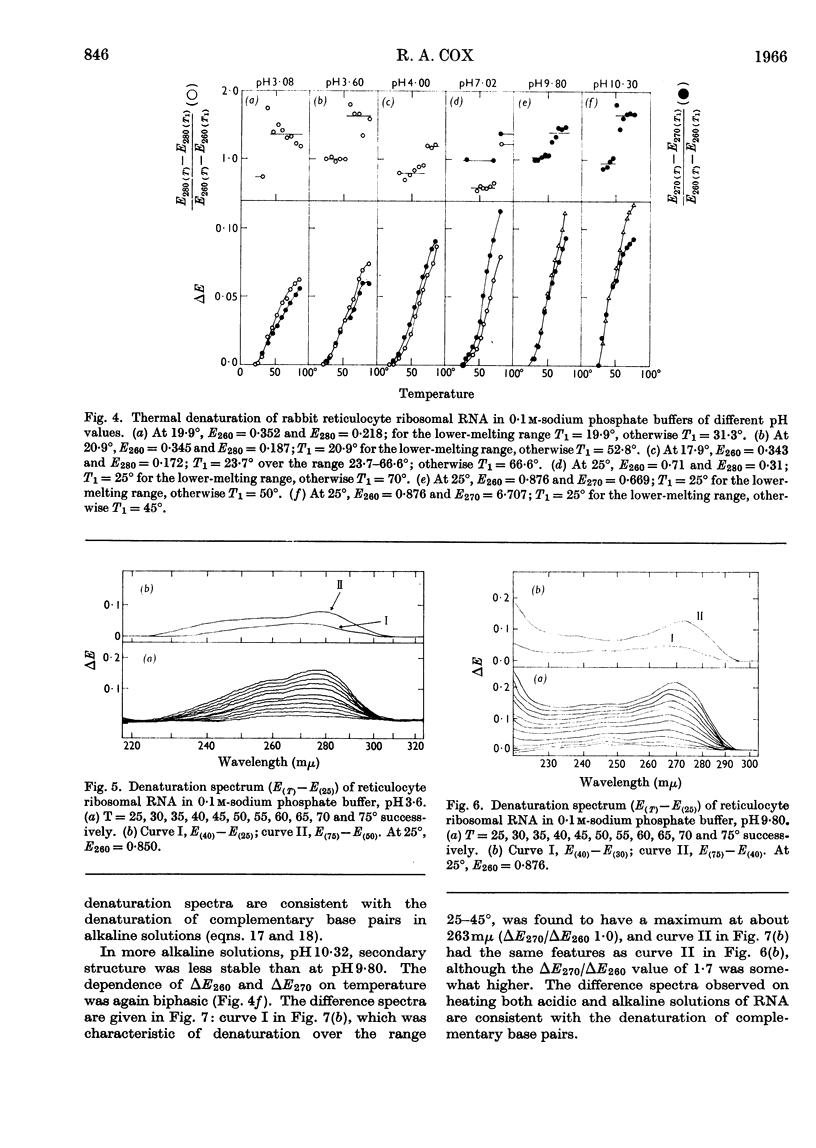
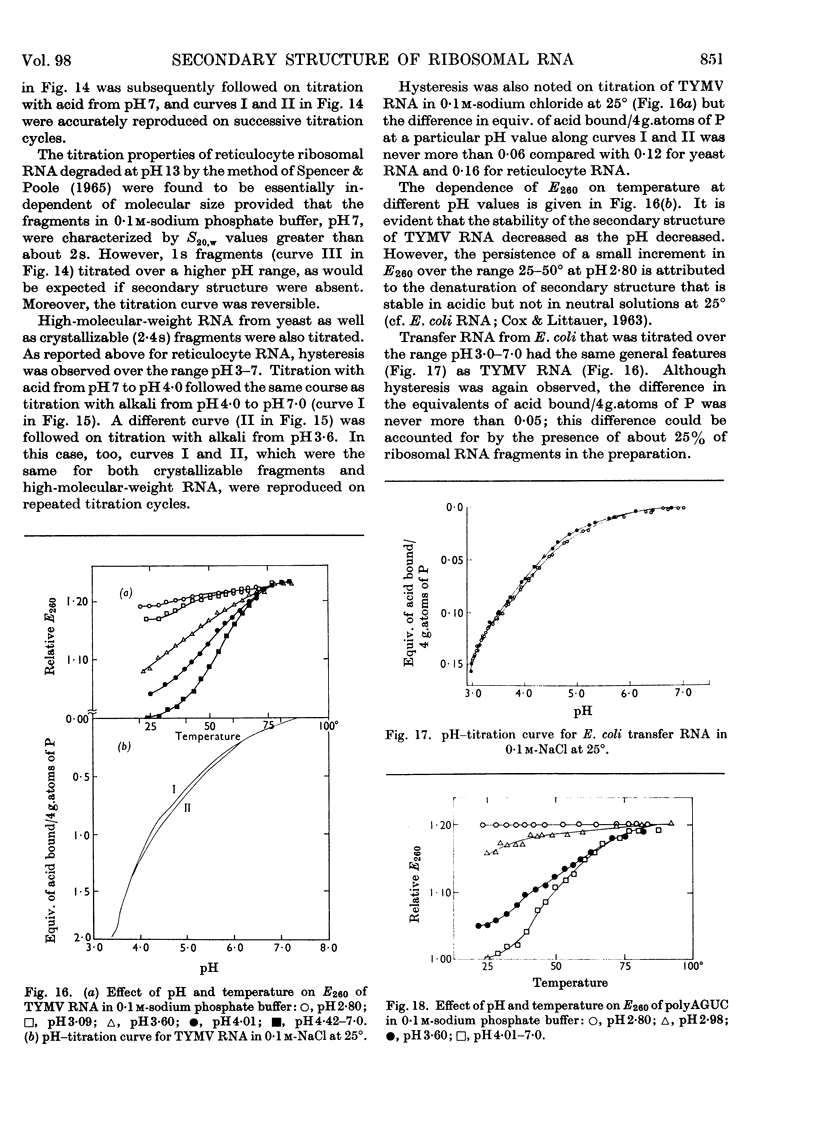
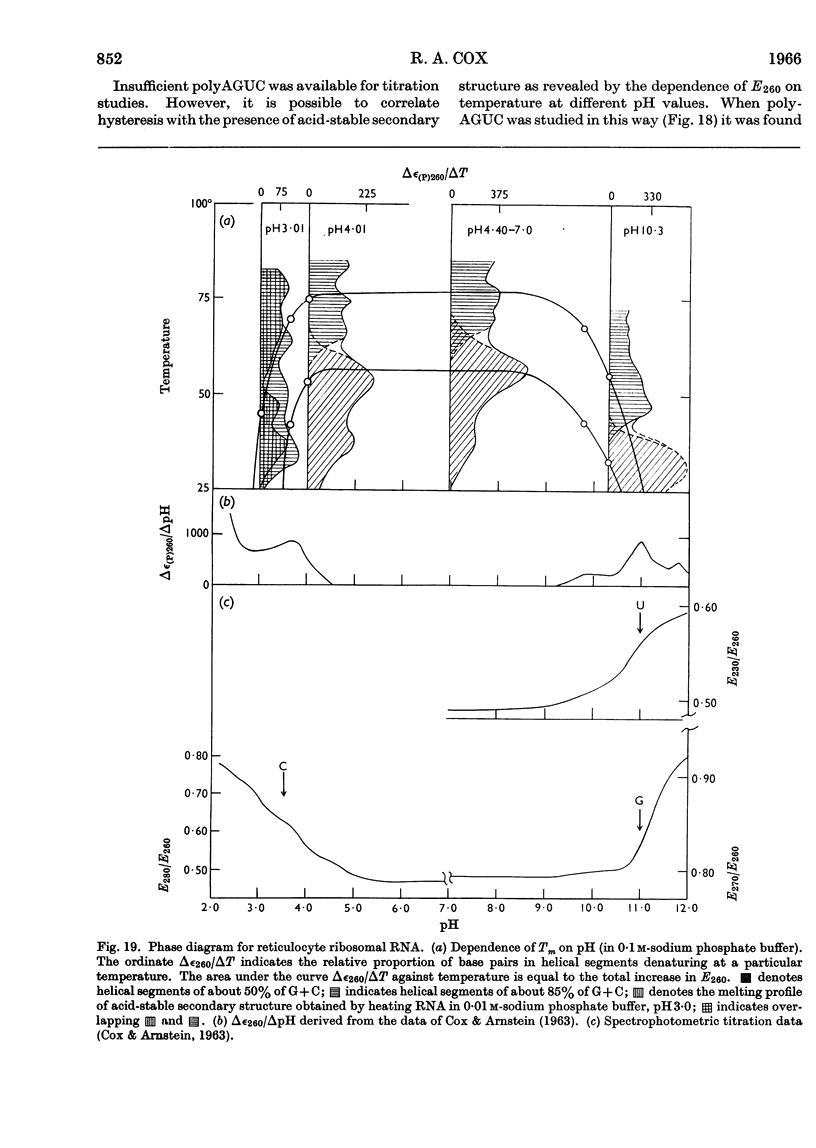
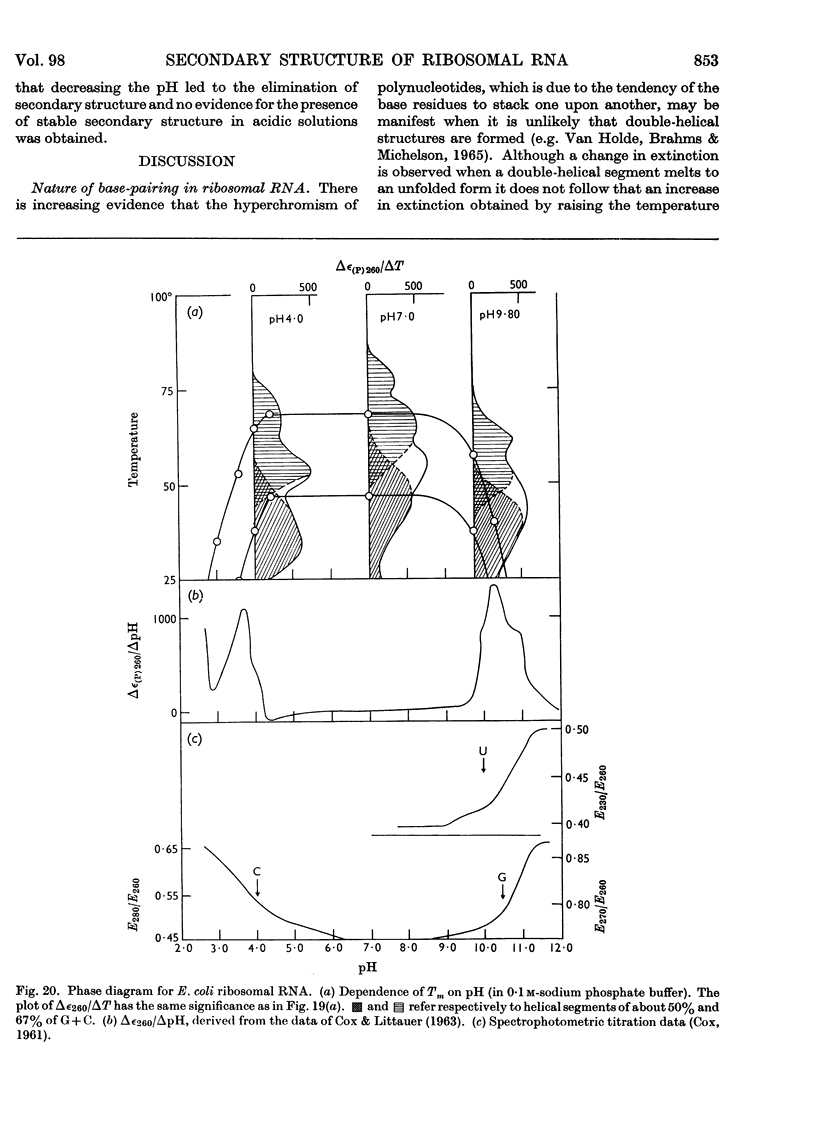
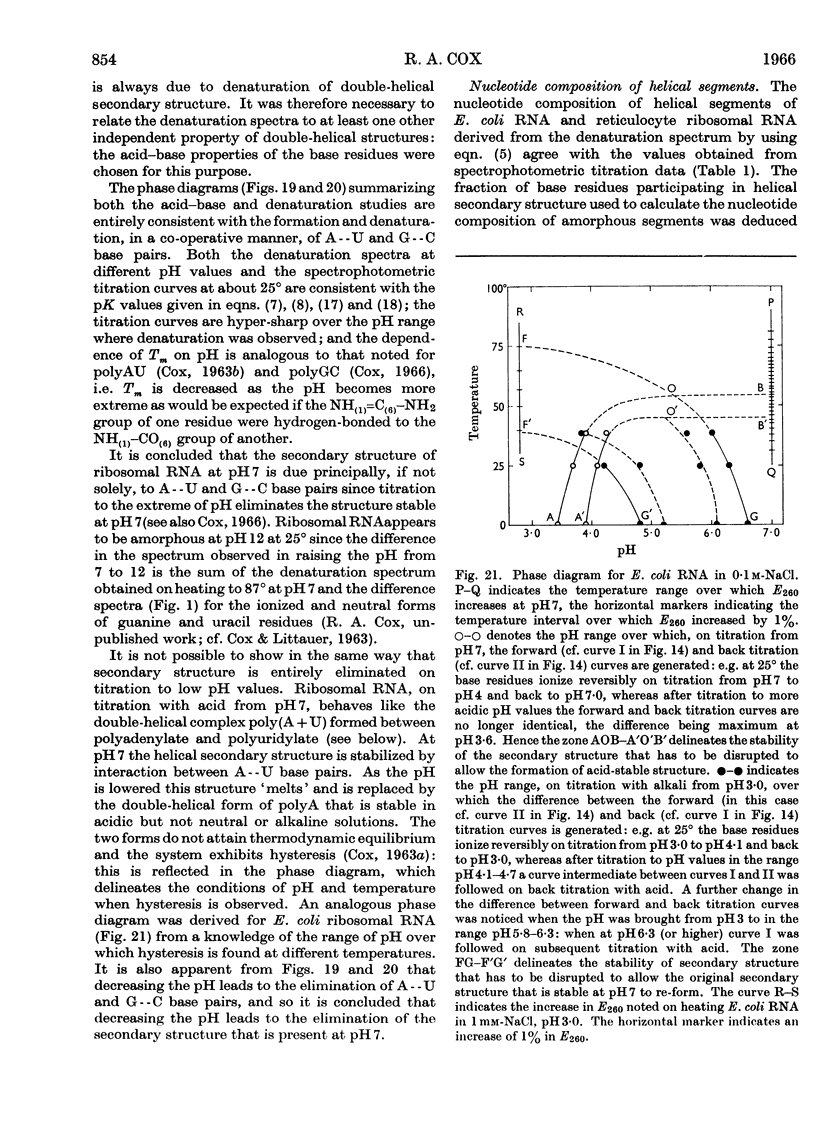
1. The u.v.-absorption spectrum of ribosomal RNA from rabbit reticulocytes was studied as a function of temperature at different pH values. The changes in the spectrum over the range 220–320mμ were interpreted on the basis of the assumption that the effect of denaturation and ionization are additive. The results suggest that in neutral salt solutions the secondary structure of the ribosomal RNA samples studied is due to two species of helical segments stabilized principally, if not solely, by complementary base pairs but differing in nucleotide composition: each species appears to be heterogeneous in other respects in view of the breadth of the melting ranges. 2. The number of base pairs per helical segment was estimated to be small (between 4 and 17) on the basis of the relation between melting temperature and chain length previously established by Lipsett and others for model compounds. Small fragments (about 2s) obtained by alkaline hydrolysis appeared to form the same helical segments as the intact molecule in accord with the estimated size of these segments. 3. Specific nucleotide sequences appear necessary to account for the hysteresis observed on titrating ribosomal RNA with acid or alkali within the range pH3·0–7·0 since this phenomenon was less pronounced for Escherichia coli transfer RNA and for RNA from turnip yellow-mosaic virus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Gould H., Potter H. A comparison of methods for the isolation and fractionation of reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):500–506. doi: 10.1042/bj0960500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUTZ E. K., BAUTZ F. A. THE INFLUENCE OF NONCOMPLEMENTARY BASES ON THE STABILITY OF ORDERED POLYNUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1476–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A., ARNSTEIN H. R. THE ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM RABBIT-RETICULOCYTE RIBOSOMES. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:574–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0890574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A. Dissociation properties of ribonucleic acid. I. Titration of rat-liver RNA and model polynucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A., LITTAUER U. Z. Dissociation properties of Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:188–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX R. A. The acid-base properties of ribonucleic acid. II. Spectrophotometric titration studies of poly-AU. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:203–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., SMITH K. C., ALLEN F. W. The preparation and characterization of ribonucleic acids from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD G., SANDEEN G. The dispersion of the hyperchromic effect in thermally induced transitions of nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1962 Dec;5:587–610. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRESCO J. R., ALBERTS B. M., DOTY P. Some molecular details of the secondary structure of ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1960 Oct 8;188:98–101. doi: 10.1038/188098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N. COMPLEX FORMATION BETWEEN POLYCYTIDYLIC ACID AND GUANINE OLIGONUCLEOTIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1256–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N., HEPPEP L. A., BRADLEY D. F. Complex formation between oligonucleotides and polymers. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTAUER U. Z., EISENBERG H. Ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli; preparation, characterization and physical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:320–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN E. M., YEGIAN C., STENT G. S. SPECIFICITY OF THE AMINO ACID TRANSFER REACTION IN E. COLI STRAINS CARRYING DIFFERENT ALLELES OF THE RNA CONTROL (RC) GENE. Z Vererbungsl. 1963 Nov 21;94:303–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00894774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTAGNIER L., SANDERS F. K. REPLICATIVE FORM OF ENCEPHALOMYOCARDITIS VIRUS RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Nature. 1963 Aug 17;199:664–667. doi: 10.1038/199664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER M., FULLER W., WILKINS M. H., BROWN G. L. Determination of the helical configuration of ribonucleic acid molecules by X-ray diffraction study of crystalline amino-acid-transfer ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1962 Jun 16;194:1014–1020. doi: 10.1038/1941014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER M., POOLE J. ON THE ORIGIN OF CRYSTALLIZABLE RNA FROM YEAST. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:314–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER R. F., BEERS R. F., Jr Polynucleotides. VII. Interaction of polyriboadenylic and polyribouridylic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Holde K. E., Brahms J., Michelson A. M. Base interactions of nucleotide polymers in aqueous solution. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):726–739. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


