Abstract
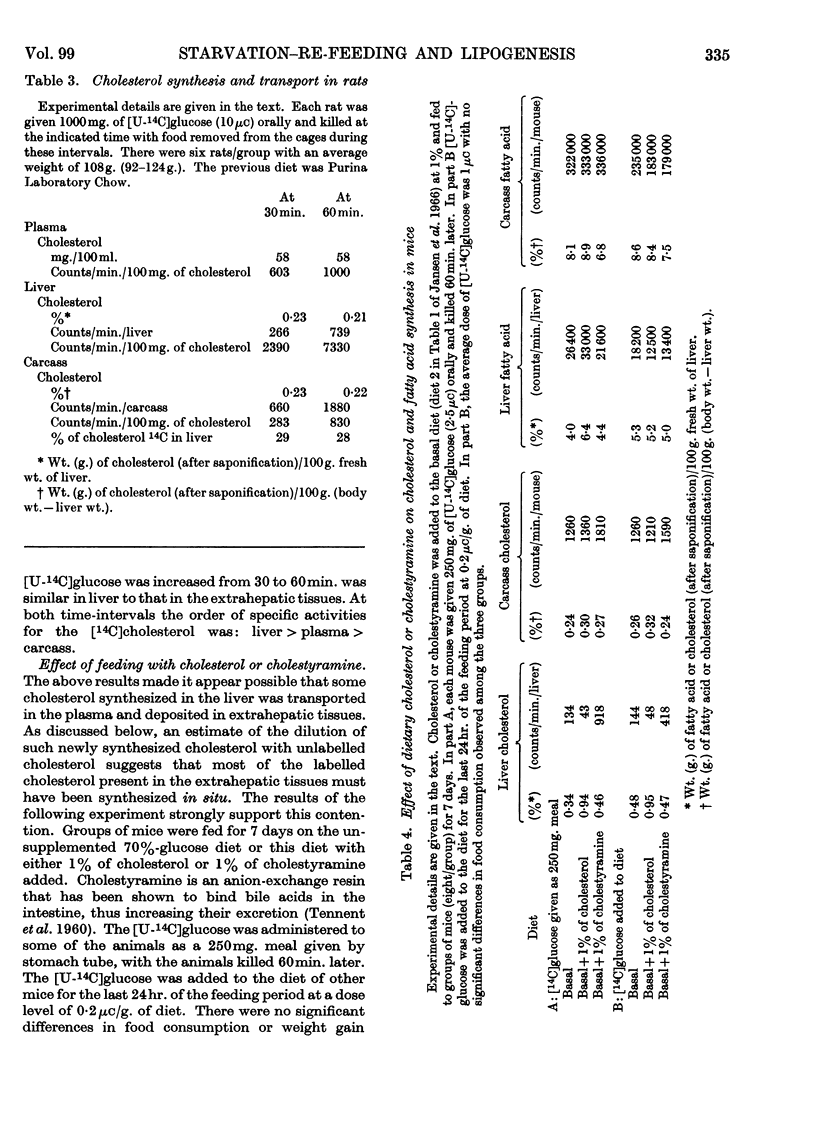
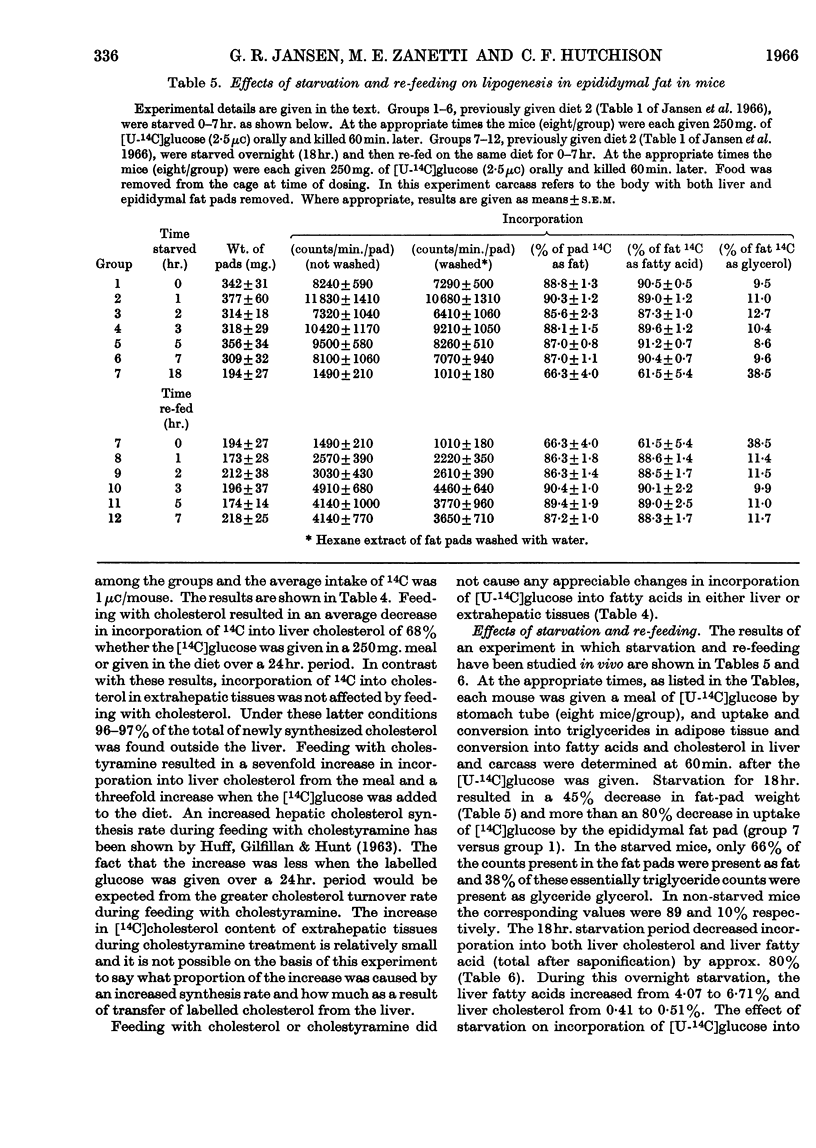
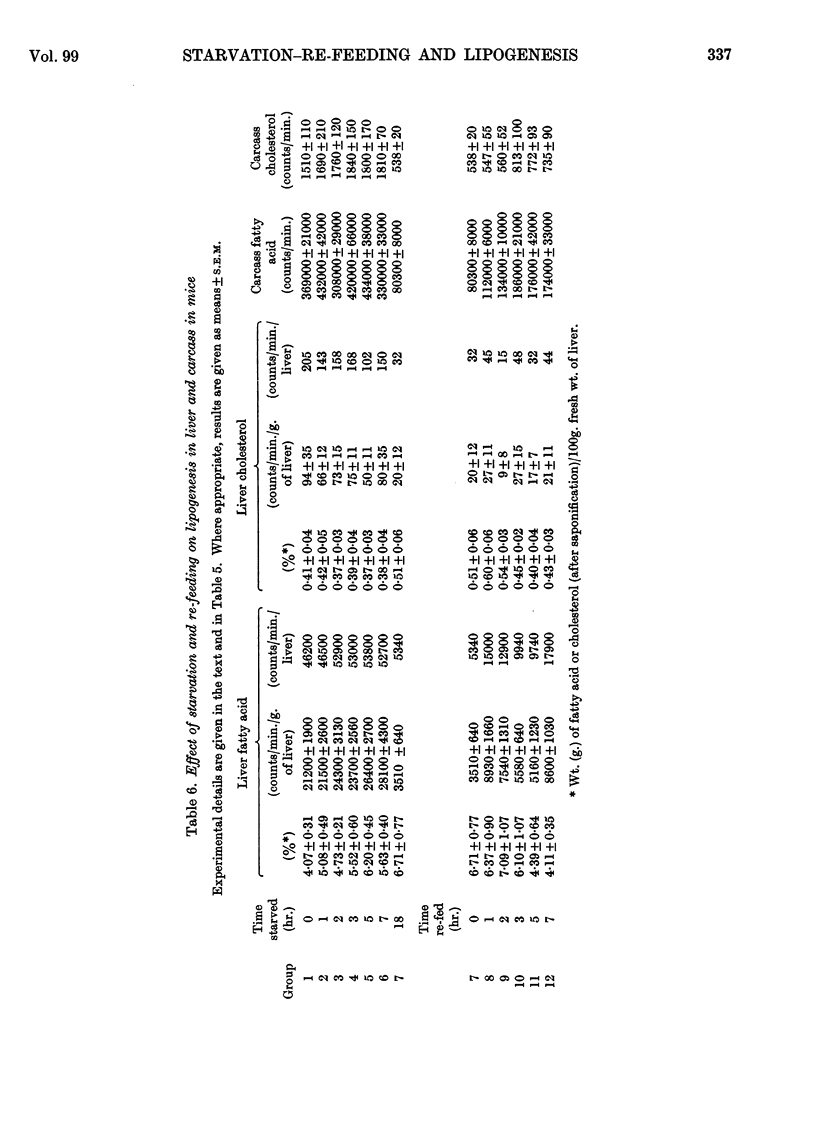
1. Studies in vivo have been carried out on hepatic and extrahepatic cholesterol synthesis and also on the effects of starvation and re-feeding on both cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis. 2. In rats and mice fed on a stock diet, extrahepatic tissues accounted for about 4 times as much newly synthesized cholesterol as did the liver. The liver appeared to be somewhat more important in the rat than the mouse. Feeding with cholesterol greatly decreased and cholestyramine greatly increased hepatic cholesterol synthesis without much effect on extrahepatic synthesis. 3. Mice starved for up to 7hr. did not lose any of the ability to convert a [U-14C]glucose meal into fat, whereas 18hr. of starvation resulted in an 80% loss of fatty acid synthesis in liver and carcass, an 80% loss in liver cholesterol synthesis and a 65% decrease in carcass cholesterol synthesis; 18hr. of food deprivation also decreased the proportion of counts in epididymal fat pads present as fat and increased the proportion present as glyceride glycerol. 4. Re-feeding for up to 7hr. restored fatty acid synthesis from a [U-14C]glucose meal to about 50% of the values for non-starved mice but had no effect on hepatic cholesterol synthesis. The altered distribution of counts in the epididymal fat pads caused by starvation was restored to normal after feeding for 1hr.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM S., KOPELOVICH L., CHAIKOFF I. L. DIETARY AND HORMONAL REGULATION OF THE HEPATIC CITRATE-CLEAVAGE ENZYME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:185–187. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORTZ W. M., LYNEN F. THE INHIBITION OF ACETYL COA CARBOXYLASE BY LONG CHAIN ACYL COA DERIVATIVES. Biochem Z. 1963 Aug 14;337:505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCKBURN R. M., VAN BRUGGEN J. T. Acetate metabolism in vivo; effect of refeeding. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):431–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER D. W., BLOOM B. A reciprocal relationship between fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 18;70:341–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90759-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G., TAYLOR C. B., HAGERMAN J. S., WARNER I., CAMPBELL D. J. Cholesterol metabolism. I. Effect of dietary cholesterol on the synthesis of cholesterol in dog tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Hydrolysis of long-chain monoglycerides in micellar solution by pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 18;70:317–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90755-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUFF J. W., GILFILLAN J. L., HUNT V. M. EFFECT OF CHOLESTYRAMINE, A BILE ACID-BINDING POLYMER ON PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND FECAL BILE ACID EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Nov;114:352–355. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G. R., Hutchon C. F., Zanetti M. E. Studies on lipogenesis in vivo. Effect of dietary fat or starvation on conversion of [14]glucose into fat ad turnover of newly synthsized fat. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):323–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0990323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORCHAK H. M., MASORO E. J. INHIBITORY MECHANISMS IN THE CONTROL OF LIPOGENESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 27;70:647–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90809-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASORO E. J., CHAIKOFF I. L., CHERNICK S. S., FELTS J. M. Previous nutritional state and glucose conversion to fatty acids in liver slices. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):845–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASRI M. S., LYON I., CHAIKOFF I. L. Nature of the stimulating action of insulin on lipogenesis from acetate in fasted rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(2):621–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS M. D., CHAIKOFF I. L., FELTS J. M., ABRAHAM S., FANSAH N. O. The origin of serum cholesterol in the rat; diet versus synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):1039–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR C. B., PATTON D., YOGI N., COX G. E. Diet as source of serum cholesterol in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:768–772. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENNENT D. M., SIEGEL H., ZANETTI M. E., KURON G. W., OTT W. H., WOLF F. J. Plasma cholesterol lowering action of bile acid binding polymers in experimental animals. J Lipid Res. 1960 Oct;1:469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Metabolism of glucose-1-C-14 and glucose-6-C-14 by liver slices of refed rats. Am J Physiol. 1961 May;200:1069–1073. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.5.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TZUR R., TAL E., SHAPIRO B. ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE AS REGULATORY FACTOR IN FATTY ACID ESTERIFICATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 24;84:18–23. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN BRUGGEN J. T., HUTCHENS T. T., CLAYCOMB C. K., CATHEY W. J., WEST E. S. The effect of fasting upon lipogenesis in the intact rat. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):389–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKIL S. J., PUGH E. L., SAUER F. THE MECHANISM OF FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:106–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


