Abstract
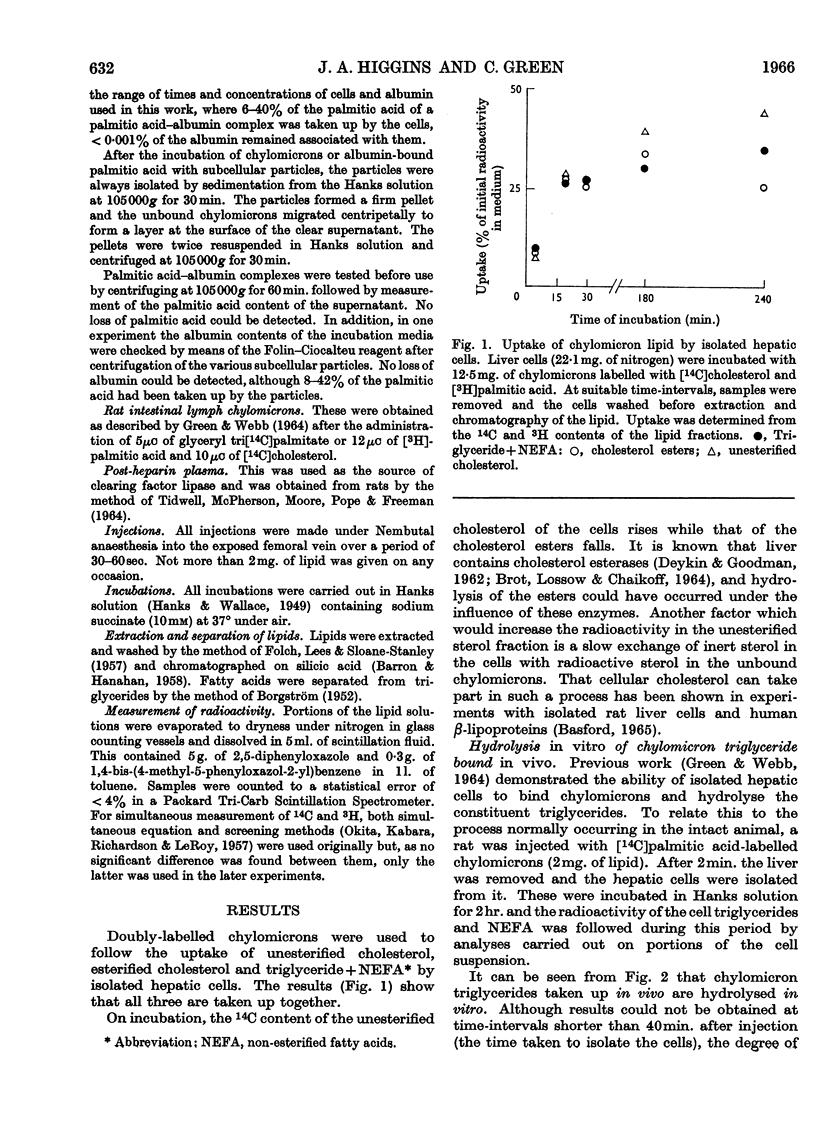
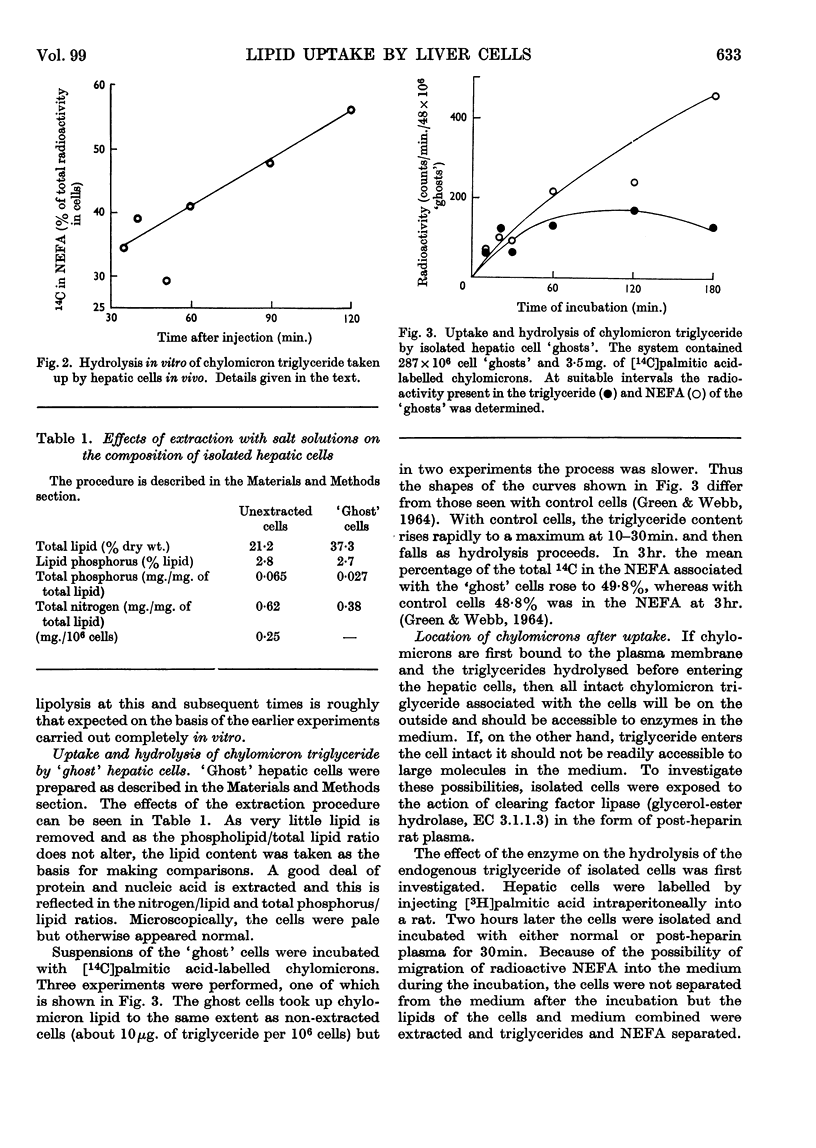
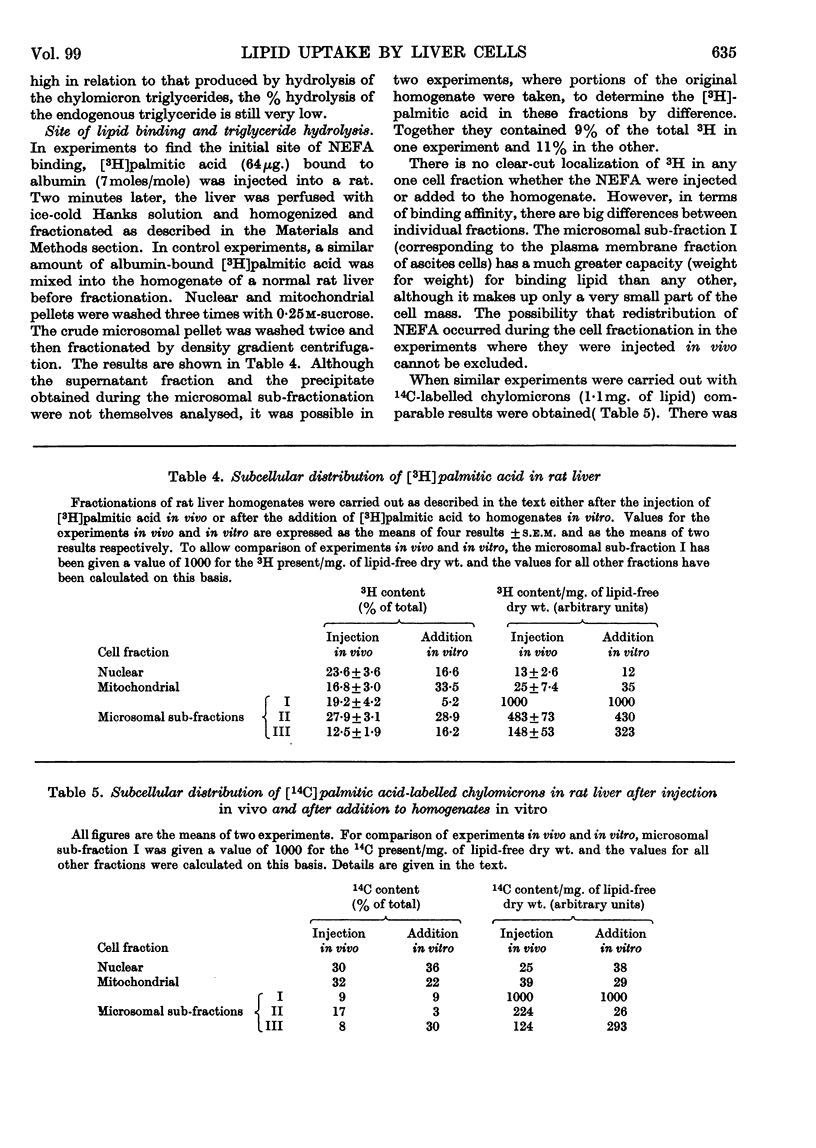
1. Unesterified cholesterol, cholesterol esters and triglycerides of chylomicrons were taken up at the same rate by isolated hepatic parenchymal cells. 2. On incubation of hepatic cells, isolated 2min. after the injection of chylomicrons in vivo, the chylomicron triglyceride associated with the cells underwent hydrolysis. 3. In cells isolated 5min. after the injection of chylomicrons, the chylomicron triglyceride bound to the hepatic cells was accessible to added clearing factor lipase. 4. `Ghost' hepatic cells had the same binding capacity and lipolytic activity per cell as intact cells. 5. Of all subcellular fractions studied, the `plasma membrane' fraction showed the greatest capacity per unit weight for non-esterified fatty acid and chylomicron triglyceride binding and for triglyceride hydrolysis. 6. Once non-esterified fatty acids entered the hepatic cell, they were apparently metabolized in the same manner, whether taken up from the circulation as such or derived from chylomicron triglyceride.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH C. T., STEMBRIDGE V. A., SANDERS E. Lipid absorption, transport and hepatic assimilation with electron microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jun;198:1326–1328. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.6.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth L. A., Green C. Plasma membranes: phospholipid and sterol content. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):210–211. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRON E. J., HANAHAN D. J. Observations on the silicic acid chromatography of the neutral lipides of rat liver, beef liver, and yeast. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):493–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELFRAGE P., BORGSTROM B., OLIVERCRONA T. The tissue distribution of radioactivity following the injection of varying levels of fatty acid labeled chylomicrons in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1963 Jun-Jul;58:111–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1963.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B. Investigation on lipid separation methods. Separation of cholesterol esters, glycerides and free fatty acids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Jun 6;25(2-3):111–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEYKIN D., GOODMAN D. S. The hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acid esters of cholesterol with rat liver enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3649–3656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELOT P., BOS C. J., BENEDETTI E. L., RUEMKE P. STUDIES ON PLASMA MEMBRANES. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND ENZYME CONTENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANES ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:126–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITZ I. B. CARNITINE EFFECTS ON PALMITATE-I-C-14 CONVERSION TO CO2 AND GLYCERIDES BY VARIOUS TISSUES. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1217–1222. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts J. M., Mayes P. A. Lack of uptake and oxidation of chylomicron triglyceride to carbon dioxide and ketone bodies by the perfused rat liver. Nature. 1965 Apr 10;206(980):195–196. doi: 10.1038/206195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOVER J., GREEN C. Sterol metabolism. 3. The distribution and transport of sterols across the intestinal mucosa of the guinea pig. Biochem J. 1957 Oct;67(2):308–316. doi: 10.1042/bj0670308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOERANSSON G., OLIVECRONA T. THE METABOLISM OF FATTY ACIDS IN THE RAT. I. PALMITIC ACID. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Nov;62:224–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb03970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. Preparation of human serum albumin free of long-chain fatty acids. Science. 1957 Jun 28;125(3261):1296–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3261.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesterol ester in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1886–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI104645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN E., THOMAS L. E. Cellular lipoproteins. III. The insoluble lipoproteins of rat liver cell fractions. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:363–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS B. THE METABOLISM OF FREE FATTY ACIDS AND CHYLOMICRON TRIGLYCERIDES BY THE ISOLATED PERFUSED LIVER OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:564–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J., HAVEL R. J., BEZMAN A. METABOLISM OF CONSTITUENT LIPIDS OF DOG CHYLOMICRONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1313–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI104815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVILLE D. M., Jr The isolation of a cell membrane fraction from rat liver. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:413–422. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVECRONA T., BELFRAGE P. MECHANISMS FOR REMOVAL OF CHYLE TRIGLYCERIDE FROM THE CIRCULATING BLOOD AS STUDIED WITH (14C)GLYCEROL AND (3H)PALMITIC ACID- LABELED CHYLE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:81–93. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RESHEF L., SHAPIRO B. FATTY ACID ADSORPTION BY LIVER- AND ADIPOSE-TISSUE PARTICLES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:73–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M., SCOW R. O., CHERNICK S. S. REMOVAL AND METABOLISM OF TRIGLYCERIDES BY PERFUSED LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN Y., SHAPIRO B. Uptake and metabolism of triglycerides by the rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1960 Jul;1:326–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIDWELL H. C., MCPHERSON J. C., MOORE W. T., POPE J. L., FREEMAN A. LIPOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN THE BLOOD AFTER LIPASE INGESTION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:720–723. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. F., ULLREY D. STUDIES ON THE SURFACE AND CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANES OF EHRLICH ASCITES CARCINOMA CELLS. II. ALKALI-CATION-ACTIVATED ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE HYDROLYSIS IN A MICROSOMAL MEMBRANE FRACTION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 29;88:620–629. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. F., ULLREY D. Studies on the surface and cytoplasmic membranes of Ehrlich ascites-carcinoma cells. I. The hydrolysis of ATP and related nucleotides by microsomal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 5;64:526–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T., Lapresle C. Isolation and study of rabbit antibodies specific for certain of the antigenic groups of human serum albumin. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):24–31. doi: 10.1042/bj0910024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


