Abstract
1. A new method of purification of renin is described. This method employs the following procedures: ethanol precipitation; saline extraction; precipitation of renin with 40% ammonium sulphate; precipitation of impurities with 3% ammonium sulphate at pH2·5; chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and CM-Sephadex; gel filtration on Sephadex G-100 (both normal and superfine grade); finally, starch-gel electrophoresis. 2. The final renin preparation had a specific activity 104 times that of the initial saline extract. 3. A single band of stained protein corresponding to the renin activity was present on starch-gel electrophoresis in the final step and a single precipitin line was obtained to this material with rabbit anti-(pig renin) serum. 4. Double diffusion in agar with rabbit anti-(pig renin) serum showed one major precipitin line, probably due to renin–anti-renin complex, and in addition two minor components.
Full text
PDF


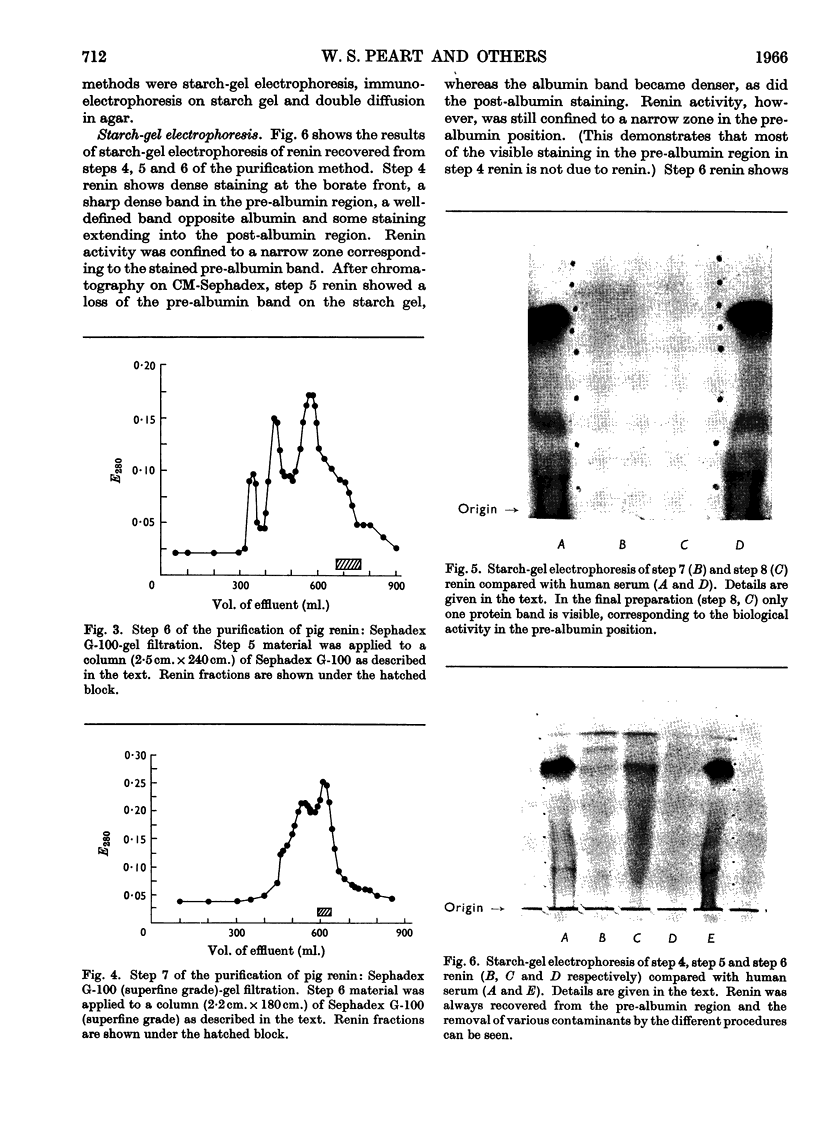
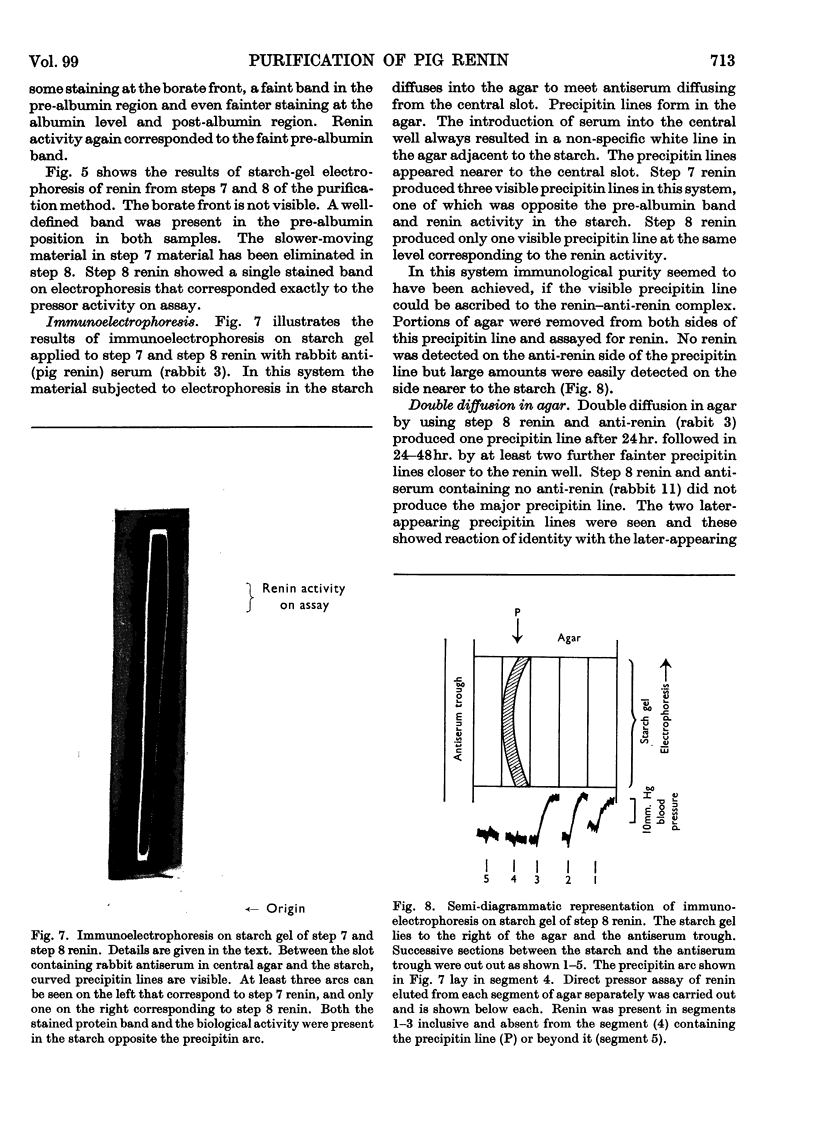
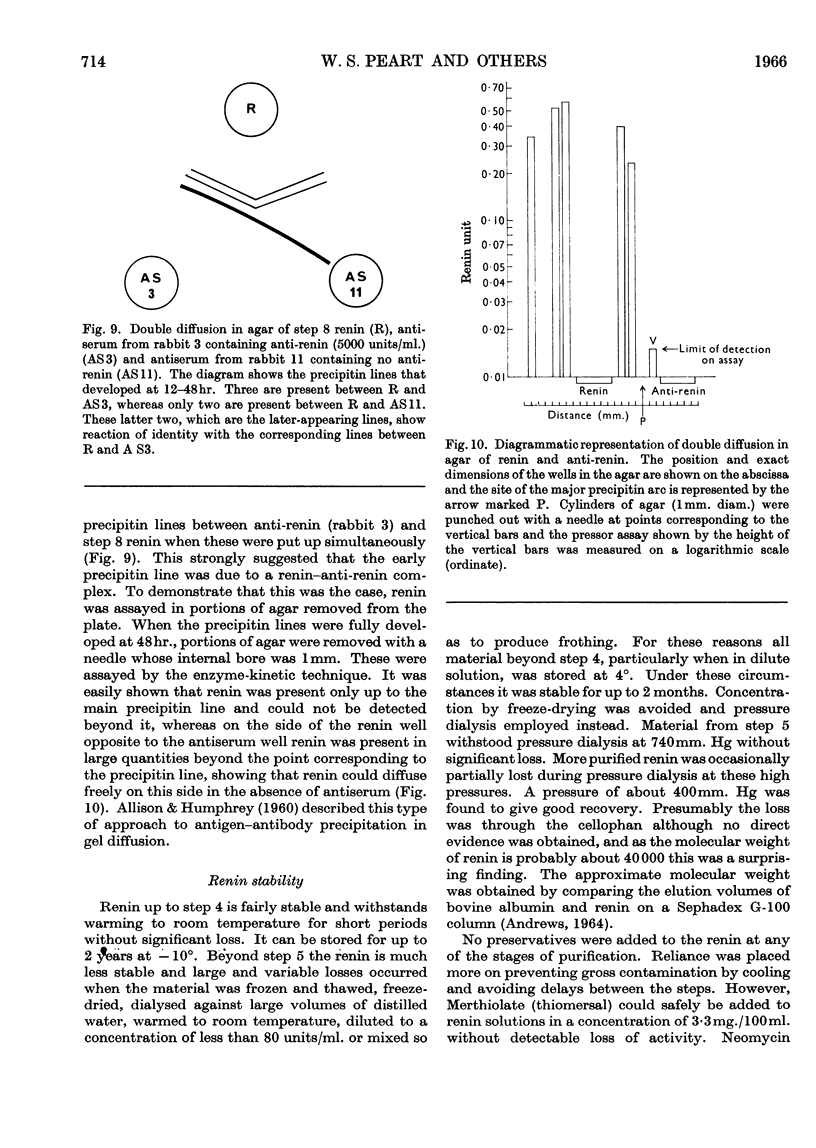


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., HUMPHREY J. H. A theoretical and experimental analysis of double diffusion precipitin reactions in gels, and its application to characterization of antigens. Immunology. 1960 Jan;3:95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAS E., LAMFROM H., GOLDBLATT H. Isolation and purification of hog renin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):368–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMFROM H., HAAS E., GOLDBLATT H. Studies on antirenin. Am J Physiol. 1954 Apr;177(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER A. F., PEART W. S. Renin and angiotensin-like activity in renal lymph. J Physiol. 1962 Mar;160:548–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A. F., Robertson J. I., Tree M. The estimation of renin in plasma by an enzyme kinetic technique. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):346–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0910346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIRN R. C., CHADWICK C. S., FRASER K. B. Purification of renin by electrophoresis, adsorption and immunological methods. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Jun;41:214–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASSANANTI G. T. The purification of renin by use of ion-exchange chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:246–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEART W. S. A new method of large-scale preparation of hypertensin, with a note on its assay. Biochem J. 1955 Feb;59(2):300–302. doi: 10.1042/bj0590300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Starch gel electrophoresis in a discontinous system of buffers. Nature. 1957 Dec 28;180(4600):1477–1479. doi: 10.1038/1801477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOPES R. K. Starch-gel electrophoresis of pig serum proteins. Nature. 1963 Mar 23;197:1201–1201. doi: 10.1038/1971201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]