Abstract
1. The use of two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography is described that allows the rapid and simultaneous determination of phospholipid classes and their constituent plasmalogens. 2. The method is based on the specific hydrolysis of plasmalogens to (2-acyl) lysophospholipid in the presence of a mercuric chloride spray reagent. 3. The proportion of mercuric chloride-labile phospholipid present in each phospholipid class, calculated on the basis of phosphorus recoveries from the charred chromatogram, was compared with the proportion of long-chain aldehyde and of total lipid phosphorus found in small-scale preparations of each class of phospholipid. 4. The method permits the determination of individual plasmalogens on preparations containing as little as 0·2μg.atom of total lipid phosphorus.
Full text
PDF


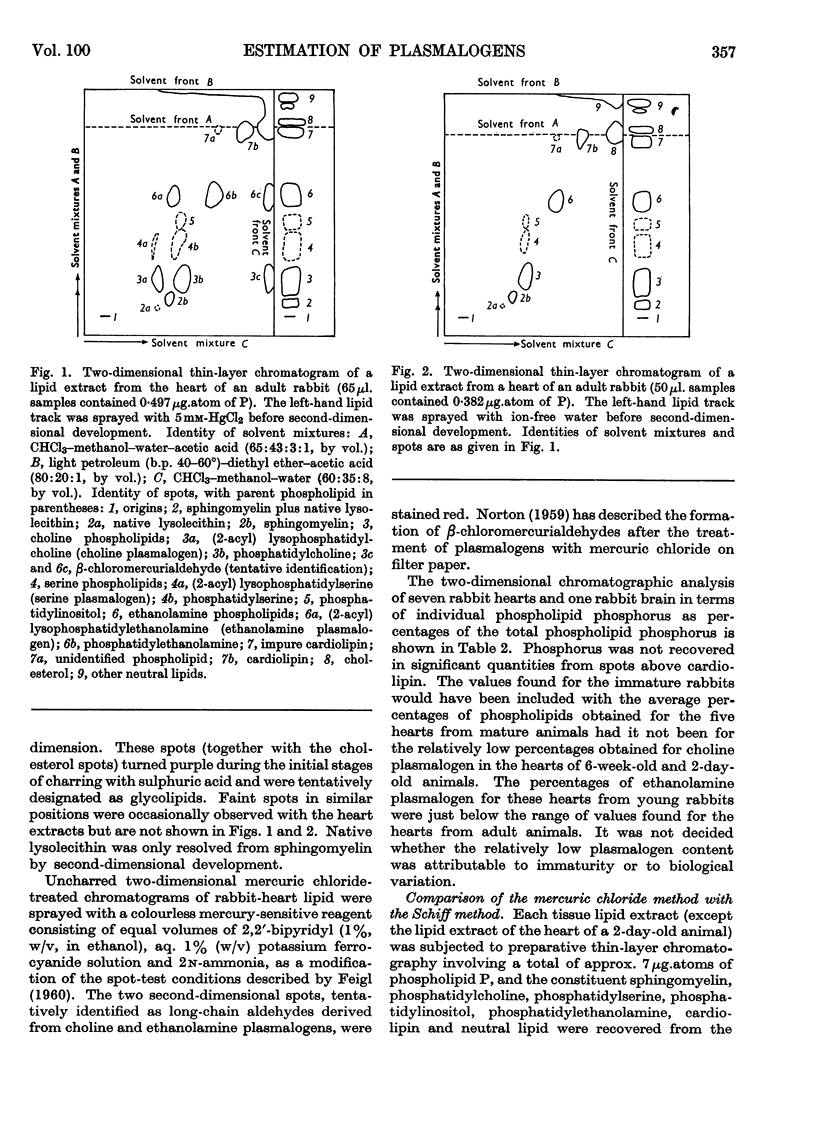
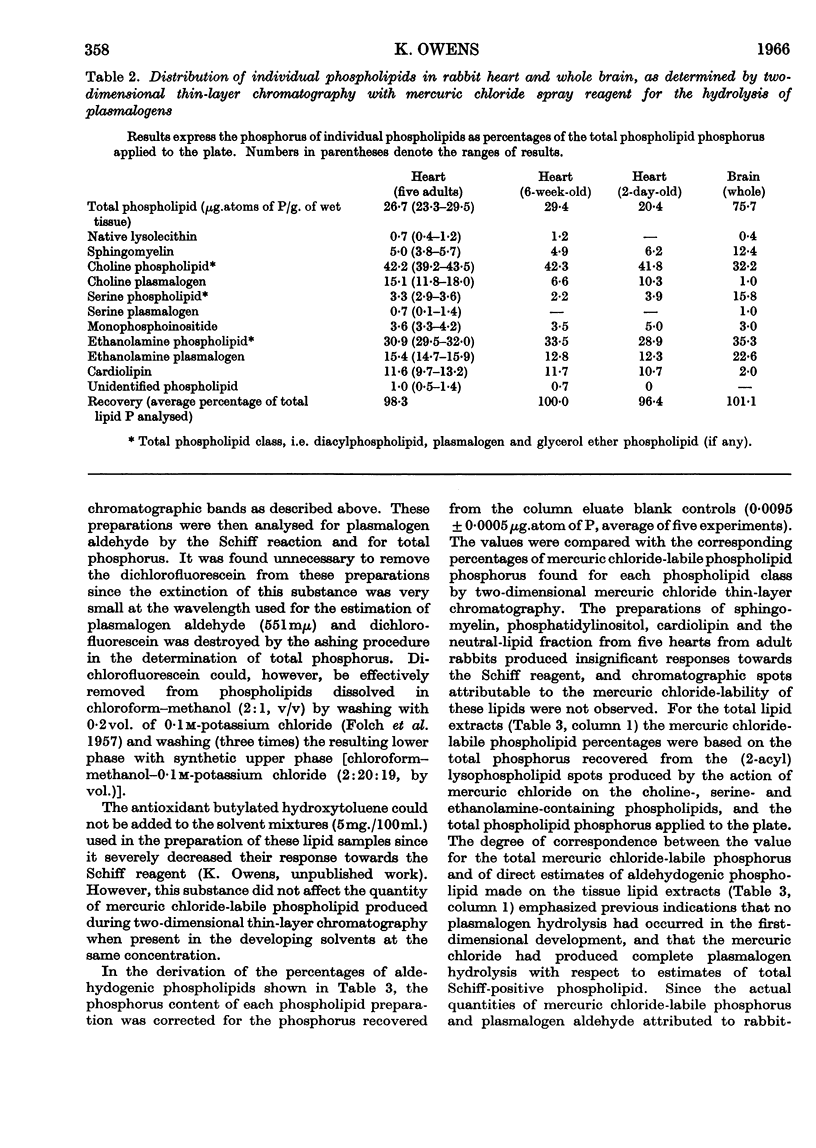
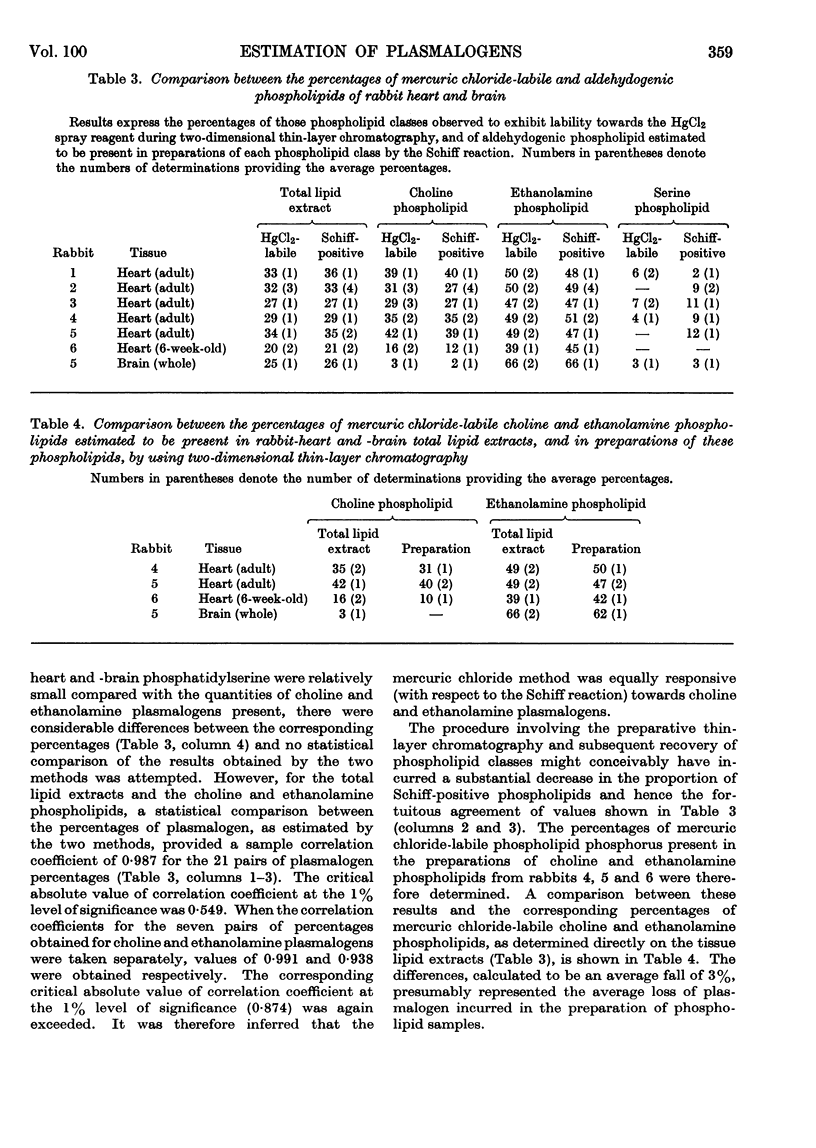


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON D., BLECHER M. QUANTITATIVE TWO-DIMENSIONAL THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NATURALLY OCCURRING PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:628–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTFRIED E. L., RAPPORT M. M. The biochemistry of plasmalogens. I. Isolation and characterization of phosphatidal choline, a pure native plasmalogen. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY G. M., MACFARLANE M. G. Separation and composition of the phospholipids of ox heart. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):409–425. doi: 10.1042/bj0700409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., JAMES A. T. Phosphatide components of fowl blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jul 8;50:478–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Staples D. A. Chromatographic separation of brain lipids. 2. Ethanolamine-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):557–562. doi: 10.1042/bj0800557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V., ERBLAND J., STOTZ E. The quantitative analysis of plasmalogens by paper chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jan;31(1):251–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON W. T. Reaction of mercuric chloride with plasmalogen. Nature. 1959 Oct 10;184(Suppl 15):1144–1145. doi: 10.1038/1841144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIETRUSZKO R., GRAY G. M. The products of mild alkaline and mild acid hydrolysis of plasmalogens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:232–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90560-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., ALONZO N. F. The structure of plasmalogens. V. Lipids of marine invertebrates. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:1953–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., FRANZL R. E. The structure of plasmalogens. III. The nature and significance of the aldehydogenic linkage. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., LERNER B. The structure of plsmalogens. IV. Lipids in normal and neoplastic tissues of man and in normal tissues of rabbit and rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., NORTON W. T. Chemistry of the lipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1962;31:103–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.31.070162.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSER G., GALLI C., KRITCHEVSKY G. LIPID CLASS COMPOSITION OF NORMAL HUMAN BRAIN AND VARIATIONS IN METACHROMATIC LEUCODYSTROPHY, TAY-SACHS, NIEMANN-PICK, CHRONIC GAUCHER'S AND ALZHEIMER'S DISEASES. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 May;42:404–410. doi: 10.1007/BF02635576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT G., OTTENSTEIN B., SPENCER W. A., KECK K., BLIETZ R., PAPAS J., PORTER D., LEVIN M. L., THANNHAUSER S. J. The partition of tissue phospholipides by phosphorus analysis. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 2):691–708. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010693007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKIPSKI V. P., PETERSON R. F., SANDERS J., BARCLAY M. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING SILICA GEL WITHOUT CALCIUM SULFATE BINDER. J Lipid Res. 1963 Apr;4:227–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIELE O. W. [Biocatalytic release of plasmal from plasmalogen. II. Existence and properties of a catalyst in crude phosphatides]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959 Oct 30;316:137–145. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.316.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTENBERG J. B., KOREY S. R., SWENSON F. H. The determination of higher fatty aldehydes in tissues. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


