Abstract
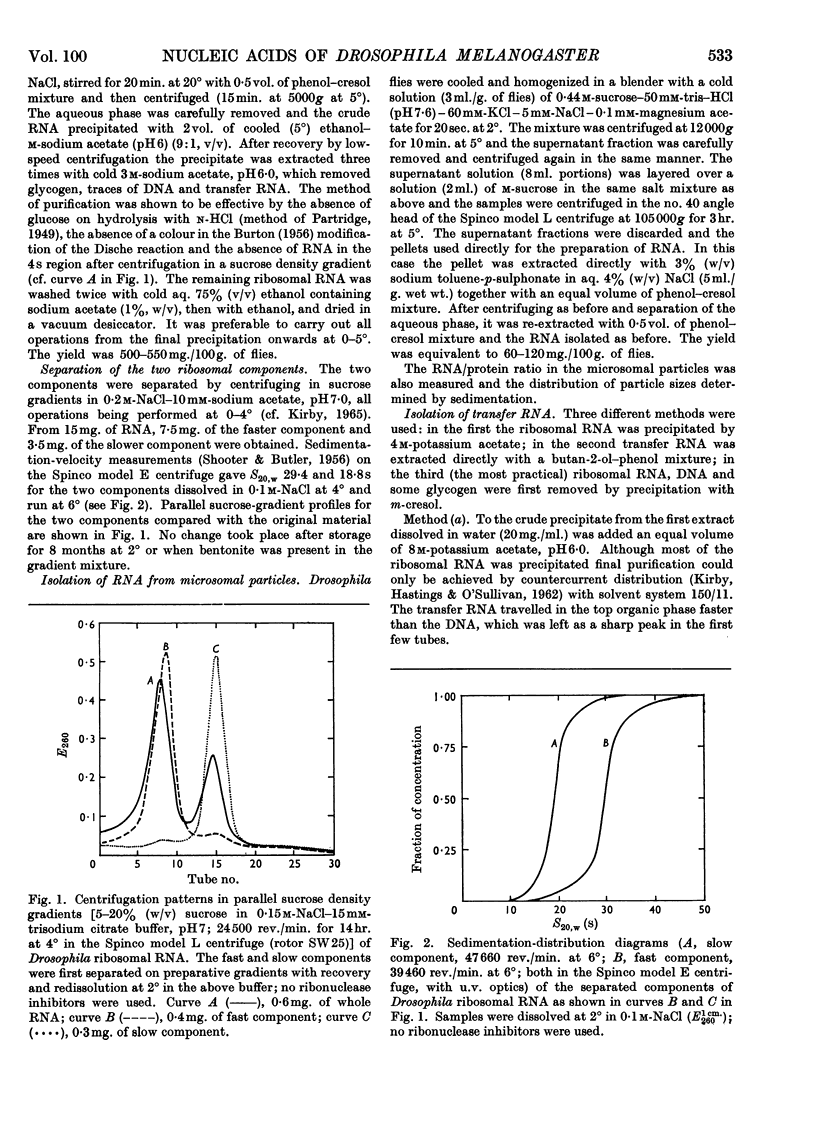
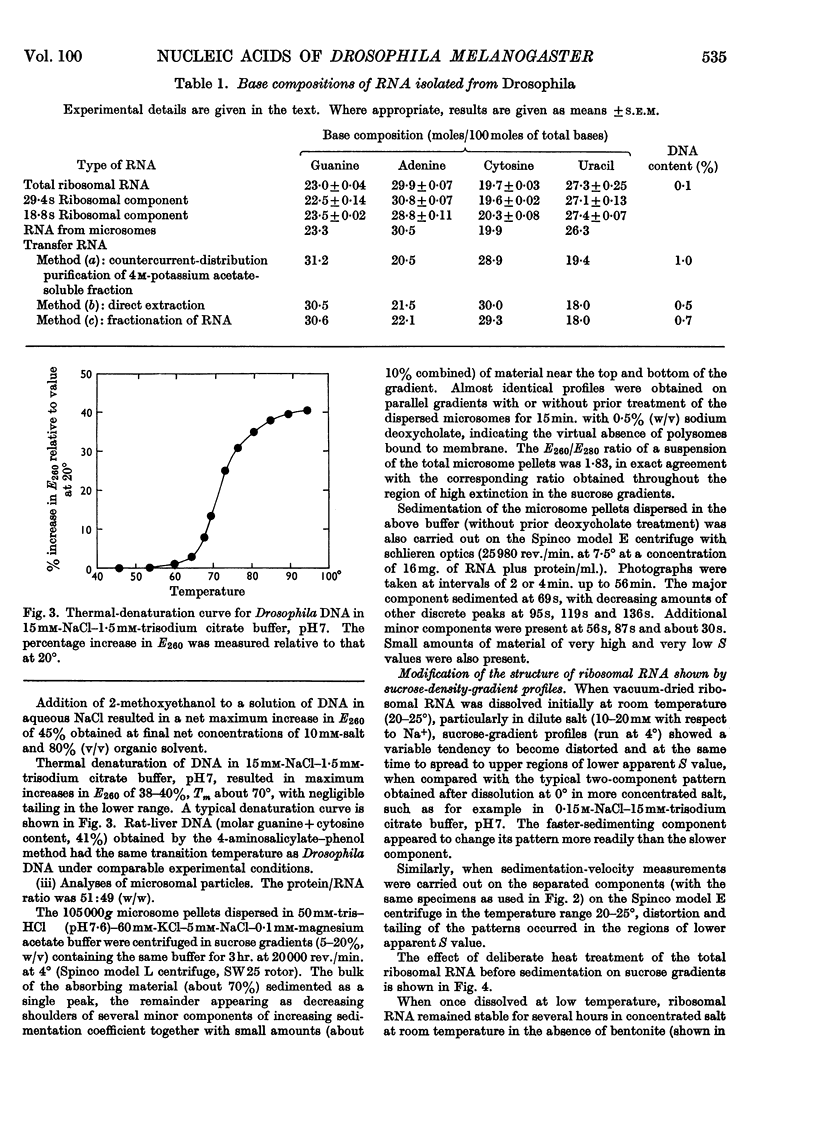
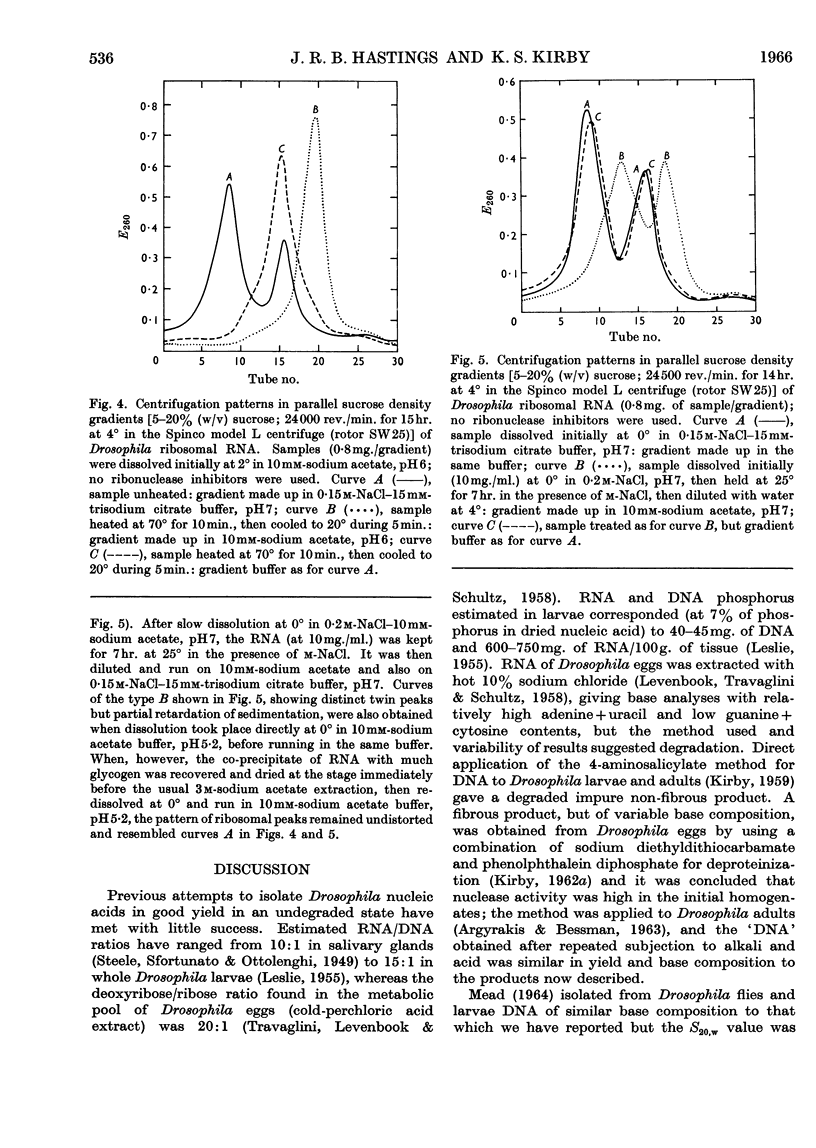
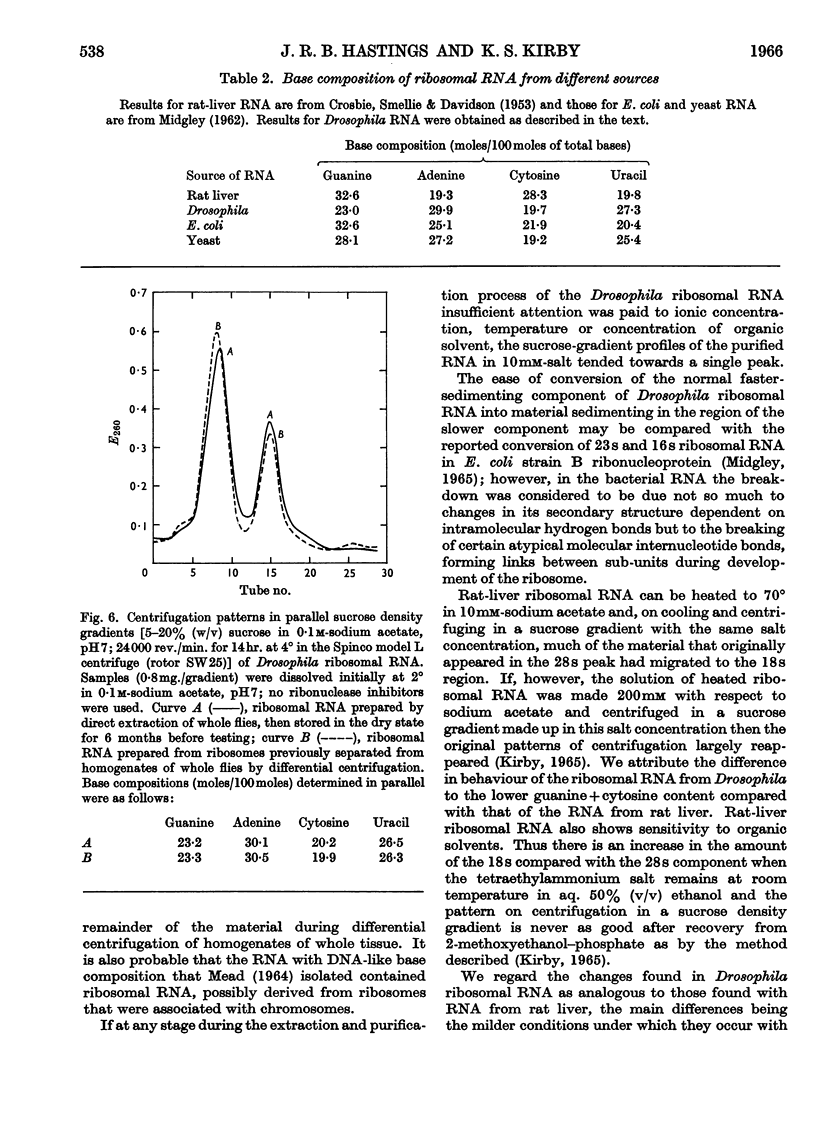
1. Nucleic acids of whole Drosophila adults were prepared in good yield and substantially free from impurities by new modifications of the phenol method. 2. The average molar base compositions of the DNA (41% of guanine+cytosine) and transfer RNA (60% of guanine+cytosine) resemble those of mammalian nucleic acids; the ribosomal RNA has a DNA-like molar base composition (43% of guanine+cytosine), and it is considered that this is reflected in the lower stability of its secondary structure compared with mammalian ribosomal RNA. 3. The two main ribosomal forms were separated and average base compositions and sedimentation values determined.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARGYRAKIS M. P., BESSMAN M. J. Analysis of the base composition of the DNA from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:122–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBIE G. W., SMELLIE R. M., DAVIDSON J. N. Phosphorus compounds in the cell. V. The composition of the cytoplasmic and nuclear ribonucleic acids of the liver cell. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):287–292. doi: 10.1042/bj0540287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGIEV G. P. Bystryi metod polucheniia dezoksiribonukleinovoi kisloty v vysokopolimernom sostoianii. Biokhimiia. 1959 May-Jun;24(3):472–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acids; evidence on the nature of bonds between deoxyribonucleic acid and protein. Biochem J. 1957 Jul;66(3):495–504. doi: 10.1042/bj0660495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of ribonucleic acids from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):405–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0640405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. Deoxyribonucleic acids. IV. Preparation of deoxyribonucleic acid from Drosophila eggs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:382–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90794-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S., HASTINGS J. R., O'SULLIVAN M. A. Countercurrent distribution of ribonucleic acids. IV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:978–979. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:266–269. doi: 10.1042/bj0960266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. Ribonucleic acids. II. Improved preparation of rat-liver ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:545–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90988-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. The preparation of deoxyribonucleic acids by the p-aminosalicylate-phenol method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:117–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENBOOK L., TRAVAGLINI E. C., SCHULTZ J. Nucleic acids and their components as affected by the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Constitution and amount of the ribonucleic acids in the unfertilized egg. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Aug;15(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD C. G. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID-ASSOCIATED RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:550–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDGLEY J. E. EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT EXTRACTION PROCEDURES ON THE MOLECULAR CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIAL RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 8;95:232–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. D., MARKHAM R. Chromatographic studies on nucleic acids; the quantitative analysis of ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1950 May;46(5):509–513. doi: 10.1042/bj0460509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., MARMUR J., DOTY P., 2nd Dependence of the density of deoxyribonucleic acids on guanine-cytosine content. Nature. 1959 May 23;183(4673):1429–1431. doi: 10.1038/1831429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAVAGLINI E. C., LEVENBOOK L., SCHULTZ J. Nucleic acids and their components as affected by the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Nucleosides and related compounds in the acid soluble fraction of the unfertilized egg. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Aug;15(1):62–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


