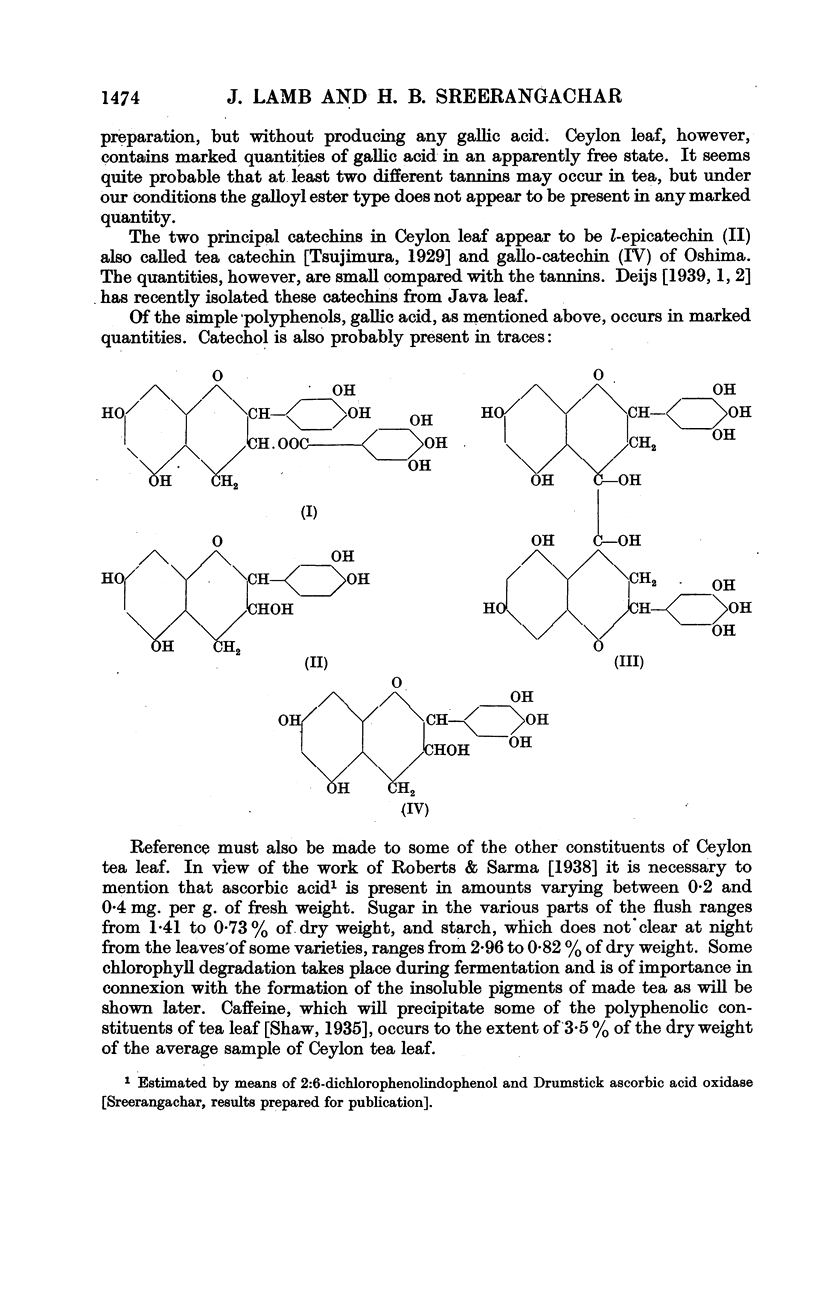
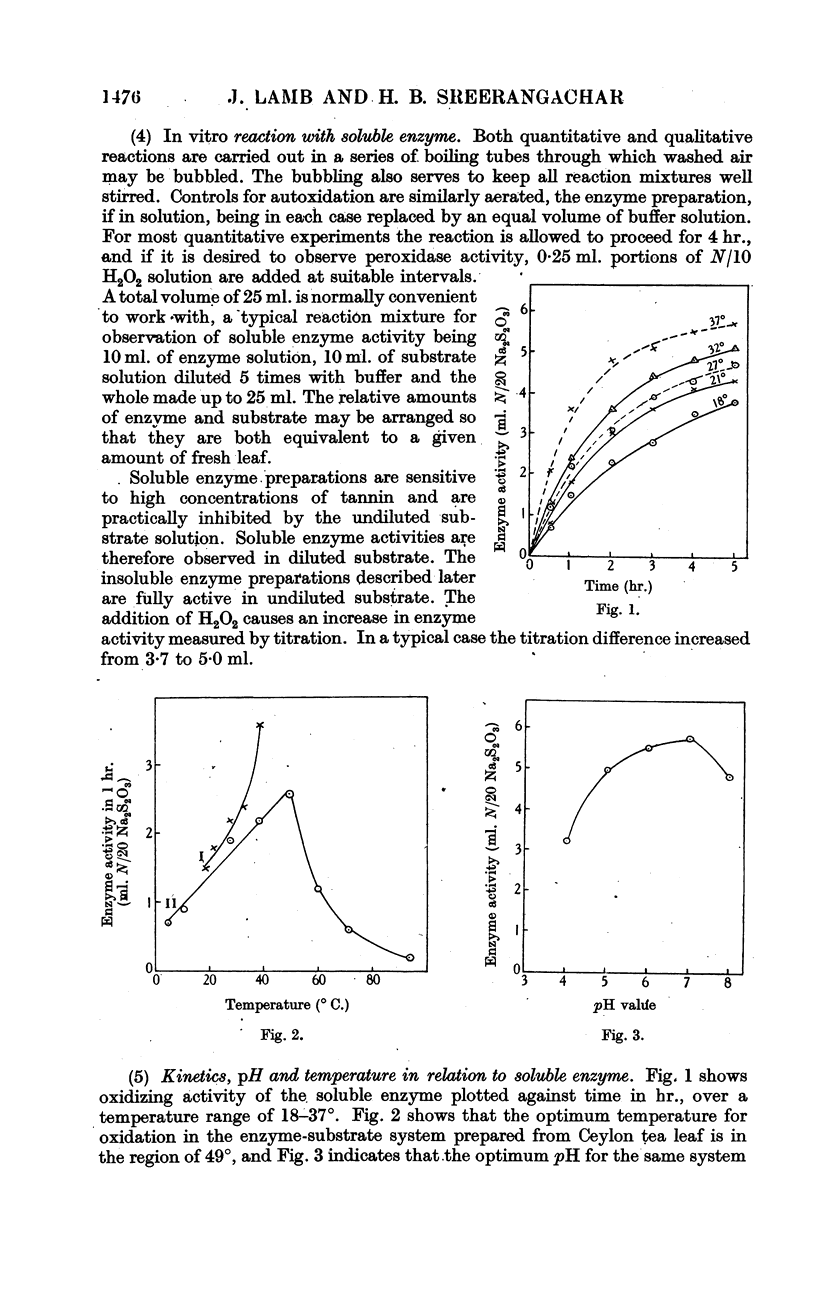
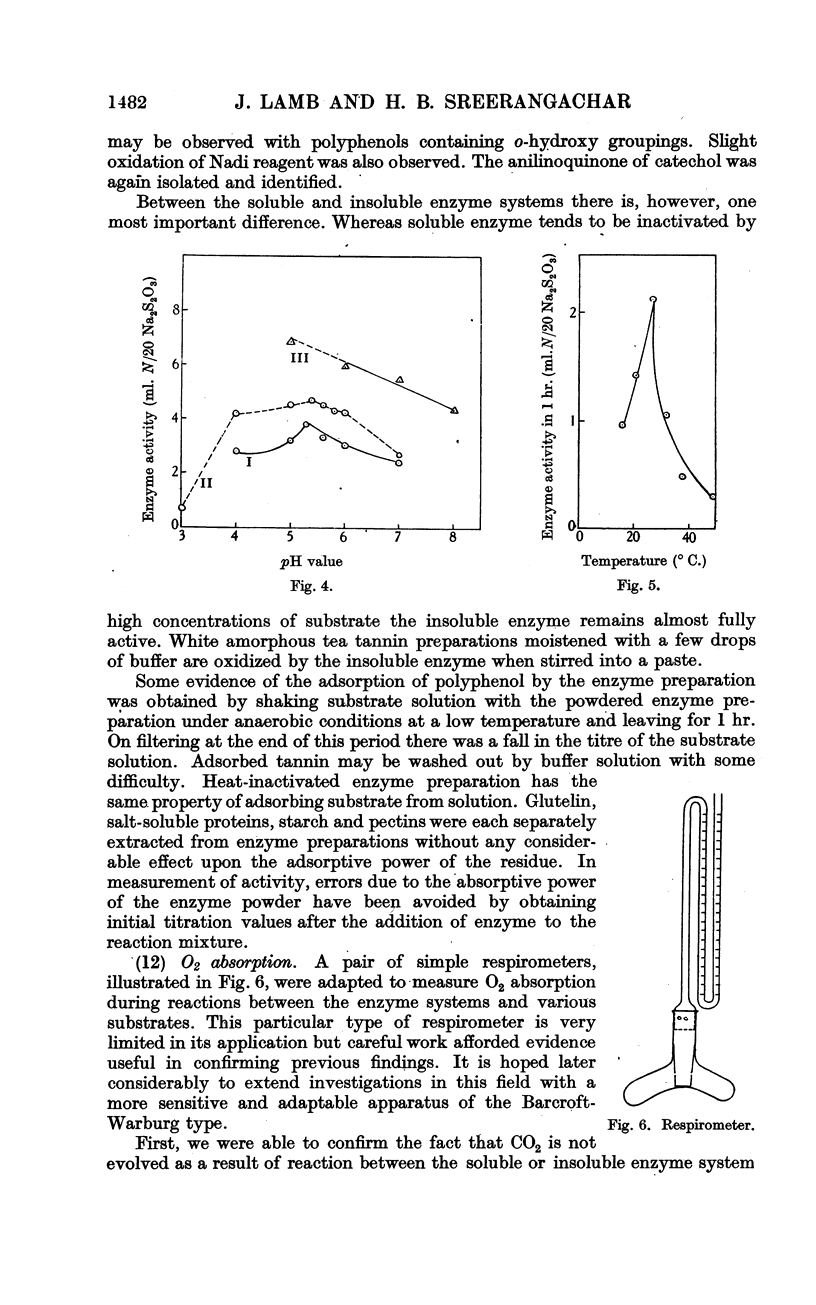
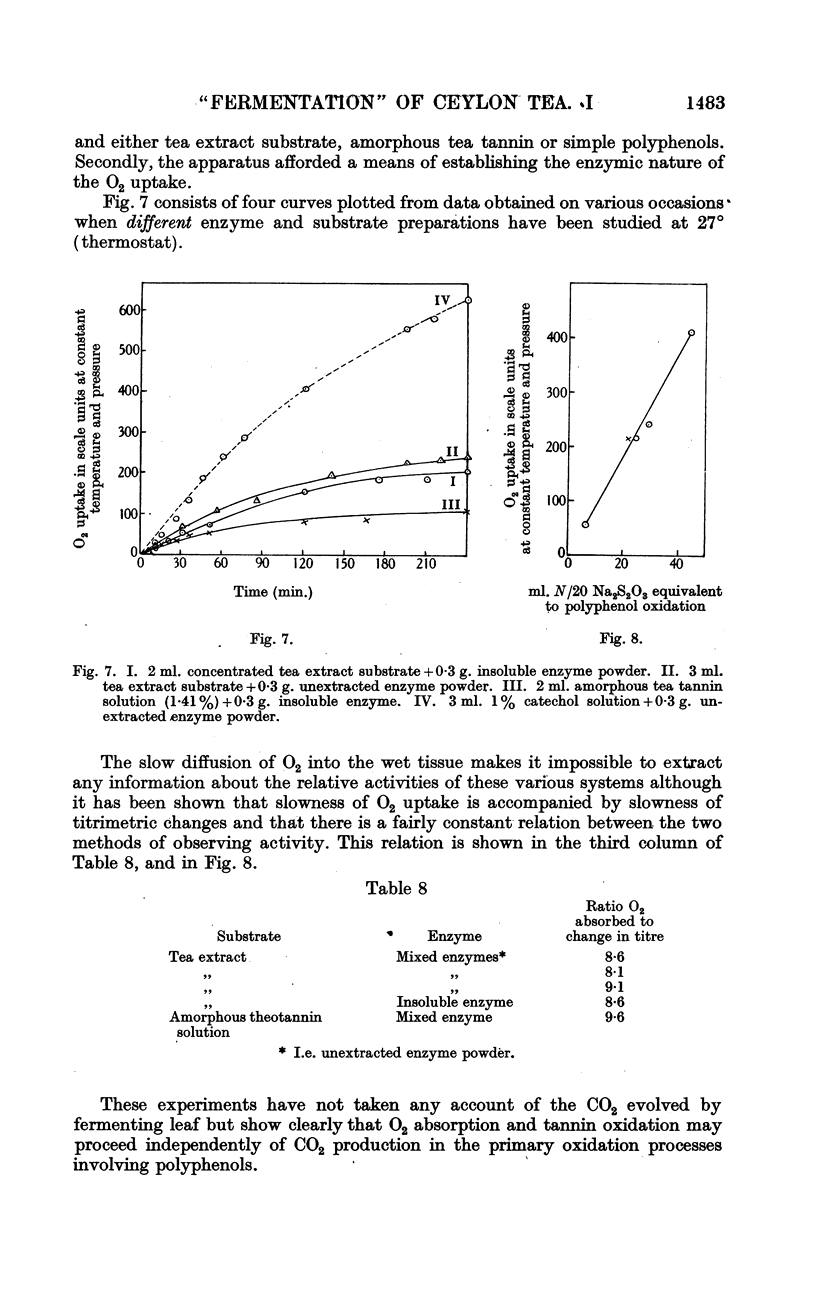
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jackson H. The oxidation of catechol and 1:2:4-trihydroxybenzene by polyphenol oxidase. Biochem J. 1939 Sep;33(9):1452–1459. doi: 10.1042/bj0331452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. E., Raper H. S. The Action of Tyrosinase on Phenols: With some Observations on the Classification of Oxidases. Biochem J. 1927;21(6):1370–1383. doi: 10.1042/bj0211370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E. A., Sarma S. N. The fermentation process in tea manufacture: The role of peroxidase. Biochem J. 1938 Oct;32(10):1819–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0321819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E. A. The fermentation process in tea manufacture: Some properties of tea peroxidase. III. The mechanism of fermentation. Biochem J. 1939 May;33(5):836–852. doi: 10.1042/bj0330836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan M. Ascorbic acid oxidase from drumstick, Moringa pterygosperma. Biochem J. 1936 Nov;30(11):2077–2084. doi: 10.1042/bj0302077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


