Full text
PDF

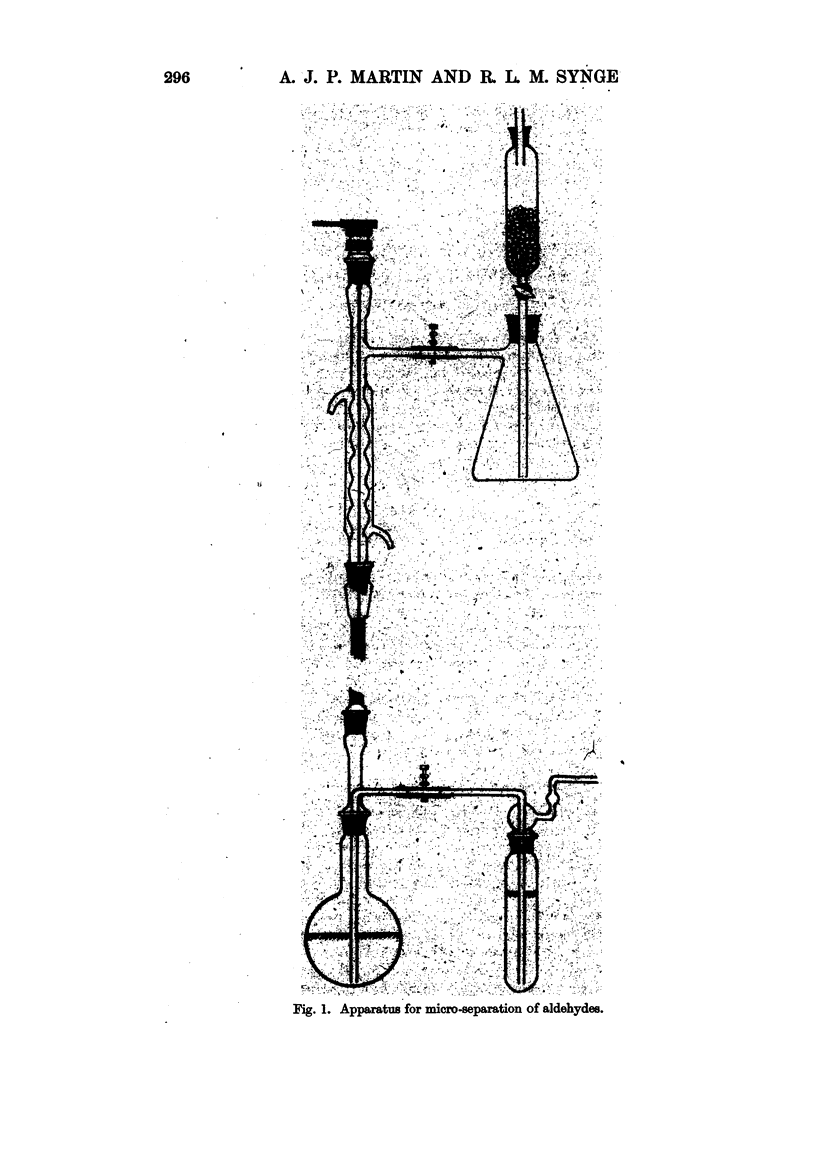




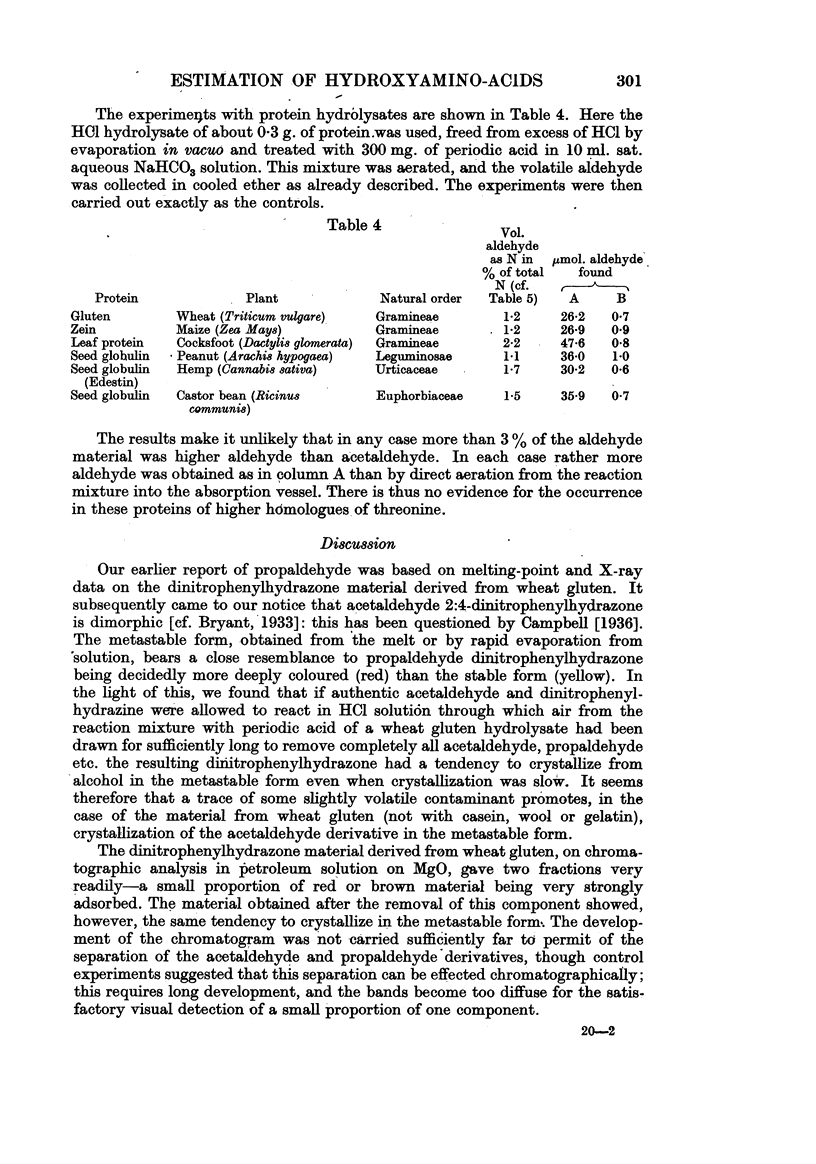













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Damodaran M., Ramachandran B. V. Enzymic proteolysis: Amino-acids of casein phosphopeptone. Biochem J. 1941 Jan;35(1-2):122–134. doi: 10.1042/bj0350122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara T. J., Plimmer R. H. Analysis of proteins: Dephosphocaseose or depocaseose. Biochem J. 1940 Nov;34(10-11):1431–1448. doi: 10.1042/bj0341431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. G. The amino-acid composition of rabbit myosin. Biochem J. 1939 May;33(5):679–693. doi: 10.1042/bj0330679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synge R. L. Experiments on amino-acids: A method for the isolation of hydroxy-amino-acids from protein hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1939 Dec;33(12):1924–1930. doi: 10.1042/bj0331924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Slyke D. D., Hiller A. An Unidentified Base among the Hydrolytic Products of Gelatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1921 Jul;7(7):185–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.7.7.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]