Abstract
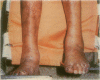
In Parkinson's disease there is degeneration of neurons in the substantia nigra, with consequent depletion of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The triad of tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia is the clinical hallmark. Drugs currently used for palliative therapy fall into three categories: anticholinergic agents, dopamine precursors (levodopa combined with extracerebral decarboxylase inhibitors) and artificial dopamine agonists. It has been argued, on theoretical grounds, that some drugs slow the progress of Parkinson's disease, although no firm evidence has supported this. Treatment must be individualized, and more than one type of drug can be given concurrently after a careful build-up in dosage. We review the adverse effects of various drugs and consider new developments such as slow-release preparations, selective D-1 and D-2 agonists and transplants of dopaminergic cells into the brain. The treatment of Parkinson's disease can be demanding, rewarding and sometimes frustrating, but it remains a most challenging exercise in pharmacotherapy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnt J., Hyttel J. Differential involvement of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in the circling behaviour induced by apomorphine, SK & F 38393, pergolide and LY 171555 in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;85(3):346–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00428200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backlund E. O., Granberg P. O., Hamberger B., Knutsson E., Mårtensson A., Sedvall G., Seiger A., Olson L. Transplantation of adrenal medullary tissue to striatum in parkinsonism. First clinical trials. J Neurosurg. 1985 Feb;62(2):169–173. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.2.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankiewicz K. S., Oldfield E. H., Chiueh C. C., Doppman J. L., Jacobowitz D. M., Kopin I. J. Hemiparkinsonism in monkeys after unilateral internal carotid artery infusion of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Life Sci. 1986 Jul 7;39(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau A., Roy M., Langston J. W. Neurological consequence of industrial exposure to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Lancet. 1985 Mar 30;1(8431):747–747. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone P., Bankiewicz K. S., Corsini G. U., Kopin I. J., Chase T. N. Dopaminergic mechanisms in hemiparkinsonian monkeys. Neurology. 1987 Oct;37(10):1592–1595. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.10.1592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone P., Braun A. R., Chase T. N. D-1/D-2 dopamine receptor interactions in the regulation of extrapyramidal motor function: studies in animal models and parkinsonian patients. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1986;9 (Suppl 4):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer H., Birkmayer W., Hornykiewicz O., Jellinger K., Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Dec;20(4):415–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmayer W., Riederer P., Youdim M. B. (-)Deprenyl in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1982;5(2):195–230. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198205020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun A., Fabbrini G., Mouradian M. M., Serrati C., Barone P., Chase T. N. Selective D-1 dopamine receptor agonist treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm. 1987;68(1-2):41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01244638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Lees A. J. Late progression of post-encephalitic Parkinson's syndrome. Can J Neurol Sci. 1988 May;15(2):135–138. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100027499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., McGeer P. L. Tissue transplantation for Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1988 Nov;15(4):364–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Rinne U. K. Controversies in the management of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 1986;1(3):159–162. doi: 10.1002/mds.870010301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne S., Schoenberg B., Martin W., Uitti R. J., Spencer P., Calne D. B. Familial Parkinson's disease: possible role of environmental factors. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3):303–305. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100026664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M., Breck L., Kutt H., McDowell F. H. Controlled-release levodopa/carbidopa. I. Sinemet CR3 treatment of response fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):233–241. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernow B., Rainey T. G., Lake C. R. Endogenous and exogenous catecholamines in critical care medicine. Crit Care Med. 1982 Jun;10(6):409–416. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198206000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasta J. F., Kirby M. G. Pharmacology and therapeutic use of low-dose dopamine. Pharmacotherapy. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):304–310. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1986.tb03492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond S. G., Markham C. H., Hoehn M. M., McDowell F. H., Muenter M. D. Multi-center study of Parkinson mortality with early versus later dopa treatment. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jul;22(1):8–12. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher G. H., Starr M. S. SKF 38393 and apomorphine modify locomotion and exploration in rats placed on a holeboard by separate actions at dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 19;117(3):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb W. R., Griffith D. N. Levodopa withdrawal syndrome identical to neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 1986 Jan;62(723):59–60. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.62.723.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. J., Lees A. J., Stern G. M. On-off fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. A clinical and neuropharmacological study. Brain. 1984 Jun;107(Pt 2):487–506. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joynt R. J., Gash D. M. Neural transplants: are we ready? Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):455–456. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J. A., Feldman R. G. The role of L-dopa holiday in the long-term management of Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1986;9(1):1–13. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198602000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kish S. J., Shannak K., Hornykiewicz O. Uneven pattern of dopamine loss in the striatum of patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Pathophysiologic and clinical implications. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 7;318(14):876–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804073181402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Jr, Weiner W. J. Attempted use of haloperidol in the treatment of L-dopa induced dyskinesias. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Apr;37(4):427–430. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. E. Treatment of Parkinson's disease with agents other than levodopa and dopamine agonists: controversies and new approaches. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):210–220. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhermitte F., Agid Y., Signoret J. L. Onset and end-of-dose levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Possible treatment by increasing the daily doses of levodopa. Arch Neurol. 1978 May;35(5):261–263. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500290007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindvall O., Backlund E. O., Farde L., Sedvall G., Freedman R., Hoffer B., Nobin A., Seiger A., Olson L. Transplantation in Parkinson's disease: two cases of adrenal medullary grafts to the putamen. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):457–468. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrazo I., Drucker-Colín R., Díaz V., Martínez-Mata J., Torres C., Becerril J. J. Open microsurgical autograft of adrenal medulla to the right caudate nucleus in two patients with intractable Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):831–834. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier Hoehn M. M. Parkinsonism treated with levodopa: progression and mortality. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1983;19:253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Schachter M. Assessment of extrapyramidal disorders. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;11(2):129–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Cote L., Williams J. B. Altered serotonin metabolism in depressed patients with parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1984 May;34(5):642–646. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.5.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Williams J. B., Stern Y., Côté L. Depression and Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1984;40:241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y. Parkinson's disease--a new therapy? N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):872–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D., Sharpless N. S., Tyce G. M., Darley F. L. Patterns of dystonia ("I-D-I" and "D-I-D-") in response to l-dopa therapy for Parkinson's disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Mar;52(3):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D. Should levodopa therapy be started early or late? Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):195–199. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt J. G., Fellman J. H. Pharmacokinetics of levodopa. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1984;7(1):35–49. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198403000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt J. G., Woodward W. R., Carter J. H. Clinical and biochemical studies with controlled-release levodopa/carbidopa. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1206–1211. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Barbeau A. Erythrocyte antioxidant activity in human patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 10;75(3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90547-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn N., Marsden C. D., Parkes J. D. Complicated response fluctuations in Parkinson's disease: response to intravenous infusion of levodopa. Lancet. 1982 Aug 21;2(8295):412–415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne U. K., Siirtola T., Sonninen V. L-deprenyl treatment of on-off phenomena in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm. 1978;43(3-4):253–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01246962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondot P., de Recondo J., Coignet A., Ziegler M. Mental disorders in Parkinson's disease after treatment with L-DOPA. Adv Neurol. 1984;40:259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner C. M., Goetz C. G., Glantz R. H., Glatt S. L., Klawans H. L. Pergolide mesylate and idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1175–1179. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner C. M., Goetz C. G., Glantz R. H., Glatt S. L., Klawans H. L. Pergolide mesylate and idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1175–1179. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. E., Saint-Cyr J. A., Lang A. E. Frontal lobe dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. The cortical focus of neostriatal outflow. Brain. 1986 Oct;109(Pt 5):845–883. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.5.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. F., Wagner H. N., Jr, Dannals R. F., Links J. M., Frost J. J., Ravert H. T., Wilson A. A., Rosenbaum A. E., Gjedde A., Douglass K. H. Effects of age on dopamine and serotonin receptors measured by positron tomography in the living human brain. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1393–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6334363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]