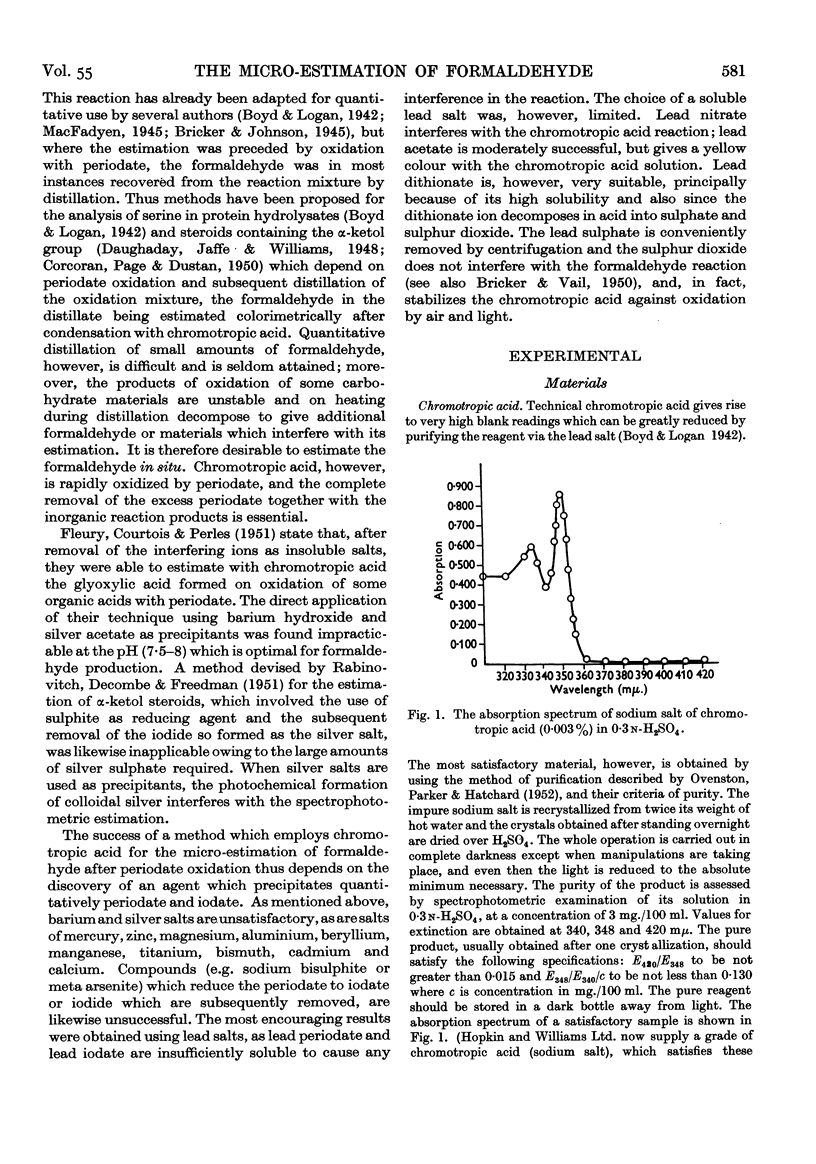
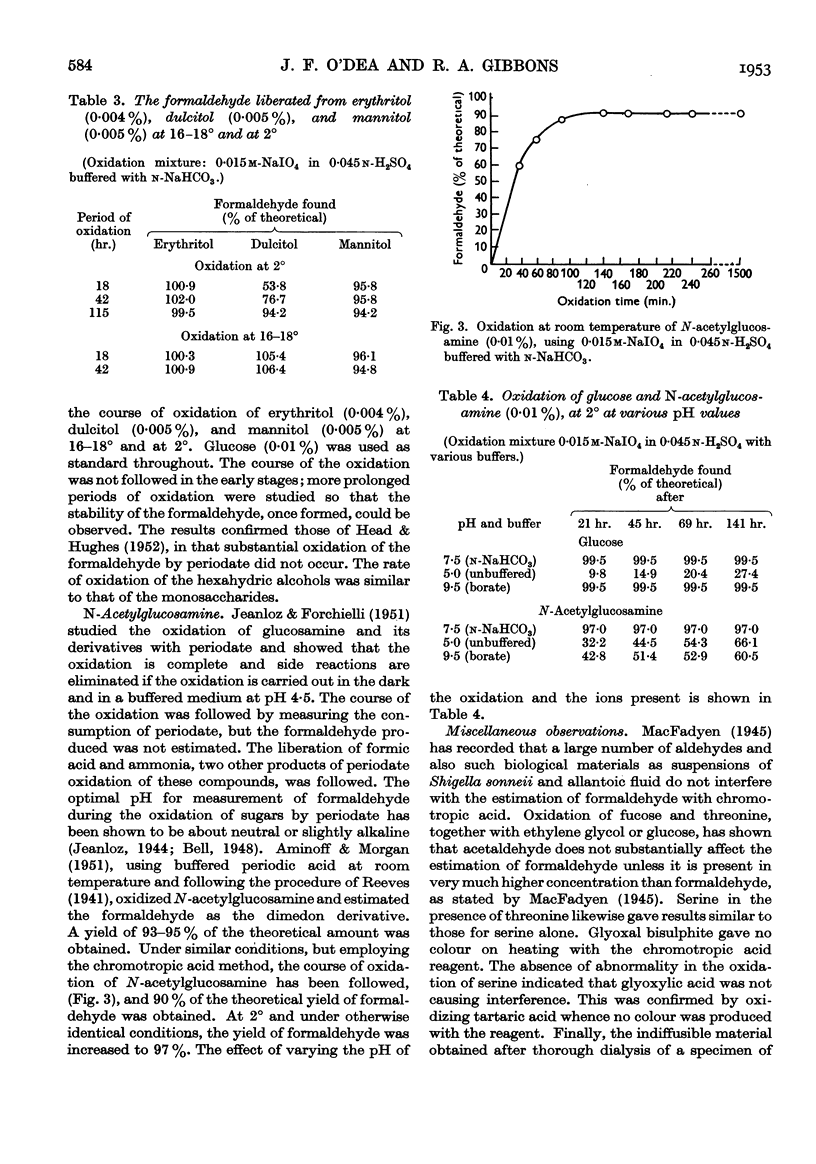
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D., MORGAN W. T. J. Studies in immunochemistry; the oxidation of the human blood-group A substance with the periodate ion. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):74–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORCORAN A. C., PAGE I. H., DUSTAN H. P. Urinary formaldehydogenic corticoids: normal values and observations in hypertension. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Aug;36(2):297–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANLOZ R. W., FORCHIELLI E. Studies on hyaluronic acid and related substances. II. Periodate oxidation of glucosamine and derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. J., Synge R. L. Some applications of periodic acid to the study of the hydroxyamino-acids of protein hydrolysates: The liberation of acetaldehyde and higher aldehydes by periodic acid. 2. Detection and isolation of formaldehyde liberated by periodic acid. 3. Ammonia split from hydroxyamino-acids by periodic acid. 4. The hydroxyamino-acid fraction of wool. 5. ;Hydroxylysine' With an Appendix by Florence O. Bell Textile Physics Laboratory, University of Leeds. Biochem J. 1941 Mar;35(3):294–314.1. doi: 10.1042/bj0350294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOVITCH J., DECOMBE J., FREEDMAN A. Simplified method of estimating formaldehydogenic corticosteroids in urine. Lancet. 1951 Dec 29;2(6696):1201–1202. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)93204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARKAR P. B. Decomposition of formic acid by periodate. Nature. 1951 Jul 21;168(4264):122–123. doi: 10.1038/168122b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


