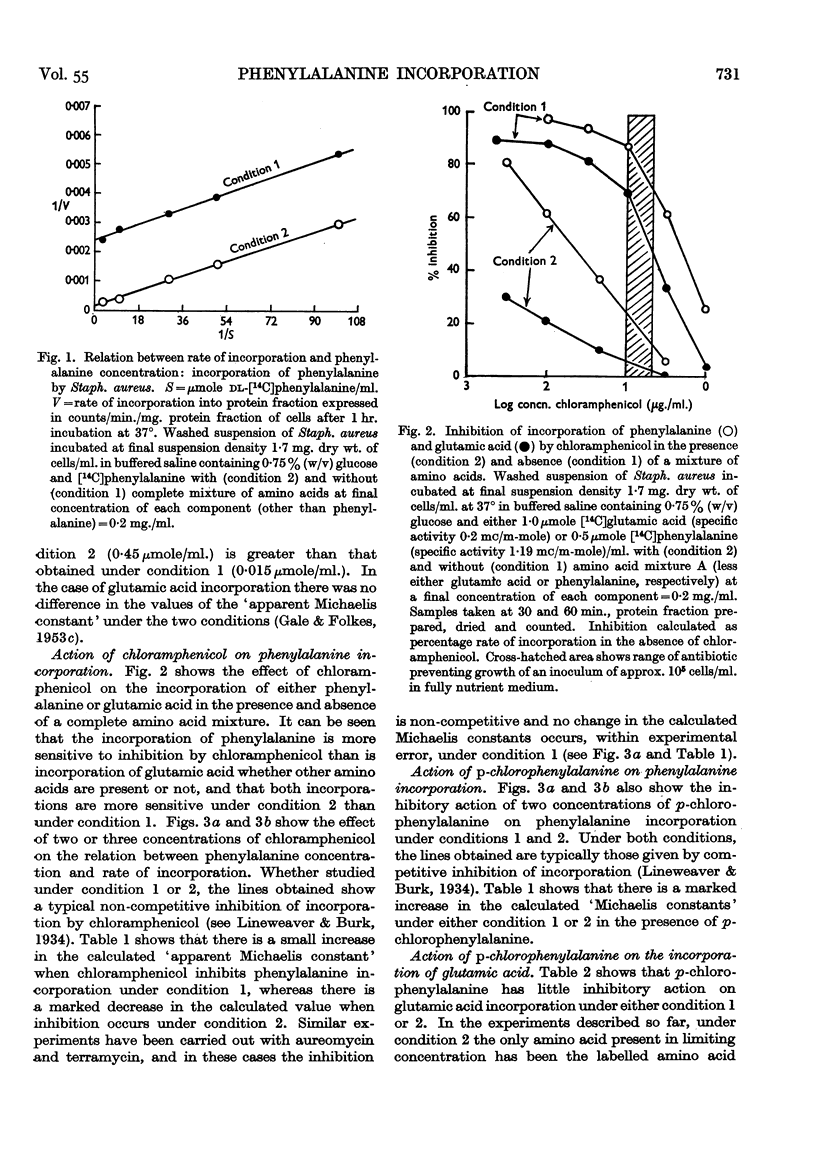
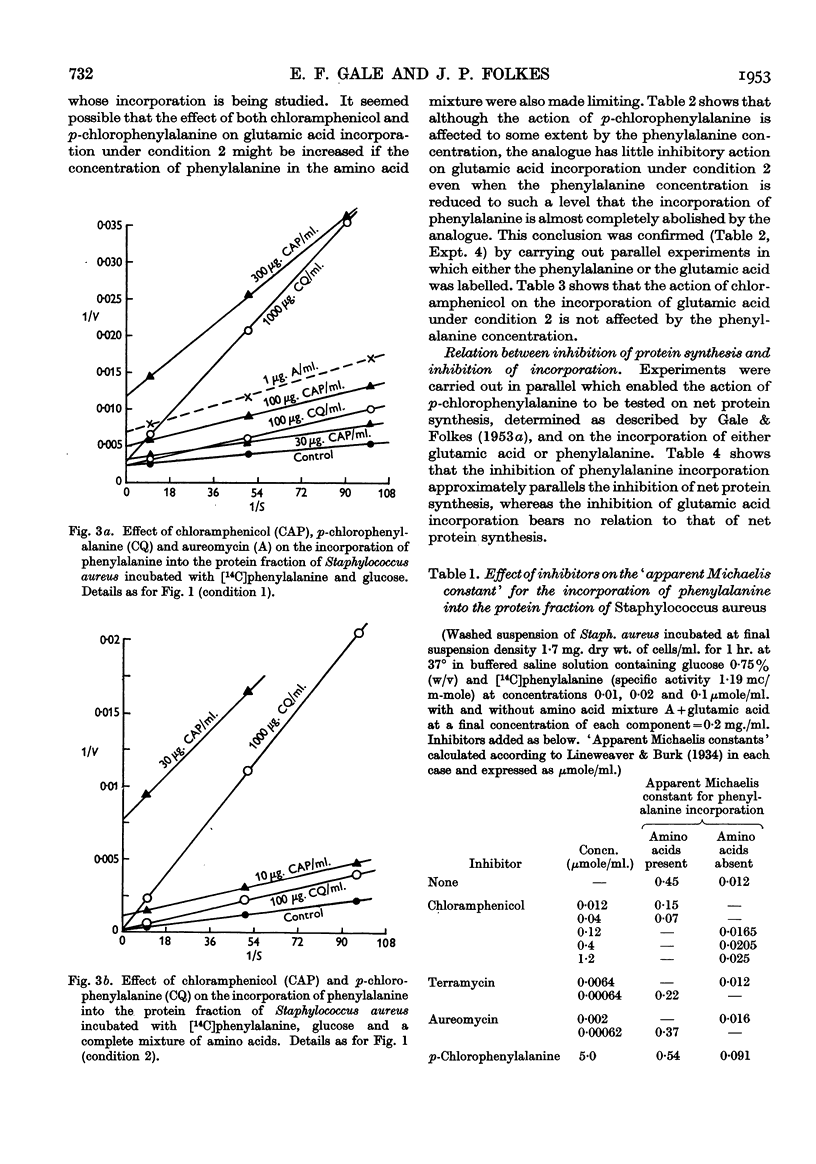
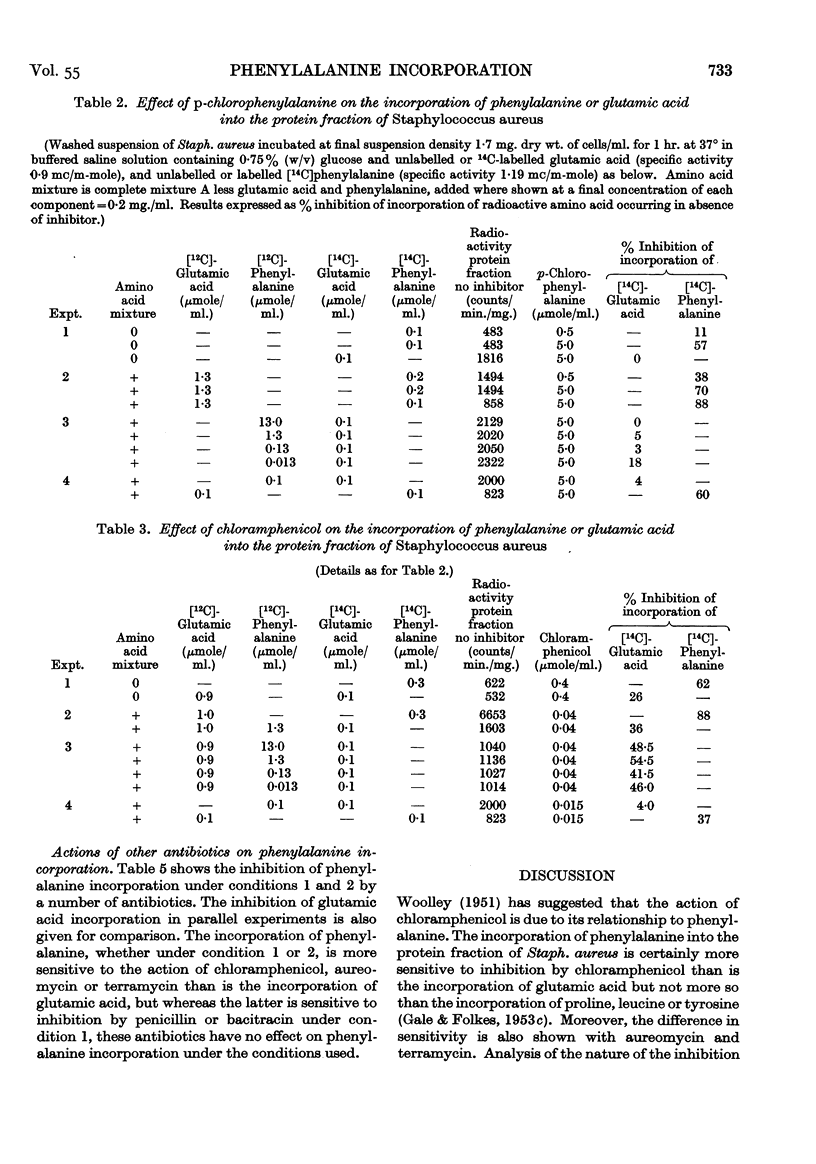
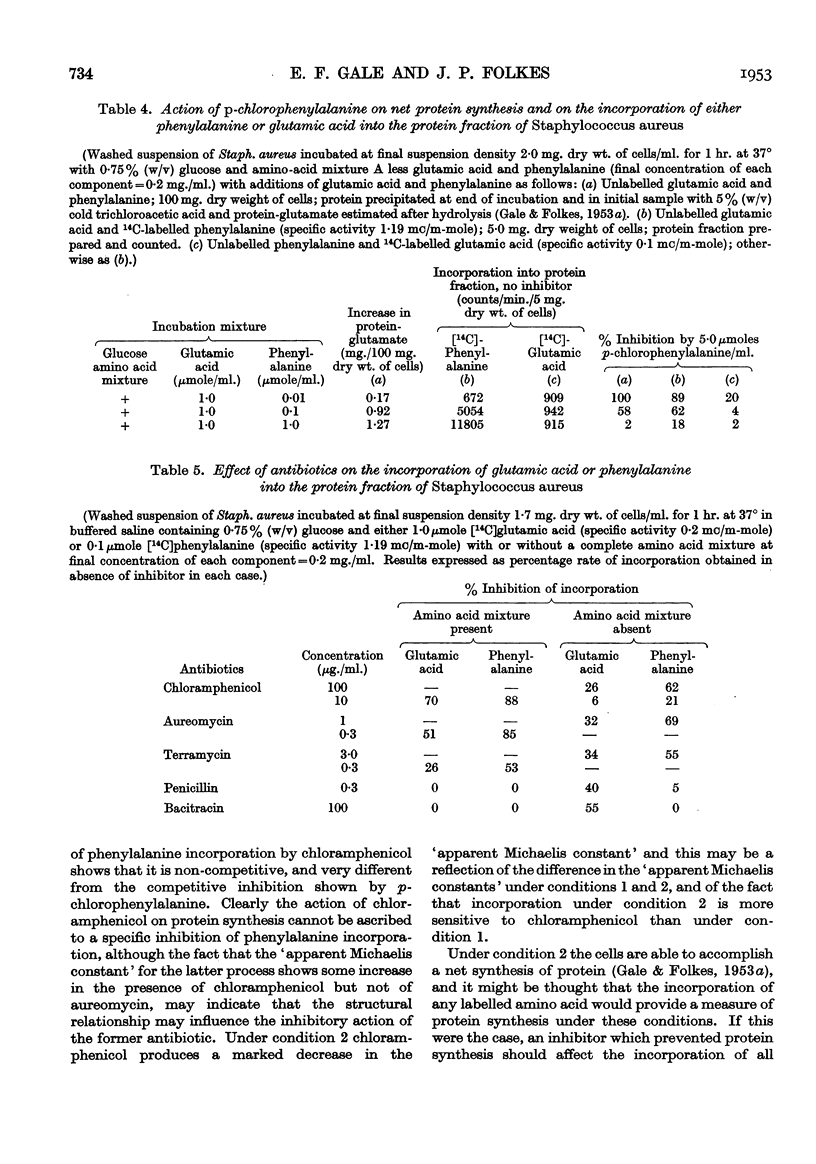
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino acids by bacteria. 18. The incorporation of glutamic acid into the protein fraction of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):721–729. doi: 10.1042/bj0550721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino-acids by bacteria. XV. Actions of antibiotics on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):493–498. doi: 10.1042/bj0530493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. O., SPIEGELMAN S. The inhibition of enzyme formation by amino acid analogues. J Bacteriol. 1952 Aug;64(2):207–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.2.207-221.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. W. A study of non-competitive antagonism with chloromycetin and related analogues of phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jul;185(1):293–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


